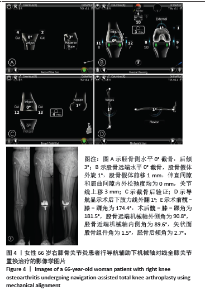
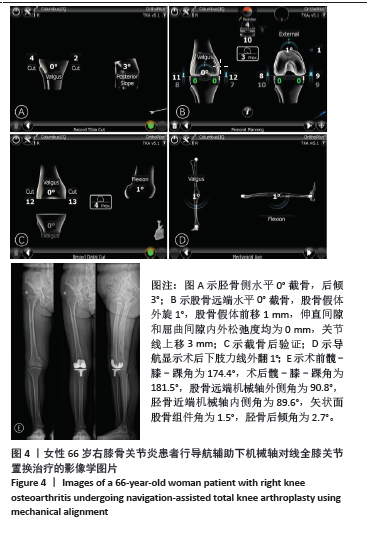
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (27): 5810-5818.doi: 10.12307/2025.825
Previous Articles Next Articles
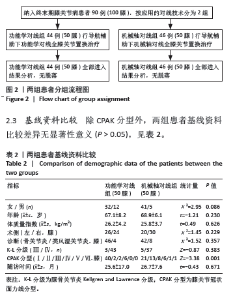
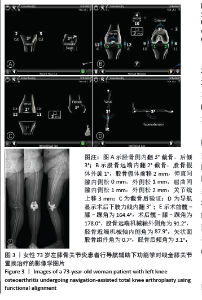
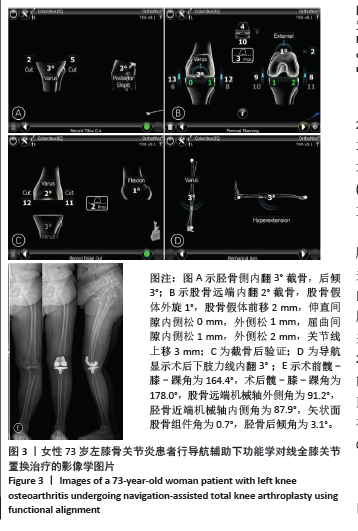
Navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty using functional alignment restores constitutional alignment and joint line obliquity
Wang Yijun1, Zheng Kai2, Zhang Lianfang1, Zhu Feng1, Zhang Weicheng1, Li Rongqun1, Zhou Jun1, Xu Yaozeng1
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, Xiamen 361000, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2024-06-25Accepted:2024-08-12Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-03-05 -
Contact:Xu Yaozeng, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Wang Yijun, MS, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82072498 (to XYZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yijun, Zheng Kai, Zhang Lianfang, Zhu Feng, Zhang Weicheng, Li Rongqun, Zhou Jun, Xu Yaozeng. Navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty using functional alignment restores constitutional alignment and joint line obliquity[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5810-5818.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
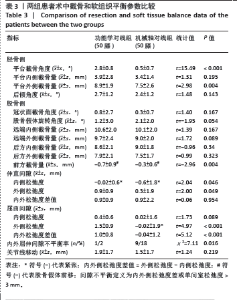
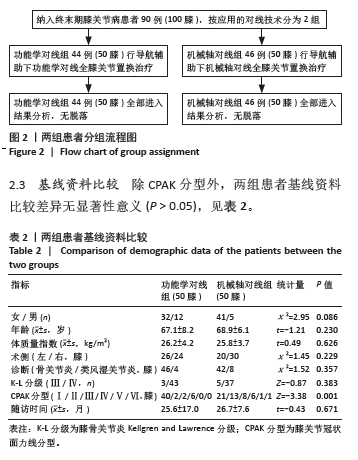
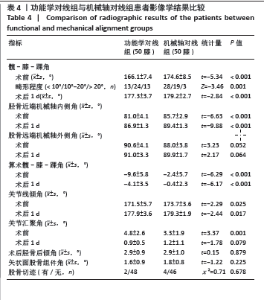
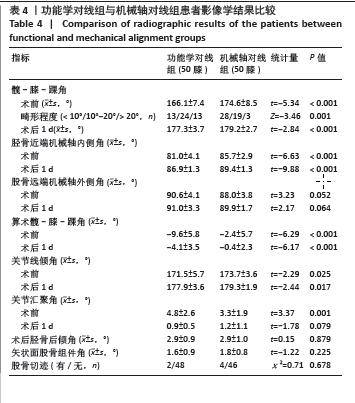
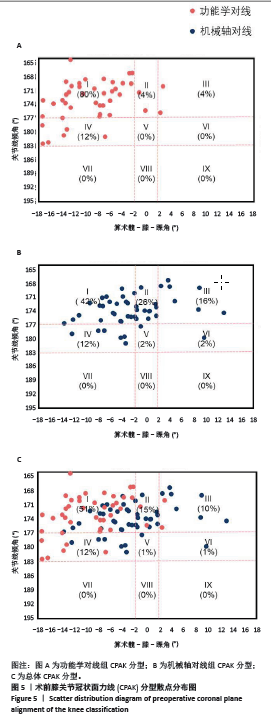
2.4 手术情况 如表3所示,与机械轴对线组相比,功能学对线组术中胫骨平台截骨角度、平台外侧截骨量、伸直间隙内侧松弛度、伸直间隙外侧松弛度、屈曲间隙外侧松弛度、屈曲间隙内外侧松弛度差值增大,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。功能学对线组前方截骨量为(-0.7±0.9) mm,间隙不平衡比例为1例(2%),小于机械轴对线组的(-0.3±0.6) mm、9例(18%),差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。两组胫骨平台内侧截骨量、后倾角度、股骨冠状面截骨、旋转角度、股骨远端及后方截骨量、伸直间隙内外侧松弛度差值、屈曲间隙内侧松弛度和关节线移动等参数相比差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。"
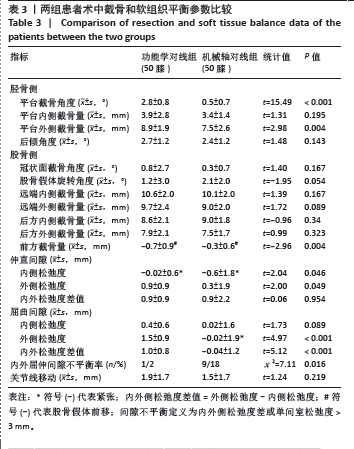
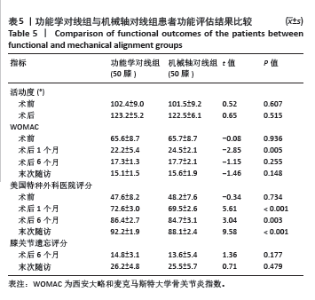
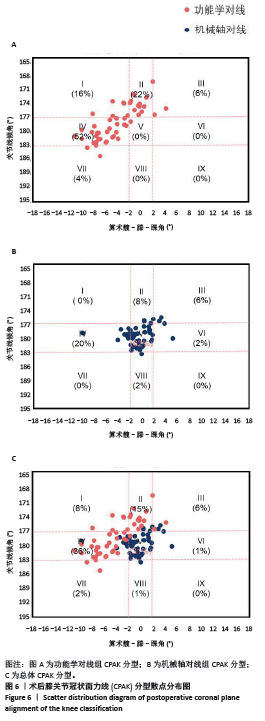
2.8 功能评估结果 如表5所示,功能学对线组术后1个月、6个月、末次随访美国特种外科医院评分较机械轴对线组升高,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);功能学对线组术后1个月WOMAC较机械轴对线组降低,差异有显著性意义(t=-2.85,P=0.005)。两组术后膝关节活动度、术后6个月、末次随访的WOMAC及膝关节遗忘评分相比差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.9 并发症情况 随访期间,功能学对线组发现5例(10%)下肢深静脉血栓,机械轴对线组有7例(12%),多为膝关节水平以下的肌间静脉血栓,经常规抗凝治疗后好转。两组均未见伤口感染、垫片脱位、假体周围骨折及假体松动下沉等并发症。植入物生物相容性良好,未出现植入物周围感染、过敏反应、免疫反应及排斥反应。"
| [1] OUSSEDIK S, ABDEL MP, VICTOR J, et al. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2020;102-B(3):276-279. [2] INSALL JN, BINAZZI R, SOUDRY M, et al. Total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;(192):13-22. [3] KARASAVVIDIS T, PAGAN CA, DEBBI EM, et al. No difference in limb alignment between kinematic and mechanical alignment robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39(8S1): S200-S205. [4] MACDESSI SJ, GRIFFITHS-JONES W, HARRIS IA, et al. Coronal plane alignment of the knee (cpak) classification. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(2): 329-337. [5] KAYANI B, KONAN S, PIETRZAK JRT, et al. Iatrogenic bone and soft tissue trauma in robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty compared with conventional jig-based total knee arthroplasty: A prospective cohort study and validation of a new classification system. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(8):2496-2501. [6] MACDESSI SJ, GRIFFITHS-JONES W, CHEN DB, et al. Restoring the constitutional alignment with a restrictive kinematic protocol improves quantitative soft-tissue balance in total knee arthroplasty: A randomized controlled trial. Bone Joint J. 2020;102-B(1):117-124. [7] BERCOVY M, KERBOULL L, MULLER JH, et al. Satisfactory mid- to long-term outcomes of tka aligned using conventional instrumentation for flexion gap balancing with minimal soft tissue release. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(2):627-637. [8] NAM D, NUNLEY RM, BARRACK RL. Patient dissatisfaction following total knee replacement: A growing concern? Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(11 Supple A):96-100. [9] DEFRANCE MJ, SCUDERI GR. Are 20% of patients actually dissatisfied following total knee arthroplasty? A systematic review of the literature. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38(3):594-599. [10] BEGUM FA, KAYANI B, MAGAN AA, et al. Current concepts in total knee arthroplasty : Mechanical, kinematic, anatomical, and functional alignment. Bone Jt Open. 2021;2(6):397-404. [11] CHANG JS, KAYANI B, WALLACE C, et al. Functional alignment achieves soft-tissue balance in total knee arthroplasty as measured with quantitative sensor-guided technology. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(3): 507-514. [12] CHOI BS, KIM SE, YANG M, et al. Functional alignment with robotic‑arm assisted total knee arthroplasty demonstrated better patient-reported outcomes than mechanical alignment with manual total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(3): 1072-1080. [13] RIVIERE C, IRANPOUR F, AUVINET E, et al. Alignment options for total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017;103(7):1047-1056. [14] 郑恺,孙厚义,梁晓龙,等. 调整限制性运动学对线在导航辅助全膝关节置换术中的初步应用[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2022,42(20): 1348-1357. [15] MARQUES LUIS N, VARATOJO R. Radiological assessment of lower limb alignment. EFORT Open Rev. 2021;6(6):487-494. [16] ZHENG K, SUN H, ZHANG W, et al. Mid-term outcomes of navigation-assisted primary total knee arthroplasty using adjusted mechanical alignment. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(1):230-238. [17] VAN ESSEN J, STEVENS J, DOWSEY MM, et al. Kinematic alignment results in clinically similar outcomes to mechanical alignment: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee. 2023;40:24-41. [18] CORTINA G, ZA P, PAPALIA GF, et al. Restricted kinematic alignment is clinically non-inferior to mechanical alignment in the short and mid-term: A systematic review. Knee. 2023;45:137-146. [19] KHLOPAS A, CHUGHTAI M, HAMPP EL, et al. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty demonstrated soft tissue protection. Surg Technol Int. 2017;30:441-446. [20] MASILAMANI ABS, JAYAKUMAR T, MULPUR P, et al. Functional alignment is associated with increased incidence of pre-balance, reduced soft-tissue release, and post-operative pain compared to mechanical alignment in patients undergoing simultaneous bilateral robotic-assisted tka. J Robot Surg. 2023;17(6):2919-2927. [21] HE X, CAI H, ZHANG K. Pie-crusting technique is effective and safe to release superficial medial collateral ligament for total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Translat. 2018;13:33-40. [22] SIONG FT, KIM TW, KIM SC, et al. Efficacy and safety of functional medial ligament balancing with stepwise multiple needle puncturing in varus total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(2):380-387. [23] NIKI Y, HARATO K, NAGAI K, et al. Effects of reduction osteotomy on gap balancing during total knee arthroplasty for severe varus deformity. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(12):2116-2120. [24] BOURNE RB, CHESWORTH BM, DAVIS AM, et al. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty: Who is satisfied and who is not? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(1):57-63. [25] VIGDORCHIK JM, WAKELIN EA, KOENIG JA, et al. Impact of component alignment and soft tissue release on 2-year outcomes in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(10):2035-2040 e2035. [26] MACDESSI SJ, OUSSEDIK S, ABDEL MP, et al. The language of knee alignment : Updated definitions and considerations for reporting outcomes in total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2023;105-B(2):101. [27] KAYANI B, KONAN S, TAHMASSEBI J, et al. A prospective double-blinded randomised control trial comparing robotic arm-assisted functionally aligned total knee arthroplasty versus robotic arm-assisted mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasty. Trials. 2020;21(1):194. [28] BLOOM DA, KAPLAN DJ, MOJICA E, et al. The minimal clinically important difference: A review of clinical significance. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(2):520-524. [29] OSTOJIC M, WINKLER PW, KARLSSON J, et al. Minimal clinically important difference: Don’t just look at the “p-value”. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(10):4077-4079. [30] CHENG J, FENG M, CAO G, et al. Patient outcomes in anteromedial osteoarthritis patients over 80 years old undergoing oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in china. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):446. [31] CLEMENT ND, BARDGETT M, WEIR D, et al. What is the minimum clinically important difference for the womac index after tka? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476(10):2005-2014. [32] PARRATTE S, VAN OVERSCHELDE P, BANDI M, et al. An anatomo-functional implant positioning technique with robotic assistance for primary tka allows the restoration of the native knee alignment and a natural functional ligament pattern, with a faster recovery at 6 months compared to an adjusted mechanical technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(4):1334-1346. [33] VANDEKERCKHOVE PTK, MATLOVICH N, TEETER MG, et al. The relationship between constitutional alignment and varus osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(9): 2873-2879. [34] BELLEMANS J, COLYN W, VANDENNEUCKER H, et al. The chitranjan ranawat award: Is neutral mechanical alignment normal for all patients? The concept of constitutional varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(1):45-53. [35] MULPUR P, DESAI KB, MAHAJAN A, et al. Radiological evaluation of the phenotype of indian osteoarthritic knees based on the coronal plane alignment of the knee classification (cpak). Indian J Orthop. 2022;56(12):2066-2076. |
| [1] | Zhou Daobin, Wang Kehao, Xie Yang, Ning Rende. Biomechanical characteristics of volar locking plate only versus combined dorsal mini-plate fixation of distal radius fractures with dorsal ulnar fragment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2255-2261. |
| [2] | Fu Lyupeng, Yu Peng, Liang Guoyan, Chang Yunbing. Electroactive materials applied in spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2113-2123. |
| [3] | Zhang Anqi, Hua Haotian, Cai Tianyuan, Wang Zicheng, Meng Zhuo, Zhan Xiaoqian, Chen Guoqian . Pain after total knee arthroplasty: current status and trend analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 795-804. |
| [4] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Wang Chaolu. High tibial osteotomy on a single plane: femorofibular angle as a reference marker for mechanical axis correction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 570-576. |
| [5] | Ma Jingbo, Yang Guangnan, Liu Jiang, Jiang Qiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Han Jiaheng, Ding Yu. Endoscopic lumbar canal decompression for upper lumbar spinal stenosis: a comparison of biomechanical stability of three surgical models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 577-585. |
| [6] | Jia Yingao, Gao Shitao, Wang Fei. Application of 3D printed titanium cage cutting model in anterior cervical vertebrae subtotal decompression and bone graft fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 604-611. |
| [7] | Wang Jiangjing, Zhao Na, Hu Xiaona, Zhao Na . Safety of 3D printed titanium alloy bone trabecular cup prosthesis combined with modified Kidney Tonifying and Blood Activating Decoction for elderly hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 612-619. |
| [8] | Du Xue, Luo Siyang, Feng Hongchao, Liu Jianguo, Luo Yi, Sun Jiangling, Chang Xingtao, Li Yuting, Wang Ruijie. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of Schneiderian membrane after maxillary sinus elevation and implantation under different bone quality conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3524-3535. |
| [9] | Huang Hailun, Wei Yatao, Liu Yongai, Wu Junzhe, Gao Heng, Sun Kui, Cao Zhenwen. Visualization analysis of lumbar spondylolisthesis treatment research from a bibliometric perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2618-2628. |
| [10] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [11] | Yu Ming, Wang Wen. Posterior cruciate ligament tibial attachment point avulsion fracture: materials, implants, and internal fixation techniques in arthroscopic treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 872-880. |
| [12] | Wang Lei, Li Chengsong, Zhang Shenshen, Wang Qing. Finite element analysis of biomechanical characteristics of three internal fixation methods in treatment of inferior patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7048-7054. |
| [13] | Yang Wanzhong, Ma Rong, Guo Wei, Wang Zhiqiang, Yang Wei, Chen Zhen, Wang Zemin, Zhang Honglai, Ge Zhaohui. One-stage posterior hemivertebra resection and pedicle screw fixation in treatment of congenital scoliosis: a 2-year follow-up of correction effect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7173-7180. |
| [14] | Cao Yong, Li Xin, Chen Zhigang, Gu Honglin, Lyu Shujun. Compensatory alignment changes of cervical and thoracic spine after correction of lumbar degenerative scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7196-7202. |
| [15] | Wang Yong, Li Hongyu, Liu Yuhang, Wang Fengxing. Knowledge map of surgical treatment for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a bibliometric analysis of data from 2005 to 2024 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7250-7260. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||