Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (20): 4361-4368.doi: 10.12307/2025.719
Previous Articles Next Articles
Association between monounsaturated fatty acids and low back pain and patient all-cause mortality: causal inferences based on NHANES epidemiology
Tang Xiaochen1, Yang Jingyan2, Cheng Yupei3, Hao Huatao2, Li Hanyu2, Yu Dong1
- 1The Third Clinical Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; 2The Third Clinical School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; 3First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300381, China
-
Received:2024-07-22Accepted:2024-09-02Online:2025-07-18Published:2024-12-25 -
Contact:Yu Dong, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, The Third Clinical Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China -
About author:1The Third Clinical Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; 2The Third Clinical School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; 3First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300381, China Tang Xiaochen, Physician, The Third Clinical Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China Yang Jingyan, Master’s candidate, The Third Clinical School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China Tang Xiaochen and Yang Jingyan contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:2022 Cultivation Project of the Ministry of Education Engineering Research Center for “Intelligent Treatment of Traditional Chinese Medicine Orthopaedic Injury and Sports Rehabilitation,” The Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, No. BZYSY-2022-GCYJZXQX-08 (to YD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Xiaochen, Yang Jingyan, Cheng Yupei, Hao Huatao, Li Hanyu, Yu Dong. Association between monounsaturated fatty acids and low back pain and patient all-cause mortality: causal inferences based on NHANES epidemiology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4361-4368.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
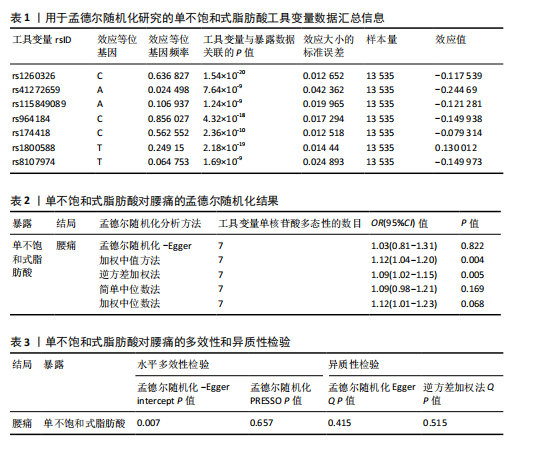
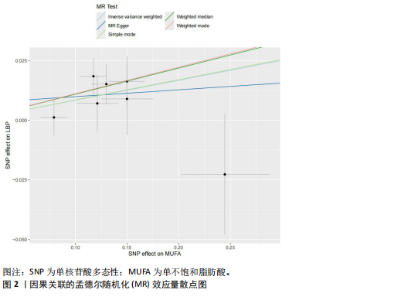
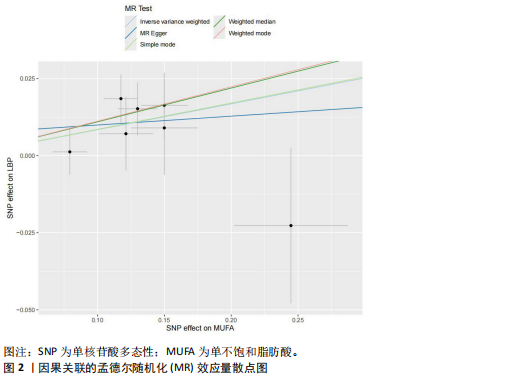
2.1 孟德尔随机化研究结果 在使用clumped函数去除连锁不平衡后,经计算后得出此次研究每单个SNP对应的F值均> 10(单不饱和脂肪酸:36.97-87.04),提示不存在弱工具变量偏倚,删除回文单核苷酸多态性后经MR-PRESSO分析无离群值,最终得出用于分析的7个工具变量(见表1)。其中逆方差加权法:[OR(95% CI):1.09(1.02-1.15),P=0.005]、加权中值法 :[OR(95%CI):1.12(1.04-1.20),P=0.004],以上方法结果均P < 0.05。 简单中位数法:[OR(95%CI):1.09 (0.98-1.21),P=0.169]、孟德尔随机化-Egger:[OR(95%CI):1.03(0.81-1.31),P=0.822],加权中位数法:[OR(95%CI):1.12(1.01-1.23),P=0.068]结果无统计学意义,但是5种方法因果效应方向一致(OR值均> 1),散点图显示回归线无明显偏移(见图2),表明上述因果关系可靠。以上数据细节见表2。 敏感性分析结果中MR-Egger回归分析结果均P > 0.05 ,提示数据未检测到潜在的水平多效性,MR PRESSO未发现异常值,说明单不饱和脂肪酸的工具变量均并不通过暴露数据以外的途径影响结局,符合排他性假设。而在对工具变量兼容性的Cochran’s Q异质性检验中未发现潜在的异质性。同时在留一法分析证明排除单个SNP时,SNP的效应结果均稳健。以上数据细节见表3。"
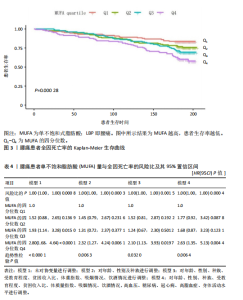
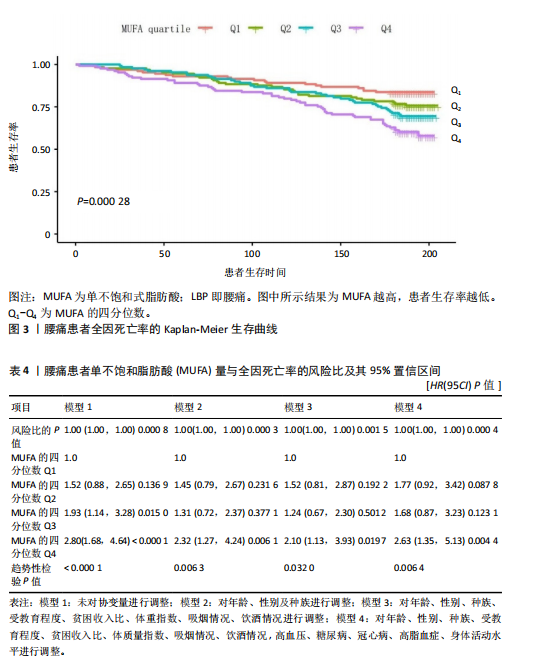
2.2 NHANES研究结果 2.2.1 研究人群的基线特征 在NHANES数据库的研究中,共有1 405名参与者被纳入,其中腰痛人群有516人(见图3)。首先,根据疼痛与否对总样本、腰痛和无腰痛组的基线特征进行比较,结果显示腰痛和无腰痛的参与者在受教育程度、贫困收入比、吸烟情况等方面存在一定差异(P < 0.05)。相比之下,腰痛患者更容易是低学历、低收入以及吸烟人群。之后还描述了腰痛人群按性别划分的基线情况并观察到了若干具有统计学意义的差异。体质量指数(kg/m2)在男性(均值=27.85,标准差=5.05)与女性(均值=29.13,标准差=6.27)间存在显著差异(P=0.020),男性的体质量指数普遍低于女性。吸烟行为在男性(32.77%)比女性(19.57%)更为常见,差异显著(P < 0.001)。饮酒习惯分析显示,男性中的重度饮酒者比例(23.83%)显著高于女性(12.46%,P < 0.001)。冠心病在男性中的发病率(8.09%)也显著高于女性(3.56%,P=0.026)。关于身体活动,从事繁重工作或负重活动的男性(14.04%)显著多于女性(2.14%,P < 0.001)。这些结果揭示了腰痛人群中生理健康指标和行为习惯上的性别差异。 2.2.2 单不饱和脂肪酸与腰痛患者全因死亡率的关联 根据之前孟德尔随机化分析的结果,进一步探讨了单不饱和脂肪酸对腰痛患者全因死亡率的影响,为此按四分位数对单不饱和脂肪酸进行分类,并构建了多变量Cox回归模型(见表4),模型结果显示,单不饱和脂肪酸的增加可能会增加腰痛患者的全因死亡率风险。在单不饱和脂肪酸的粗调整模型中,与最低四分位数的相比,最高四分位数的腰痛患者全因死亡率风险显著增加[风险比=2.80,95% CI (1.68,4.64),P < 0.000 1]。在单不饱和脂肪酸的完全调整模型情况下,同样与最低四分位数的相比,最高四分位数的腰痛患者全因死亡率风险显著增加 [风险比=2.63,95%CI(1.35,5.13),P=0.004 4]。并且趋势性检验均显著(P for trend < 0.05)。Kaplan-Meier生存曲线同样表明,较高的单不饱和脂肪酸与腰痛患者较高的全因死亡率相关(log rank P值<"
| [1] GBD 2021 Other Musculoskeletal Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of low back pain, 1990-2020, its attributable risk factors, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5(6):e316-e329. [2] DAMMERS R, KOEHLER PJ. Lumbar disc herniation: level increases with age. Surg Neurol. 2002;58(3-4):209-212; discussion 12-3. [3] ZHENG CJ, CHEN J. Disc degeneration implies low back pain. Theor Biol Med Model. 2015;12:24. [4] DRISCOLL T, JACKLYN G, ORCHARD J, et al. The global burden of occupationally related low back pain: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):975-981. [5] VOS T, MURRAY CJ, BARUA L, et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1204-1222. [6] LI W, GONG Y, LIU J, et al. Peripheral and Central Pathological Mechanisms of Chronic Low Back Pain: A Narrative Review. J Pain Res. 2021;14:1483-1494. [7] Calder PC. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: from molecules to man. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017;45(5):1105-1115. [8] QIAN F, KORAT AA, MALIK V, et al. Metabolic Effects of Monounsaturated Fatty Acid-Enriched Diets Compared With Carbohydrate or Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Enriched Diets in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(8):1448-1457. [9] ASAI A, SUZUKI F, TSUJIGUCHI H, et al. Relationship between fatty acid intake and chronic neck/shoulder/upper limb pain without elevated CRP in a Japanese population: a cross-sectional analysis of the Shika study. J Nutr Sci. 2022;11:e38. [10] BENNETT SM, HAYES JE. Differences in the chemesthetic subqualities of capsaicin, ibuprofen, and olive oil. Chem Senses. 2012;37(5):471-478. [11] BURGESS S, DAVEY SMITH G, DAVIES NM, et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023;4:186. [12] NAZARZADEH M, PINHO-GOMES AC, BIDEL Z, et al. Plasma lipids and risk of aortic valve stenosis: a Mendelian randomization study. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(40):3913-3920. [13] LAWLOR DA, HARBORD RM, STERNE JA, et al. Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med. 2008;27(8):1133-1163. [14] HARRIS WS, TINTLE NL, IMAMURA F, et al. Blood n-3 fatty acid levels and total and cause-specific mortality from 17 prospective studies. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2329. [15] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621. [16] QIU S, ZHENG K, HU Y, et al. Genetic correlation, causal relationship, and shared loci between vitamin D and COVID-19: A genome-wide cross-trait analysis. J Med Virol. 2023;95(5):e28780. [17] CODD V, NELSON CP, ALBRECHT E, et al. Identification of seven loci affecting mean telomere length and their association with disease. Nat Genet. 2013;45(4):422-427.
[18] LI W, LU Q, QIAN J, et al. Assessing the causal relationship between genetically determined inflammatory biomarkers and low back pain risk: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1174656. [19] XIE J, WANG Z, WANG J, et al. Intakes of omega-3 fatty acids and risks of all-cause and cause-specific mortality in people with diabetes: a cohort study based on NHANES 1999-2014. Acta Diabetol. 2023;60(3):353-362. [20] DAKING L, DODDS L. ICD-10 mortality coding and the NCIS: a comparative study. Health Inf Manag. 2007;36(2):11-23; discussion-5. [21] MAZIDI M, KENGNE AP, SIERVO M, et al. Association of Dietary Intakes and Genetically Determined Serum Concentrations of Mono and Poly Unsaturated Fatty Acids on Chronic Kidney Disease: Insights from Dietary Analysis and Mendelian Randomization. Nutrients. 2022;14(6). [22] LIU H, WANG L, CHEN C, et al. Association between Dietary Niacin Intake and Migraine among American Adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutrients. 2022;14(15):3052. [23] RATTAN P, PENRICE DD, AHN JC, et al. Inverse Association of Telomere Length With Liver Disease and Mortality in the US Population. Hepatol Commun. 2022;6(2):399-410. [24] BURGESS S, SCOTT RA, TIMPSON NJ, et al. Using published data in Mendelian randomization: a blueprint for efficient identification of causal risk factors. Eur J Epidemiol. 2015;30(7):543-552. [25] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016; 40(4):304-314. [26] ZHAO J, WANG J, XU H, et al. Intervertebral Disk Degeneration and Bone Mineral Density: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Calcif Tissue Int. 2024;114(3):228-236. [27] YUAN S, MIAO Y, RUAN X, et al. Therapeutic role of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in pancreatic diseases: mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023; 14:1240754. [28] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525. [29] BURGESS S, DUDBRIDGE F, THOMPSON SG. Combining information on multiple instrumental variables in Mendelian randomization: comparison of allele score and summarized data methods. Stat Med. 2016;35(11):1880-1906. [30] FERRERI C, MASI A, SANSONE A, et al. Fatty Acids in Membranes as Homeostatic, Metabolic and Nutritional Biomarkers: Recent Advancements in Analytics and Diagnostics. Diagnostics. 2017;7(1):1. [31] ANDONE S, FARCZÁDI L, IMRE S, et al. Fatty Acids and Lipid Paradox-Neuroprotective Biomarkers in Ischemic Stroke. Int J Molecul Sci. 2022;23(18):10810. [32] BJØRKKJAER T, BRUN JG, VALEN M, et al. Short-term duodenal seal oil administration normalised n-6 to n-3 fatty acid ratio in rectal mucosa and ameliorated bodily pain in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2006;5:6. [33] SANDERS AE, WEATHERSPOON ED, EHRMANN BM, et al. Circulating polyunsaturated fatty acids, pressure pain thresholds, and nociplastic pain conditions. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2022;184:102476. [34] PREGO-DOMINGUEZ J, HADRYA F, TAKKOUCHE B. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pain Physician. 2016;19(8):521-535. [35] ALEIDI SM, AL-ANSARI MM, ALNEHMI EA, et al. Lipidomics profiling of patients with low bone mineral density (LBMD). Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):12017. [36] KOU J, HE CY, CUI L, et al. Discovery of potential biomarkers for postmenopausal osteoporosis based on untargeted GC/LC-MS. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13:849076. [37] YU LS, QI HH, AN GH, et al. Association between metabolic profiles in urine and bone mineral density of pre- and postmenopausal Chinese women. Menopause. 2019;26(1):94-102. [38] SHARMA T, MANDAL CC. Omega-3 fatty acids in pathological calcification and bone health. J Food Biochem. 2020;44(8):e13333. [39] ANDREEVA VA, SZABO DE EDELENYI F, DRUESNE-PECOLLO N, et al. Macronutrient Intake in Relation to Migraine and Non-Migraine Headaches. Nutrients. 2018;10(9):1309. |
| [1] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [2] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [3] | Zheng Xiang, Zhang Mingxing, Huang Ya, Shan Sharui. Improvement of lower limb walking function in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain by biofeedback assisted electrical stimulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 547-553. |
| [4] | Liu Jiashun, Xie Hongru, Sun Yunkai, Li Shujin, Mao Tengfei, An Yaoyao, Zhang Qin. Correlation and mechanism between lumbar disc degeneration and paraspinal muscle changes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5897-5906. |
| [5] | Wang Runzheng, Fu Su, Dong Chao, Li Dongzhe, Wang Yongkui. Relationship between bone mineral density and lumbar disc degeneration in middle-aged and elderly men and postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5079-5085. |
| [6] | Wang Zikun, Li Shudong, Gao Shuang, Fan Shuhao, Li Cheng, Meng Chunyang. Relationship between intervertebral disc degeneration and 473 gut microbiotas: what can be learned from big data information in the FinnGen database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4369-4378. |
| [7] | Fang Zhijie, Ma Qiangping, Dong Wantao, Wu Junyuan, Lu Yunlin. Genetic causal relationship between gut microbiota and osteoporosis: analysis of 211 gut microbiota from the UK database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3941-3947. |
| [8] | Liu Kedi, Chen Yongxi, Qin Haibiao, Guo Shenghui, Qin Zhongshe, Meng Juewei, Cui Shanlin, Fan Junhong. Causal relationship between peripheral blood cells and osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2605-2613. |
| [9] | Ge Jin, Huang Dong, Yan Jinlian, Xu Zhengquan, Wang Yehua. Relationship between low back pain and spinal-pelvic sagittal parameter changes in patients with hip-spine syndrome after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5823-5827. |
| [10] | Huang Jie, Jiang Qiang, Han Jiaheng, Liu Jiang, Zhang Yan, Lu Zhencao, Ding Yu. Mechanism by which interleukin-1beta regulates the expression of Semaphorin 3A to induce intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3680-3685. |
| [11] | Han Zhongxiao, Ou Yaying, Zhuang Xinqing, Zhang Xiang, Li Biaoping, Jiang Zhirui, Zhang Jingyi, Yang Jiashun, Tang Ling, Xiao Wei. Mechanical puncture combined with tumor necrosis factor alpha and complete Freund’s adjuvant to construct a rat discogenic low back pain model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1672-1677. |
| [12] | Zhang Qiming, Bao Sairong, Shan Sharui, Zhong Zhiliang, Liu Chunlong. Effect of deep muscle stimulation on muscle tone and stiffness of erector spinaes in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain: a digital muscle testing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1250-1256. |
| [13] | Zhu Hongliu, Wang Wei. Correlation analysis of low back pain in middle-aged and elderly people in China and construction of a linear graph prediction mode [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4937-4942. |
| [14] | Luo Wei, Zhong Tao, Huang Zhirui, Gao Yan, Huang Zhen. Static balance and limits of stability in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4362-4366. |
| [15] | Chen Jin, Li Jiabin, Gu Mingxing, Tang Rong, Lu Jianxia. Effect of deep muscle stimulation on psoas surface electromyography and spatiotemporal and kinetic gait parameters in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2894-2899. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||