Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (48): 7726-7731.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.48.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of horse chestnut seed extract on early hidden blood loss and limb circumference changes after total knee arthroplasty
Gao Fu-qiang1, Sun Wei1, Ma Jin-hui2, Li Zi-rong1
- 1Center for Osteonecrosis & Joint-Preserving Reconstruction, Department of Orthopedics, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China; 2Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2014-10-01Online:2014-11-26Published:2014-11-26 -
Contact:Sun Wei, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Center for Osteonecrosis & Joint-Preserving Reconstruction, Department of Orthopedics, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China -
About author:Gao Fu-qiang, M.D., Attending physician, Center for Osteonecrosis & Joint-Preserving Reconstruction, Department of Orthopedics, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81372013; the General Program of China-Japan Friendship Hospital, No. 2013-MS-27
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Fu-qiang, Sun Wei, Ma Jin-hui, Li Zi-rong. Effects of horse chestnut seed extract on early hidden blood loss and limb circumference changes after total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(48): 7726-7731.
share this article
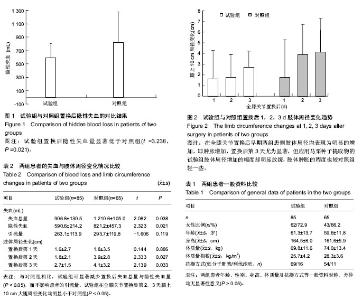
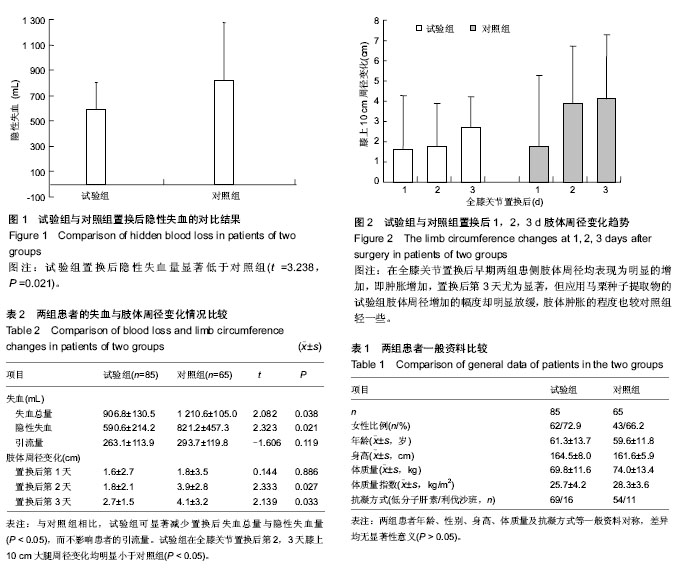
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理,所有150例行初次全膝关节置换患者均进入结果分析,无中途退出者。 2.2 基线资料比较 两组患者年龄、性别、身高、体质量及与抗凝方式等一般资料对称,差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性,见表1。 2.3 隐性失血量的计算结果 病例统计结果显示:试验组和对照组置换后隐性失血量分别为(590.6±214.2),(821.2± 457.3) mL,差异有显著性意义(t=3.238,P=0.021),如 图1所示。 2.4 肢体周径变化趋势 通过分析两组全膝关节置换后不同时间段肢体周径变化分布趋势发现,在全膝关节置换后早期两组患侧肢体周径均表现为明显的增加,即肿胀增加,置换后第3天尤为显著,但应用马栗种子提取物的试验组肢体周径增加的幅度却明显放缓,肢体肿胀的程度也较对照组轻一些,见图2。 2.5 全膝关节置换后失血与肢体肿胀比较 如表2所示,与对照组相比,试验组可显著减少置换后失血总量与隐性失血量,而不影响患者的引流量。两组置换后第1天膝上 10 cm大腿周径变化差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),而试验组在全膝关节置换后第2,3天膝上10 cm大腿周径变化均明显小于对照组(P < 0.05)。 2.6 典型病例 男性患者,67岁,术前诊断为右膝重度骨关节炎,在腰硬联合麻醉下行右侧全膝关节置换,所选择假体为Nexgen LPS-High Flex,美国Zimmer公司。患者于术日起,口服马栗种子提取物0.3 g,3次/d,连续服药14 d。患者肢体肿胀不严重,功能康复良好,1周内患者的膝关节活动度在0°-90°。 随访时间为3个月,随访效果满意,随访期间未出现任何不良事件。 2.7 不良事件 两组患者无切口感染、症状性肺栓塞以及下肢深静脉血栓形成等情况出现,未见马栗种子提取物相关药物不良反应。"
| [1] Park JH, Rasouli MR, Mortazavi SM, et al.Predictors of perioperative blood loss in total joint arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(19):1777-1783. [2] 宋海峰,翁习生,邱贵兴,等.人工全膝关节置换术围手术期血液管理的研究进展[J].中华医学杂志,2008,88(25):1796-1798. [3] 高福强,李子剑,张克,等.初次全膝关节置换术后隐性失血的影响因素研究[J].中华外科杂志,2011,49(5):419-423. [4] Sehat KR,Evans R,Newman JH. How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty? Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee. 2000;7(3):151-155. [5] 高福强,李子剑,刘延青,等.初次全膝关节置换术后肢体肿胀程度与隐性失血量的相关性研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(3): 199-202. [6] Gao FQ, Li ZJ, Zhang K, et al.Risk factors for lower limb swelling after primary total knee arthroplasty.Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124(23):3896-3899. [7] 王毅,孙波,富学禹,等.人工关节置换术后隐性失血对下肢深静脉血栓形成的影响[J].中国微循环,2008,12(5):296-298.田华,宋飞,张克,等.阿司匹林预防关节置换术后血栓栓塞性疾病的疗效和安全性研究[J].中华医学杂志,2007,87(47): 3349-3352. [8] Yu Z, Su P.Effect of beta-aescin extract from Chinese buckeye seed on chronic venous insufficiency. Pharmazie. 2013;68(6):428-430. [9] Pittler MH, Ernst E.Horse chestnut seed extract for chronic venous insufficiency. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;11: CD003230. [10] Ward CF, Meathe EA, Benumof JL. A computer nomogram for blood loss replacement.Anesthesiology. 1980;53(3): S126-130. [11] Gross JB. Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology. 1983;58(3):277-280. [12] Nadler SB, Hidalgo JU, Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;51(2):224-232. [13] Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty.Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(4):561-565. [14] Li B, Wen Y, Wu HS, et al. The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2009; 33(5):1263-1268. [15] Prasad N, Padmanabhan V, Mullaji A,et al.Blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of risk factors.Int Orthop. 2007; 31(1):39-44. [16] Rosencher N, Kerkkamp HE, Macheras G, et al. Orthopedic Surgery Transfusion Hemoglobin European Overview (OSTHEO) study: blood management in elective knee and hip arthroplasty in Europe. Transfusion. 2003;43(4):459-469. [17] Erskine JG, Fraser C, Simpson IT, et al. Blood loss with knee joint replacement. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1981;26(5):295-297. [18] McManus KT,Velehik MG,Alavi A,et al. Non-invasive assessment of postoperative bleeding in TKA patients with Tc-99m RBCs.J Nuclear Med. 1987;28(Suppl):565-567. [19] 刘雄,廖前德,曹焕新,等.马栗树籽提取物(迈之灵)对肢体创伤患者血清细胞因子IL-6、IL-1β和TNF影响的研究[J].中南药学, 2009,7(10):777-780. [20] Korthuis RJ, Granger DN, Townsley MI, et al. The role of oxygen-derived free radicals in ischemia-induced increases in canine skeletal muscle vascular permeability. Circ Res. 1985;57(4):599-609. [21] Wilson JS, Miranda A, Johnson BL, et al.Vascular injuries associated with elective orthopedic procedures. Ann Vasc Surg. 2003;17(6):641-644. [22] Sirtori CR. Aescin: pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic profile. Pharmacol Res. 2001;44(3):183-193. [23] Montopoli M, Froldi G, Comelli MC, et al.Aescin protection of human vascular endothelial cells exposed to cobalt chloride mimicked hypoxia and inflammatory stimuli.Planta Med. 2007; 73(3):285-288. [24] Matsuda H, Li Y, Yoshikawa M.Possible involvement of 5-HT and 5-HT2 receptors in acceleration of gastrointestinal transit by escin Ib in mice. Life Sci. 2000;66(23):2233-2238. [25] Islekel S, Islekel H, Güner G, et al.Alterations in superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase and catalase activities in experimental cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Res Exp Med (Berl). 1999;199(3):167-176. [26] 石士平,李伟,张伟,等.膝骨性关节炎分级与全膝关节置换后隐性失血[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,35(3):6234-6239. [27] 刘丙根,庞清江.氨甲环酸用于全髋关节置换有效性与安全性的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,35(22):5699-5706. [28] 喻长纯,杨明路,杜兴升,等.全膝关节置换后高负压引流下的隐性失血[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,48(3):8313-8318. [29] 雷招宝.51例β-七叶皂苷不良反应病例报告分析[J].中成药, 2011, 9(5):1641-1644. [30] Jang B, Kao M, Bohm MT, et al. Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2014;22(2): 146-149. [31] 李少斐,郭亭,赵建宁,等.围髋关节置换期隐性失血相关危险因素及预后[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,13(7):2006-2011. [32] 许杰,马若凡,李亮平,等.应用低分子肝素对初次全髋及全膝关节置换后失血的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,48(7): 8963-8967. [33] 张蓓,陈蓉.马栗树种子提取物制剂的研究进展[J].中草药,2011, 42(8):1658-1660. [34] 尹勇,马广文,黄斐,等.氨甲环酸减少全髋关节置换失血量的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,17(22):2752-2757. [35] 刘志刚,张上上,陈如见,等.全髋关节置换后的隐性失血[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,13(4):2305-2312. [36] 邹玥,田少奇,王远贺,等.阿司匹林和利伐沙班预防全膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,13(8): 2012-2017. [37] 卞宁.利尿药物联合威利坦治疗高龄慢性心力衰竭患者下肢水肿的临床分析[J].医学综述,2013,19(23):4358-4360. [38] 叶川,刘日光,汤晋等.膝骨性关节炎双侧同期全膝关节置换和单侧膝关节置换的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,35(2): 5583-5588. [39] 董盼锋,陈跃平,康杰,等.人工膝关节置换的引流效应[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,17(5):2649-2654. [40] 田仁元,叶鹏,邓江,等.髋关节置换后引流对患者康复影响的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,35(13):6300-6305. [41] Barry S, Wallace L, Lamb S.Cryotherapy after total knee replacement: a survey of current practice.Physiother Res Int. 2003;8(3):111-120. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||