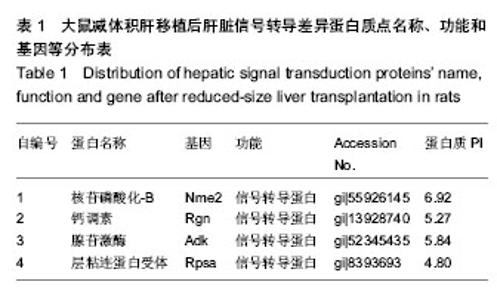
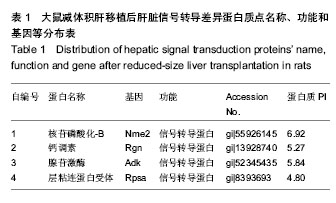
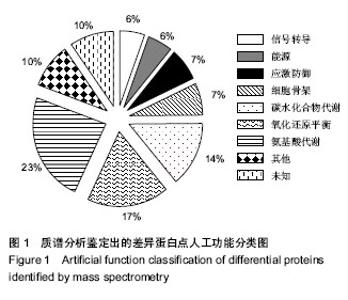
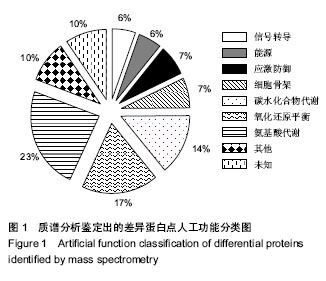
| [1] 胡进武,徐敏,谭长军,等. 大鼠肝移植(LTx)急性排斥反应(AR)血清蛋白质组学分析[J].复旦学报:医学版,2014,41(4):427- 434.
[2] 李彦,梁艳,刘煜,等.肝移植前后人血清中蛋白质双向电泳图谱比较[J].武警医学,2013,24(12):1066-1068,1072.
[3] 吴斌,陆敏强.肝移植缺血再灌注损伤的比较蛋白质组学研究[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2011,17(11):886-890.
[4] 张国伟,周杰.大鼠肝移植急性排斥反应的淋巴细胞蛋白质组学研究[J].中华外科杂志,2008,46(13):1002-1005.
[5] 曹晓林,董宝玮.蛋白质组学在肝脏疾病中的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(5):966-970.
[6] 叶启发,熊力,明英姿.肝移植的蛋白质组学研究探讨[J].中华普通外科学文献:电子版,2007,1(3):186-188.
[7] 明英姿,熊力,叶启发.进行肝移植蛋白质组学研究可行性探讨[J].中国医学工程,2007,15(2):155-159.
[8] Okayama A, Miyagi Y, Oshita F,et al.Proteomic Analysis of Proteins Related to Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma.J Proteome Res. 2014. [Epub ahead of print]
[9] Martins-de-Souza D.Proteomics, metabolomics, and protein interactomics in the characterization of the molecular features of major depressive disorder.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2014; 16(1):63-73.
[10] Petrotchenko EV, Borchers CH.Modern mass spectrometry-based structural proteomics.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2014;95:193-213.
[11] Walsh BJ, Molloy MP, Williams KL.The Australian Proteome Analysis Facility (APAF): assembling large scale proteomics through integration and automation.Electrophoresis. 1998; 19(11):1883-1890.
[12] 刘静,李江,张升宁,等.改良法构建大鼠减体积肝移植模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复杂志,2010,14(18):3252-3257.
[13] Ashcroft AE.Protein and peptide identification: the rôle of mass spectrometry in proteomics.Nat Prod Rep. 2003;20(2): 202-215.
[14] Mo W, Karger BL.Analytical aspects of mass spectrometry and proteomics.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2002;6(5):666-675.
[15] Lombardi D, Mileo AM.Protein interactions provide new insight into Nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinase functions.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2003;35(1):67-71.
[16] Otero AS.NM23/nucleoside diphosphate kinase and signal transduction.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2000;32(3):269-275.
[17] Desvignes T, Pontarotti P, Fauvel C,et al.Nme protein family evolutionary history, a vertebrate perspective.BMC Evol Biol. 2009;9:256.
[18] Lacombe ML, Wallet V, Troll H, et al.Functional cloning of a nucleoside diphosphate kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum.J Biol Chem. 1990;265(17):10012-10018.
[19] Twigger SN, Shimoyama M, Bromberg S,et al.The Rat Genome Database, update 2007--easing the path from disease to data and back again.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35(Database issue):D658-D662.
[20] Hoffmann R, Valencia A.A gene network for navigating the literature.Nat Genet. 2004;36(7):664.
[21] Bult CJ, Eppig JT, Kadin JA,et al.The Mouse Genome Database (MGD): mouse biology and model systems.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(Database issue):D724-728.
[22] Nordgård O, Singh G, Solberg S,et al.Novel molecular tumor cell markers in regional lymph nodes and blood samples from patients undergoing surgery for non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e62153.
[23] Lacombe ML, Milon L, Munier A,et al.The human Nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinases.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2000;32(3):247-258.
[24] Lascu I, Gonin P.The catalytic mechanism of nucleoside diphosphate kinases.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2000;32(3): 237-246.
[25] Desvignes T, Fauvel C, Bobe J.The NME gene family in zebrafish oogenesis and early development.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011;384(4-5):439-449.
[26] Shimada N, Ishikawa N, Munakata Y,et al.A second form (beta isoform) of nucleoside diphosphate kinase from rat. Isolation and characterization of complementary and genomic DNA and expression.J Biol Chem. 1993;268(4):2583-2589.
[27] Lakso M, Steeg PS, Westphal H.Embryonic expression of nm23 during mouse organogenesis.Cell Growth Differ. 1992; 3(12):873-879.
[28] Ouatas T, Sélo M, Sadji Z,et al.Differential expression of nucleoside diphosphate kinases (NDPK/NM23) during Xenopus early development.Int J Dev Biol. 1998;42(1):43-52.
[29] Steeg PS, Bevilacqua G, Kopper L,et al.Evidence for a novel gene associated with low tumor metastatic potential.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988;80(3):200-204.
[30] Jarrett SG, Novak M, Harris N,et al.NM23 deficiency promotes metastasis in a UV radiation-induced mouse model of human melanoma.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2013;30(1):25-36.
[31] Wang Q, Liang KC, Czader A,et al.The effect of macromolecular crowding, ionic strength and calcium binding on calmodulin dynamics.PLoS Comput Biol. 2011;7(7): e1002114.
[32] Chin D, Means AR.Calmodulin: a prototypical calcium sensor.Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10(8):322-328.
[33] Slavov N, Carey J, Linse S.Calmodulin transduces Ca2+ oscillations into differential regulation of its target proteins. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013;4(4):601-612.
[34] Li CJ, Heim R, Lu P,et al.Dynamic redistribution of calmodulin in HeLa cells during cell division as revealed by a GFP-calmodulin fusion protein technique.J Cell Sci. 1999;112 ( Pt 10):1567-1577.
[35] Iwasaki T, Murata-Hori M, Ishitobi S,et al.Diphosphorylated MRLC is required for organization of stress fibers in interphase cells and the contractile ring in dividing cells.Cell Struct Funct. 2001;26(6):677-683.
[36] Gonda K, Katoh M, Hanyu K,et al.Ca(2+)/calmodulin and p85 cooperatively regulate an initiation of cytokinesis in Tetrahymena.J Cell Sci. 1999;112 ( Pt 21):3619-3626.
[37] Hansen AJ, Zeuthen T.Extracellular ion concentrations during spreading depression and ischemia in the rat brain cortex. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981;113(4):437-445.
[38] Pepke S, Kinzer-Ursem T, Mihalas S,et al.A dynamic model of interactions of Ca2+, calmodulin, and catalytic subunits of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010;6(2):e1000675.
[39] Davies KD, Alvestad RM, Coultrap SJ,et al.AlphaCaMKII autophosphorylation levels differ depending on subcellular localization.Brain Res. 2007;1158:39-49.
[40] Berkowitz SA, Wolff J.Intrinsic calcium sensitivity of tubulin polymerization. The contributions of temperature, tubulin concentration, and associated proteins.J Biol Chem. 1981; 256(21):11216-11223.
[41] Single B, Leist M, Nicotera P.Simultaneous release of adenylate kinase and cytochrome c in cell death.Cell Death Differ. 1998;5(12):1001-1003.
[42] Chen RP, Liu CY, Shao HL,et al.Adenylate kinase 2 (AK2) promotes cell proliferation in insect development.BMC Mol Biol. 2012;13:31. |