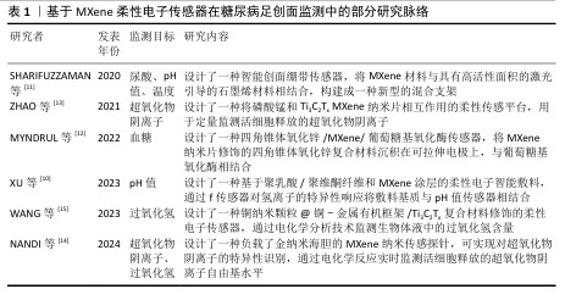
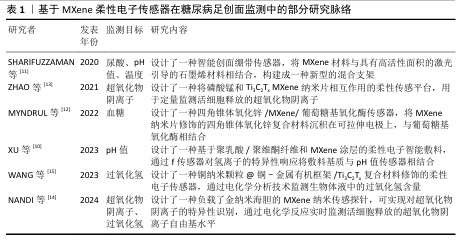
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 2023-2032.doi: 10.12307/2026.056
Previous Articles Next Articles
Advantages of MXene-based flexible electronic sensors and their application in monitoring diabetic foot wounds
Pan Zhiyi, Huang Jiawen, Xue Wenjun, Xu Jianda
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (Changzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-21Accepted:2025-03-21Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-17 -
Contact:Pan Zhiyi, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (Changzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Xu Jianda, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (Changzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant No. 12372305 (to XJD); a grant from Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Jiangsu Province, No. YB20200053 (to XJD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Pan Zhiyi, Huang Jiawen, Xue Wenjun, Xu Jianda. Advantages of MXene-based flexible electronic sensors and their application in monitoring diabetic foot wounds[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2023-2032.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
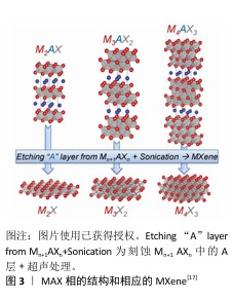
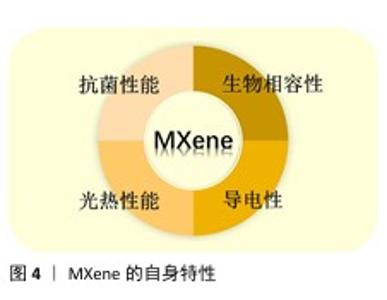
2.2 MXene的概述 MXene是一类由过渡金属碳氮化物组成的新型二维层状纳米材料,化学通式为Mn+1XnTx (n=1,2或3),其中M表示过渡金属元素,X表示碳、氮或者碳氮,Tx代表表面基团(例如-O、-OH、-Cl或-F等)[16]。 在常规的MXene制备流程中,通常采用选择性刻蚀碳/氮化物的母体(MAX)相(图3[17]),M代表过渡金属元素;A通常是第13或14族元素,如Al或Si;X代表碳或氮[18]。由于MA键的强度比MX键更弱,因此通过刻蚀剂除去易被破坏、活性更强的A组元素,能够保留非常稳定的Mn+1Xn的层状结构[19]。Mxene丰富的表面官能团在不同制备、刻蚀方式下呈现出不同的结构性质,从而影响MXene材料的特性。目前已通过实验制备出的MXene材料有30多种(包括Ti3C2、Ti2C、Nb2C、V2C、Ti3Cn、Nb2CF2等)[20],其中医学领域最常见且研究最多的是Ti3C2Tx。 "

2.3.1 导电性 相对于其他二维材料,MXene表现出更卓越的导电性能,通过自组装、聚合和共价相互作用能够赋予MXene不同强度的导电率。由于MXene具备与金属类似的内部电子运动状态和性能传递,不仅能形成近金属高达9 880 S/cm的导电率[22],呈现出电阻率与温度之间的线性关系,随着温度的降低,低电阻率使其在生物医学应用方面具备更高的性能[23]。 同时,MXene通过与不同的材料聚合获得不同的电化学性能,例如与水凝胶结合时,利用强度较小的蚀刻剂使获得的MXene纳米片面积更大、厚度更小[24],制成的水凝胶表现出更显著的导电性。 2.3.2 抗菌性 相关研究表明,革兰阳性菌(如金黄色葡萄球菌 S.aureus)和革兰阴性菌(如大肠杆菌 E. coli)是糖尿病足感染的最重要原因之一[25],而MXene材料具有良好的抗菌性,对这两种菌的抑菌率分别达到了77.78%和85.82%,表现出了有效抗菌和感染控制的能力[26]。MXene的抗菌机制主要有以下几种:①通过MXene锋利边缘形成的“纳米刀”结构,造成部分细菌细胞壁与细胞膜的物理损伤及细胞质泄露[27];②氧化还原产生活性氧自由基,致使细菌细胞内的谷胱甘肽氧化应激[28],从而消灭细菌;③随着MXene浓度的提高,细胞会包裹在作为抗菌药物载体的 MXene纳米片上,使药物能够更大程度地被细胞摄取,实现药物的靶向传递和控制释放;④在光热介导下可将吸附的光能转化为热能,致使蛋白质降解,阻断DNA复制,同时产生活性氧自由基破坏细菌膜的结构,使细菌失活或死亡。 2.3.3 光热性能 不同结构的MXene材料能产生不同程度的光热效应,例如,Ti3C2Tx具有良好的优异转换能 力[29],可在近红外激光照射下将吸收的光能转移到细菌上,促进细菌结构的消融,从而消灭病原体。LI团队[30]成功研发出一种多功能可注射性水凝胶,在过氧化氢/偏硼酸体系下将透明质酸-多巴胺和MXene@聚多巴胺的儿茶酚基团进行氧化偶联,同时,MXene在近红外辐射下产生的热量结合轻度热刺激能够激活偏硼酸的催化作用,进而促使氧载体精确、定量地释放氧气,对糖尿病创面愈合起到了积极显著的促进作用。 2.3.4 生物相容性 生物相容性是决定材料在生物医学领域应用潜力的最重要因素。MXene表面存在着大量亲水官能团(如-OH、-O及-F),提高了MXene的适应能力,赋予其优异的生物相容性[31]。MXene因比表面积和自身电荷的特性,能够利用各种大分子、聚合物发生表面化学反应,引入新的化学官能团以提高生物相容性,并来赋予材料不同的功能。RASHID 等[32]用聚丙烯乙二醇和聚乙二醇修饰Ti3C2Tx纳米片,评估了该纳米片对正常细胞(如HaCaT人永生化角质细胞和MCF-10A人正常乳腺上皮细胞)和癌性细胞(如MCF-7人乳腺癌细胞和A375人恶性黑色素瘤细胞)的细胞毒性,为纳米材料在创面敷料中的应用提供了参考价值。ALIREZA团队[33]创造性地将蜂蜜和 MXene渗入壳聚糖基水凝胶,蜂蜜中的生物活性化合物对Mxene纳米材料的表面结构进行有机改性,所形成的多功能导电复合材料比一般的壳聚糖基水凝胶表现出更优异的生物相容性。 "

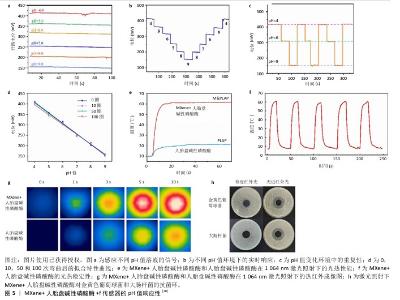
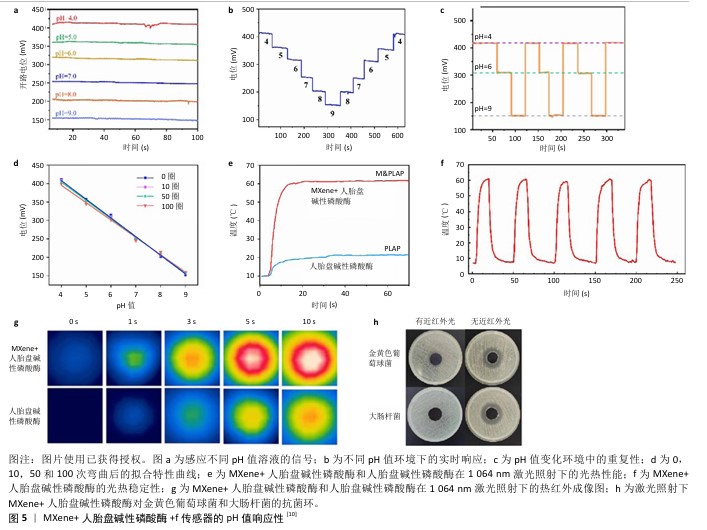
2.4 MXene柔性电子传感器在糖尿病足创面监测中的应用及作用机制 在糖尿病足的临床防治中,对创面的实时监测不仅有利于早期评估创面状态(包括感染情况、愈合情况)来帮助医生有效判断病情、疗效及预后,而且通过监测数据可及时有效地实施有针对性的干预措施,为患者提供更为高效的诊疗服务。面对糖尿病足发生发展的复杂机制,当前已经在监测pH值、温度、尿酸、血糖、超氧化物阴离子及过氧化氢水平等方面取得了一定成果,通过实现动态监测各项指标的实时数值及波动,为糖尿病足的防治提供了有效途径。 2.4.1 监测pH值 正常足部皮肤pH值为4.5-5.6,糖尿病足患者由于受到感染、缺氧等因素的影响,皮肤常处于炎性反应阶段,pH值常在碱性范围内波动。慢性创面的pH值在愈合之前处于碱性状态,它会随着治疗的进展逐渐变成中性,然后转变为酸性[34-35]。多项研究表明,弱酸性环境可降低蛋白酶活性、抑制细菌生长,继而有效控制感染、促进创面愈合[36]。据此,XU团队[10]开发出一种基于聚乳酸/聚维酮纤维和Mxene涂层的柔性电子智能敷料,依靠f传感器对H+的特异性响应将敷料基质与pH传感器相结合,当该复合材料暴露在不同pH值的缓冲液时,借助f传感器的灵敏度和记录的输出电位及时高效地动态监测创面的pH值,进而判断感染情况(图5)。"
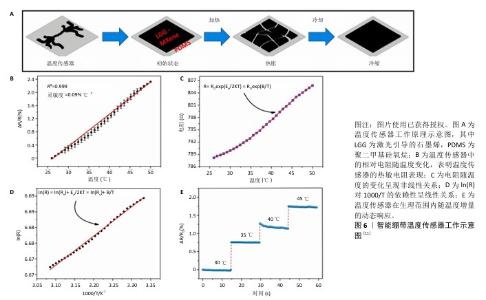
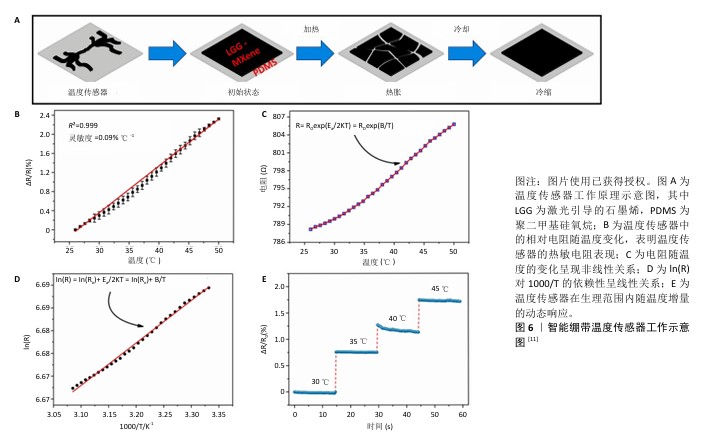
2.4.2 监测温度 由于局部压力、神经炎症等因素的影响,糖尿病足局部往往会表现出不同的温度,并且足部皮肤表面温度变化与糖尿病足溃疡的发生风险呈线性关系[37],因此,针对糖尿病患者实施足部温度监测被认为是及时发现足部炎症、组织破坏的有效方式。以往临床研究常采用红外热像仪可视化监测足部皮肤表面温度分布[38],通过接收皮肤向外辐射的红外能量并将它转化为电信号,经过处理后形成与皮肤表面的热分布场相对应的红外热像图,继而确定皮肤温度异常区域及数值,但该类监测方式往往具有严重的滞后性,诊断价值有限。 近来,可实现实时监测的MXene柔性电子传感器成为糖尿病足患者足部温度监测的焦点。其中,凭借Mxene材料出色的导电性,SHARIFUZZAMAN团队[11]将MXene材料与具有高活性面积的激光引导的石墨烯材料相结合构建成一种新型的混合支架,以此制备出一种智能创面绷带传感器,这款传感器以激光引导的石墨烯-MXene/聚二甲基硅氧烷电极作为热敏电阻,紧密贴合在创面周边区域,聚二甲基硅氧烷电极在高热环境下受热膨胀致使混合支架间产生裂缝,夹层中的声子散射加剧,电阻值随着温度的升高而增大,表现出对25-50 ℃这一区间的温度变化迅速捕捉(图6),精准反馈、稳定呈现动态温度响应,全方位彰显了监测的及时性、准确性、可靠性。"
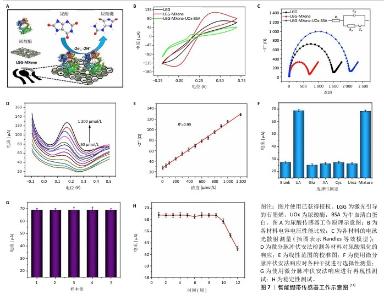
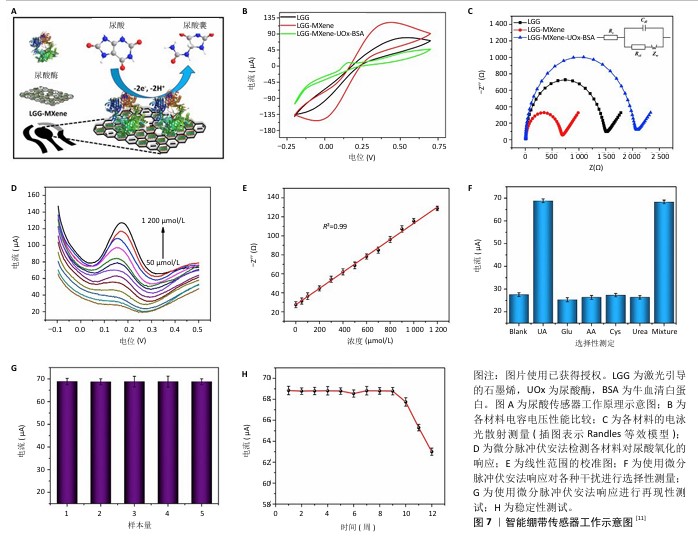
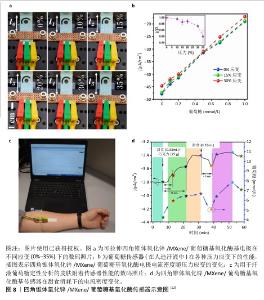
2.4.3 监测尿酸水平 高尿酸血症是一种因体内嘌呤代谢紊乱致使血尿酸生成过多或排泄减少,造成血尿酸水平升高的代谢性疾病,临床上通常以成人在正常嘌呤饮食下(不区分性别),非同日2次空腹血尿酸水平超过420 μmol/L (70 mg/L)作为高尿酸血症的诊断标准[39]。血尿酸是由于长时间高水平的尿酸盐出现晶体沉淀,在胰腺中不断积累导致血糖异常,有研究推测它通过胰岛β细胞参与2型糖尿病的发生[40],故高血尿酸水平也常被认为是2型糖尿病的独立危险因素[41],与糖尿病足患者的溃疡预后密切相关。 在SHARIFUZZAMAN团队[11]制备的智能创面绷带中,尿酸传感器由3个电极WE(激光引导的石墨烯-MXene/聚二甲基硅氧烷)、CE(激光引导的石墨烯-MXene/聚二甲基硅氧烷)和RE(Ag/AgCl)组成,其中WE电极上激光引导的石墨烯-MXene表面官能团可以与尿酸酶通过氢键结合,当尿酸分子接触电极时,两者即刻发生氧化还原反应并通过尿酸酶将尿酸催化氧化成尿囊素;随着尿酸浓度的增长,电极界面的微分脉冲伏安法测得的峰值电流也随之同步增加[42],微分脉冲伏安法峰值电流与尿酸浓度之间表现出高度线性关联(图7)。通过微分脉冲伏安法峰值电流的实时监测可以较好地精准反映尿酸浓度的细微波动。这些发现充分证实了该尿酸传感器对创面尿酸浓度实时监测的可行性,为临床应用提供了极具潜力的技术手段。 "
2.4.4 监测血糖水平 糖尿病足患者应积极控制血糖以降低糖尿病足溃疡感染的发生率和截肢风险, 高糖化血红蛋白被认为是截肢的独立危险因素[43-44]。研究表明,糖尿病大鼠创面局部高血糖可以诱导活性氧自由基生成并引起一系列病理反应,使创面长期处于氧化应激状态,不利于糖尿病患者创面的愈合[45]。因此,通过随时监控血糖波动、控制血糖水平是预防糖尿病足患者发生感染及截肢的有效之策。 传统的血糖监测基本依赖于指尖采血,这种方式不仅给患者带来手指刺痛和感染的风险,也无法实现连续实时监测。MYNDRUL团队[12]将MXene纳米片修饰的四角锥体氧化锌复合材料作为电活性换能器层沉积在可拉伸电极上,相较于原始的四角锥体氧化锌和MXene,该纳米复合材料展现出对PBS和人工汗液中葡萄糖氧化更强的催化活性,证实了电极在稳定信号下电极的电流密度与葡萄糖浓度之间存在线性关系(图8)。该复合材料可通过在摄入甜食、进行锻炼等不同应用场景下实时全程记录电流密度变化,使得连续实时监测血糖成为了可能。 "

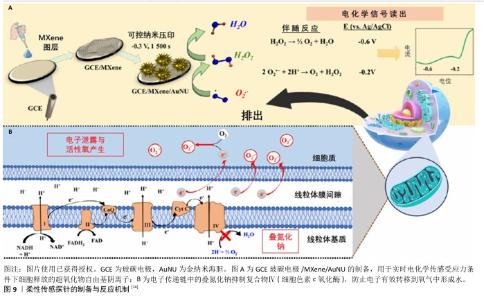
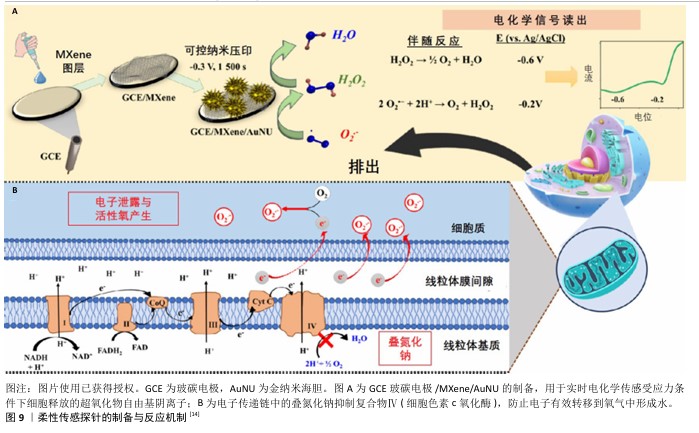
2.4.5 监测超氧化物阴离子水平 糖尿病患者由于糖代谢紊乱会出现血糖升高的现象,在非酶催化的条件下,蛋白质的氨基与糖的醛基发生更加活跃的化学反应并产生糖基化终末产物和活性氧自由基,导致糖尿病足创面聚集了大量糖基化终末产物,降低了血管内皮细胞的增殖效率和血管内皮生成因子的表达,阻碍了新血管形成,是影响糖尿病足创面预后的重要因素[46]。除此之外,通过激活烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸氧化酶也促进了更多的活性氧释放[47]。另一方面,糖尿病足创面反复的炎症反应也会导致中性粒细胞在局部滞留,进而释放出蛋白酶和活性氧自由基[48]。在活性氧自由基的生成过程中,超氧化物阴离子作为主要产物能迅速和其他自由基发生反应,损伤DNA并导致细胞死亡。研究表明,糖尿病中超氧阴离子水平升高是影响糖尿病创面愈合的关键因素之一[49]。 目前用于测量超氧化物阴离子的常用方法包括分光光度法、荧光法、化学发光法等,但由于设备成本高、对操作者的技术要求高、响应速度慢、灵敏度和选择性较少等劣势导致实时监测难以实现。ZHAO团队[13]通过使用Mn3(PO4)2和Ti3C2Tx MXene纳米片制备了柔性传感平台,两种材料的二维特性以及复合材料强烈的表面相互作用促进了超氧化物阴离子的吸附和电化学氧化,能够实现对活细胞释放超氧化物阴离子的定量监测。另外,NANDI团队[14]制备出负载了金纳米海胆的MXene纳米片并附着在电极表面,作为无介质和无受体的传感探针,依靠MXene较大的比表面积和金纳米海胆电催化活性的同步效应(图9),使得复合材料具有优异的电催化性能,可实现对超氧化物阴离子-的特异性识别,该探针通过电化学反应能够灵敏地实时监测活细胞释放的超氧化物阴离子自由基水平,具有良好的实用性和可行性。 "

2.4.6 监测过氧化氢浓度 过氧化氢是一种重要的活性氧,在细胞、组织的各个生理病理过程中都起着关键的作用,可减少感染、募集中性粒细胞,并促进角质细胞再生和新血管的形成[50]。近年来,过氧化氢被大量用于创面愈合的治疗中,不同浓度的过氧化氢对愈合进程产生完全不同的影响。有研究表明,10 mmol/L过氧化氢能够有效促进创面愈合和血管生成,但166 mmol/L过氧化氢(0.5%)可通过减少结缔组织的形成和损害内皮细胞而导致延迟愈合[51]。另一方面来说,如果创面组织出现细菌感染,过氧化氢的浓度会大幅度升高,驱使吞噬细胞和中性粒细胞起到抑菌作用[52]。 因此,对糖尿病创面中的过氧化氢浓度进行实时监测响应对于创面愈合进程的判断和预后具有重要意义。 目前为止,已经发展了许多监测过氧化氢浓度的方法,如荧光探针、等离子体共振等[53],而电化学传感器由于操作便捷、稳定性高受到广泛关注。例如,负载了金纳米海胆的MXene纳米复合传感器具有卓越的催化性能和导电性,通过表面发生快速电子转移促进过氧化氢还原,表现出了较高的峰值分辨率,从而实现对过氧化氢的高效监测[14]。另外,WANG团队[15]将铜纳米颗粒@铜-金属有机框架/Ti3C2Tx复合材料修饰在柔性丝网印刷电极表面,研究表明铜纳米颗粒具有抑制金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌等多种细菌的能力,该纳米颗粒释放的铜离子能够有效抑制糖尿病小鼠创面的细菌[54],促进糖尿病创面愈合,而该复合材料通过电化学分析技术来追踪生物体液中的过氧化氢含量,在检测过氧化氢上表现出了良好的精确性、稳定性、灵敏度。 综上所述,根据MXene材料的固有特性,通过对传统柔性传感器进行创造性表面改性,不仅能够赋予传感器良好的抗菌能力、有效控制感染并促进创面愈合,还显著提升了传感器的综合性能,通过增强对病理信号变化的敏感度展现出更高的氧化还原电流响应,实现了精确、稳定的动态监测。在对创面的实时监测中,分析各项参数来及时评估创面状态和调整治疗方案,对糖尿病足创面的愈合起到了积极作用。 尽管基于MXene柔性电子在糖尿病足创面监测中取得了较大进展,但目前大多数研究仍处于初始阶段,实验测试都是在理想条件下进行的,如何在临床实践中得到切实的应用还面临着许多有待考量的问题:①MXene柔性材料具有良好的生物相容性,但当前的结论更多依赖于较为短期的实验研究,缺乏长期直接接触创面情况下的系统、全面安全性评估;②人体生理环境复杂,糖尿病足创面与MXene柔性电子材料长期直接接触,湿度、温度及各种生物分子的变化都可能会对材料的结构、性能产生不利影响,从而降低数据的准确性;③除了对各项参数指标的实时监测,如何兼顾MXene材料的各种优异性能,开发出集监测、治疗、给药等多功能一体的柔性电子器件仍处于探索阶段,尚未能充分满足临床实践对糖尿病足治疗的多样化需求。 "

| [1] WANG Y, SHAO T, WANG J, et al. An update on potential biomarkers for diagnosing diabetic foot ulcer at early stage. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133:110991. [2] BUS SA, VAN NETTEN JJ, HINCHLIFFE RJ, et al. Standards for the development and methodology of the 2019 International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot guidelines. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020; 36(S1):e3267. [3] MCDERMOTT K, FANG M, BOULTON AJM, et al. Etiology, Epidemiology, and Disparities in the Burden of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(1):209-221. [4] NUBE VL, ALISON JA, TWIGG SM. Frequency of sharp wound debridement in the management of diabetes-related foot ulcers: exploring current practice. J Foot Ankle Res. 2021;14(1):52. [5] HUANG Q, WANG JT, GU HC, et al. Comparison of Vacuum Sealing Drainage and Traditional Therapy for Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Meta-Analysis. J FooT Ankle Surg. 2019;58(5):954-958. [6] JIANG Y, WANG X, XIA L, et al. A cohort study of diabetic patients and diabetic foot ulceration patients in China. Wound Repair Regen. 2015;23(2):222-230. [7] ILO A, ROMSI P, MAKELA J. Infrared Thermography and Vascular Disorders in Diabetic Feet. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2020;14(1):28-36. [8] 邵盛奇,樊凯,李杜娟,等.可穿戴无创葡萄糖传感器在糖尿病管理中的应用进展[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2022, 41(6):732-743. [9] QURESHI A, NIAZI JH. Biosensors for detecting viral and bacterial infections using host biomarkers: a review. Analyst. 2020;145(24):7825-7848. [10] XU L, DING LQ, SUN YH, et al. Stretchable, flexible and breathable polylactic acid/polyvinyl pyrrolidone bandage based on Kirigami for wounds monitoring and treatment. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;237: 124204. [11] SHARIFUZZAMAN M, CHHETRY A, ABU ZAHED M, et al. Smart bandage with integrated multifunctional sensors based on MXene-functionalized porous graphene scaffold for chronic wound care management. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020;169:112637. [12] MYNDRUL V, COY E, BABAYEVSKA N, et al. MXene nanoflakes decorating ZnO tetrapods for enhanced performance of skin-attachable stretchable enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;207:12. [13] ZHAO SF, HU FX, SHI ZZ, et al. 2-D/2-D heterostructured biomimetic enzyme by interfacial assembling Mn3(PO4)2 and MXene as a flexible platform for realtime sensitive sensing cell superoxide. Nano Res. 2021;14(3):879-886. [14] NANDI I, KUMARI R, KACHHAWAHA K, et al. Electrochemical Sensor Based on a MXene Nanosheet-Gold Nanourchin Hybrid as a Superoxide Dismutase Mimic for Real-Time Detection of Superoxide Anions Released from Living Cells. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2024;7(10): 12171-12183. [15] WANG K, ZHENG XF, QI ML, et al. Flexible screen-printed electrochemical platform to detect hydrogen peroxide for the indication of periodontal disease. Sens Actuator B-Chem. 2023;390:10. [16] IBRAGIMOVA R, ERHART P, RINKE P, et al. Surface Functionalization of 2D MXenes: Trends in Distribution, Composition, and Electronic Properties. J Phys Chem Lett. 2021;12(9):2377-2384. [17] NAGUIB M, MOCHALIN VN, BARSOUM MW, et al. 25th Anniversary Article: MXenes: A New Family of Two-Dimensional Materials. Adv Mater. 2014;26(7):992-1005. [18] GAO L, LI C, HUANG W, et al. MXene/Polymer Membranes: Synthesis, Properties, and Emerging Applications. Chem Mater. 2020;32(5):1703-1747. [19] LEI JC, ZHANG X, ZHOU Z. Recent advances in MXene: Preparation, properties, and applications. Front Phys. 2015;10(3):276-286. [20] HANTANASIRISAKUL K, GOGOTSI Y. Electronic and Optical Properties of 2D Transition Metal Carbides and Nitrides (MXenes). Adv Mater. 2018;30(52):30. [21] HAN ST, PENG H, SUN Q, et al. An Overview of the Development of Flexible Sensors. Adv Mater. 2017;29(33). doi: 10.1002/adma.201700375. [22] HAO S, HAN H, YANG Z, et al. Recent Advancements on Photothermal Conversion and Antibacterial Applications over MXenes-Based Materials. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022;14(1): 178. [23] YAO Z, SUN H, SUI H, et al. 2D/2D Heterojunction of R-scheme Ti3C2 MXene/MoS2 Nanosheets for Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2020;15(1):78. [24] LUKATSKAYA MR, KOTA S, LIN Z, et al. Ultra-high-rate pseudocapacitive energy storage in two-dimensional transition metal carbides. Nat Energy. 2017;2(8):1-12. [25] MAHMOUDVAND G, ROUZBAHANI AK, RAZAVI ZS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for non-healing diabetic foot ulcer infection: New insight. Front Bioeng Biotech. 2023;11:1158484. [26] LI M, ZHANG Y, LIAN L, et al. Flexible Accelerated‐Wound‐Healing Antibacterial MXene‐Based Epidermic Sensor for Intelligent Wearable Human‐Machine Interaction. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(47): 2208141. [27] IRAVANI S, VARMA RS. MXene-based composites against antibiotic-resistant bacteria: current trends and future perspectives. RSC Advances. 2023;13(14): 9665-9677. [28] GE J, LAN M, ZHOU B, et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat Commun. 2014;5(1):4596. [29] GAO F, XUE C, ZHANG T, et al. MXene-Based Functional Platforms for Tumor Therapy. Adv Mater. 2023;35(51):19. [30] LI Y, FU RZ, DUAN ZG, et al. Artificial Nonenzymatic Antioxidant MXene Nanosheet-Anchored Injectable Hydrogel as a Mild Photothermal-Controlled Oxygen Release Platform for Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Nano. 2022;16(5):7486-7502. [31] YANG GH, LIU FL, ZHAO JY, et al. MXenes-based nanomaterials for biosensing and biomedicine. Coord Chem Rev. 2023;479:19. [32] RASHID B, ANWAR A, SHAHABUDDIN S, et al. A Comparative Study of Cytotoxicity of PPG and PEG Surface-Modified 2-D Ti3C2 MXene Flakes on Human Cancer Cells and Their Photothermal Response. Materials. 2021;14(16):14. [33] ALIREZA R, LESTER SG, WEIANG Y, et al. Sweet-MXene hydrogel with mixed-dimensional components for biomedical applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;101:6. [34] LIU L, LI X, NAGAO M, et al. A pH-Indicating Colorimetric Tough Hydrogel Patch towards Applications in a Substrate for Smart Wound Dressings. Polymers. 2017;9(11):15. [35] MCARDLE C, LAGAN K, SPENCE S, et al. Diabetic foot ulcer wound fluid: the effects of pH on DFU bacteria and infection. J Foot Ankle Res. 2015;8(S1):A8. [36] PERCIVAL SL, MCCARTY S, HUNT JA, et al. The effects of pH on wound healing, biofilms, and antimicrobial efficacy. Wound Repair Regen. 2014;22(2):174-186. [37] HOUGHTON VJ, BOWER VM, CHANT DC. Is an increase in skin temperature predictive of neuropathic foot ulceration in people with diabetes? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Foot Ankle Res. 2013;6:13. [38] GATT A, FALZON O, CASSAR K, et al. Establishing Differences in Thermographic Patterns between the Various Complications in Diabetic Foot Disease. Int J Endocrinol. 2018;2018:1-7. [39] 中华医学会内分泌学分会.中国高尿酸血症与痛风诊疗指南(2019)[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2020,36(1):1-13. [40] 赵振国,许继炜,洪娟.血尿酸与胰岛β细胞分泌功能在2型糖尿病周围神经病变患者中交互作用的研究[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2024,32(11):813-820. [41] WU WC, LAI YW, CHOU YC, et al. Serum Uric Acid Level as a Harbinger of Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Observation in Taiwan. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(7):2277. [42] VERMA S, CHOUDHARY J, SINGH KP, et al. Uricase grafted nanoconducting matrix based electrochemical biosensor for ultrafast uric acid detection in human serum samples. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;130: 333-341. [43] ELSAYED NA, ALEPPO G, BANNURU RR, et al. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024;47: S20-S42. [44] FERREIRA L, CARVALHO A, CARVALHO R. Short-term predictors of amputation in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018;12(6): 875-879. [45] ZHOU XQ, LI M, XIAO MF, et al. ERβ Accelerates Diabetic Wound Healing by Ameliorating Hyperglycemia-Induced Persistent Oxidative Stress. Front Endocrinol. 2019;10:499. [46] HAN YF, SUN TJ, TAO R, et al. Clinical application prospect of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells on clearance of advanced glycation end products through autophagy on diabetic wound. Eur J Med Res. 2017;22:11. [47] SINGH A, KUKRETI R, SASO L, et al. Mechanistic Insight into Oxidative Stress-Triggered Signaling Pathways and Type 2 Diabetes. Molecules. 2022;27(3):950. [48] HOLL J, KOWALEWSKI C, ZIMEK Z, et al. Chronic Diabetic Wounds and Their Treatment with Skin Substitutes. Cells. 2021;10(3):655. [49] LÓPEZ-DELIS A, ROSA S, DE SOUZA PEN, et al. Characterization of the Cicatrization Process in Diabetic Foot Ulcers Based on the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species. J Diabetes Res. 2018;2018:4641364. [50] IAKOVOU E, KOURTI M. A Comprehensive Overview of the Complex Role of Oxidative Stress in Aging, The Contributing Environmental Stressors and Emerging Antioxidant Therapeutic Interventions. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:827900. [51] LOO AEK, WONG YT, HO RJ, et al. Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide on Wound Healing in Mice in Relation to Oxidative Damage. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49215. [52] LI XY, XIU WJ, YANG DL, et al. Ultrasound-responsive microbubbles in antibacterial therapy. Biomed Eng Commun. 2023;2(2): 1-3. [53] HUANG JM, ZHENG Y, NIU HC, et al. A Multifunctional Hydrogel for Simultaneous Visible H2O2 Monitoring And Accelerating Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024; 13(3):e2302328. [54] XIAO JS, ZHU YX, HUDDLESTON S, et al. Copper Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticles Stabilized with Folic Acid Improve Wound Healing in Diabetes. ACS Nano. 2018;12(2):1023-1032. [55] GONG F, ZHANG Y, CHENG SL, et al. Inhibition of TGFβ1/Smad pathway by NF-ΚB induces inflammation leading to poor wound healing in high glucose. Cells Dev. 2022;172:203814. |
| [1] | Li Meiyun, Liu Sen, Chen Kaiyuan, Shi Ling, Song Meichen, Cao Jiahong, Wu Yan, Yu Jing. MXene nanoparticles Ti3C2Tx and photothermal effect promote wound healing in diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6052-6060. |
| [2] | Zhao Zixi, Xu Jun, Ding Min, Li Xiwen, Zhang Jinghang, Wang Penghua. Changes of type I and III collagen and matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 on the wound of diabetic foot ulcer with external application of medical collagen dressing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1544-1550. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||