Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (16): 4045-4053.doi: 10.12307/2026.707
Previous Articles Next Articles
Predictive efficacy of machine learning models for postoperative prognosis in older adult patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage
Chen Feijun, Chen Yingguo, Li Zhengyang, Hu Yuan, Li Fang
- Yichun People's Hospital, Yichun 336000, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2025-04-22Accepted:2025-08-26Online:2026-06-08Published:2025-11-26 -
Contact:Chen Feijun, Associate chief physician, Yichun People's Hospital, Yichun 336000, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Chen Feijun, Associate chief physician, Yichun People's Hospital, Yichun 336000, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:Jiangxi Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission Science and Technology Program, No. 20204762 (to CFJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Feijun, Chen Yingguo, Li Zhengyang, Hu Yuan, Li Fang. Predictive efficacy of machine learning models for postoperative prognosis in older adult patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4045-4053.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
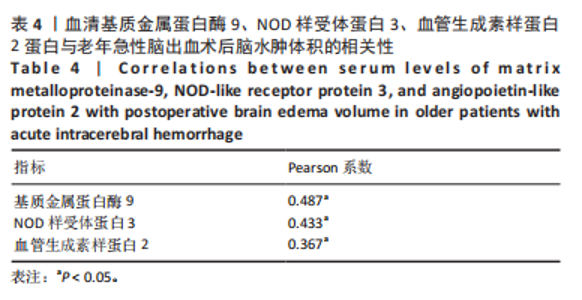
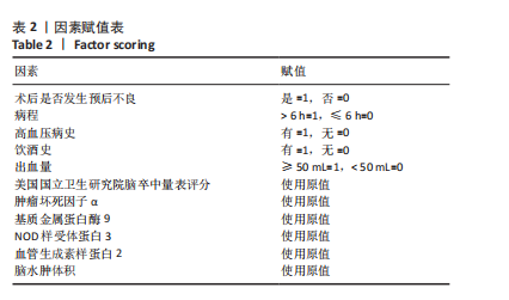
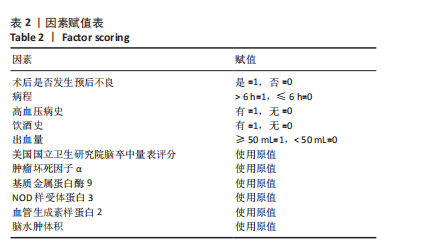
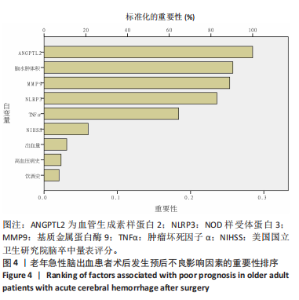
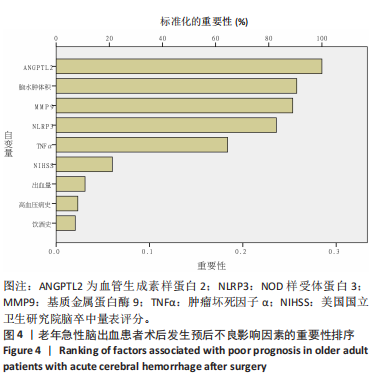
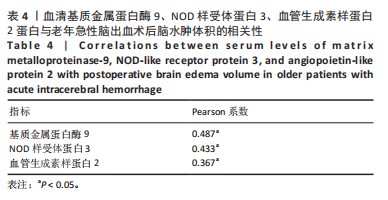
模型公式:Logit(p)=0.036×基质金属蛋白酶9+ 4.160×NOD样受体蛋白3+4.413×血管生成素样蛋白2+1.925×脑水肿体积-51.59,敏感度为0.973, 特异度为0.985,Youden指数为0.958,P < 0.001,Hosemer- Lemeshow检验显示,χ2=4.972,P > 0.05。 2.5 血清基质金属蛋白酶9、NOD样受体蛋白3、血管生成素样蛋白2蛋白与老年急性脑出血术后脑水肿体积的相关性 将老年急性脑出血患者外周血清基质金属蛋白酶9、NOD样受体蛋白3、血管生成素样蛋白2蛋白与其脑水肿体积进行相关性分析,可见血清基质金属蛋白酶9、NOD样受体蛋白3、血管生成素样蛋白2蛋白均与其脑水肿体积呈正相关(均P < 0.05),对比详见表4。"
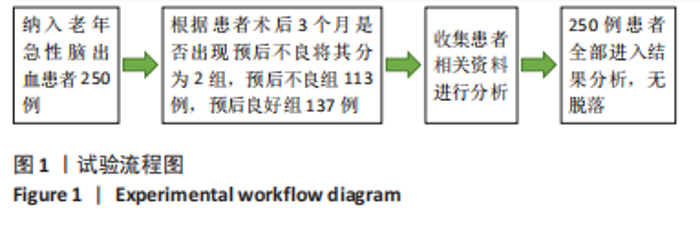
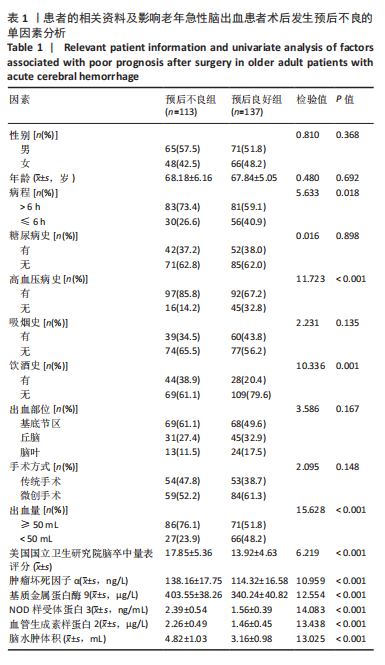
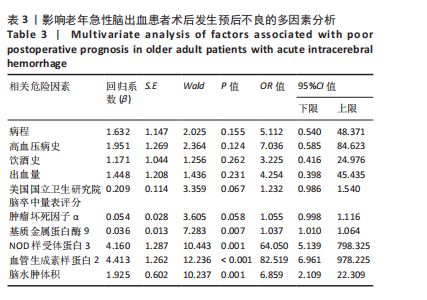
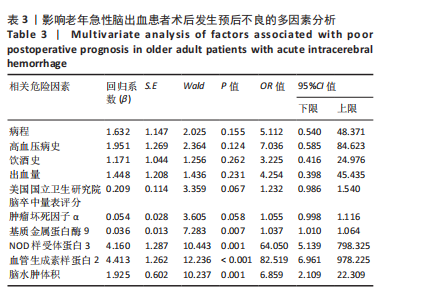
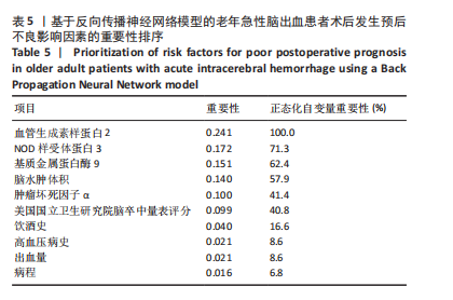
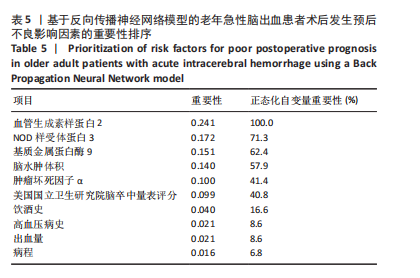
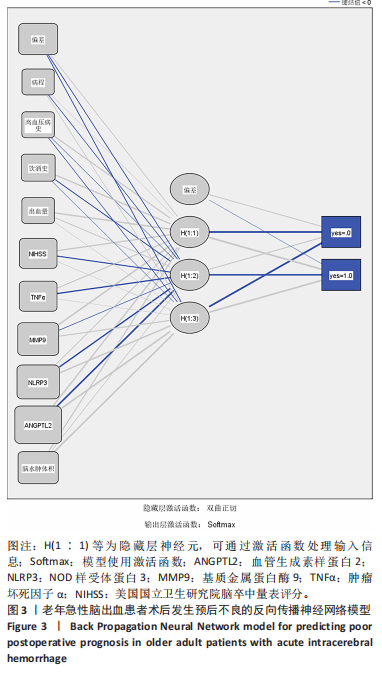
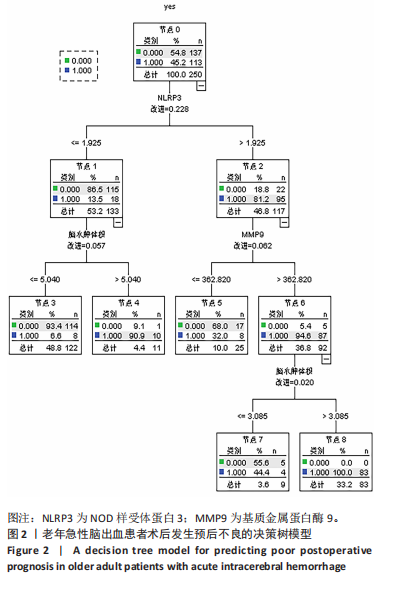
2.6 老年急性脑出血患者术后发生预后不良的决策树模型构建 基于决策树模型构建的分类树模型共4层、8个节点、5个终结点。分类所用影响因素包括NOD样受体蛋白3、脑水肿体积及基质金属蛋白酶9,其中NOD样受体蛋白3为根节点,当NOD样受体蛋白3≤1.925 ng/mL时,其预后不良患者占比为13.5%,从此处往下,当脑水肿体积≤5.040 mL时其预后不良患者占比为6.6%,当脑水肿体积> 5.040 mL时其预后不良患者占比为90.9%。回到根节点,当NOD样受体蛋白3 > 1.925 ng/mL时其预后不良患者占比为81.2%,从此处往下,当基质金属蛋白酶9≤362.82 μg/L时其预后不良患者占比为32.0%,当基质金属蛋白酶9 > 362.82 μg/L时则为94.6%;从此处往下,当脑水肿体积≤3.085 mL时,预后不良患者占比为44.4%,当脑水肿体积> 3.085 mL时,预后不良患者占比为100%,见图2。 2.7 老年急性脑出血患者术后发生预后不良的反向传播模型构建 采用反向传播神经网络构建老年急性脑出血患者术后发生预后不良的反向传播模型,以250例患者中的169例为建模集,81例为验证集做神经网络模型拟合,设置隐藏层数最小1,最大50,其中包含H(1∶1)、H(1∶2)、H(1∶3)3个节点,隐藏层激活函数为双曲正切,输出层激活函数为Softmax。"
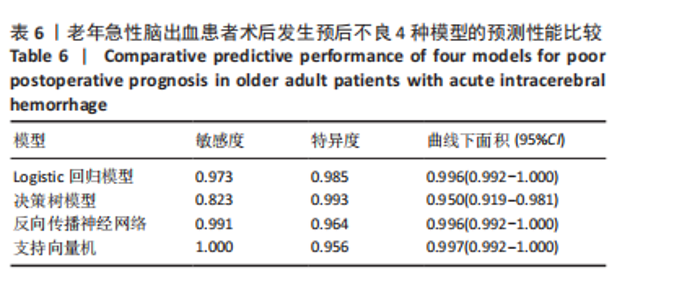
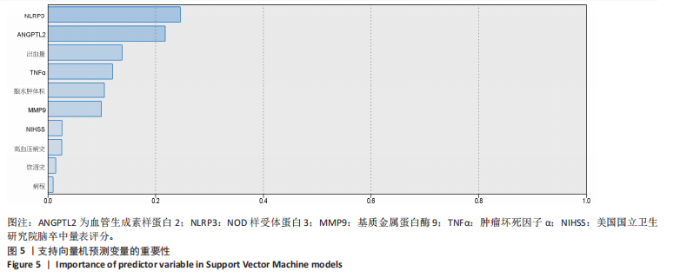
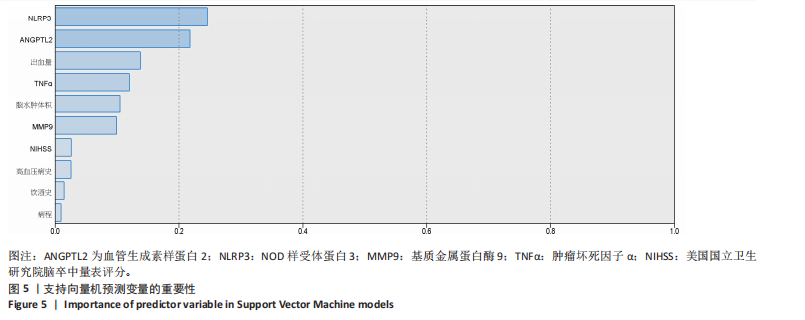
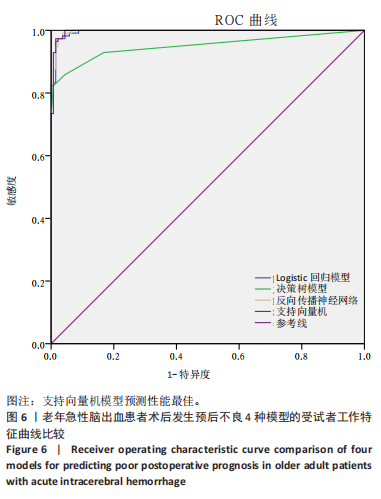
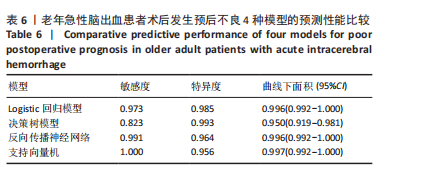
2.8 老年急性脑出血患者术后发生预后不良的支持向量机模型 支持向量机模型设置规则化参数为10,回归精确度0.1,内核类型径向基函数,径向基函数伽马系数为0.1。结果显示影响老年急性脑出血患者术后发生预后不良影响因素重要性的前5位排序为NOD样受体蛋白3(预测变量重要性=0.25)、血管生成素样蛋白2(预测变量重要性=0.22)、出血量(预测变量重要性=0.14)、肿瘤坏死因子α(预测变量重要性=0.12)、脑水肿体积(预测变量重要性=0.10),见图5。 2.9 模型预测性能比较 以4个预测模型计算得到预测变量为测试变量,患者有无出现预后不良为状态变量绘制受试者工作特征曲线,结果可见,Logistic回归曲线下面积为0.996,敏感度为0.973,特异度为0.985;决策树的曲线下面积为0.950,敏感度为0.823,特异度为0.993;反向传播神经网络的曲线下面积为0.996,敏感度为0.991,特异度为0.964;支持向量机的曲线下面积为0.997,敏感度为1.000,特异度为0.956,可见其中支持向量机的曲线下面积大于其他模型,见表6及图6。"
| [1] MAGID-BERNSTEIN J, GIRARD R, POLSTER S, et al. Cerebral Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Future Directions.Circ Res. 2022;130(8):1204-1229. [2] KASE CS, HANLEY DF. Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Advances in Emergency Care. Neurol Clin. 2021;39(2):405-418. [3] MOROTTI A, BOULOUIS G, DOWLATSHAHI D, et al. Intracerebral haemorrhage expansion: definitions, predictors, and prevention. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(2):159-171. [4] 张琳.急性脑出血疾病严重程度及预后的影响因素分析[J].航空航天医学杂志,2024,35(9):1051-1053 [5] WANG M, GE P, JIAO Y, et al. Emergency neurosurgical hybrid operating platform for acute intracranial hemorrhage (E-HOPE). Chin Neurosurg J. 2024;10(1):33. [6] 刘诗宇,任建伟,刘洁莹.不同时间点中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比值与急性脑出血后脑水肿程度和短期预后的关系[J].中国现代医学杂志,2021,31(9):18-22 [7] CHEN S, LI L, PENG C, et al. Targeting Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response for Blood-Brain Barrier Protection in Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022;37(1-3):115-134. [8] ZHANG BW, SUN KH, LIU T, et al. The Crosstalk Between Immune Cells After Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neuroscience. 2024;537:93-104. [9] WAN Y, HOLSTE KG, HUA Y, et al. Brain edema formation and therapy after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;176:105948. [10] DENG Q, YANG Y, BAI H, et al. Predictive Value of Machine Learning Models for Cerebral Edema Risk in Stroke Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Brain Behav. 2025;15(1):e70198. [11] 顾双双,沙杜鹃,高凤娟,等.基质金属蛋白酶9和中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比值预测自发性脑出血患者的迟发性血肿周围脑水肿[J].国际脑血管病杂志,2021,29(2):114-119 [12] WANG Y, HUANG H, HE W, et al. Association between serum NLRP3 and malignant brain edema in patients with acute ischemic stroke. BMC Neurol. 2021;21(1):341. [13] FENG M, AN Y, QIN Q, et al. Sphk1/S1P pathway promotes blood-brain barrier breakdown after intracerebral hemorrhage through inducing Nlrp3-mediated endothelial cell pyroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2024;15(12):926. [14] BELLUT M, PAPP L, BIEBER M, et al. NLPR3 inflammasome inhibition alleviates hypoxic endothelial cell death in vitro and protects blood-brain barrier integrity in murine stroke. Cell Death Dis. 2021;13(1):20. [15] 李净,温松楠.基于3种机器学习法的太阳辐射模拟研究[J].遥感技术与应用,2020,35(3):615-622. [16] 杨翀,李旭东,吕良福,等.基于机器学习预测动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血预后模型的临床研究与应用[J].中国医院药学杂志,2024, 44(3):257-262. [17] HU P, LI Y, LIU Y, et al. Comparison of Conventional Logistic Regression and Machine Learning Methods for Predicting Delayed Cerebral Ischemia After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Multicentric Observational Cohort Study. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:857521. [18] 王家良.临床流行病学:临床科研设计,测量与评价[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2014: 157-159. [19] 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国脑出血诊治指南(2019)[J].中华神经科杂志,2019,52(12): 994-1005. [20] 潘慧斌,王志翔,凌莉,等.神经危重症患者脑水肿急性治疗指南[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2020,29(9):1162-1164 [21] 孙冲,徐迪荣,李碧磊.改良Rankin量表在急性大面积脑梗死长期生存的预后价值[J].医学研究杂志,2012,41(12):179-182 [22] 李倩,刘芸宏,吴晓慧,等.基于决策树和Logistic回归预测出血性脑卒中手术后医院感染风险[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2021, 31(23):3556-3561 [23] 邹琼,吴曦,张杨,等.基于麻雀搜索算法优化的BP神经网络模型对2型糖尿病肾病的预测研究[J].中国全科医学,2024,27(8):961-970. [24] 张娟,李海芬,李小曼,等.糖尿病足溃疡复发风险预测模型的构建:基于Logistic回归和支持向量机及BP神经网络模型[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(32):4013-4019. [25] ZHANG XW, WU Y, WANG DK, et al. Expression changes of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β and HO-1 in hematoma surrounding brain areas after intracerebral hemorrhage. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2019;33(5):1359-1367. [26] HUANG L, WU Q, YE F, et al. Apolipoprotein E-ε4 allele is associated with perihematomal brain edema and poor outcomes in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):5682. [27] WAN Y, HOLSTE KG, HUA Y, et al. Brain edema formation and therapy after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;176:105948. [28] CHEN Y, CHEN S, CHANG J, et al. Perihematomal Edema After Intracerebral Hemorrhage: An Update on Pathogenesis, Risk Factors, and Therapeutic Advances. Front Immunol. 2021;12:740632. [29] 张奎明,葛鸾蝶,崔应麟,等.康益胶囊对缺血再灌注脑水肿大鼠脑组织AQP4、MMP-9蛋白的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2023, 43(16):3954-3960. [30] DODD WS, NODA I, MARTINEZ M, et al. NLRP3 inhibition attenuates early brain injury and delayed cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):163. [31] 王萃,王强,赵燕,等. 血清NLRP3、ANGPTL2水平与高血压脑出血患者术后发生脑水肿的关系[J].山东医药,2024,64(31):75-77. [32] WARE JB, DOLUI S, DUDA J, et al. Relationship of Cerebral Blood Flow to Cognitive Function and Recovery in Early Chronic Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2020;37(20):2180-2187. [33] SUN C, QIN B, ZHANG J, et al. Increased brain volume in the early phase of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage leads to delayed cerebral ischemia. Front Surg. 2024;11:1467154. [34] SUN X, SUN G, HE B, et al. Application of 3D visualization technology based on hematoma edge key points setting for emergency hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage surgery in primary hospitals. J Clin Neurosci. 2024;119:39-44. [35] 郭燕霞,颜敏,李丽,等.有氧运动通过调节海马小胶质细胞表型极化缓解青春期间歇性酒精暴露所致的成年期大鼠认知障碍[J].中国病理生理杂志,2023,39(1):45-54 [36] 王勇,刘海军,徐瑞春,等.MMP-9、TAT及S100β蛋白在老年急性脑出血中的表达及对脑水肿的预测价值[J].中国老年学杂志, 2021,41(19):4172-4175. [37] 崔承,陈飞龙,李禄全,等.机器学习在新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎诊疗中的研究进展[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2023,25(7):767-773. [38] CHOI RY, COYNER AS, KALPATHY-CRAMER J, et al. Introduction to Machine Learning, Neural Networks, and Deep Learning. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2020;9(2):14. [39] HAUG CJ, DRAZEN JM. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Clinical Medicine, 2023. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(13):1201-1208. [40] CHEN Y, DU H, WEI BH, et al. Development and validation of risk-stratification delirium prediction model for critically ill patients:a prospective,observational,single-center study. Medicine. 2017; 96(29):e7543. |
| [1] | Lai Jiaming, , Song Yuling, Chen Zixi, Wei Jinghuan, Cai Hao, , Li Guoquan, . Screening of diagnostic markers for endothelial cell Senescence in mice with radiation-induced heart disease and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1450-1463. |
| [2] | Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105. |
| [3] | Gu Fucheng, Yang Meixin, Wu Weixin, Cai Weijun, Qin Yangyi, Sun Mingyi, Sun Jian, Geng Qiudong, Li Nan. Effects of Guilu Erxian Glue on gut microbiota in rats with knee osteoarthritis: machine learning and 16S rDNA analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1058-1072. |
| [4] | Guan Yujie, Zhao Bin. Application and prospect of artificial intelligence in screening and diagnosis of scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 721-730. |
| [5] | Wang Zhipeng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Hongwei, Zhao Xiyun, Li Yuanzhen, Guo Chenglong, Qin Daping, Ren Zhen. A systematic review of application value of machine learning to prognostic prediction models for patients with lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 740-748. |
| [6] | Yu Weijie, Cao Dongdong, Guo Tianci, Niu Puyu, Yang Jialin, Wang Simin, Liu Aifeng. Risk prediction models of recurrence after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 749-759. |
| [7] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [8] | Lu Liwei, Huang Keqi, Chen Yueping, Zhuo Yinghong, Zhu Naihui, Wei Peng. Bioinformatics-based analysis of shared genes and associations in immune mechanisms between rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4253-4264. |
| [9] | Sun Meilan, Zhao Xiaoliang, Yan Tianyuan, Zhang Shizhe, Niu Guochang, Guan Yulong, Li Hua. Correlation between quantitative indicators of three-dimensional deformity of the first metatarsal bone and functional prognosis after osteotomy and orthopedic treatment in patients with hallux valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(15): 3855-3861. |
| [10] | Wu Jun, Zhang Yuzhu, Dong Xiaojie, Wang Kaidi, Sun Bin. Experimental validation of cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathway related gene signatures and molecular subtypes in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3145-3155. |
| [11] | Qi Xiang, Cao Shan, Chen Jian, Zhang Yijia, Liu Keke, Xu Zifu, Liu Wang, Fu Xiaoxiao, Yin Xiaolei. Screening of genes related to mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis in atherosclerosis and target prediction of regulatory traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2641-2652. |
| [12] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [13] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [14] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| [15] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||