Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (30): 6556-6565.doi: 10.12307/2025.786
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of transcranial direct current stimulation in improving lower limb motor dysfunction in stroke patients
Wang He1, Yu Shaohong2, 3
- 1College of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2College of Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 3Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250001, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-08-20Accepted:2024-10-16Online:2025-10-28Published:2025-03-29 -
Contact:Yu Shaohong, MD, Professor, College of Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250001, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wang He, Master candidate, College of Rehabilitation Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. ZR2024MH048 (to YSH); Ministry of Education Industry-University Cooperation Collaborative Education Project, No. 202102424004 (to YSH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang He, Yu Shaohong, . Meta-analysis of transcranial direct current stimulation in improving lower limb motor dysfunction in stroke patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6556-6565.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
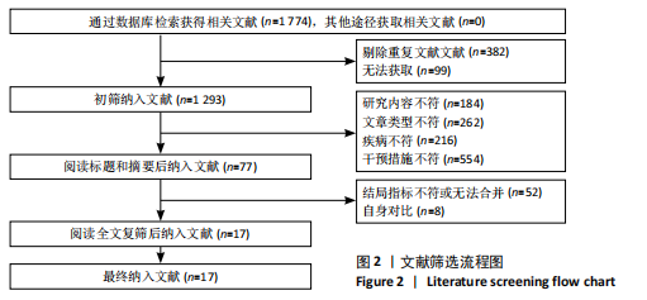
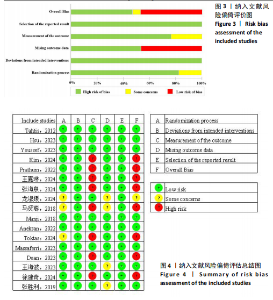
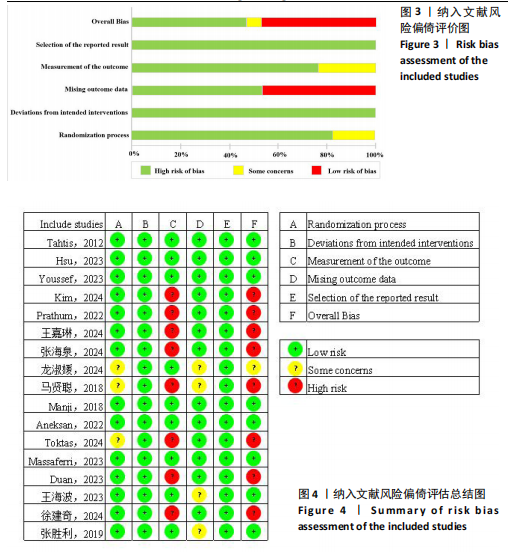
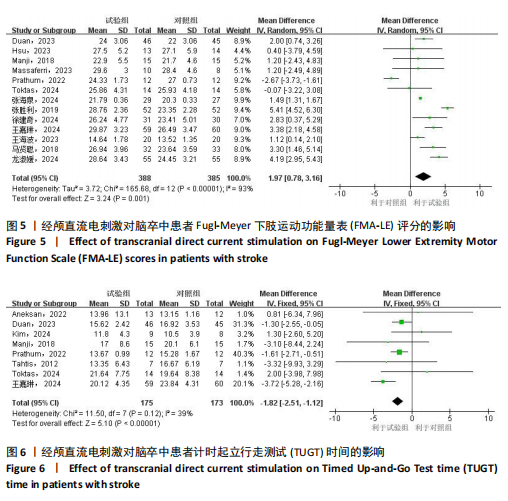
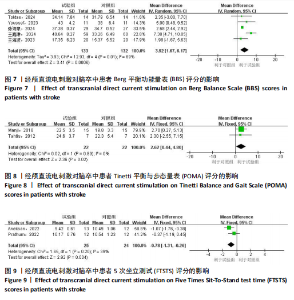
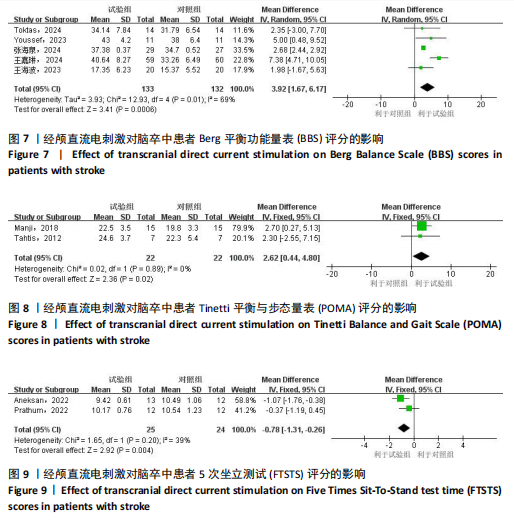
2.1 文献检索流程及结果 初检共获得相关文献1 774篇,剔除重复文献和无法获取的文献481篇,通过阅读文献标题和摘要剔除1 216篇文献,通过阅读全文剔除60篇文献,最终共纳入17篇随机对照试验。文献检索流程及结果见图2。 2.2 纳入研究的基本特征 最终纳入17项研究[7,22-37],发表时间在2012-2024年,涉及851例患者,受试者平均年龄在50岁以上。所纳入研究中,有13项研究采用FMA-LE量表评估下肢运动功能[23,26-37];2项研究采用FTSTS评估患者的下肢功能性肌肉力量[7,26],8项研究采用TUGT评估步态功能[7,22,25-27,31-32,34];2项研究[22,31]、5项研究分别采用POMA量表和BBS量表评估移动能力、平衡能力和跌倒风险[24,27-28,32,35]。纳入研究基本特征见表1。 2.3 纳入文献的质量评价 14项研究报告了具体的随机方法(包括随机数字表法、随机信封盲法分组)[17,22-28,31,33-37];3项研究随机分组但未提及具体随机方法[29-30,32]。13项研究在治疗过程中对患者或治疗师采用盲法[7,22-28,31-34,36],8项研究有病例中途退出或失访[25-28,30,32,34,36],文中均指明具体脱落原因。风险偏倚评估结果见图3和图4。 2.4 传统Meta分析结果 2.4.1 FMA-LE 纳入13篇文献[23,26-37],共涉及773例患者,其中试验组388例,对照组385例。I2=93%,P > 0.1,各研究间异质性较大,采用随机效应模型分析。结果显示,经颅直流电刺激能够显著提高脑卒中患者的FMA-LE评分[MD=1.97,95%CI(0.78,3.16),P < 0.01],见图5。 2.4.2 TUGT 纳入8篇文献[7,22,25-27,31-32,34],共涉及348例患者,其中试验组175例,对照组173例。I2=39%,P=0.12,各研究间异质性小,采用固定效应模型分析。结果显示,经颅直流电刺激能够显著降低脑卒中患者的TUGT时间[MD=-1.82,95%CI (-2.51,-1.12),P < 0.01],见图6。 2.4.3 BBS 纳入5篇文献[24, 27-28,32,35],共涉及265例患者,其中试验组133例,对照组132例。I2=69%,P=0.01,各研究间异质性较大,采用随机效应模型分析。结果显示,经颅直流电刺激能够提高脑卒中患者的BBS评分[MD=3.92,95%CI(1.67,6.17),P < 0.01],见图7。 2.4.4 POMA 纳入2篇文献[22,31],共涉及44例患者,其中试验组22例,对照组22例。I2=0%,P=0.89,各研究间异质性小,采用固定效应模型分析。结果显示,经颅直流电刺激能够提高脑卒中患者的POMA评分[MD=2.62,95%CI(0.44,4.80),P < 0.05],见图8。 2.4.5 FTSTS 纳入2篇文献[7,26],共涉及49例患者,其中试验组25例,对照组24例。I2=39%,P=0.20,各研究间异质性小,采用固定效应模型分析。结果显示,经颅直流电刺激能够降低脑卒中患者的FTSTS时间[MD=-0.78,95%CI( -1.31,-0.26),P < 0.01],见图9。"
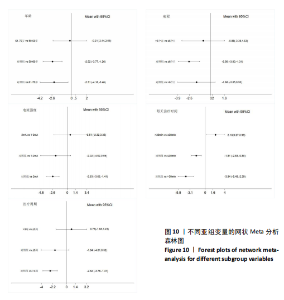
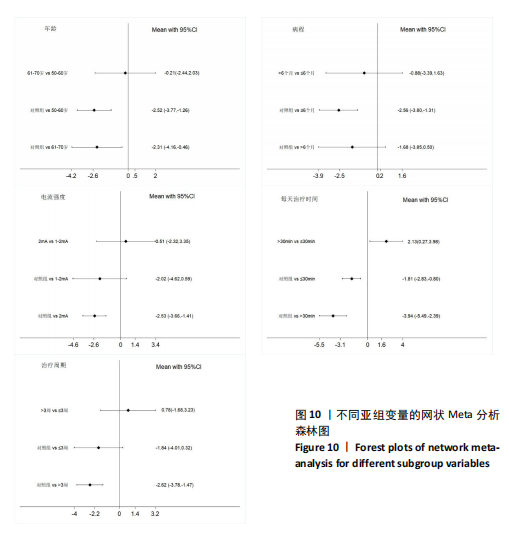
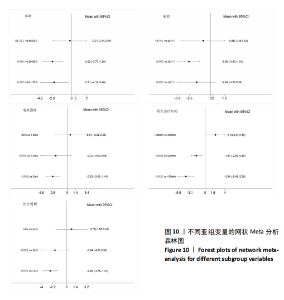
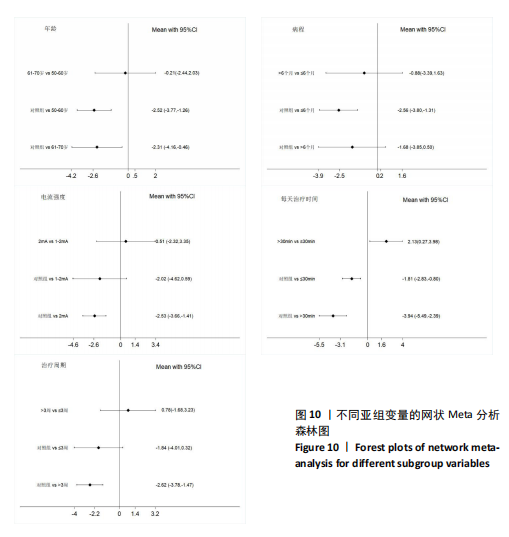
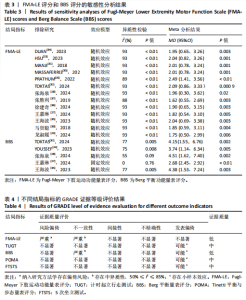
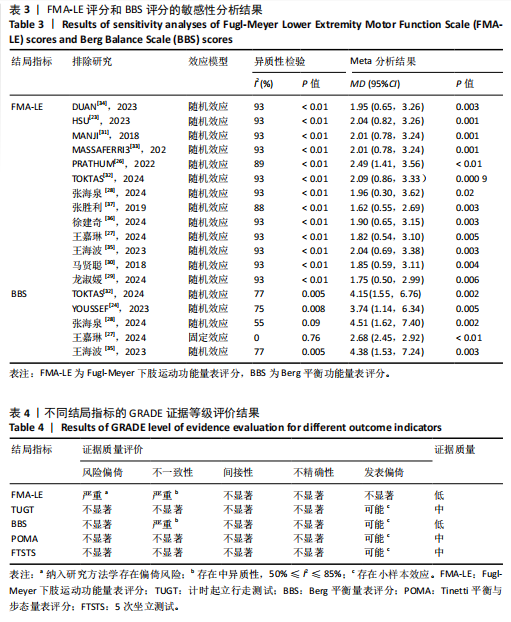
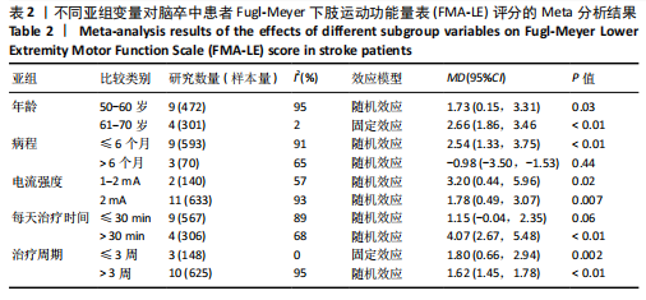
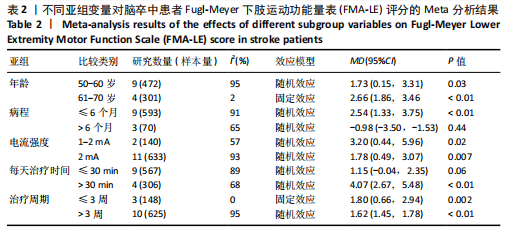
FMA-LE评分的亚组进行网状Meta分析。①在年龄组别方面,经颅直流电刺激对于年龄50-60岁、61-70岁脑卒中患者FMA-LE评分的改善效果均优于对照组(P < 0.05),其余组别间比较无显著性差异(P > 0.05);②在病程组别方面,经颅直流电刺激对病程≤ 6个月脑卒中患者FMA-LE评分的改善效果优于对照组(P < 0.05),其余组别间比较无显著性差异(P > 0.05);③在电流强度组别方面,2 mA电流强度的经颅直流电刺激对脑卒中患者FMA-LE评分的改善效果优于对照组(P < 0.05),其余组别间比较无显著性差异(P > 0.05);④在每天治疗时间组别方面,每天≤ 30 min的经颅直流电刺激和每天> 30 min的经颅直流电刺激对脑卒中患者下肢运动功能改善效果均优于对照组(P < 0.05),且每天≤ 30 min与每天> 30 min两组间比较有显著性差异(P < 0.05);⑤在治疗周期组别方面,经颅直流电刺激治疗周期> 3周对脑卒中患者FMA-LE评分的改善效果优于对照组(P < 0.05),其余组别间比较无显著性差异(P > 0.05),见图10。 2.6.2 概率排序 根据累计排序概率曲线下面积,对不同亚组的治疗效果进行排序。结果显示,经颅直流电刺激对于50-60岁、病程≤ 6个月的脑卒中患者下肢运动功能干预效果更好;电刺激强度为2 mA、每天治疗时间> 30 min、干预周期> 3周的经颅直流电刺激治疗方案对于脑卒中患者的下肢运动功能改善效果更佳,见图11。 2.7 敏感性分析 采用逐一剔除法,对FMA-LE评分和BBS评分这2项具有高异质性的结局指标进行敏感性分析。 2.7.1 FMA-LE评分 剔除张胜利[37]研究后,I2由93%降至88%,FMA-LE评分的合并效应[MD=1.62,95%CI (0.55-2.69),P < 0.01],试验组与对照组相比有显著性差异;剔除PRATHUM等[26]研究后,I2由93%降至89%,FMA-LE评分的合并效应[MD=2.49,95%CI(1.41,3.56),P < 0.01],试验组与对照组相比有显著性差异。剔除其他单个研究后合并效应MD的范围为1.75-2.49,I2的范围稳定在93%,P < 0.05,说明FMA-LE评分的合并效应"
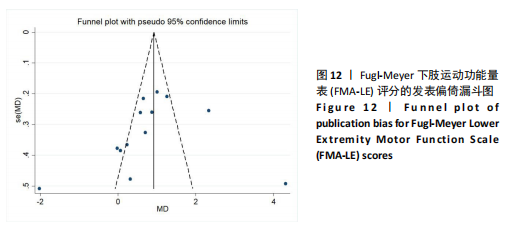
MD和I2值在稳定范围内,合并结果的稳健性较好,见表3。 经分析发现,张胜利[37]研究中的脑卒中患者每次接受30 min的经颅直流电刺激治疗,而其他研究的患者每次接受20 min的经颅直流电刺激治疗,提示单次治疗时间可能为异质性来源之一;PRATHUM等[26]研究的干预场地为患者家中,由患者本人进行经颅直流电刺激干预,在治疗初期提供口头反馈,治疗后期则改为远程监护以确保运动程序的科学和安全,而其他研究的干预场地为医疗中心,由康复治疗师全程进行经颅直流电刺激干预,提示干预场地和干预人员可能为异质性来源。 2.7.2 BBS评分 剔除王嘉琳等[27]研究后,I2由69%降至0%,试验组BBS评分显著高于对照组[MD=2.68,95%CI(2.45,2.92),P < 0.01],试验组与对照组相比有显著性差异;剔除张海泉等[28]研究后,I2由69%降至55%,试验组BBS评分显著高于对照组[MD=4.51,95%CI(1.62,7.40),P < 0.01],试验组与对照组相比有显著性差异。剔除其他单个研究后合并效应MD的范围为2.01-2.83,I2的范围为75%-77%,P均< 0.01,说明BBS评分的合并效应MD和I2在稳定范围内,合并结果稳健性较好,见表3。 经分析发现,王嘉琳等[27]研究的脑卒中患者年龄为60岁以上,而其他研究患者年龄均为60岁以下,提示年龄可能为异质性来源之一;张海泉等[28]研究的经颅直流电刺激阴极电极片放置于健侧大脑初级运动皮质区,而其他研究的阴极电极片则放置于健侧眼眶区,提示经颅直流电刺激的阴极电极片放置部位可能是异质性来源之一。 2.8 发表偏倚评估 对纳入研究数≥10篇的FMA-LE结局指标进行发表偏倚评估。由图可见,漏斗图对称性欠佳,提示可能存在发表偏倚,且部分黑点落在漏斗图底部及外侧,提示可能存在小样本效应,见图12。 2.9 证据等级评价 对纳入研究进行GRADE证据等级评价,结果显示,TUGT、POMA和FTSTS结局指标的证据质量为中级,FMA-LE和BBS结局"
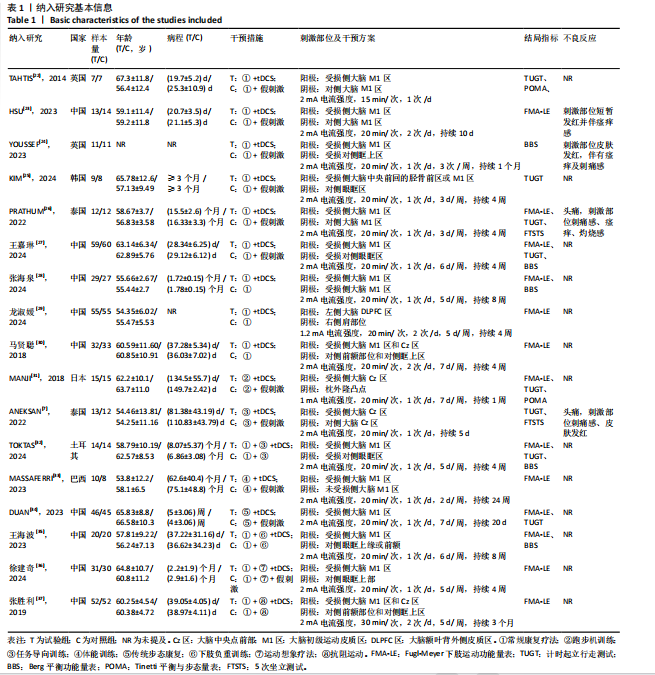
| [1] NETS TRIAL COLLABORATION GROUP. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to test efficacy and safety of transcranial direct current stimulation to the motor cortex after stroke (NETS): study protocol. Neurol Res Pract. 2022;4(1):14. [2] VELDEMA J, JANSEN P. Resistance training in stroke rehabilitation: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2020;34(9): 1173-1197. [3] VELDEMA J, JANSEN P. Ergometer Training in Stroke Rehabilitation: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;101(4):674-689. [4] QURAT-UL-AIN, AHMAD Z, ILYAS S, et al. Comparison of a single session of tDCS on cerebellum vs. motor cortex in stroke patients: a randomized sham-controlled trial. Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2252439. [5] BAI X, GUO Z, HE L, et al. Different Therapeutic Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Upper and Lower Limb Recovery of Stroke Patients with Motor Dysfunction: A Meta-Analysis. Neural Plast. 2019;2019:1372138. [6] FLEMING MK, PAVLOU M, NEWHAM DJ, et al. Non-invasive brain stimulation for the lower limb after stroke: what do we know so far and what should we be doing next? Disabil Rehabil. 2017;39(7):714-720. [7] ANEKSAN B, SAWATDIPAN M, BOVONSUNTHONCHAI S, et al. Five-Session Dual-Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation With Task-Specific Training Does Not Improve Gait and Lower Limb Performance Over Training Alone in Subacute Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Neuromodulation. 2022;25(4):558-568. [8] PLOW EB, CUNNINGHAM DA, BEALL E, et al. Effectiveness and neural mechanisms associated with tDCS delivered to premotor cortex in stroke rehabilitation: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2013;14:331. [9] LOWENTHAL-RAZ J, LIEBERMANN DG, FRIEDMAN J, et al. Kinematic descriptors of arm reaching movement are sensitive to hemisphere-specific immediate neuromodulatory effects of transcranial direct current stimulation post stroke. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):11971. [10] TSENG SC, CHERRY D, KO M, et al. The effects of combined transcranial brain stimulation and a 4-week visuomotor stepping training on voluntary step initiation in persons with chronic stroke-a pilot study. Front Neurol. 2024;15:1286856. [11] DA CUNHA MJ, PINTO C, SCHIFINO GP, et al. Bicephalic Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation Does Not Add Benefits to a Footdrop Stimulator for Improving Functional Mobility in People With Chronic Hemiparesis After Stroke: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys Ther. 2022;102(8):pzac079. [12] CHANG MC, KIM DY, PARK DH. Enhancement of Cortical Excitability and Lower Limb Motor Function in Patients With Stroke by Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation. Brain Stimul. 2015;8(3):561-566. [13] COPPENS MJM, STARING WHA, NONNEKES J, et al. Offline effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on reaction times of lower extremity movements in people after stroke: a pilot cross-over study. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2019;16(1):136. [14] GHOSH S, HATHORN D, EISENHAUER J, et al. Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation over the Vertex Enhances Leg Motor Cortex Excitability Bilaterally. Brain Sci. 2019;9(5):98. [15] KINDRED JH, KAUTZ SA, WONSETLER EC, et al. Single Sessions of High-Definition Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Do Not Alter Lower Extremity Biomechanical or Corticomotor Response Variables Post-stroke. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:286. [16] 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组.中国各类主要脑血管病诊断要点2019[J].中华神经科杂志,2019,52(9):710-715. [17] 朱涛,刘津池,刘畅,等.整群随机试验和交叉试验偏倚风险评价工具RoB2.0 (2021修订版)解读[J].中国循证医学杂志,2022,22(7):842-852. [18] CUMPSTON M, LI T, PAGE MJ, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;10(10):ED000142. [19] PATSOPOULOS NA, EVANGELOU E, IOANNIDIS JP. Sensitivity of between-study heterogeneity in meta-analysis: proposed metrics and empirical evaluation. Int J Epidemiol. 2008;37(5):1148-1157. [20] SHIM S, YOON BH, SHIN IS, et al. Network meta-analysis: application and practice using Stata. Epidemiol Health. 2017;39:e2017047. [21] 陆瑶,杨秋玉,赖鸿皓,等.诊断试验准确性比较研究系统评价的证据分级[J].中国循证医学杂志,2022,22(10):1233-1240. [22] TAHTIS V, KASKI D, SEEMUNGAL BM. The effect of single session bi-cephalic transcranial direct current stimulation on gait performance in sub-acute stroke: A pilot study. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2014; 32(4):527-532. [23] HSU SP, LU CF, LIN BF, et al. Effects of bihemispheric transcranial direct current stimulation on motor recovery in subacute stroke patients: a double-blind, randomized sham-controlled trial. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2023;20(1):27. [24] YOUSSEF H, MOHAMED NAE, HAMDY M. Comparison of bihemispheric and unihemispheric M1 transcranial direct current stimulations during physical therapy in subacute stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. Neurophysiol Clin. 2023; 53(3):102895. [25] KIM HM, NA JM, JO HS, et al. Feasibility of Simultaneous Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation During Gait Training in Chronic Stroke Patients: A Randomized Double-Blind Pilot Clinical Trial. J Integr Neurosci. 2024;23(8):154. [26] PRATHUM T, PIRIYAPRASARTH P, ANEKSAN B, et al. Effects of home-based dual-hemispheric transcranial direct current stimulation combined with exercise on upper and lower limb motor performance in patients with chronic stroke. Disabil Rehabil. 2022;44(15):3868-3879. [27] 王嘉琳,刘立芝,官艳林,等.经颅直流电刺激联合运动康复训练对脑卒中患者下肢运动功能和血清Hcy水平的影响[J].川北医学院学报,2024,39(1):34-37.
[28] 张海泉,胡川,黄磊,等.高精度经颅直流电刺激联合悬吊运动训练对脑卒中患者下肢运动功能的影响[J].康复学报, 2024,34(2):110-116. [29] 龙淑媛,叶经香,王桂瑜.左背外侧前额叶阳极经颅直流电刺激联合康复训练对脑卒中后肢体运动障碍患者的心理和运动功能的影响[J].国际精神病学杂志, 2024,51(4):1230-1232+1236. [30] 马贤聪,鲍晓,杨泉,等.抗阻运动联合经颅直流电刺激对脑卒中偏瘫患者肢体运动功能的影响[J].临床与病理杂志, 2018,38(4):805-811. [31] MANJI A, AMIMOTO K, MATSUDA T, et al. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation over the supplementary motor area body weight-supported treadmill gait training in hemiparetic patients after stroke. Neurosci Lett. 2018;662:302-305. [32] TOKTAS N, DURUTURK N, GÜZEL Ş, et al. The effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on balance, gait function and quality of life in patients with stroke. Neurol Res. 2024;46(9):868-875. [33] MASSAFERRI R, MONTENEGRO R, DE FREITAS FONSECA G, et al. Multimodal physical training combined with tDCS improves physical fitness components in people after stroke: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2023;30(7):635-648. [34] DUAN Q, LIU W, YANG J, et al. Effect of Cathodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation for Lower Limb Subacute Stroke Rehabilitation. Neural Plast. 2023; 2023:1863686. [35] 王海波,陶媛媛,李静,等.经颅直流电刺激协同患侧下肢强制性负重训练对脑卒中Pusher综合征的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2023,29(3):269-274. [36] 徐建奇,王舒,沈晓艳,等.经颅直流电刺激联合动觉运动想象疗法对恢复期脑卒中患者下肢功能的疗效[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2024,19(6):366-368. [37] 张胜利.抗阻运动联合经颅直流电刺激治疗对卒中后偏瘫患者肢体功能影响观察[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2019,40(12): 1499-1500. [38] FULK GD, HE Y, BOYNE P, et al. Predicting Home and Community Walking Activity Poststroke. Stroke. 2017;48(2):406-411. [39] LONGO V, BARBATI SA, RE A, et al. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Enhances Neuroplasticity and Accelerates Motor Recovery in a Stroke Mouse Model. Stroke. 2022;53(5):1746-1758. [40] GEIGER M, SUPIOT A, ZORY R, et al. The effect of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on locomotion and balance in patients with chronic stroke: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2017;18(1):492. [41] KAMII Y, KOJIMA S, ONISHI H. Transcranial direct current stimulation over the posterior parietal cortex improves visuomotor performance and proprioception in the lower extremities. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022;16:876083. [42] MITSUTAKE T, SAKAMOTO M, NAKAZONO H, et al. The Effects of Combining Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation and Gait Training with Functional Electrical Stimulation on Trunk Acceleration During Walking in Patients with Subacute Stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021;30(4):105635. [43] SHEN QR, HU MT, FENG W, et al. Narrative Review of Noninvasive Brain Stimulation in Stroke Rehabilitation. Med Sci Monit. 2022;28:e938298. [44] MADHAVAN S, CLELAND BT, SIVARAMAKRISHNAN A, et al. Cortical priming strategies for gait training after stroke: a controlled, stratified trial. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2020;17(1):111. [45] NAVARRO-LÓPEZ V, MOLINA-RUEDA F, JIMÉNEZ-JIMÉNEZ S, et al. Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined with Physiotherapy on Gait Pattern, Balance, and Functionality in Stroke Patients. A Systematic Review. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(4):656. [46] KOO WR, JANG BH, KIM CR. Effects of Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Somatosensory Recovery After Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;97(7):507-513. [47] KUMARI N, TAYLOR D, OLSEN S, et al. Cerebellar Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation for Motor Learning in People with Chronic Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Brain Sci. 2020;10(12):982. [48] LIMA E, DE SOUZA NETO JMR, ANDRADE SM. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on lower limb function, balance and quality of life after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol Res. 2023;45(9):843-853. [49] QURAT-UL-AIN, AHMAD Z, ISHTIAQ S, et al. Short term effects of anodal cerebellar vs. anodal cerebral transcranial direct current stimulation in stroke patients, a randomized control trial. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:1035558. [50] SEAMON BA, BOWDEN MG, KINDRED JH, et al. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Electrode Montages May Differentially Impact Variables of Walking Performance in Individuals Poststroke: A Preliminary Study. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2023;40(1):71-78. [51] VIMOLRATANA O, ANEKSAN B, SIRIPORNPANICH V, et al. Effects of anodal tDCS on resting state eeg power and motor function in acute stroke: a randomized controlled trial. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2024; 21(1):6. [52] PAVLOVA EL, SEMENOV RV, GUEKHT AB. Effect of tDCS on Fine Motor Control of Patients in Subacute and Chronic Post-Stroke Stages. J Mot Behav. 2020;52(4): 383-395. [53] CAO Z, Elkins MR. Stroke rehabilitation. J Physiother. 2024;70(1):5-6. [54] OJARDIAS E, AZÉ OD, LUNEAU D, et al. The Effects of Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on the Walking Performance of Chronic Hemiplegic Patients. Neuromodulation. 2020;23(3):373-379. [55] PARIKH V, MEDLEY A, CHUNG YC, et al. Optimal timing and neural loci: a scoping review on the effect of non-invasive brain stimulation on post-stroke gait and balance recovery. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2023;30(1): 84-100. [56] CHHATBAR PY, RAMAKRISHNAN V, KAUTZ S, et al. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Post-Stroke Upper Extremity Motor Recovery Studies Exhibit a Dose-Response Relationship. Brain Stimul. 2016;9(1):16-26. [57] 李宪东,裴轶丰,张楚潍,等.经颅直流电刺激在急性缺血性卒中应用的研究进展[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2023,20(1):41-48. [58] TAKECHI U, MATSUNAGA K, NAKANISHI R, et al. Longitudinal changes of motor cortical excitability and transcallosal inhibition after subcortical stroke. Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;125(10):2055-2069. [59] REHME AK, EICKHOFF SB, ROTTSCHY C, et al. Activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of motor-related neural activity after stroke. Neuroimage. 2012;59(3):2771-2782. [60] CUYPERS K, LEENUS DJ, VAN DEN BERG FE, et al. Is motor learning mediated by tDCS intensity? PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e67344. [61] ELSNER B, KUGLER J, POHL M, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for improving activities of daily living, and physical and cognitive functioning, in people after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;11(11):CD009645. [62] BRUNONI AR, NITSCHE MA, BOLOGNINI N, et al. Clinical research with transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS): challenges and future directions. Brain Stimul. 2012; 5(3):175-195. [63] NUDO RJ. Recovery after brain injury: mechanisms and principles. Front Hum Neurosci. 2013;7:887. [64] CLARK B, WHITALL J, KWAKKEL G, et al. The effect of time spent in rehabilitation on activity limitation and impairment after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021;10(10):CD012612. [65] 赵天芮,张丽华,张赛雅,等.首发脑卒中偏瘫患者主动功能锻炼的现状及干预措施研究进展[J].保健医学研究与实践, 2024,21(6):149-156. [66] ZHANG Y, QIU X, JIN Q, et al. Influencing factors of home exercise adherence in elderly patients with stroke: A multiperspective qualitative study. Front Psychiatry. 2023;14:1157106. [67] WULF G. Self-controlled practice enhances motor learning: implications for physiotherapy. Physiotherapy. 2007;93(2):96-101. [68] KERSTEN P, ELLIS-HILL C, MCPHERSON KM, et al. Beyond the RCT - understanding the relationship between interventions, individuals and outcome - the example of neurological rehabilitation. Disabil Rehabil. 2010;32(12):1028-1034. [69] JANSSON AB, CARLSSON G. Physical activity on prescription at the time of stroke or transient ischemic attack diagnosis - from a patient perspective. Disabil Rehabil. 2021; 43(8):1121-1128. |
| [1] | Zhang Xinxin, Gao Ke, Xie Shidong, Tuo Haowen, Jing Feiyue, Liu Weiguo. Network meta-analysis of non-surgical treatments for foot and ankle ability and dynamic balance in patients with chronic ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1931-1944. |
| [2] | Wang Yida, Liu Jun, Wang Xiaoling, Wang Liyan, Yang Chengru, Zhang Xuexiao. Effects of wearable electronic device-based interventions on physical activity and sedentary behavior in healthy adolescents: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1693-1704. |
| [3] | Zhang Zixian, Xu Youliang, Wu Shaokui, Wang Xiangying. Effects of blood flow restriction training combined with resistance training on muscle indicators in college athletes: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1705-1713. |
| [4] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [5] |
Liang Xiaoxiao, Zheng Jiejiao, Duan Linru, Chen Xi, Zhang Tingyu.
Characterization of postural stability in elderly patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1208-1213.
|
| [6] | Wu Yihan, Liu Zhongqiang, Wei Qiaoye, Liu Mingdong, Chen Keyi, Li Zhigang. Effect of balance training with different visual conditions on proprioception in patients with chronic ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1050-1057. |
| [7] | Wen Zixing, Xu Xin, Zhu Shengqun. Correlations between gastrocnemius morphology parameters and physical activity capacity in elderly females under high-frequency ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1058-1063. |
| [8] | Zhang Xiaoyu, Wei Shanwen, Fang Jiawei, Ni Li. Prussian blue nanoparticles restore mitochondrial function in nucleus pulposus cells through antioxidation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7318-7325. |
| [9] | Wang Xuesong, Wang Yue, Xu Yan, Zeng Wenhui, Lu Wenming, Tang Xingkun, Chen Wenjie, Ye Junsong. Brain-computer interface combined with different therapies for limb dysfunction in stroke patients: effectiveness and mechanism analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6538-6546. |
| [10] | Gou Yanyun, Hou Meijin, Jiang Zheng, Chen Shaoqing, Chen Xiang, Gao Yuzhan, Wang Xiangbin. Biomechanical characteristics of walking in patients with idiopathic scoliosis: cross-sectional analysis of three-dimensional motion capture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 471-477. |
| [11] | Zheng Xiang, Zhang Mingxing, Huang Ya, Shan Sharui. Improvement of lower limb walking function in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain by biofeedback assisted electrical stimulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 547-553. |
| [12] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei. Causal association between metabolites and sarcopenia: a big data analysis of genome-wide association studies in the European population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6369-6380. |
| [13] | Nan Songhua, Peng Chaojie, Cui Yinglin. Mitochondrial dysfunction and brain aging: a bibliometrics analysis based on the Web of Science Core Collection database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5642-5651. |
| [14] | Zhu Tianrui, Shi Jipeng, Sun Jiahe, Wang Luyi, Zhang Chen, Xu Hongqi, Quan Helong. Effectiveness of different exercise regimens to reduce fall risks in older adults: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5662-5672. |
| [15] | Lei Senlin, Chen Xiaoan, Chen Ping, Wang Zhaofeng. Exercise prevention and treatment of Parkinson’ s disease mediated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor: role and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5454-5468. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||