Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (18): 4685-4693.doi: 10.12307/2026.749
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison and evaluation of three methods for preparing insomnia mouse models
Li Feifan, Zhang Yibo, Wang Jing, Zhu Jinqiang, Zheng Wenke
- Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China
-
Received:2025-07-01Accepted:2025-09-24Online:2026-06-28Published:2025-12-06 -
Contact:Zhu Jinqiang, PhD, Associate researcher, Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China Co-corresponding author: Zheng Wenke, PhD, Researcher, Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China -
About author:Li Feifan, MS candidate, Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China -
Supported by:Tianjin Municipal Health Commission Research Project on Traditional Chinese Medicine and Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, No. 2023079 (to ZJQ); Heilongjiang Province “Best Candidate” Scientific Research Project, No. 2023ZXJ02C01 (to ZWK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Feifan, Zhang Yibo, Wang Jing, Zhu Jinqiang, Zheng Wenke. Comparison and evaluation of three methods for preparing insomnia mouse models[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4685-4693.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
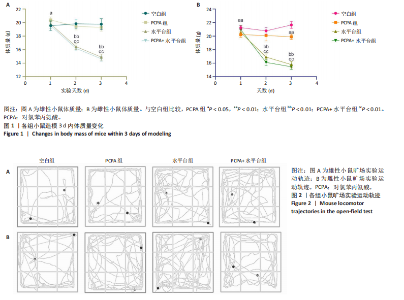
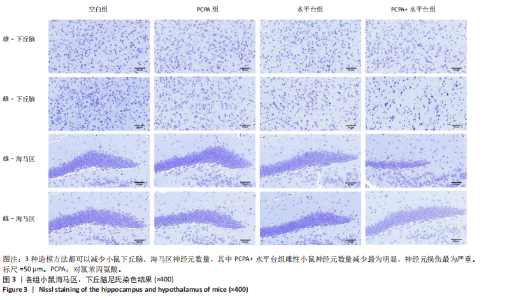
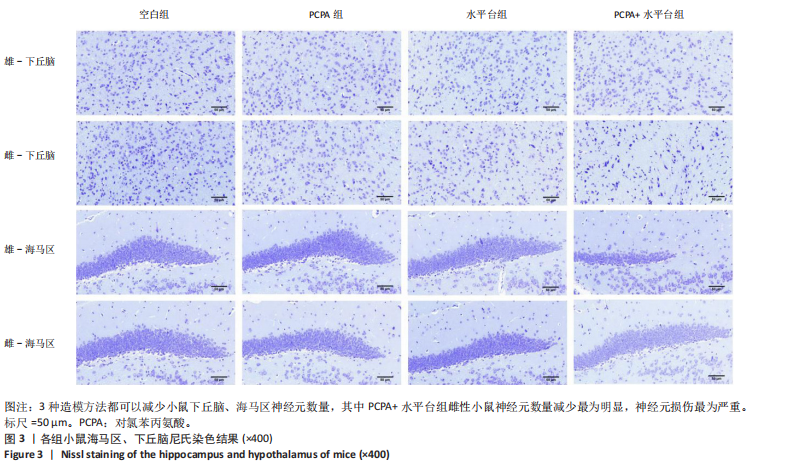
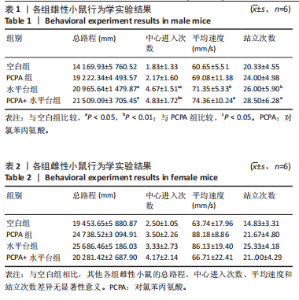
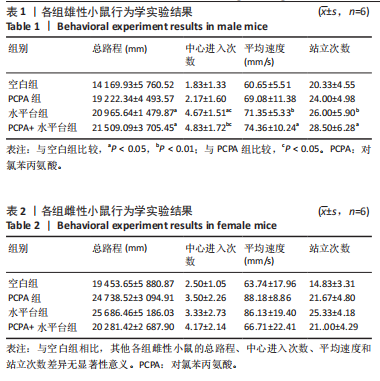
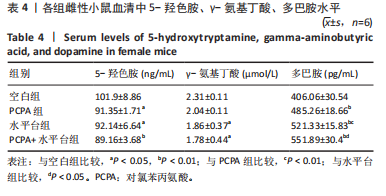
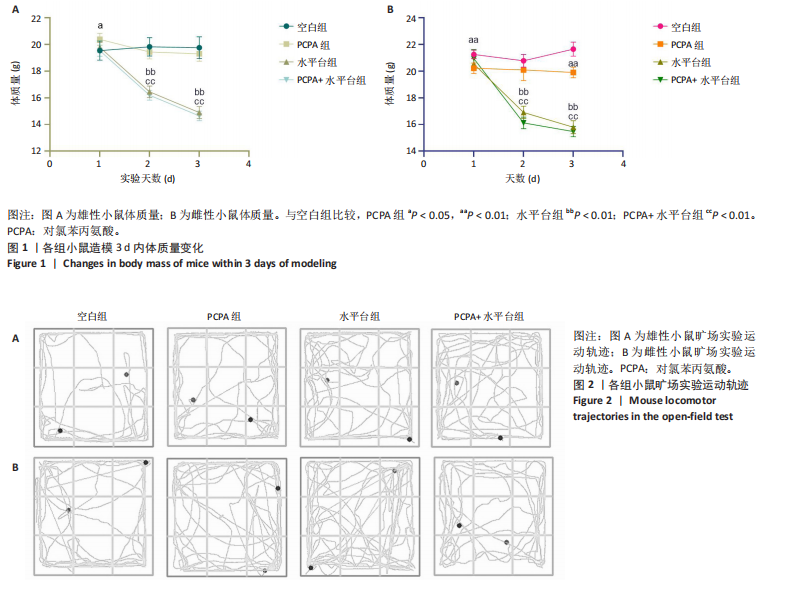
2.1 实验动物数量分析 参与实验的各组小鼠在实验过程中均无死亡,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 小鼠一般情况观察 实验过程中,空白组雄、雌小鼠精神状态均良好,毛发鲜亮柔顺有光泽,活动灵敏,体质量无明显变化。PCPA组雄、雌小鼠活动均增加,昼夜节律紊乱;与空白组相同性别小鼠相比,PCPA组雄性小鼠体质量在造模第1天显著增加(P < 0.05),雌性小鼠体质量在造模第1天显著降低(P < 0.01)。与空白组相同性别小鼠相比,水平台组雄性小鼠毛发略欠光泽,精神兴奋,易怒,体质量在造模第1天无显著性变化,造模第2,3天显著降低(P < 0.01);水平台组雌性小鼠毛发略显粗糙,精神兴奋,易怒,体质量在造模第1天无显著性变化,造模第2,3天显著降低(P < 0.01)。与空白组相同性别小鼠相比,PCPA+水平台组雄性小鼠毛发粗糙,造模第1天表现出精神亢奋,易受惊;造模第2,3天小鼠精神不振,食欲减退,体质量显著降低(P < 0.01);PCPA+水平台组雌性小鼠毛发粗糙,随着剥夺天数增加,小鼠逐渐从亢奋状态转为萎靡状态,活动减少,低头站立且四肢蜷缩,常因短暂睡眠而落入水中,惊醒后爬上平台;造模第2,3天体质量显著降低(P < 0.01),见图1。 2.3 小鼠旷场实验结果 采用SuperMaze动物行为分析软件,分析并生成雄、雌小鼠旷场实验运动轨迹,见图2。与空白组雄性小鼠相比,PCPA组雄性小鼠的运动总路程、中心进入次数、平均速度和站立次数的变化趋势有所增加但无显著差异;水平台组和PCPA+水平台组雄性小鼠的运动总路程、中心进入次数显著增加(P < 0.05),平均速度和站立次数显著增加(P < 0.01);与PCPA组雄性小鼠相比,水平台组和PCPA+水平台组雄性小鼠中心进入次数显著增加(P < 0.05)。与空白组雌性小鼠相比,3种模型各组雌性小鼠的总路程、中心进入次数、平均速度和站立次数的变化趋势有所增加,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表1,2。 2.4 小鼠下丘脑尼氏染色结果 尼氏染色结果见图3。空白组雄性小鼠下丘脑的神经细胞清晰、完整,"
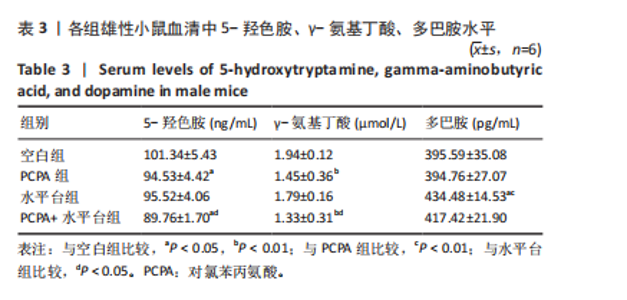
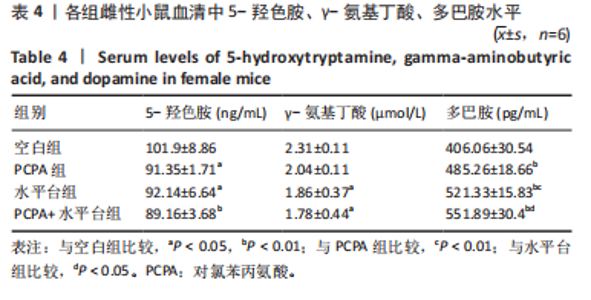
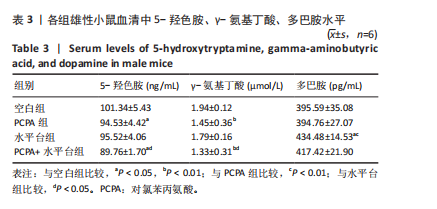
细胞核清晰可见,尼氏小体均匀分布,神经细胞数量正常。与空白组雄性小鼠相比,PCPA组雄性小鼠下丘脑的神经细胞轮廓、细胞核较为清晰,尼氏小体数量减少,排列松散;水平台组雄性小鼠下丘脑的神经细胞轮廓模糊,细胞间隙增大,尼氏小体分布不均匀;PCPA+水平台组雄性小鼠下丘脑的神经细胞轮廓较为模糊,细胞核皱缩,细胞明显水肿,尼氏小体固缩、核模糊,且分布不均匀,数量明显减少;空白组雌性小鼠下丘脑的神经细胞和细胞核清晰、完整,尼氏小体分布均匀,神经细胞数量正常。与空白组雌性小鼠下丘脑相比,PCPA组雌性小鼠下丘脑细胞皱缩,出现水肿,尼氏小体分布不均匀,数量减少;水平台组雌性小鼠下丘脑的神经细胞轮廓模糊,细胞间隙增大,细胞密度降低,尼氏小体数量减少且分布不均;PCPA+水平台组雌性小鼠下丘脑神经细胞轮廓模糊,细胞间隙增大,尼氏小体固缩、核模糊且分布不均匀,数量明显减少。 2.5 小鼠海马尼氏染色结果 见图3。空白组雄性小鼠海马区神经元细胞结构完整、排列紧密,尼氏小体分布均匀、染色清晰。与空白组雄性小鼠相比,PCPA组雄性小鼠的海马区神经元细胞排列略显紊乱,部分神经细胞出现固缩;水平台组雄性小鼠的神经元细胞排列稀疏,出现神经元丢失、细胞间隙增宽的现象,尼氏小体数量降低,部分细胞呈不规则形状;PCPA+水平台组雄性小鼠神经元细胞排列紊乱,神经元细胞数量显著减少,出现神经元丢失、细胞间隙增宽、细胞固缩、细胞轮廓不清的现象。空白组雌性小鼠海马区神经元结构完整、排列紧密,神经元数量正常,神经元细胞大且圆,无皱缩,尼氏小体分布均匀、染色清晰。与空白组雌性小鼠海马区相比,PCPA组雌性小鼠的神经元细胞排列稀疏,出现尼氏小体丢失、细胞间隙增宽的现象;水平台组雌性小鼠的神经元细胞排列稀疏,细胞间隙增宽,部分神经元细胞皱缩、轮廓不清;PCPA+水平台组雌性小鼠的神经元细胞排列紊乱,神经元细胞数量显著减少,出现神经元丢失、细胞间隙增宽、细胞固缩、细胞轮廓不清和尼氏小体着色变浅的现象。 2.6 小鼠血清中5-羟色胺、γ-氨基丁酸、多巴胺水平 与空白组雄性小鼠相比,PCPA组雄性小鼠血清中5-羟色胺、γ-氨基丁酸水平显著降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),多巴胺水平升高但无显著性;水平台组雄性小鼠血清中多巴胺水平显著降低(P < 0.01),5-羟色胺和γ-氨基丁酸水平降低但无显著性;PCPA+水平台组雄性小鼠血清中5-羟色胺、γ-氨基丁酸水平显著降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),多巴胺水平升高但无显著性。与PCPA组雄性小鼠比较,水平台组雄性小鼠多巴胺水平显著升高(P < 0.05)。与水平台组雄性小鼠比较,PCPA+水平台组雄性小鼠5-羟色胺、γ-氨基丁酸水平显著降低(P < 0.05)。与空白组雌性小鼠相比,PCPA组雌性小鼠血清中5-羟色胺水平显著降低(P < 0.05),多巴胺水平显著升高(P < 0.01),γ-氨基丁酸水平有降低趋势但无显著性;水平台组雌性小鼠血清中5-羟色胺、γ-氨基丁酸水平显著降低(P < 0.05),多巴胺水平显著升高(P < 0.01);PCPA+水平台组雌性小鼠血清中5-羟色胺、γ-氨基丁酸水平显著降低(P < 0.01,P < 0.05),多巴胺水平显著升高(P < 0.01)。与PCPA组雌性小鼠比较,水平台组雌性小鼠、PCPA+水平台组雌性小鼠多巴胺水平显著升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),见表3,4。"
| [1] ATROOZ F, SALIM S. Sleep deprivation, oxidative stress and inflammation. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020;119:309-336. [2] PERLIS ML, POSNER D, RIEMANN D, et al. Insomnia. Lancet. 2022; 400(10357):1047-1060. [3] RIEMANN D, BAGLIONI C, BASSETTI C, et al.European guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of insomnia. J Sleep Res. 2017;26(6):675-700. [4] 李颖莹. 基于数据挖掘的李灿东教授治疗失眠的临床用药特点研究[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2022. [5] 郑永博, 师乐, 朱婕, 等.《中国睡眠医学中心标准化建设指南》:肩负医学时代使命,心系人民睡眠健康[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2023,54(2):223-225. [6] FUTENMA K, TAKAESU Y, KOMADA Y, et al. Delayed sleep-wake phase disorder and its related sleep behaviors in the young generation. Front Psychiatry. 2023;14:1174719. [7] CHAPAGAI S, FINK AM. Cardiovascular diseases and sleep disorders in South Asians: A scoping review. Sleep Med. 2022;100:139-149. [8] HERRERO BABILONI A, BARIL AA, CHARLEBOIS-PLANTE C, et al. The putative role of neuroinflammation in the interaction between traumatic brain injuries, sleep, pain and other neuropsychiatric outcomes: a state-of-the-art review. J Clin Med. 2023;12(5):1793. [9] RICHARD GREEN A. Neuropharmacology of 5‐hydroxytryptamine. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;147(S1):S145-S152. [10] SHARON O, BEN SIMON E, SHAH VD, et al. The new science of sleep: From cells to large-scale societies. Plos Biology. 2024;22(7):e3002684. [11] 黄会珍,赵洪庆,王宇红,等.抑郁症失眠大鼠模型的构建与评价[J].中国实验动物学报,2021,29(3):323-331. [12] 胡霞,常海霞,谢艳红,等.模拟不同模式的睡眠剥夺对雌性大鼠脑组织损害及行为学影响的研究[J].新疆医科大学学报,2025, 48(5):614-620. [13] 刁华琼,张婧,王敏,等.改良的多平台水环境法在睡眠剥夺动物模型中的应用与评价[J].中国实验动物学报,2023,31(1):120-128. [14] XIE JF, SHAO YF, WANG HL, et al. Neuropeptide S counteracts paradoxical sleep deprivation-induced anxiety-like behavior and sleep disturbances. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:64. [15] DIAO H, LI Y, SUN W, et al. REM sleep deprivation induced by the modified multi-platform method has detrimental effects on memory: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav Brain Res. 2023;454: 114652. [16] LIN H, XU Y, XIONG H, et al. Mechanism of action of Panax ginseng alcohol extract based on orexin-mediated autophagy in the treatment of sleep and cognition in aged sleep-deprived rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025;337:118907. [17] YUNHUA S, LAN Z, GUANGLEI LEI, et al. Effects of Ozonated Autohemotherapy on Melatonin and Oxidative Stress in Rats with Sleep Deprivation.Lab Anim Comp Med. 2020;40(2):110. [18] 刁华琼,张婧,王敏,等.改良的多平台水环境法在睡眠剥夺动物模型中的应用与评价[J].中国实验动物学报,2023,31(1):120-128. [19] 谭甜,张梦,李彩琴,等.电针对对氯苯丙氨酸致失眠大鼠小胶质细胞及炎性因子的影响[J].中国比较医学杂志,1-10[2025-06-26]. [20] 郭海波,王慧.对氯苯丙氨酸在动物失眠模型中的应用概述[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2019,29(6):135-140. [21] PETERS A, ROSENE DL, MOSS MB, et al. Neurobiological bases of age-related cognitive decline in the rhesus monkey. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1996;55(8):861-874. [22] 赵淑月,邱智东,刘锐,等.苍术挥发油对失眠小鼠的作用机制研究及其微乳制备[J].中草药,2025,56(9):3175-3186.、 [23] KOCEVSKA D, LYSEN TS, DOTINGA A, et al. Sleep characteristics across the lifespan in 1.1 million people from the Netherlands, United Kingdom and United States: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nat Hum Behav. 2021;5(1):113-122. [24] HAJALI V, SHEIBANI V, ESMAEILI-MAHANI S, et al. Female rats are more susceptible to the deleterious effects of paradoxical sleep deprivation on cognitive performance. Behav Brain Res. 2012;228(2):311-318. [25] WANG L, QI X, WANG S, et al. Banxia-Yiyiren alleviates insomnia and anxiety by regulating the gut microbiota and metabolites of PCPA-induced insomnia model rats.Front Microbiol. 2024;15:1405566. [26] 伞雨晴,史佳宁,张振贤.光照、咖啡因及联合法诱导建立斑马鱼失眠模型的比较研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2024,34(11):59-67. [27] 黄晓巍,王宇,王亚杰,等.枣仁茯苓玉竹膏改善阴虚型失眠作用研究[J].人参研究,2022,34(2):21-26. [28] 戴梅竹,张钰成,向星亮,等.加味甘麦大枣汤的物质基础及其对睡眠剥夺小鼠的药效作用研究[J].时珍国医国药,2025,36(2):266-272. [29] 张认真,叶钰娟,魏玉婷,等.肝郁气滞型失眠实验动物模型复制方法及评价概述[J].中医杂志,2024,65(14):1496-1503. [30] 呙霞.睡眠剥夺小鼠模型的建立及宁心安神法的干预作用[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学,2015. [31] 李博之.基于代谢组学和肠道微生物组学探讨调肝治法抗抑郁的作用机制[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2024. [32] 胡金,韦姗姗,彭君美,等.药物筛选的常用失眠动物模型的研究状况[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2023,39(18):2708-2712. [33] ZHANG W, ZHANG X, YAN D, et al. Establishment of insomnia model of chronic unpredictable stress in rats. Heliyon. 2023;9(7):e18134. [34] DRESSLE RJ, RIEMANN D. Hyperarousal in insomnia disorder: Current evidence and potential mechanisms.J Sleep Res. 2023;32(6):e13928. [35] 包可,康宏向,后少俊,等.夜间蓝光暴露诱发小鼠焦虑、抑郁行为及其神经机制研究[J].军事医学,2025,49(6):450-457. [36] CHEN F, BERTELSEN AB, HOLM IE, et al. Hippocampal volume and cell number in depression, schizophrenia, and suicide subjects. Brain Res. 2020;1727:146546. [37] ZHANG S, ZHANG Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates sleep deprivation-induced inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis via VEGF-VEGFR2 signaling and inhibits neuroinflammation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165:115085. [38] 刘金雨,张紫萦,郑秀茜,等.舒更解郁方通过调节Nrf2/HO-1信号通路对围绝经期抑郁的作用机制研究[J].现代中药研究与实践, 2025,39(3):42-48. [39] OIKONOMOU G, ALTERMATT M, ZHANG R, et al. The serotonergic raphe promote sleep in zebrafish and mice. Neuron. 2019;103(4):686-701. e8. [40] VARINTHRA P, ANWAR SNMN, SHIH SC, .et al. The role of the GABAergic system on insomnia. Tzu Chi Med J. 2024;36(2):103-109. [41] JU YH, CHO J, PARK JY, et al. Tonic excitation by astrocytic GABA causes neuropathic pain by augmenting neuronal activity and glucose metabolism. Exp Mol Med. 2024;56(5):1193-1205. [42] EBAN-ROTHSCHILD A, ROTHSCHILD G, GIARDINO WJ, et al. VTA dopaminergic neurons regulate ethologically relevant sleep–wake behaviors. Nat Neurosci. 2016;19(10):1356-1366. [43] GONG L, CHEN K, ZHANG H, et al. Dopamine multilocus genetic profile influence on reward network in chronic insomnia disorder with depression. Sleep Med. 2023;112:122-128. [44] TRUJILLO V, CAMILO TA, VALENTIM-LIMA E, et al. Neonatal treatment with para-chlorophenylalanine (pCPA) induces adolescent hyperactivity associated with changes in the paraventricular nucleus Crh and Trh expressions. Behav Brain Res. 2024;462:114867. [45] ARTHAUD S, VARIN C, GAY N, et al. Paradoxical (REM) sleep deprivation in mice using the small‐platforms‐over‐water method: polysomnographic analyses and melanin‐concentrating hormone and hypocretin/orexin neuronal activation before, during and after deprivation. J Sleep Res. 2015;24(3):309-319. [46] 侯小斌,宋美卿,仝立国,等. PCPA小平台水环境睡眠剥夺大鼠脑干神经递质变化[C]//第十二届中国北方实验动物科技年会论文集. 2014:158-164. [47] 邱振刚,张洪斌,王世军,等.小平台水环境间断睡眠剥夺法复制大鼠失眠模型的评价[J].中国科技论文在线精品论文,2008,1(15): 1733-1738. [48] ZHAO Y, FANG R, BIAN H, et al. Comparative analysis of sleep deprivation models: Impacts on sleep architecture, emotional state, cognitive function, and biochemical indicators in male rats. Behav Brain Res. 2025;482:115451. |
| [1] | Zhang Qingtong, Chen Leqin, Liu Chang, Chen Yuting, Guo Ruiwu. Neuromechanism of the endocannabinoid system in regulating exercise motivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Min Changqin, Huang Ying. Construction of pH/near-infrared laser stimuli-responsive drug delivery system and its application in treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1940-1951. |
| [3] | Yang Jing, Wang Houmei, Wang Yi, Song Min, Ren Jie, Dai Lujun, Xiao Ziwen. Constructing a rat animal model of pelvic organ prolapse: a comparison of three modeling methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 864-872. |
| [4] | Sun Danhe, Guo Xiaoling, Zhao Lingzhou. Construction and osteogenic activity of titanium dioxide nanotube and polydopamine composite coating on titanium implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5167-5177. |
| [5] | Wang Xinyue, Li Hongli, Guo Chunhui, Chen Jibing, Yu Hua. Changes in the expression of six microRNAs in ovarian tissue from animal models of premature ovarian failure and in peripheral blood of patients with premature ovarian failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4675-4684. |
| [6] | Fu Jingyue, Zhou Qinfeng, Li Muzhe, Ma Yong, Pan Yalan, Sun Jie, Huang Xiangyang, Guo Yang. Preparation and evaluation of an animal model of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis comorbidity in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4299-4308. |
| [7] | Peng Hao, Jiang Yang, Song Yanping, Wu Quan, Yao Na, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. H-type angiogenesis and its role in various skeletal disease animal models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4154-4165. |
| [8] | Wu Tianyi, Miao Yiming, Wan Kaichen, Teng Yun, Zou Jun. Protective effect of mesoporous ZLN005@polydopamine nanoparticles on chondrocytes in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3576-3585. |
| [9] | Zhang Yingbi, Li Minghui, Zhang Xiaorui, Yin Jihong, Wang Peng. The roles and mechanisms of axon guidance molecules in alpha-synuclein-related neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2834-2845. |
| [10] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [11] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [12] | Li Mingzhe, Ye Xiangling, Wang Bing, Yu Xiang. Preparation and osteogenic properties of liquid crystal display light-cured polylactic acid scaffold loaded with nano-tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 670-677. |
| [13] | Chen Lijuan, Gao Xinxue, Wu Jin, Du Ying, Lyu Meijun, Sui Guoyuan, Jia Lianqun, Pan Guowei. Construction and evaluation of spleen-deficiency hyperlipidemia mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6237-6242. |
| [14] | Li Shuyuan, Yang Dawen, Zeng Zhanpeng, Cai Qunbin, Zhang Jingtao, Zhou Qishi. Application of induced membrane technique for repairing critical-sized bone defects: advantages and future development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6083-6093. |
| [15] | Lei Senlin, Chen Xiaoan, Chen Ping, Wang Zhaofeng. Exercise prevention and treatment of Parkinson’ s disease mediated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor: role and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5454-5468. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||