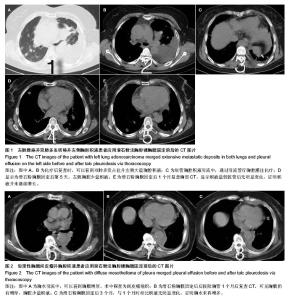
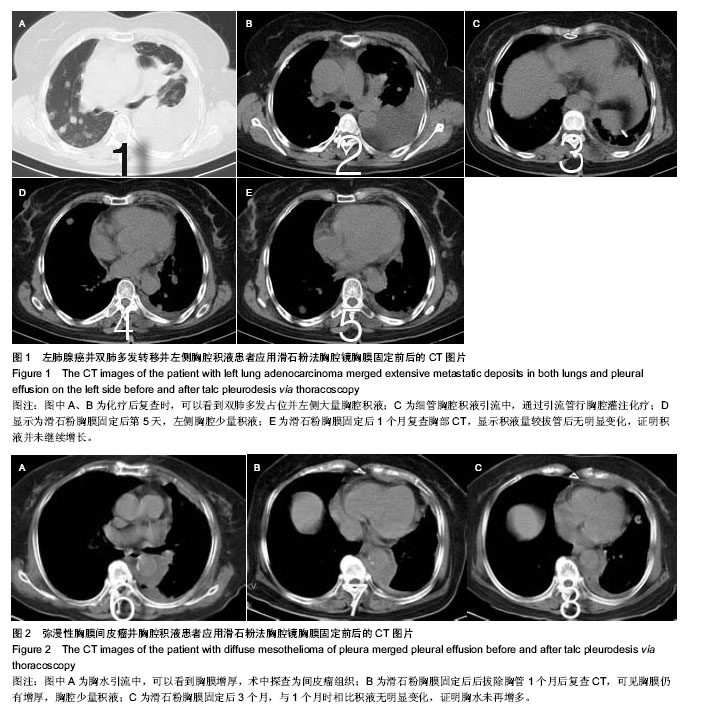
| [1] Heffner JE. Diagnosis and management of malignant pleural effusions. Respirology.2008;13(1):5-20.
[2] Lee YC,Baumann MH,Maskell NA,et al. Pleurodesis practice for malignant pleural effusions in five English-speakingcountries. Chest.2003;124(6):2229-2238.
[3] Hartman DL,Gaither JM,Kesler KA,et al.Comparison of insuff lat ed talc under thoracoscopic guidance with st and ardtetracycline and bl eomycin pleurodes is for control of malignantpleural effusions.J Thorac Cardiovadc Surg. 1993; 105(4):743-748.
[4] 林殿杰,田广燕,丘蕾.经胸腔镜滑石粉胸膜固定联用简易负压吸抽治疗恶性胸腔积液[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2002,25(5): 295-296.
[5] 林殿杰,王茂芬,刘庆化,等.经胸腔镜胸膜闭锁术对顽固性肝性胸腔积液的治疗[J].中华消化杂志,2001,21(5):319-320.
[6] 吴孟超,仲剑平.外科学新理论与新技术[M].上海:上海科学技术教育出版社,1996:165-168.
[7] 戈烽,Ming Lui,李琦.基础胸外科学[M].北京:中国协和医科大学出版社,2003:532.
[8] 谢灿茂,Light RW.滑石粉浆对兔胸膜固定术的急性反应[J].中山医科大学学报,2000, 21(1):21-23,26.
[9] van den Heuvel MM, Smit HJ,Barbierato SB,et al. Talc-induced inflammation in the pleural cavity.Eur Respir J.1998;12(6):1419-1423.
[10] Nasreen N,Hartman DL,Mohammed KA,et al.Talcinducued expression of C- C and C-X- C chemokines and intercellular adhesion molecule- 1 in mesothelial cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.1998;158(3):971-978.
[11] Antony VA,Kamal MA,Godbey D,et al.Talcinduced pleur odesis:role of basic fibroblast.Eur Respir J. 1997;10(25): 403S .
[12] 程东升,谢灿茂,Richard WL.抗肿瘤坏死因子α多克隆抗体对滑石粉和多西环素胸膜固定术效果的影响[J].中华结核与呼吸杂志, 2001,24(1):25-28.
[13] Xie C,Teixeira LR,McGovern JP,et al.Systemic corticosteroids decrease the effectiveness of talc pleurodesis.Am J Res pir CirtCare Med.1998;157(5):1441-1444.
[14] Gary Lee YC,Teixeira LR,Devin CJ,et al.Transforming growth factor-beta2 induces pleurodesis significantly faster than talc.Am J Respir Crit Care Med.2001;163(3 Pt 1):640-644.
[15] Hurewitz AN,zucker S,Mancuso P,et al.Type collagenase/gelatinase activity: unexplained high levels of pleural effsions.Am Rev Respir Dis.1991;143(4):323.
[16] D'Agostino P,Camemi AR,Caruso R,et al.Matrixm et alloprot einases production in malignant pleural effusions after talc pleurodesis. Clin Exp Immunol.2003;134 (1): 138-142.
[17] Hurewitz AN,Wu CL,Mancuso P,et al.Tetracycline and doxycycline inhibit pleural fluid metalloproteinases. A possible mechanism for chemical pleurodesis. Chest.1993; 103(4): 1113-1117.
[18] Mitchem RE,Herndon BL,Fiorella RM,et al.Pleurodes is by autologous blood, doxycycline, and talc in a rabbit model.Ann Thorac Surg.1999;67(4):917-921.
[19] Ong KC,Indumathi V,Raghuram J,et al.A comparative study of pleurodesis using talc slurry and bleomycin in the management of malignant pleural effusions. Respirology. 2000;5(2):99-103.
[20] 俞森洋,张进川.当代呼吸疗法[M].北京:中国协和医科大学、北京医科大学联合出版社, 1994:10.
[21] 赖小刚,王宪东,刘大治,等.DP化疗方案联合博来霉素胸腔内注射治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌并发恶性胸腔积液的疗效观察[J].中国癌症防治杂志,2014,6(1):60-62.
[22] 刘雅芸,钱源.胸腔灌注四环素治疗恶性胸腔积液的疗效观察[J].中国医院指南,2013,9(11):106-107.
[23] 刘俊,赵子文.多西环素和博来霉素治疗恶性胸腔积液的疗效和不良反应分析[J].临床医学工程,2013,20(12):1519-1520.
[24] 牛中喜,郭金成,王冬玲.胸腔镜胸膜固定术在肺癌并胸腔积液综合治疗中的应用[J].中国综合临床,2006,6(6):542-543.
[25] Maskell NA,Lee YCG,Gleeson FV,et al.Randomized trails describing lung inflammation after pleurodesis with talc of varying particle size. Am J Crit Med. 2004;170(4):377-382.
[26] Ferrer J,Montes JF,Villarino MA,et al.Influence of particle size on extrapleural talc dissemination after talc slurry pleurodesis. Chest.2002;122(8):1018-1027.
[27] 廖槐,谢灿茂.兔胸腔内注射滑石粉致肺及肺外全身系统性播散[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2013,34(6):861-866.
[28] Lee YC,Lane KB,Zoia O,et al.Transforming growth factor-beta induces collagen synthesis without inducing IL-8 production inmesothelial cells.Eur Respir J.2003;22(2): 197-202.
[29] Kinoshita T,Miyoshi S,Suzuma T,et al.Intrapleural administration of a large amount of diluted fibrin glue for intractable pneumothorax. A clinical study based on 57 cases: including 2 unsuccessful cases.Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2003;51(2):41-47. |