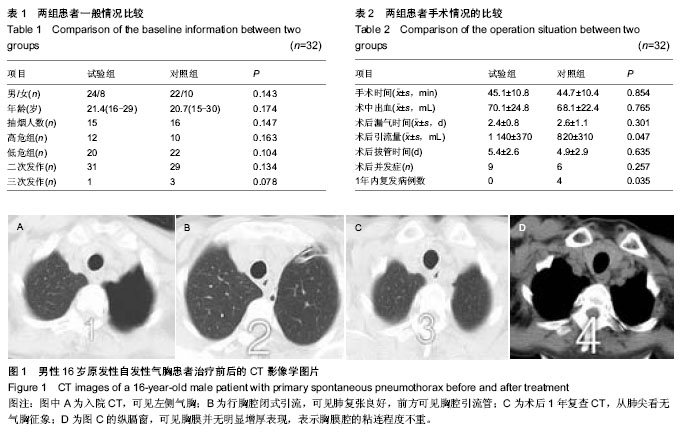
| [1] Kaneda H,Nakano T,Taniguchi Y,et al.Three-step management of pneumothorax: time for a re-think on initial management. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013;16(2): 186-192.
[2] Al-Qudah A.Treatment options of spontaneous pneumothorax. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci.2006;48:191-200.
[3] Luh SP.Review: Diagnosis and treatment of primary spontaneous pneumothorax.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010; 11(10):735-744.
[4] Brims FJ,Maskell NA.Ambulatory treatment in the management of pneumothorax: a systematic review of the literature.Thorax.2013;68(7):664-669.
[5] 周达,李虹彦,李志宏,等.原发性自发性气胸术后复发相关因素的临床分析[J].中国现代医学杂,2011,21(2):240-244.
[6] 程少毅,冯征,王艳,等.碘伏法电视胸腔镜治疗原发性自发性气胸98例的临床研究[J].现代生物医学进展, 2014,28(17): 3283-3285.
[7] 谢灿茂,Light RW.滑石粉浆对兔胸膜固定术的急性反应[J].中山医科大学学报,2000, 21(1):21-23,26.
[8] van den Heuvel MM,Smit HJ,Barbierato SB,et al.Talc-induced inflammation in the pleural cavity.Eur Respir J.1998;12(6): 1419-1423.
[9] Nasreen N,Hartman DL,Mohammed KA,et al.Talcinducued expression of C- C and C-X- C chemokines and intercellular adhesion molecule- 1 in mesothelial cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.1998;158(3):971-978.
[10] Antony VA,Kamal MA,Godbey D,et al.Talcinduced pleur odesis: role of basic fibroblast.Eur Respir J. 1997;10(25):403S.
[11] 谢灿茂,容中生.化学性胸膜固定术的现状和展望[J].新医学, 1996, 27(8):397.
[12] 曾勉,谢灿茂.红霉素胸膜固定术对自发性气胸的治疗价值[J].中国呼吸与危重监护杂志,2004,3(2):110-112.
[13] 徐元峰,阚积香.负压吸引下自体血胸腔粘连术治疗难治性气胸临床研究[J].临床肺科杂志,2009,9(8):154-156.
[14] 藤维亚.自发性气胸研究进展[J].国外医学:呼吸系统分册, 2009, 15(1):28.
[15] Wither JN.Spontaneous pnemothorax: suggested etiology and comparison of treatment method. Surg. 2000;108:772-776.
[16] 胡虞志.儿童少年卫生学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1994:8-20.
[17] 徐乐天.现代胸外科学[M].北京:科学出版社,2004:225-234.
[18] 孙明.内科治疗学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2001:168-170.
[19] 张其刚.谭胜,张晓峰,等.扁平胸廓青少年自发性气胸发病原因的生物力学研究[J].中华胸心外科杂志,2005,21(3):163-165.
[20] 施毅.现代呼吸系统急诊医学[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 1998:105.
[21] 刘昌起.呼吸疾病治疗学[M].天津:科学技术出版社,2000:249.
[22] Fröhlich BA,Zeitz C,Mátyás G,et al.Novel mutations in the folliculin gene associated with spontaneous pneumothorax. Eur Respir J.2008;32(5):1316-1320.
[23] 王俊.胸部疾病胸腔镜全真手术[M].南京:江苏科学技术出版社, 2007:45-51.
[24] 徐瑞芳,左京昱.付极,等.影响原发性自发性气胸复发的因素[J].临床内科杂志,2001,18(2):136.
[25] 刘彦国,卜梁.再次胸腔镜手术治疗胸腔镜术后复发气胸11 例分析[J].中国微创外科杂志,2008,8(11):970-973.
[26] Sadikot RT,Greene T,Meadows K,et al.Recurrenceof primary spontaneous pneumothorax.Thorax.1997;52:805-809.
[27] Bridevaux PO,Tschopp JM,Cardillo G,et al.Short-term safety of thoracoscopic talc pleurodesis for recurrent primary spontaneous pneumothorax: a prospective European multicentre study.Eur Respir J.2011;38(4):770-773.
[28] 张素娟,刘皓,潘顺全,等. 3%滑石粉悬液治疗复发性气胸的疗效和安全性[J].实用医学杂志,2007,23(19):128-130.
[29] Ho KK,Ong ME,Koh MS,et al.A randomized controlled trial comparing minichest tube and needle aspiration in outpatient management of primary spontaneous pneumothorax.Am J Emerg Med.2011;29(9):1152-1157.
[30] 俞森洋,张进川.当代呼吸疗法[M].北京:中国协和医科大学、北京医科大学联合出版社, 1994:10.
[31] Viskum K,Lange P,Mortensen J.Long term sequelae after talc pleurodesis for spontaneous pneumothorax. Pneumologie. 2011;43(2):105-106.
[32] Galbois A,Ait-Oufella H,Baudel JL.Pleural ultrasound compared with chest radiographic detection of pneumothorax resolution after drainage. Chest.2010;138(3):648-655
[33] Lee YC,Lane KB.Transforming growth factor-beta induces collagen synthesis without inducing IL-8 production inmesothelial cells.Eur Respir J.2003;22(2): 197-202.
[34] Kinoshita T,Miyoshi S,Suzuma T,et al.Intrapleural administration of a large amount of diluted fibrin glue for intractable pneumothorax. A clinical study based on 57 cases: including 2 unsuccessful cases.Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;51(2):41-47. |