Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (24): 5203-5211.doi: 10.12307/2025.792
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of exercise intervention on cardiopulmonary function in stroke patients
Deng Yiran1, Wang Xianliang1, Li Dandan2
- 1School of Physical Education, Shandong University, Jinan 250061, Shandong Province, China; 2School of Education and Psychology, University of Jinan, Jinan 250022, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-08-05Accepted:2024-10-25Online:2025-08-28Published:2025-02-05 -
Contact:Wang Xianliang, PhD, Research fellow, Doctoral supervisor, School of Physical Education, Shandong University, Jinan 250061, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Deng Yiran, Master candidate, School of Physical Education, Shandong University, Jinan 250061, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China, No. 2020YFC2006804 (to WXL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Deng Yiran, Wang Xianliang, Li Dandan. Meta-analysis of exercise intervention on cardiopulmonary function in stroke patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5203-5211.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
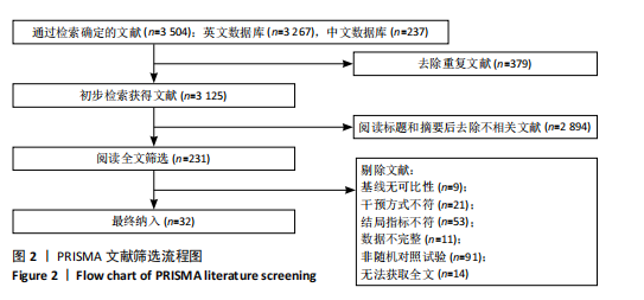
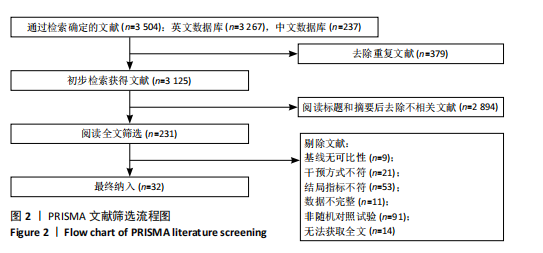
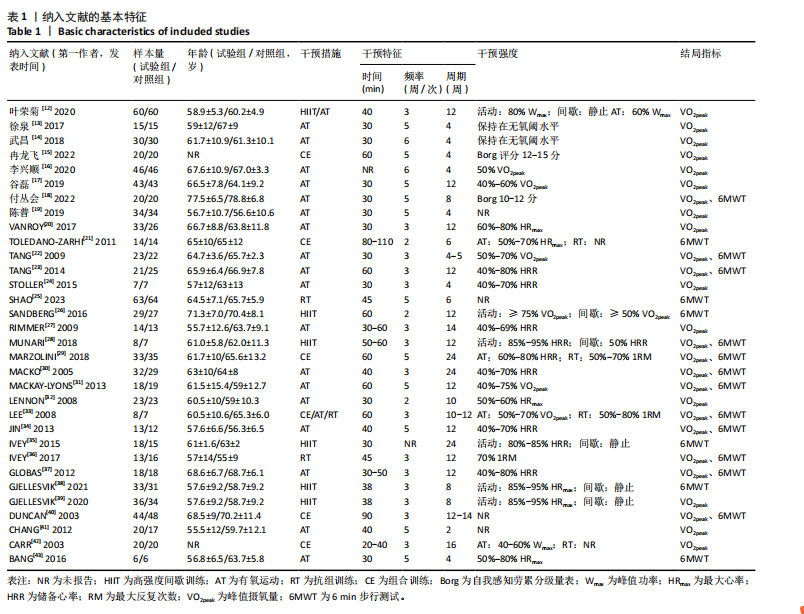
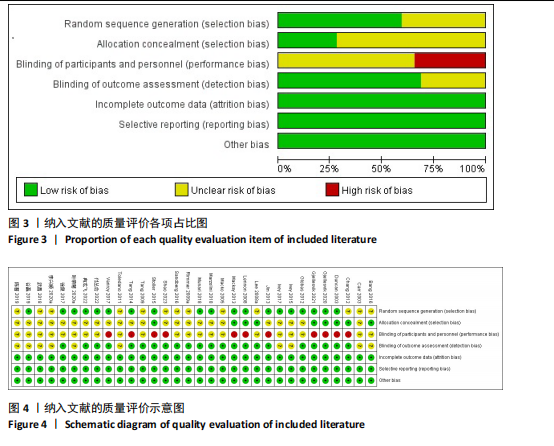
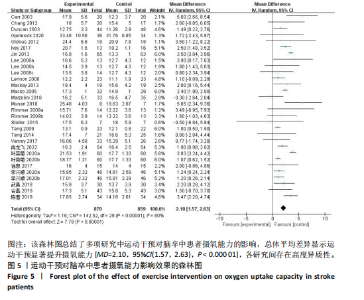
2.1 文献检索与筛选结果 通过对上述7个数据库检索后确定了3 504篇相关文献。首先删除379篇重复文献后剩余3 125篇文章;其次根据标题、摘要并按照纳入与排除标准进行全文审查后排除了2 894篇文献,文献筛选流程如图2所示。最终筛选出符合标准的32篇文献纳入Meta分析[12-43],其中英文文献24篇,中文文献8篇。 2.2 纳入文献的基本特征 纳入的32篇文献中共包含脑卒中患者1 826例,其中试验组933例,对照组893例;运动干预方案主要包括高强度间歇训练、有氧训练、抗阻训练以及组合训练;运动干预剂量方面,单次干预时间从20-110 min不等,干预频率每周2-6次不等,干预周期从4-24周不等;结局指标均报告了峰值摄氧量或6 min步行测试成绩。纳入文献的其他特征见表1。 2.3 质量评价结果 按照Cochrane协作网偏倚风险评估评估工具标准对纳入文献进行质量评价,结果见图3,4。"
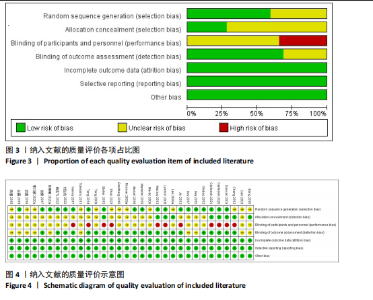
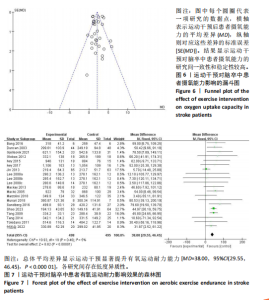
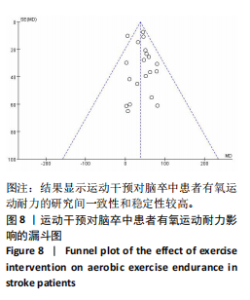
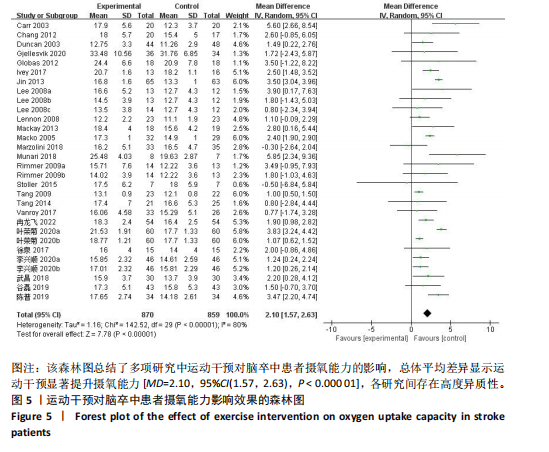
19篇文献报告了随机分配方案,剩余13篇文献的随机分配方案不清楚;9篇文献报告了具体分配隐藏方法,23篇文献的分配隐藏方法不清楚;22篇满足了单盲或双盲的要求;所有文献均无结果数据不完整、选择性报告和其他偏倚。 2.4 Meta分析结果 2.4.1 运动干预对脑卒中患者摄氧能力的影响 整体性检验:运动干预对脑卒中患者峰值摄氧量影响的分析共纳入25篇文献 [12-17,19-20,22-24,27-34,36-37,39-42],共包含1 729例脑卒中患者。异质性检验发现各研究间存在高度异质性(I2=80%,P < 0.000 01)。因此采用随机效应模型进行效应检验。结果如图5所示,与对照组相比,干预组脑卒中患者的摄氧能力有显著提高[MD=2.10,95%CI(1.57,2.63),P < 0.000 01]。"
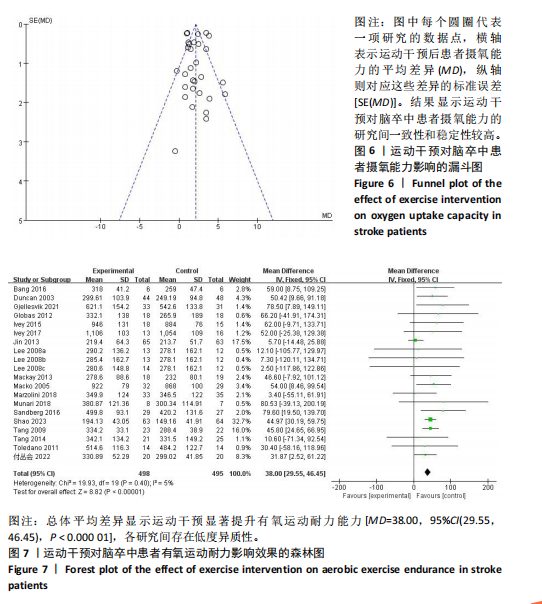
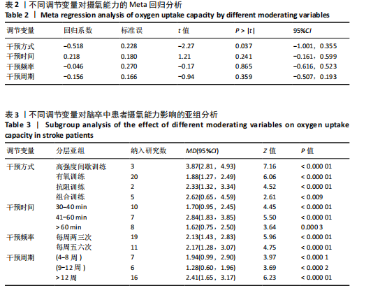
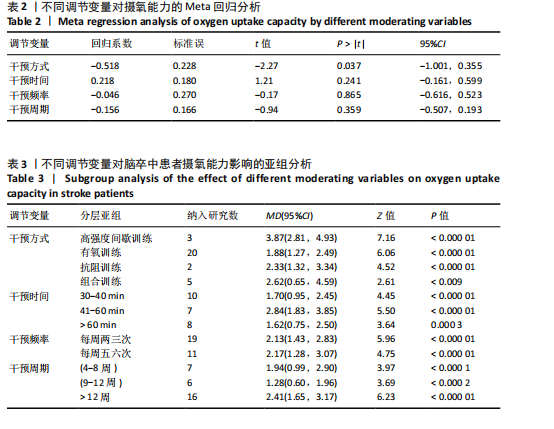
发表偏倚检验:漏斗图显示大多数研究均匀分布在平均效应两侧(图6)。Egger检验结果(t=0.17,P=0.864)进一步说明不存在明显的发表偏倚。 Meta回归和调节变量亚组分析:因合并效应量异质性高于50%,故根据纳入文献特征提取干预方式、干预时间、干预频率、干预周期作为调节变量进行Meta分析。结果如表2所示,干预方式(P=0.037)的不同可能是产生异质性的主要原因之一。 将干预方式、干预时间、干预频率、干预周期分别作为分组依据,尝试探索运动改善脑卒中患者摄氧能力的最佳运动方案。亚组分析结果见表3。干预方式方面,高强度间歇训练效果最好(MD=3.87),组合训练次之(MD=2.62);干预时间方面,每次干预41-60 min的效果最好(MD=2.84),每次干预30-40 min(MD=1.70)与≥60 min(MD=1.62)的效果相似;干预频率方面,每周干预五六次(MD=2.17)的效果要强于两三次(MD=2.13),但两种干预频率的效应量相近;干预周期方面,超过12周的干预效果最好(MD=2.41),其次是干预4-8周(MD=1.94)。 敏感性分析:首先,在随机效应和固定效应模型之间切换并重新进行统计分析后发现,所有统计结果无显著变化。其次,通过依次排除一项研究来评估每项研究的影响,结果显示,合并效应量(MD)的范围在1.99-2.17之间,I2的范围在73%-80%之间, P < 0.000 01。表明Meta分析结果稳定可靠。 2.4.2 运动干预对脑卒中患者有氧运动耐力的影响 整体性检验:运动干预对脑卒中患者6 min步行测试成绩的分析共纳入18篇文献 [18,21-23,25-26,28-31,33-38,40,43],共包含993例脑卒中患者。异质性检验发现各研究间存在低度异质性(I2=5%,P=0.40)。因此采用固定效应模型进行效应检验。结果如图7所示,与对照组相比,干预组脑卒中患者的有氧运动耐力水平有很大提高,且具有统计学意义[MD=38.00,95%CI(29.55,46.45),P < 0.000 01]。 发表偏倚检验:漏斗图显示大多数研究均匀分布在平均效应两侧"
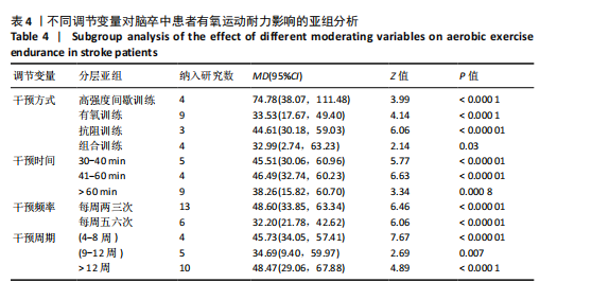
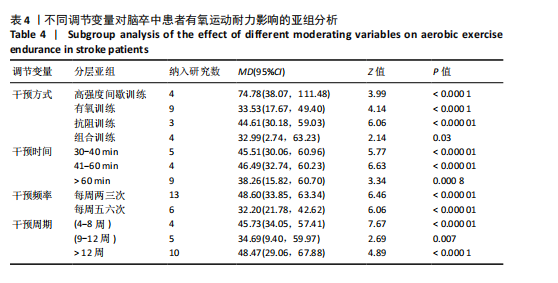
调节变量亚组分析:同样以干预方式、干预时间、干预频率、干预周期分别作为分组依据进行亚组分析,结果见表4。干预方式方面,高强度间歇训练仍然是最优选择(MD=74.48),抗阻训练效果次之(MD=44.61),有氧训练(MD=33.53)和组合训练(MD=32.99)效果相近;干预时间方面,每次干预41-60 min效果最好(MD=46.49),干预时间30-40 min的效果次之(MD=45.51);干预频率方面,每周干预两三次的效果(MD=48.60)优于干预五六次的效果(MD=32.20);干预周期方面,持续12周以上的干预效果最佳(MD=48.47),其次是4-8周(MD=45.73)。 敏感性分析:首先,在随机效应和固定效应模型之间切换并重新进行统计分析后发现,所有统计结果无显著变化;其次,通过依次排除某一项研究后发现删除任何一项研究对总体效应量和异质性的影响都不明显,并且结果仍然具有统计学意义,表明Meta分析结果稳定可靠。"
| [1] SACCO RL, KASNER SE, BRODERICK JP, et al. An updated definition of stroke for the 21st century: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2013;44(7):2064-2089. [2] LINDSAY MP, NORRVING B, SACCO RL, et al. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2019. Int J Stroke. 2019;14(8):806-817. [3] SMITH AC, SAUNDERS DH, MEAD G. Cardiorespiratory fitness after stroke: a systematic review. Int J Stroke. 2012;7(6): 499-510. [4] PASE MP, BEISER A, ENSERRO D, et al. Association of Ideal Cardiovascular Health With Vascular Brain Injury and Incident Dementia. Stroke. 2016;47(5):1201-1206. [5] SUTBEYAZ ST, KOSEOGLU F, INAN L, et al. Respiratory muscle training improves cardiopulmonary function and exercise tolerance in subjects with subacute stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2010;24(3):240-250. [6] KIM J, PARK JH, YIM J. Effects of respiratory muscle and endurance training using an individualized training device on the pulmonary function and exercise capacity in stroke patients. Med Sci Monit. 2014;20: 2543-2549. [7] WANG C, XU Y, ZHANG L, et al. Comparative efficacy of different exercise methods to improve cardiopulmonary function in stroke patients: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Neurol. 2024;15:1288032. [8] LV W, WANG X, LIU J, et al. Eight-Section Brocade Exercises Improve the Sleep Quality and Memory Consolidation and Cardiopulmonary Function of Older Adults With Atrial Fibrillation-Associated Stroke. Front Psychol. 2019;10:2348. [9] STOLLER O, DE BRUIN ED, KNOLS RH, et al. Effects of cardiovascular exercise early after stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2012;12:45. [10] HIGGINS JPT, THOMPSON SG, DEEKS JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557-560. [11] 王丹, 翟俊霞, 牟振云, 等. Meta分析中的异质性及其处理方法[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2009,9(10):1115-1118. [12] 叶荣菊, 孙乐山, 张琴, 等. 有氧运动强度对脑卒中合并冠心病患者心功能及运动耐力的影响[J]. 心血管康复医学杂志, 2020,29(5):536-540. [13] 徐泉, 潘钰, 杨晓辉, 等. 有氧运动联合常规康复治疗对卒中偏瘫患者心肺运动功能及康复效果的影响[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志,2017,14(9):465-469. [14] 武昌, 秦小虎, 田智. 有氧运动联合常规康复治疗对卒中偏瘫患者心肺运动功能及康复效果的影响[J]. 临床医药文献电子杂志,2018,5(24):32-33. [15] 冉龙飞, 聂志强, 郭军辉, 等. 等速肌力训练联合有氧运动对脑卒中患者心肺功能及下肢运动功能的影响[J]. 中国疗养医学,2022,31(12):1298-1302. [16] 李兴顺. 定量评估有氧训练对老年脑卒中偏瘫患者心肺功能和身体恢复指标的影响[J]. 白求恩医学杂志,2020,18(4): 352-354. [17] 谷磊, 武亮, 孙兴国. 定量评估有氧训练对老年脑卒中偏瘫病人心肺功能的影响[J]. 实用老年医学,2019,3(2):149-152. [18] 付丛会, 陈梅, 李小通, 等. 抗阻训练对卒中慢性期患者呼吸功能、运动耐力及负性情绪的影响[J]. 中国卒中杂志,2022, 17(6):573-578+572. [19] 陈普. 有氧运动+常规康复治疗对卒中偏瘫患者心肺功能及康复效果的影响评价[J]. 按摩与康复医学,2019,10(3):15-16. [20] VANROY C, FEYS H, SWINNEN A, et al. Effectiveness of Active Cycling in Subacute Stroke Rehabilitation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;98(8):1576-1585.e5. [21] TOLEDANO-ZARHI A, TANNE D, CARMELI E, et al. Feasibility, safety and efficacy of an early aerobic rehabilitation program for patients after minor ischemic stroke: A pilot randomized controlled trial. NeuroRehabilitation. 2011;28(2):85-90. [22] TANG A, SIBLEY KM, THOMAS SG, et al. Effects of an Aerobic Exercise Program on Aerobic Capacity, Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters, and Functional Capacity in Subacute Stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009;23(4):398-406. [23] TANG A, ENG JJ, KRASSIOUKOV AV, et al. Exercise-induced changes in cardiovascular function after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. I Int J Stroke. 2014;9(7): 883-889. [24] STOLLER O, DE BRUIN ED, SCHINDELHOLZ M, et al. Efficacy of Feedback-Controlled Robotics-Assisted Treadmill Exercise to Improve Cardiovascular Fitness Early After Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2015;39(3):156-165. [25] SHAO C, WANG Y, GOU H, et al. Strength Training of the Nonhemiplegic Side Promotes Motor Function Recovery in Patients With Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(2):188-194. [26] SANDBERG K, KLEIST M, FALK L, et al. Effects of Twice-Weekly Intense Aerobic Exercise in Early Subacute Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97(8):1244-1253. [27] RIMMER JH, RAUWORTH AE, WANG EC, et al. A Preliminary Study to Examine the Effects of Aerobic and Therapeutic (Nonaerobic) Exercise on Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Coronary Risk Reduction in Stroke Survivors. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009;90(3):407-412. [28] MUNARI D, PEDRINOLLA A, SMANIA N, et al. High-intensity treadmill training improves gait ability, VO2peak and cost of walking in stroke survivors: preliminary results of a pilot randomized controlled trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2018;54(3):408-418. [29] MARZOLINI S, BROOKS D, OH P, et al. Aerobic With Resistance Training or Aerobic Training Alone Poststroke: A Secondary Analysis From a Randomized Clinical Trial. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2018;32(3): 209-222. [30] MACKO RF, IVEY FM, FORRESTER LW, et al. Treadmill Exercise Rehabilitation Improves Ambulatory Function and Cardiovascular Fitness in Patients With Chronic Stroke. Stroke. 2005;36(10):2206-2211. [31] MACKAY-LYONS M, MCDONALD A, MATHESON J, et al. Dual Effects of Body-Weight Supported Treadmill Training on Cardiovascular Fitness and Walking Ability Early After Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2013; 27(7):644-653. [32] LENNON O, CAREY A, GAFFNEY N, et al. A pilot randomized controlled trial to evaluate the benefit of the cardiac rehabilitation paradigm for the non-acute ischaemic stroke population. Clin Rehabil. 2008;22(2): 125-133. [33] LEE MJ, KILBREATH SL, SINGH MF, et al. Comparison of Effect of Aerobic Cycle Training and Progressive Resistance Training on Walking Ability After Stroke: A Randomized Sham Exercise–Controlled Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(6): 976-985. [34] JIN H, JIANG Y, WEI Q, et al. Effects of aerobic cycling training on cardiovascular fitness and heart rate recovery in patients with chronic stroke. NeuroRehabilitation. 2013;32(2):327-335. [35] IVEY FM, STOOKEY AD, HAFER-MACKO CE, et al. Higher Treadmill Training Intensity to Address Functional Aerobic Impairment after Stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015; 24(11):2539-2546. [36] IVEY FM, PRIOR SJ, HAFER-MACKO CE, et al. Strength Training for Skeletal Muscle Endurance after Stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26(4):787-794. [37] GLOBAS C, BECKER C, CERNY J, et al. Chronic stroke survivors benefit from high-intensity aerobic treadmill exercise: a randomized control trial. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2012;26(1):85-95. [38] GJELLESVIK TI, BECKER F, TJØNNA AE, et al. Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training After Stroke (The HIIT Stroke Study) on Physical and Cognitive Function: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(9):1683-1691. [39] GJELLESVIK TI, BECKER F, TJØNNA AE, et al. Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training After Stroke (the HIIT-Stroke Study): A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;101(6): 939-947. [40] DUNCAN P, STUDENSKI S, RICHARDS L, et al. Randomized Clinical Trial of Therapeutic Exercise in Subacute Stroke. Stroke. 2003; 34(9):2173-2180. [41] CHANG WH, KIM MS, HUH JP, et al. Effects of Robot-Assisted Gait Training on Cardiopulmonary Fitness in Subacute Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Study. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2012;26(4): 318-324. [42] CARR M, JONES J. Physiological Effects of Exercise on Stroke Svivors. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2003;9(4):57-64. [43] BANG DH, SON YL. Effect of intensive aerobic exercise on respiratory capacity and walking ability with chronic stroke patients: a randomized controlled pilot trial. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(8):2381-2384. [44] GIRARD V, BELLAVANCE-TREMBLAY H, GAUDET-DROUIN G, et al. Cardiorespiratory strain during stroke rehabilitation: Are patients trained enough? A systematic review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2021;64(4): 101443. [45] LOE H, NES BM, WISLØFF U. Predicting VO2peak from Submaximal- and Peak Exercise Models: The HUNT 3 Fitness Study, Norway. PloS One. 2016;11(1):e0144873. [46] LUO L, MENG H, WANG Z, et al. Effect of high-intensity exercise on cardiorespiratory fitness in stroke survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2020;63(1):59-68. [47] MONTERO D, DIAZ-CAÑESTRO C, LUNDBY C. Endurance Training and V˙O2max: Role of Maximal Cardiac Output and Oxygen Extraction. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015; 47(10):2024-2033. [48] ROSS R, BLAIR SN, ARENA R, et al. Importance of Assessing Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Clinical Practice: A Case for Fitness as a Clinical Vital Sign: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;134(24):e653-e699. [49] TOMCZAK CR, THOMPSON RB, PATERSON I, et al. Effect of acute high-intensity interval exercise on postexercise biventricular function in mild heart failure. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011;110(2):398-406. [50] FU TC, WANG CH, LIN PS, et al. Aerobic interval training improves oxygen uptake efficiency by enhancing cerebral and muscular hemodynamics in patients with heart failure. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(1):41-50. [51] LITTLE JP, GILLEN JB, PERCIVAL ME, et al. Low-volume high-intensity interval training reduces hyperglycemia and increases muscle mitochondrial capacity in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011;111(6):1554-1560. [52] GIBALA MJ, MCGEE SL, GARNHAM AP, et al. Brief intense interval exercise activates AMPK and p38 MAPK signaling and increases the expression of PGC-1alpha in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009;106(3):929-934. [53] LITTLE JP, SAFDAR A, BISHOP D, et al. An acute bout of high-intensity interval training increases the nuclear abundance of PGC-1α and activates mitochondrial biogenesis in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011;300(6): R1303-1310. [54] TAN R, NEDERVEEN JP, GILLEN JB, et al. Skeletal muscle fiber-type-specific changes in markers of capillary and mitochondrial content after low-volume interval training in overweight women. Physiol Rep. 2018;6(5): e13597. [55] CROZIER J, ROIG M, ENG JJ, et al. High-Intensity Interval Training After Stroke: An Opportunity to Promote Functional Recovery, Cardiovascular Health, and Neuroplasticity. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2018;32(6-7):543-556. [56] 祖秀明. 耐力训练与高强度间歇训练对肥胖儿童健康相关指标的影响[J]. 西南国防医药,2014,24(4):408-411. [57] CORTE DE ARAUJO AC, ROSCHEL H, PICANÇO AR, et al. Similar health benefits of endurance and high-intensity interval training in obese children. PloS One. 2012; 7(8):e42747. [58] BIDDLE SJH, BATTERHAM AM. High-intensity interval exercise training for public health: a big HIT or shall we HIT it on the head?. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2015;12:95. [59] HERBERT P, GRACE FM, SCULTHORPE NF. Exercising caution: prolonged recovery from a single session of high-intensity interval training in older men. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63(4):817-818. [60] ROGNMO Ø, MOHOLDT T, BAKKEN H, et al. Cardiovascular risk of high- versus moderate-intensity aerobic exercise in coronary heart disease patients. Circulation. 2012;126(12):1436-1440. [61] WEWEGE MA, AHN D, YU J, et al. High-Intensity Interval Training for Patients With Cardiovascular Disease-Is It Safe? A Systematic Review. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018; 7(21):e009305. |
| [1] | Wang Mingqi, Feng Shiya, Han Yinhe, Yu Pengxin, Guo Lina, Jia Zixuan, Wang Xiuli. Construction and evaluation of a neuralized intestinal mucosal tissue engineering model in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 892-900. |
| [2] | Wang Jie, Huang Rui, Zhang Ye, Shou Zhaoxi, Yao Jie, Liu Chenxi, Liao Jian. Role and mechanism of probiotics in peri-implantitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 901-907. |
| [3] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [4] | Jiang Yang, Peng Hao, Song Yanping, Yao Na, Song Yueyu, Yin Xingxiao, Li Yanqi, Chen Qigang. Isometric exercise reduces resting blood pressure: a meta-analysis of moderating factors and dose effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 975-986. |
| [5] | Li Hanyue, Li Yini, Xiang Linmei, Li Sen. Effects of resistance exercise therapy on pain and function in patients with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 987-996. |
| [6] | Sun Jiahe, Shi Jipeng, Zhu Tianrui, Quan Helong, Xu Hongqi. Effect of exercise intervention in elderly individuals with sarcopenia and its comorbidities: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 997-1007. |
| [7] | Yang Yuanyuan, Zhou Shanshan, Cheng Xiaofei, Feng Luye, Tang Jiqin. Network meta-analysis of non-invasive brain stimulation in the treatment of lower limb motor dysfunction after stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1008-1018. |
| [8] | Zhang Xinxin, Gao Ke, Xie Shidong, Tuo Haowen, Jing Feiyue, Liu Weiguo. Network meta-analysis of non-surgical treatments for foot and ankle ability and dynamic balance in patients with chronic ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1931-1944. |
| [9] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [10] | Wang Yida, Liu Jun, Wang Xiaoling, Wang Liyan, Yang Chengru, Zhang Xuexiao. Effects of wearable electronic device-based interventions on physical activity and sedentary behavior in healthy adolescents: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1693-1704. |
| [11] | Zhang Zixian, Xu Youliang, Wu Shaokui, Wang Xiangying. Effects of blood flow restriction training combined with resistance training on muscle indicators in college athletes: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1705-1713. |
| [12] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [13] | Zheng Huakun, Yin Mingyue, Liu Qian. Effects of interval and continuous training on the quality of life in physically inactive adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1727-1740. |
| [14] | Liu Zan, An Ran, Li Baocheng. Effect of pravastatin on functional recovery from sciatic nerve crush injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 942-950. |
| [15] | Li Zhe, Li Ping, Zhang Chao, Guo Guangling. A network meta-analysis of efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells from different sources in treatment of premature ovarian failure animal models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7898-7908. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||