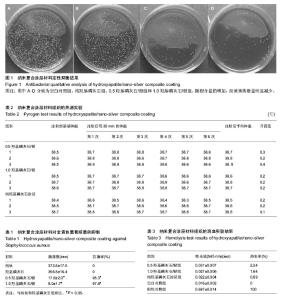
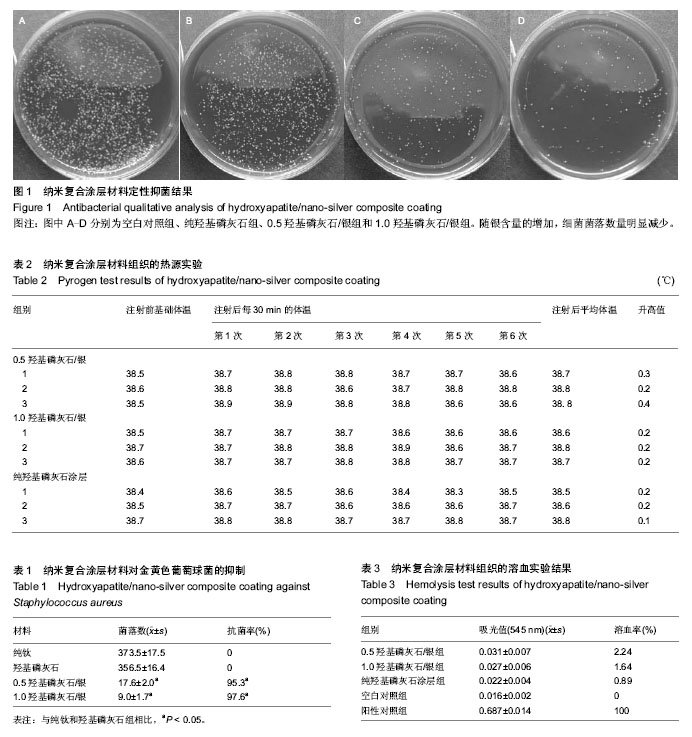
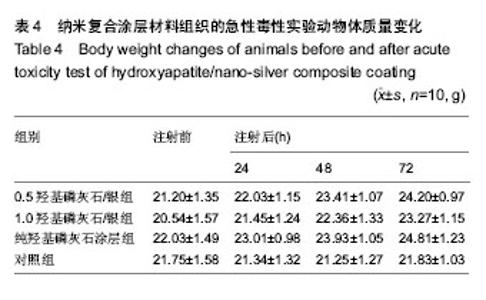
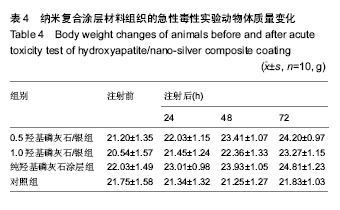
| [1] 鲜爱明,张晓岗,曹力,等.钛基表面纳米银复合涂层的缓释性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(39):6335-6341.
[2] 廖娟,费伟,郭俊,等.载银抗菌纯钛表面的制备及其抗菌性能的检测[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2014(3):303-305.
[3] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. GB/T16886. 10-2005刺激与迟发型超敏反应试验/中华人民共和国国家标准医疗器械生物学评价[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2005.
[4] 阮洪江,刘俊建,范存义,等.载银羟基磷灰石抗菌涂层体外抗菌性能及生物相容性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009,23(2): 226-230.
[5] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局.GB/T16175-2008 医用有机硅材料生物学评价试验方法[S].北京:中国标准出版社, 2008.
[6] 张岩,陶海荣,何耀华,等.可降解镁锌合金的细胞毒性和溶血实验[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(41):8162-8166.
[7] 国际标准化组织. ISO10993-2009医疗器械生物学评价[S]. 2009.
[8] 赵华福,张余,李剑,等.载银珊瑚羟基磷灰石的生物相容性评价[J].广东医学,2011,32(5):552-554.
[9] 励永明,孙皎,顾国珍,等.评价生物材料不同给予方法致急性、全身毒性作用的实验初探[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2009,9(2):83-85.
[10] 李广州,蒋电明,谭祖键,等.载银二氧化钛纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合材料的生物相容性及其安全性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(47):9231-9235.
[11] 朱辉,尹庆水,张余,等.数字化载银羟基磷灰石人工骨抗菌性及生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(47): 8745-8748.
[12] 邹兆伟.纳米载银磷酸锆抗菌聚氨酯抗菌性能及生物相容性研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2012.
[13] 唐良华,赵长虹,王爱民.载万古霉素-PDLLA钛合金钢板的毒性试验评估[J].创伤外科杂志,2009,11(3):256-259.
[14] Shuman EK, Urquhart A, Malani PN. Management and prevention of prosthetic joint infection. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2012;26(1):29-39.
[15] Peel TN, Buising KL, Choong PF. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2012;25(6):670-676.
[16] Parnham MJ. Immunomodulatory effects of antimicrobials in the therapy of respiratory tract infections. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2005;18(2):125-131.
[17] Bozic KJ, Ries MD. The impact of infection after total hip arthroplasty on hospital and surgeon resource utilization. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(8):1746-1751.
[18] Kurtz SM, Lau E, Schmier J, et al. Infection burden for hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States. J Arthroplasty. 2008; 23(7):984-991.
[19] Urquhart DM, Hanna FS, Brennan SL, et al. Incidence and risk factors for deep surgical site infection after primary total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(8):1216-1222.e1-3.
[20] Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total knee arthroplasty in the United States. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(1):45-51.
[21] Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(1):128-133.
[22] Fulkerson E, Valle CJ, Wise B, et al. Antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria infecting total joint arthroplasty sites. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(6):1231-1237.
[23] Salgado CD, Dash S, Cantey JR, et al. Higher risk of failure of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;461:48-53
[24] Walls RJ, Roche SJ, O'Rourke A, et al. Surgical site infection with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus after primary total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(3): 292-298.
[25] Burmølle M, Thomsen TR, Fazli M, et al. Biofilms in chronic infections-a matter of opportunity - monospecies biofilms in multispecies infections. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010; 59(3):324-336.
[26] Singh R, Nalwa HS. Medical applications of nanoparticles in biological imaging, cell labeling, antimicrobial agents, and anticancer nanodrugs. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2011;7(4): 489-503.
[27] Cho KH, Park JE, Osaka T, et al. The study of antimicrobial activity and preservative effects of nanosilver ingredient. Electrochim Acta. 2005;51(5):956-960.
[28] da Silva Paula MM, Franco CV, Baldin MC, et al. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity studies of poly-{styrene-acrylic acid} with silver nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C.2009;29(2):647-650.
[29] Lee BU, Yun SH, Ji JH, et al. Inactivation of S. epidermidis, B. subtilis, and E. coli bacteria bioaerosols deposited on a filter utilizing airborne silver nanoparticles. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008;18(1):176-182.
[30] Panácek A, Kolár M, Vecerová R, et al. Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles against Candida spp. Biomaterials. 2009; 30(31):6333-6340.
[31] Matsui Y, Otomo K, Ishida S, et al. Effect of silver-carrying photocatalyst “Hikari-Gintech” on mycobacterial growth in vitro. Microbiol Immunol. 2004;48(7):489-495.
[32] Cardoso RF, Cooksey RC, Morlock GP, et al. Screening and characterization of mutations in isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates obtained in Brazil. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48(9):3373-3381.
[33] Sun RW, Chen R, Chung NP, et al. Silver nanoparticles fabricated in Hepes buffer exhibit cytoprotective activities toward HIV-1 infected cells. Chem Commun (Camb). 2005; (40):5059-5061.
[34] Elechiguerra JL, Burt JL, Morones JR, et al. Interaction of silver nanoparticles with HIV-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2005; 3:6.
[35] Lu L, Sun RW, Chen R, et al. Silver nanoparticles inhibit hepatitis B virus replication. Antivir Ther. 2008;13(2):253-262.
[36] 张若愚,夏雪山,胡亮,等.Ag/Diatomite复合材料及其对禽流感病毒的杀灭研究[J].贵金属,2004,25(2):28-32.
[37] 何开勇,周素文,高华.体外人全血热原实验方法研究[J].医药导报, 2011,30(7):936-939.
[38] 秦川.实验动物学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2010:38-51.
[39] 韩雪松,刘莹,战德松.溶血试验评价奥氏体无镍不锈钢生物相容性[J].沈阳医学院学报,2010,12(2):87-89.
[40] 王翔,闫蕾,贾光,等.纳米材料潜在健康影响的研究进展[J].毒理学杂志,2005,19(1):15-17.
[41] 陈康,李瑛,谢良宪.壳聚糖聚乳酸膜的制备和毒性试验研究[J].西南国防医药,2011,21(6):585-587. |