Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (30): 6474-6481.doi: 10.12307/2025.781
Previous Articles Next Articles
Central anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of tea polyphenols in exercise fatigue model mice
Zhang Songjiang, Li Longyang, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng
- Medical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-09-09Accepted:2024-11-02Online:2025-10-28Published:2025-03-28 -
Contact:Gao Jianfeng, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Medical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Songjiang, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Medical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Key Science and Technology Research Project in Henan Province, No. 152102310100 (to ZSJ); Henan Natural Science Foundation, No. 202300410267 (to GJF); Innovation Team Project of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, No. [2016]124 (to GJF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Songjiang, Li Longyang, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Central anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of tea polyphenols in exercise fatigue model mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6474-6481.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
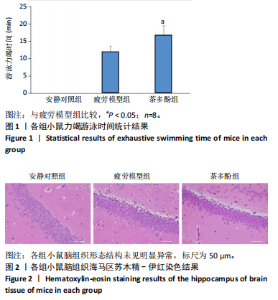
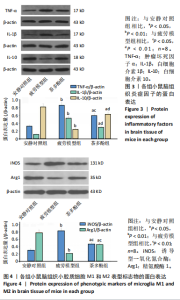
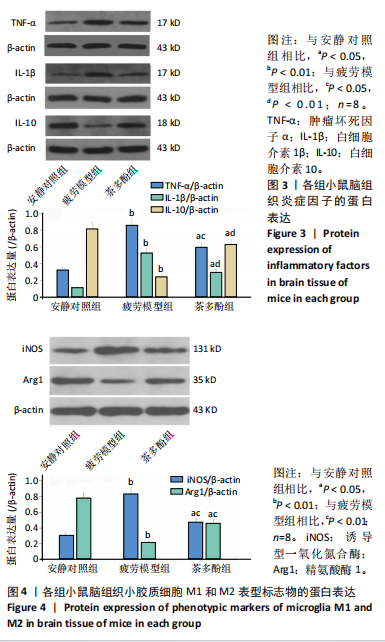
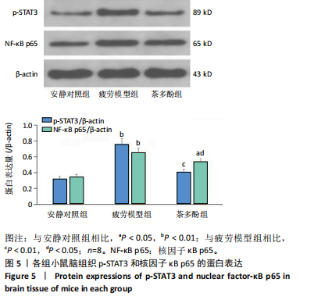
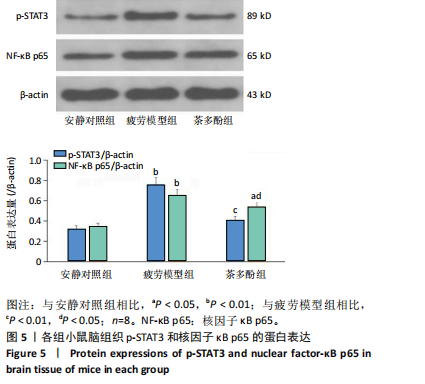
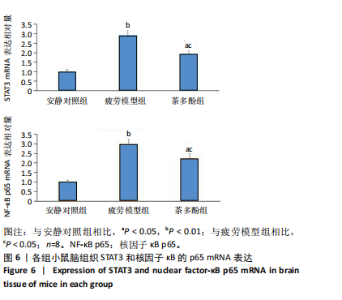
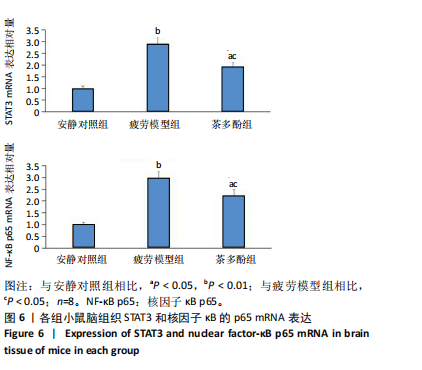
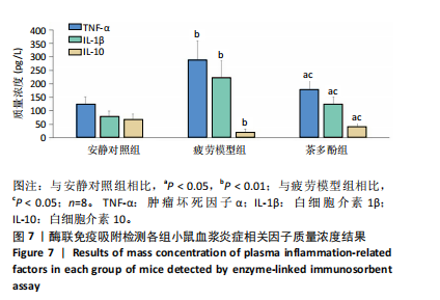
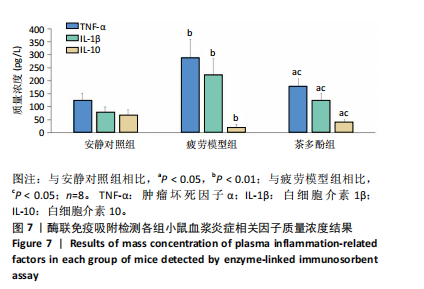
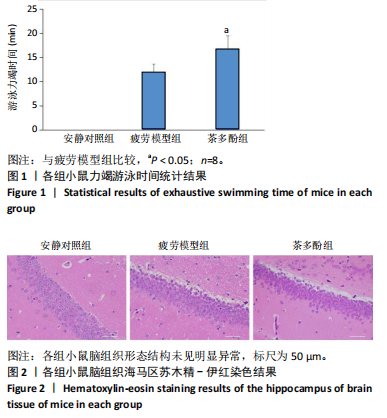
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验过程无小鼠脱失,3组小鼠共24只进入结果分析。 2.2 小鼠力竭游泳时间 与疲劳模型组相比,茶多酚组小鼠力竭游泳时间显著延长(P < 0.05),见图1。结果说明茶多酚有抗疲劳和增强小鼠运动能力的作用。 2.3 小鼠脑组织苏木精-伊红染色结果 与安静对照组相比,疲劳模型组和茶多酚组海马组织致密性没有明显变化,细胞排列整齐,紫蓝色的细胞核清晰可见,胞核与胞浆对比鲜明,形态结构未见明显异常,见图2。 2.4 小鼠脑组织肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素10蛋白表达 免疫印迹检测结果显示,与安静对照组相比,疲劳模型组小鼠脑组织肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β表达均明显增加(P < 0.01),白细胞介素10表达明显减少(P < 0.01);与疲劳模型组相比,茶多酚组小鼠脑组织肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β表达明显减少(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),白细胞介素10表达明显增加(P < 0.01);与安静对照组相比,茶多酚组小鼠脑组织肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β表达均明显增加(P < 0.05),白细胞介素10表达明显减少(P < 0.05),见图3。结果说明运动疲劳后神经中枢有炎症反应,而茶多酚有缓解炎症的作用,但是茶多酚对运动疲劳所致的中枢炎症的缓解作用尚未达到安静组水平。 2.5 小鼠脑组织诱导型一氧化氮合酶和精氨酸酶1蛋白表达 不同的小胶质细胞的亚型发挥不同的生物学效应。采用免疫印迹检测各组小鼠脑组织M1型(标志蛋白:诱导型一氧化氮合酶) 和M2型 ( 标志蛋白:精氨酸酶1 ) 小胶质细胞标志蛋白水平。结果显示,与安静对照组相比,疲劳模型组小鼠脑组织诱导型一氧化氮合酶表达明显增加(P < 0.01),精氨酸酶1表达明显减少(P < 0.01);与疲劳模型组相比,茶多酚组小鼠脑组织诱导型一氧化氮合酶表达明显降低(P < 0.01),而精氨酸酶1表达明显增加 (P < 0.01);与安静对照组相比,茶多酚组小鼠脑组织诱导型一氧化氮合酶表达明显增加(P < 0.05),精氨酸酶1表达明显减少(P < 0.05),见图4。结果说明,茶多酚抑制小胶质细胞诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达,促进精氨酸酶1的表达,对激活的小胶质细胞由M1型向M2型转化有积极的促进作用,但是茶多酚对运动疲劳所致小胶质细胞的转化作用还没有恢复到安静组水平。 2.6 小鼠脑组织p-STAT3和核因子κB p65蛋白表达 免疫印迹检测结果显示,与安静对照组相比,疲劳模型组小鼠脑组织p-STAT3和核因子κB p65表达明显增加(P < 0.01);与疲劳模型组相比,茶多酚组小鼠脑组织p-STAT3和核因子κB p65表达明显降低(P < 0.01,P < 0.05);与安静对照组相比,茶多酚组小鼠脑组织核因子κB p65表达明显增加(P < 0.05),见图5。结果说明,小鼠运动疲劳的中枢炎症反应可能是通过激活STAT3/核因子κB p65信号通路实现的,茶多酚对脑组织炎症反应缓解作用是通过抑制STAT3/核因子κB p65信号通路实现的,但是茶多酚对运动疲劳情况下的κB p65信号通路的抑制作用还没有恢复到安静组水平。 2.7 小鼠脑组织STAT3 mRNA和核因子κB p65 mRNA水平 实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应检测结果显示,与安静对照组相比,疲劳模型组小鼠脑组织STAT3 mRNA和核因子κB P65 mRNA水平明显升高(P < 0.01);与疲劳模型组相比,茶多酚组小鼠脑组织STAT3 mRNA和核因子κB p65 mRNA水平明显降低(P < 0.05)。与安静对照组相比,茶多酚组小鼠脑组织STAT3 mRNA和核因子κB p65水平明显升高(P < 0.05),见图6。结果说明,不论是运动疲劳和茶多酚的干预,STAT3/核因子κB p65信号分子水平从基因转录水平已经有了改变,而且这个改变和蛋白的表达水平是一致的。 2.8 血浆白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素10和肿瘤坏死因子α的酶联免疫吸附检测结果 见图7。酶联免疫吸附检测结果显示,与安静对照组相比,疲劳模型组小鼠血浆肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β质量浓度明显增加(P < 0.01),白细胞介素10质量浓度明显降低(P < 0.01);与疲劳模型组相比,茶多酚组小鼠血浆肿瘤坏死因子α和"
| [1] ZHANG M, ZHANG X, HO CT, et al. Chemistry and health effect of tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin 3- O-(3- O-Methyl)gallate. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(19):5374-5378. [2] 张沙骆,王丹,王芳.茶多酚对力竭运动大鼠骨骼肌组织中细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(14):3532-3535. [3] 吴秀琴,杨威,尹玉娇,等.茶多酚对一次性力竭运动大鼠氧化应激和炎症反应的影响[J].中国体育科技,2016,52(1):92-95. [4] HOOPER DR, ORANGE T, GRUBER MT, et al. Broad spectrum polyphenol supplementation from tart cherry extract on markers of recovery from intense resistance exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021;18(1):47. [5] 任盼红,聂梦俭.鱼腥草黄酮对运动疲劳大鼠骨骼肌能量代谢的影响[J].食品安全质量检测学报,2023,14(11):302-312. [6] 李昆展,王颖,郑佳,等.基于Nrf2信号通路探析桑黄多糖对运动疲劳小鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J].现代食品科技,2024,40(6):20-28. [7] 曹奕炜,宋睿,吴宁,等.脑神经炎症对小鼠运动疲劳的影响及其可能机制[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2023,37(9):655-662. [8] 金硕,李鸿扬,吉宸萱,等.运动疲劳通过基底神经节输出核团损伤大鼠工作记忆能力[J].神经解剖学杂志,2024,40(1):9- 15. [9] KIM MJ, ZHANG T, KIM KN, et al. Alleviation of cognitive and physical fatigue with enzymatic porcine placenta hydrolysate intake through reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in intensely exercised rats.Biology (Basel). 2022;11(12):1739. [10] AN Z, WANG Y, LI X, et al. Antifatigue effect of sea buck thorn seed oil on swimming fatigue in mice. J Food Sci. 2023;88(4):1482-1494.
[11] WILSON SM, OLIVER A, LARKE JA, et al. Fine-scale dietary polyphenol intake is associated with systemic and gastrointestinal inflammation in healthy adults. J Nutr. 2024;18:S0022-3166(24)00461-9.
[12] OUYANG S, LU P, LI J, et al.Inhaled tea polyphenol-loaded nanoparticles coated with platelet membranes largely attenuate asthmatic inflammation. Respir Res. 2024;25(1):311.[13] DRYER-BEERS ER, GRIFFIN J, MATTHEWS PM, et al. Higher dietary polyphenol intake is associated with lower blood inflammatory markers. J Nutr. 2024;154(8):2470-2480. [14] HAMMAD AM, ALZAGHARI LF, ALFARAJ M, et al. Green tea polyphenol nanoparticles reduce anxiety caused by tobacco smoking withdrawal in rats by suppressing neuroinflammation. Toxics. 2024;12(8):598. [15] ZHANG M, CUI S, MAO B, et al. Effects and mechanism of gastrodin supplementation on exercise-induced fatigue in mice. Food Funct. 2023;14(2):787-795. [16] LI IC, LU TY, LIN TW, et al. Hispidin-enriched Sanghuangporus sanghuang mycelia SS-MN4 ameliorate disuse atrophy while improving muscle endurance. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023;14(5):2226-2238. [17] 潘妍霓,赵欣,龙兴瑶,等.大叶苦丁茶多酚对四氯化碳致小鼠肝损伤的预防作用[J].食品工业科技,2019,40(9):287-294. [18] WANG D, WANG Y, WAN X, et al. Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate triggered hepatotoxicity in mice: responses of major antioxidant enzymes and the Nrf2 rescue pathway.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015;283(1):65-74. [19] TENG YS, WU D. Anti-fatigue effect of green tea polyphenols (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Pharmacogn Mag. 2017;13(50): 326-331. [20] 杨威. 茶多酚补充对一次性力竭运动大鼠血清炎症因子水平的影响[D].福州:福建师范大学,2015. [21] LIU L, WU X, ZHANG B, et al. Protective effects of tea polyphenols on exhaustive exercise-induced fatigue, inflammation and tissue damage. Food Nutr Res. 2017;61(1):1333390. [22] SU Y, QIU P, CHENG L, et al. Catechin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behaviour in mice by regulating neuronal and inflammatory genes. Curr Gene Ther. 2024; 24(4):292-306. [23] YAN D, GAO L, LANG J, et al. Effects of manganese on microglia M1/M2 polarization and SIRT1-mediated transcription of STAT3-dependent genes in mouse. Environ Toxicol. 2021;36(9):1729-1741. [24] LYU JX, XIE D, BHATIAT N, et al. Microglial/macro-phage polarization and functionin brain in jury and repair after stroke. CNS Neu ro sci Ther. 2021;27(5):515-527. [25] MAS, FAN L, LI J, et al. Resveratrol promoted the M2 polarization of microglia and reduced neuro inflammation after cerebral ischemia by in hibiting miR-155. Int J Neurosci. 2020;130(8):817-825. [26] SHAO Y, CHEN Y, LAN X, et al. Morin regulates M1/M2 microglial polarization via NF-kappaB p65 to alleviate vincristine-induced neuropathic pain. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024;18:3143-3156. [27] YANG Y, LIU R, SUN Y, et al. Schisandrin B restores M1/M2 balance through miR-124 in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2024;76(10):1352-1361. [28] YANG Y, KE J, CAO Y, et al. Melatonin regulates microglial M1/M2 polarization via AMPKalpha2-mediated mitophagy in attenuating sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;177:117092. [29] XIE H, FENG W, WANG X, et al. Tea polyphenols improves depression-like behavior in aged type 2 diabetes rats by regulating microglia polarization. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2024;53(1):71-87. [30] CHEN X, LE Y, TANG SQ, et al. Painful diabetic neuropathy is associated with compromised microglial IGF-1 signaling which can be rescued by green tea polyphenol EGCG in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022; 2022:6773662. [31] LIU L, ZHANG Y, LIU T, et al. Pyrroloquinoline quinone protects against exercise-induced fatigue and oxidative damage via improving mitochondrial function in mice. FASEB J. 2021;35(4):e21394. [32] ULRLKE H, CATRIN H, KRISTINA N. Anti-inflammatory diets and fatigue. Nutrients. 2019;11(10):2315. [33] WANG J, LI P, QIN T, et al. Protective effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate against neuroinflammation and anxiety-like behavior in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Brain Behav. 2020;10(6):e01633. [34] 席进,葛思堂,左芦根,等.绿茶多酚抑制肠道JAK2/STAT3信号通路保护三硝基苯磺酸诱导的小鼠结肠炎肠黏膜屏障[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2018,34(3):237-241. [35] SONG C, ZHANG Y, CHENG L, et al. Tea polyphenols ameliorates memory decline in aging model rats by inhibiting brain TLR4/NF-kappaB inflammatory signaling pathway caused by intestinal flora dysbiosis. Exp Gerontol. 2021;153:111476. [36] MATTSON M P, CULMSEE C, YU Z, et al. Roles of nuclear factor kappaB in neuronal survival and plasticity. J Neurochem. 2000;74(2):443-456. [37] ZARZISSI S, ZGHAL F, BOUCHIBA M, et al. Delayed neuromuscular fatigue recovery unveils reduced fatigue tolerance in elderly following maximal intermittent exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024;124(10): 2941-2949. [38] DALTON B, HESTER G, ALESI M, et al. Central and peripheral neuromuscular fatigue following ramp and rapid maximal voluntary isometric contractions. Front Physiol. 2024;15:1434473. [39] KEARNS RP, DOOLEY JSG, MATTHEWS M, et al. ”Do probiotics mitigate GI-induced inflammation and perceived fatigue in athletes? A systematic review”. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2024;21(1):2388085. [40] DA SILVA LA, BOEIRA D, DOEYNART R, et al. Effects of aerobic exercise during recovery from eccentric contraction on muscular performance, oxidative stress and inflammation. Curr Res Physiol. 2024;7:100129. [41] SEOANE N, PICOS A, MORAÑA-FERNÁNDEZ S, et al. Effects of sodium nitroprusside on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and disruption of blood-brain barrier. Cells. 2024;13(10):843. [42] KOBRZYCKA A, NAPORA P, PEARSON BL, et al. Peripheral and central compensatory mechanisms for impaired vagus nerve function during peripheral immune activation. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):150. [43] 安静芳,李航,杨帆,等.PKC抑制剂对力竭运动大鼠肾脏裂孔膜蛋白表达的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2022,38(2):126-131. [44] 胡琰茹,侯莉娟,王大磊,等.一次力竭运动过程中大鼠丘脑腹外侧核神经元电活动及NR2B、GABAAα-1蛋白表达变化的研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2022,37(3):296-302. [45] TWAROWSKI B, HERBET M. Inflammatory Processes in Alzheimer’s Disease-Pathomechanism, Diagnosis and Treatment: A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6518. [46] GOPINATH A, MACKIE PM, PHAN LT, et al. The complex role of inflammation and gliotransmitters in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;176:105940. |
| [1] | He Longcai, Song Wenxue, Ming Jiang, Chen Guangtang, Wang Junhao, Liao Yidong, Cui Junshuan, Xu Kaya. An experimental method for simultaneous extraction and culture of primary cortical neurons and microglial cells from SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1395-1400. |
| [2] | Zhou Ying, Tian Yong, Zhong Zhimei, Gu Yongxiang, Fang Hao. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 regulates mTORC1/ULK1 signaling and promotes autophagy to improve myocardial injury in sepsis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6434-6440. |
| [3] | Wu Xiaochou, Wang Huiying, Wang Jie, Zhang Caifeng, Hou Yanyun, Jin Bo. Protective mechanism of tanshinone IIA in mouse ovarian cryopreservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6198-6204. |
| [4] | Song Yuting, Wen Chunlei, Li Yi, Bai Xue, Gao Hong, Hu Tingju, Wang Zijun, Yan Xu. Effects of myocardial extracellular matrix remodeling on connexin 43 and its Ser368 phosphorylation and electrical conduction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6212-6218. |
| [5] | Liu Ruojing, Zhao Xue, Zhu Yizhen, Fu Lingling, Zhu Junde. Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates cerebral ischemic injury in mice by regulating microglial polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6219-6227. |
| [6] | Sun Rongyan, Xu Luchun, Jiang Guozheng, Song Jiawei, Ma Yukun, Fan Jiaojiao, Wang Guanlong, Yang Yongdong, Yu Xing. Du Meridian electroacupuncture inhibits ferroptosis and promotes neurorepair in rats with acute cervical spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6228-6238. |
| [7] | Chen Lijuan, Gao Xinxue, Wu Jin, Du Ying, Lyu Meijun, Sui Guoyuan, Jia Lianqun, Pan Guowei. Construction and evaluation of spleen-deficiency hyperlipidemia mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6237-6242. |
| [8] | Du Juan, Zhang Yi, Hao Quanshui. Effects of exercise on activation of microglia and astrocytes and neuronal apoptosis in depressed rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6243-6248. |
| [9] | Liu Haowei, Tian Haodong, Huang Li, Yu Hanglin, Peng Li. Acute effects of blood flow restriction resistance exercise on serum metabolites in obese young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6249-6259. |
| [10] | Zhang Ziyu, Chen Longhao, Sheng Wei, Lyu Hanzhe, Shen Ying, Wang Binghao, Lyu Zhizhen, Lyu Lijiang. Application of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation: evolution towards standardization, efficiency, and precision of diagnosis and treatment methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6269-6276. |
| [11] | Chen Jun, Jia Shaohui, Guo Chenggen, Xue Xinxuan, Dong Kunwei. Role and mechanism of resveratrol in delaying exercise-induced fatigue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6285-6294. |
| [12] | Chen Xiaoqing, Gong Yunzhao, Chen Wei. Association of the controlling nutritional status score and systemic immune-inflammation index with postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5071-5078. |
| [13] | Liu Kexin, Ma Chao, Liu Kai, Hao Maochen, Wang Xingru, Meng Lingting, Dong Mei, Wang Jianzhong . Screening and validation of glucose metabolism genes in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4181-4189. |
| [14] | Xu Liang, Gulimila·Muhetaer, Ju Bowei, Li Ruoning. Molecular mechanism of allicin-targeted regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor and kynureninase in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4205-4214. |
| [15] | Pei Yunxiang, Wu Hao. Hyperbaric oxygen intervention eliminates exercise-induced fatigue in a high-intensity interval training shock microcycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 2979-2988. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||