Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (27): 5869-5875.doi: 10.12307/2025.804
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of imaging findings of paraspinal muscle tissue degeneration in patients with degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis
Wang Shoukang1, Liang Gang1, Liu Xiaolei1, Hong Chunbo1, Xin Bing2
- 1Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-17Accepted:2024-06-21Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-03-06 -
Contact:Xin Bing, MS, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Wang Shoukang, Master candidate, Physician, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Shoukang, Liang Gang, Liu Xiaolei, Hong Chunbo, Xin Bing. Comparison of imaging findings of paraspinal muscle tissue degeneration in patients with degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5869-5875.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
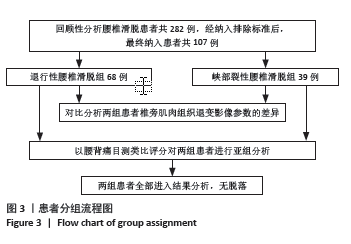
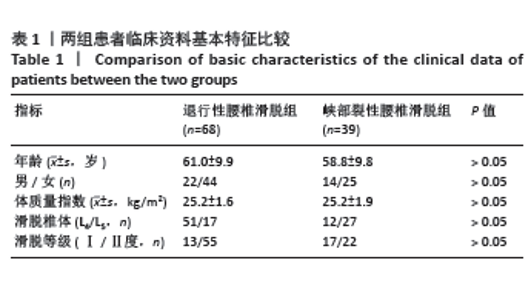
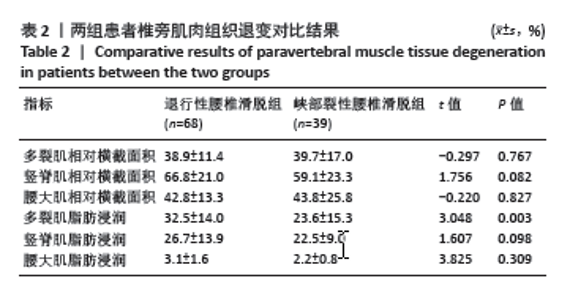
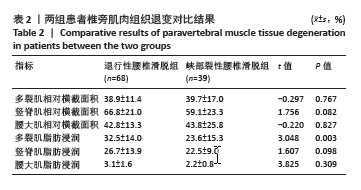
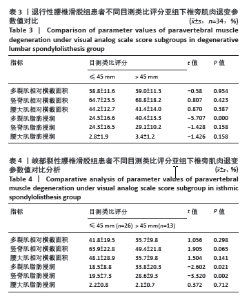
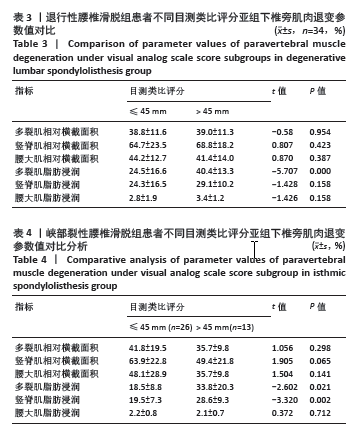
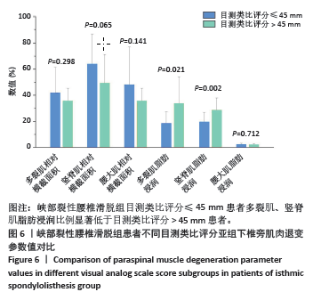
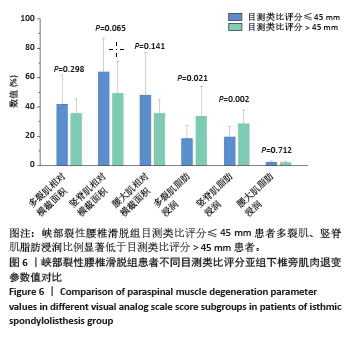
2.5 两组患者腰背痛目测类比评分分组下椎旁肌肉组织对比分析 依据患者腰背痛目测类比评分,对两组患者椎旁肌肉组织退变进行组内分析:①退行性腰椎滑脱组目测类比评分≤45 mm的患者多裂肌脂肪浸润百分比明显低于目测类比评分> 45 mm的患者(P < 0.001),见表3及图5;②峡部裂性腰椎滑脱组目测类比评分≤45 mm患者多裂肌、竖脊肌脂肪浸润百分比明显低于目测类比评分> 45 mm的患者(P=0.021,P=0.002),其余椎旁肌肉组织影像学指标无显著性差异,见表4及图6。 2.6 不良事件 此次研究共纳入107例患者,其中有1例患者发生腰椎术后感染,术后使用敏感抗生素后感染消退(症状好转,辅助检查指标恢复正常)。所有患者均未出现伤残、危及生命或死亡等严重不良事件。 "
| [1] AKKAWI I, ZMERLY H. Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: A Narrative Review. Acta Biomed. 2022;92(6):e2021313. [2] BYDON M, ALVI MA, GOYAL A. Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: Definition, Natural History, Conservative Management, and Surgical Treatment. Neurosurg Clin North Am. 2019;30(3):299-304. [3] AOKI Y, TAKAHASHI H, NAKAJIMA A, et al. Prevalence of lumbar spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in patients with degenerative spinal disease. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):6739. [4] CAI T, YANG L, CAI W, et al. Dysplastic spondylolysis is caused by mutations in the diastrophic dysplasia sulfate transporter gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(26):8064-8069. [5] HLAING SS, PUNTUMETAKUL R, KHINE EE, et al. Effects of core stabilization exercise and strengthening exercise on proprioception, balance, muscle thickness and pain related outcomes in patients with subacute nonspecific low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):998. [6] KIM YE, CHOI HW. Does stabilization of the degenerative lumbar spine itself produce multifidus atrophy? Med Eng Phys. 2017;49:63-70. [7] THAKAR S, SIVARAJU L, ARYAN S, et al. Lumbar paraspinal muscle morphometry and its correlations with demographic and radiological factors in adult isthmic spondylolisthesis: a retrospective review of 120 surgically managed cases. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(5):679-685. [8] WANG G, KARKI SB, XU S, et al. Quantitative MRI and X-ray analysis of disc degeneration and paraspinal muscle changes in degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2015;28(2):277-285. [9] HARADA T, HASHIZUME H, TANIGUCHI T, et al. Association between acetabular dysplasia and sagittal spino-pelvic alignment in a population-based cohort in Japan. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):12686. [10] YUKAWA Y, KATO F, SUDA K, et al. Normative data for parameters of sagittal spinal alignment in healthy subjects: an analysis of gender specific differences and changes with aging in 626 asymptomatic individuals. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(2):426-432. [11] ZI Y, ZHANG B, LIU L, et al. Fat content in lumbar paravertebral muscles: Quantitative and qualitative analysis using dual-energy CT in correlation to MR imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2022;148:110150. [12] FAIZ KW. [VAS--visual analog scale]. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2014; 134(3):323. [13] CRAWFORD RJ, CORNWALL J, ABBOTT R, et al. Manually defining regions of interest when quantifying paravertebral muscles fatty infiltration from axial magnetic resonance imaging: a proposed method for the lumbar spine with anatomical cross-reference. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):25. [14] RANSON CA, BURNETT AF, KERSLAKE R, et al. An investigation into the use of MR imaging to determine the functional cross sectional area of lumbar paraspinal muscles. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(6):764-773. [15] HAN G, ZOU D, LIU Z, et al. Fat infiltration of paraspinal muscles as an independent risk for bone nonunion after posterior lumbar interbody fusion. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):232. [16] HOU X, HU H, CUI P, et al. Predictors of achieving minimal clinically important difference in functional status for elderly patients with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis undergoing lumbar decompression and fusion surgery. BMC Surg. 2024;24(1):59. [17] LIN T, WANG Z, CHEN G, et al. Predictive effect of cervical spinal cord compression and corresponding segmental paravertebral muscle degeneration on the severity of symptoms in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine J. 2021;21(7):1099-1109. [18] YANG F, LIU Z, ZHU Y, et al. Imaging of muscle and adipose tissue in the spine: A narrative review. Medicine. 2022;101(49):e32051. [19] YOSHIDA Y, OHYA J, YASUKAWA T, et al. Association Between Paravertebral Muscle Mass and Improvement in Sagittal Imbalance After Decompression Surgery of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Spine. 2022; 47(6):E243-E248. [20] KÄÄRIÄINEN T, TAIMELA S, AALTO T, et al. The effect of decompressive surgery on lumbar paraspinal and biceps brachii muscle function and movement perception in lumbar spinal stenosis: a 2-year follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(3):789-794. [21] KALICHMAN L, CARMELI E, BEEN E. The Association between Imaging Parameters of the Paraspinal Muscles, Spinal Degeneration, and Low Back Pain. BioMed Res Int. 2017;2017:2562957. [22] KALPAKCIOGLU B, ALTINBILEK T, SENEL K. Determination of spondylolisthesis in low back pain by clinical evaluation. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2009;22(1):27-32. [23] SUH JH, KIM H, JUNG GP, et al. The effect of lumbar stabilization and walking exercises on chronic low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine. 2019;98(26):e16173. [24] FERNÁNDEZ-RODRÍGUEZ R, ÁLVAREZ-BUENO C, CAVERO-REDONDO I, et al. Best Exercise Options for Reducing Pain and Disability in Adults With Chronic Low Back Pain: Pilates, Strength, Core-Based, and Mind-Body. A Network Meta-analysis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2022;52(8): 505-521. [25] GENEEN LJ, MOORE RA, CLARKE C, et al. Physical activity and exercise for chronic pain in adults: an overview of Cochrane Reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;4(4):CD011279. [26] TYAGI V, STROM R, TANWEER O, et al. Posterior Dynamic Stabilization of the Lumbar Spine Review of Biomechanical and Clinical Studies. Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013). 2018;76(2):100-104. [27] GUAN J, LIU T, YU X, et al. Biomechanical and clinical research of Isobar semi-rigid stabilization devices for lumbar degenerative diseases: a systematic review. Biomed Eng Online. 2023;22(1):95. [28] HUANG Y, WANG L, ZENG X, et al. Association of Paraspinal Muscle CSA and PDFF Measurements With Lumbar Intervertebral Disk Degeneration in Patients With Chronic Low Back Pain. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:792819. [29] YAZICI A, YERLIKAYA T, ONIZ A. Evaluation of the degeneration of the multifidus and erector spinae muscles in patients with low back pain and healthy individuals. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023;36(3): 637-650. [30] JAKIMOVSKI D, BERGSLAND N. Editorial for “Paraspinal Muscle in Chronic Low Back Pain: Comparison Between Standard Parameters and Chemical Shift Encoding-Based Water-Fat MRI”. J Magn Reson Imaging . 2022;56(5):1609-1610. [31] KATZMAN WB, MILLER-MARTINEZ D, MARSHALL LM, et al. Kyphosis and paraspinal muscle composition in older men: a cross-sectional study for the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) research group. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:19. [32] SOLLMANN N, BONNHEIM NB, JOSEPH GB, et al. Paraspinal Muscle in Chronic Low Back Pain: Comparison Between Standard Parameters and Chemical Shift Encoding-Based Water-Fat MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022;56(5):1600-1608. [33] BAILEY JF, FIELDS AJ, BALLATORI A, et al. The Relationship Between Endplate Pathology and Patient-reported Symptoms for Chronic Low Back Pain Depends on Lumbar Paraspinal Muscle Quality. Spine. 2019; 44(14):1010-1017. [34] VAGASKA E, LITAVCOVA A, SROTOVA I, et al. Do lumbar magnetic resonance imaging changes predict neuropathic pain in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain? Medicine. 2019;98(17): e15377. [35] ÖZCAN-EKŞI EE, EKŞI M, TURGUT VU, et al. Reciprocal relationship between multifidus and psoas at L4-L5 level in women with low back pain. Br J Neurosurg. 2021;35(2):220-228. [36] KONRAD A, MOČNIK R, TITZE S, et al. The Influence of Stretching the Hip Flexor Muscles on Performance Parameters. A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 18(4):1936. [37] ROUSSOULY P, PINHEIRO-FRANCO JL. Biomechanical analysis of the spino-pelvic organization and adaptation in pathology. Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 5(Suppl 5): 609-618. [38] MACDONALD DA, DAWSON AP, HODGES PW. Behavior of the lumbar multifidus during lower extremity movements in people with recurrent low back pain during symptom remission. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41(3):155-164. |
| [1] |
Wang Qianliang, Zhang Qianzhongyi, Peng Yujian, Yan Jun.
Effects of unilateral biportal endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion on paraspinal muscles
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5862-5868.
|
| [2] | Liu Jiashun, Xie Hongru, Sun Yunkai, Li Shujin, Mao Tengfei, An Yaoyao, Zhang Qin. Correlation and mechanism between lumbar disc degeneration and paraspinal muscle changes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5897-5906. |
| [3] | Song Hanlin, Hu Tianyu, Gao Haoran, Shi Yaozhou, Gao Xiao, Feng Hu. Influence of paravertebral muscles on spinopelvic sagittal plane in patients with isthmic spondylolisthesis: an evaluation of muscle quantity and quality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4445-4451. |
| [4] | Cao Zhengpei, Lu Shengsheng, Zhang Jiahuan, Wang Xiaoying. Effects of silver needle comprehensive therapy on the ultrasonographic morphology of multifidus muscles in patients with lumbar disc herniation: an ultrasound morphologic assessment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2261-2267. |
| [5] | Li Chao, Zhang Peipei, Xu Mengting, Li Linlin, Ding Jiangtao, Liu Xihua, Bi Hongyan. Respiratory training improves morphological changes of the multifidus muscle in patients with chronic nonspecific lower back pain assessed by musculoskeletal ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1417-1421. |
| [6] | Li Yuqiao, Sun Tianwei, Ma Bin, Zhou Zhaohong, Dong Runbei, Wu Haiyang. A comparative study of imaging parameters and quality of life scores between subtypes of lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 943-948. |
| [7] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [8] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [9] | Young Lihjier, Ouyang Lin, Chen Dingwei, Lin Qi. A biomechanical analysis of low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5267-5271. |
| [10] | Bai Zhenjun, Liu Tong, Wang Zirun, Zhang Huiyu, Xu Peng. Effect of “Lumbar Three Needles” on expression of oxidative stress factors in rats with multifidus muscles injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5145-5150. |
| [11] | Liu Yang, Xu Baoshan, Xu Haiwei, Li Ning, Jiang Hongfeng, Wang Tao, Liu Yue. Imaging changes in spinal-pelvic sagittal alignment in sitting and standing positions in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3857-3861. |
| [12] | Liu Tong, Yu Jiani, Zou Dehui, Kuang Weichuan, Wang Xiaoyin, Wen Xi, Jiang Ye, Qiu Xiaojia, Zeng Yao, Liu Yue. Regulation of miRNA206/histone deacetylase 4 by electroacupuncture promotes myogenic differentiation during multifidus muscle repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5341-5346. |
| [13] |
Rong Feilong, Yin Ruofeng, Feng Mengmeng, Zhang Boyin, Liu Yi, Zhao Baolin.
Correlation between degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis and spinal stenosis and muscle volume around the vertebral body: CT and MRI data analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3840-3845.
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||