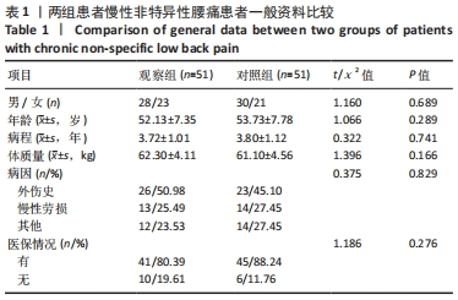
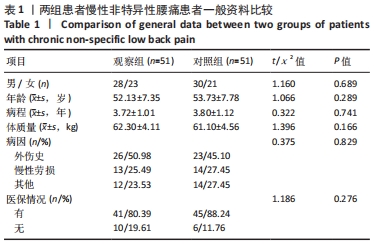
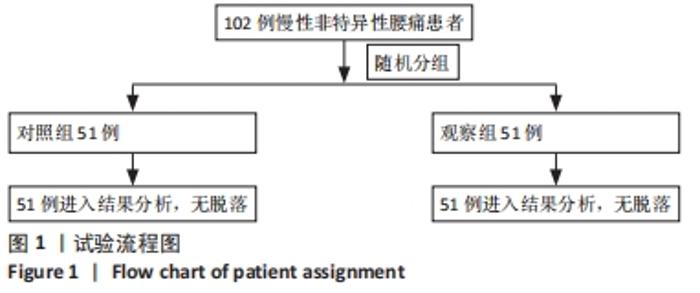
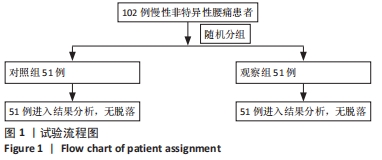
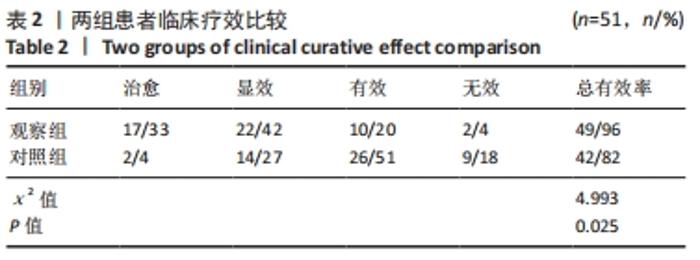
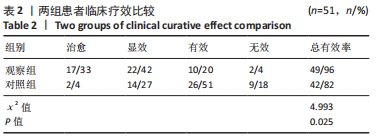
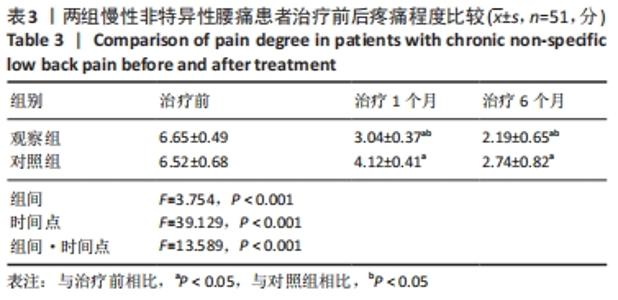
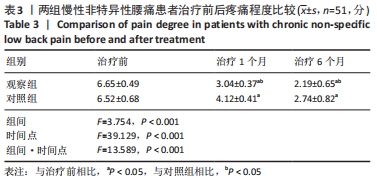
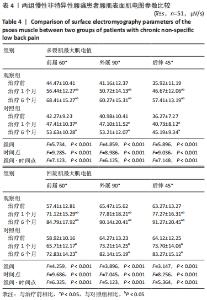
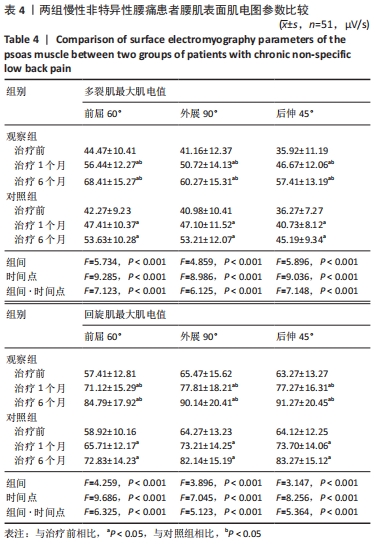
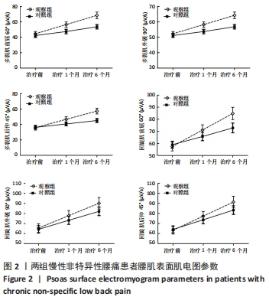
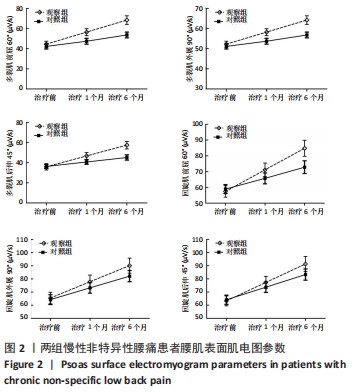
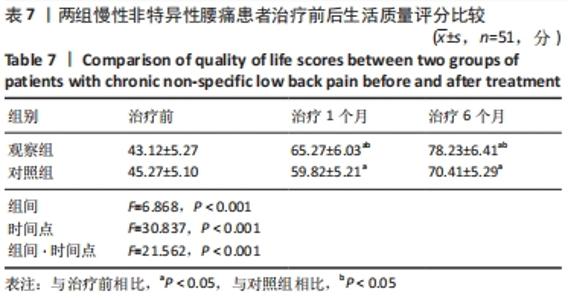
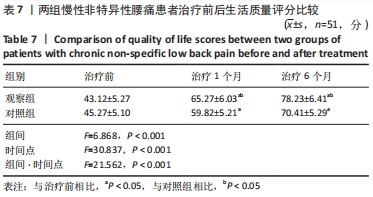
[1] COULOMBE BJ, GAMES KE, NEIL ER, et al. Core Stability Exercise Versus General Exercise for Chronic Low Back Pain. J Athl Train. 2017;52(1):71-72.
[2] 黄莉,黎敏婷,杨萃,等.深层肌肉刺激仪预防高强度抗阻训练后延迟性肌肉酸痛的疗效观察[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2020,26(4): 341-347.
[3] 赵娜.深层肌肉刺激仪(DMS)结合热敏灸与传统推拿在颈肩综合征治疗中的疗效对比[J].饮食保健,2018,5(50):115-116.
[4] 蒋黎明,张增乔,于小明,等.深层肌肉刺激治疗梨状肌综合征的临床研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(12):1439-1443.
[5] 中国康复医学会脊柱脊髓专业委员会专家组.中国急/慢性非特异性腰背痛诊疗专家共识[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(12):1134-1138.
[6] 吴宪宏,蒙倩倩,张钰,等.冠状动脉旁路移植术后镇痛效果的影响因素[J].中国医药,2019,14(5):682-685.
[7] 杨波,梁智林,唐杰,等.腰椎管狭窄症患者椎旁肌形态与其Oswestry功能障碍指数的相关性分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2020,41(2): 218-220.
[8] 周非非,张一龙,李舒扬,等.SF-36量表用于国人脊髓型颈椎病的信度分析及其与神经功能的相关性研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2020,30(3):256-262.
[9] WIELAND LS, SKOETZ N, PILKINGTON K, et al. Yoga treatment for chronic non-specific low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017; 1(1):CD010671.
[10] OLIVEIRA CB, MAHER CG, PINTO RZ, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-specific low back pain in primary care: an updated overview. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(11):2791-2803.
[11] 王欣,田秀娟,王金玲,等.悬吊运动训练治疗慢性非特异性腰痛的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(4):19-23.
[12] 陆斌,赵晨光,琚芬,等.肌内效贴联合深部肌肉刺激对非特异性颈痛的疗效[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(11):1349-1352.
[13] 韩雯.深层肌肉刺激仪在颈肩综合征的临床疗效探讨[J].颈腰痛杂志,2018,39(4):513-514.
[14] 张志杰,李亚鹏,冯亚男,等.深层振动刺激承山穴对健康人腓肠肌内外侧头及跟腱硬度的研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2019,34(11): 1365-1368.
[15] 郝又国,夏菁,陈缪存,等.体外发散式冲击波联合深部肌肉刺激治疗第三腰椎横突综合征的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2021,43(1):46-48.
[16] 杨光显,缪吉,梅强,等.深层肌肉刺激疗法对痉挛型双瘫患儿步态的影响[J].中国康复,2020,35(4):194-196.
[17] 田有粮,班东林,张昕,等.体外冲击波结合深层肌肉刺激治疗足底筋膜炎的临床研究[J].颈腰痛杂志,2019,40(5):595-597.
[18] 李进华,李洁,王国军,等.深层肌肉刺激治疗足底筋膜炎的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2018,40(11):858-859.
[19] 葛瑞东,白硕,郭京伟,等.局部肌肉振动对男性慢性非特异性腰痛患者腰背肌疲劳的即刻效应[J].中国康复医学杂志,2019,34(3): 287-292.
[20] 鲍赛荣,林利华,单莎瑞,等.电动深层肌肉刺激对脑卒中患者肱二头肌张力、弹性及硬度的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(20): 3138-3143.
[21] 刘红,侯美金,黄武杰,等.基于步态轮廓评分分析青年慢性非特异性腰痛患者的步态模式[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2020,42(3): 232-238.
[22] 任绪艳,杜艳艳,刘华.腰椎间盘突出症患者步态特征及相关机制研究进展[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2019,14(5):247-249.
[23] 宋沙沙,石润琇,林磊同,等.腰椎间盘突出症患者步态特征的研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(3):306-312.
[24] RUSSO M, DECKERS K, ELDABE S, et al. Muscle Control and Non-specific Chronic Low Back Pain. Neuromodulation. 2018;21(1):1-9.
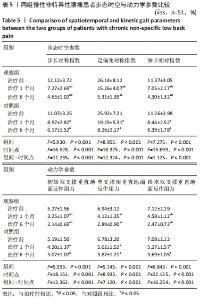
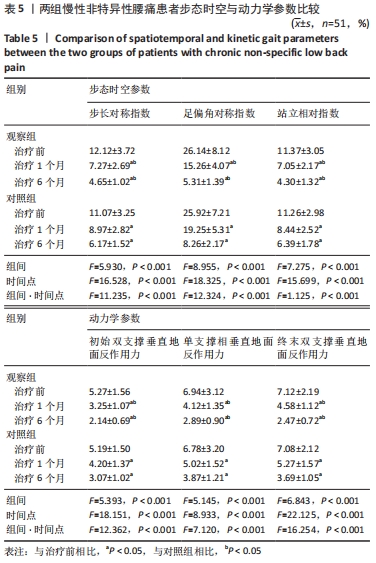
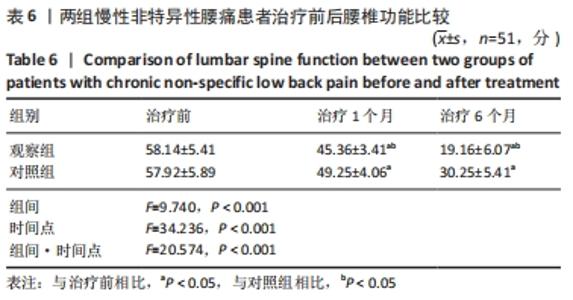
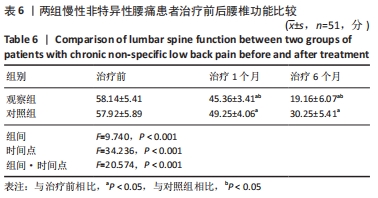
[25] 陈晓蓝,王琳,梁孝天,等.青年慢性非特异性腰痛患者步态:时空和动力学参数特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(4):556-561.
[26] 唐丽梅,邓陈英,黄辉,等.“长蛇灸”治疗寒湿型慢性非特异性腰痛及负性情绪的临床研究[J].针刺研究,2020,45(12):1014-1018, 1022.
[27] OWEN PJ, MILLER CT, MUNDELL NL, et al. Which specific modes of exercise training are most effective for treating low back pain? Network meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2020;54(21):1279-1287.
[28] 李万庭.悬吊训练联合深层肌肉刺激仪治疗非特异性下背痛的效果分析[J].常州实用医学,2019,35(2):77-80.
[29] 雷晓辉,武海英,董卓瑛,等.DMS联合多点多轴悬吊系统治疗慢性非特异性下背痛的临床疗效观察[J].中国社区医师,2019,35(33): 16-17.
[30] 张国永,闫冬,王凯,等.Mckenzie疗法配合重复周围磁刺激对慢性非特异性下腰痛患者腰椎功能及表面肌电特征的影响[J].颈腰痛杂志,2018,39(5):614-616.
[31] 方征宇,夏楠,吴祖源,等.腰椎稳定性训练结合肌内效贴治疗慢性非特异性腰背痛的临床疗效观察[J].中国康复,2018,33(6):479-481.
[32] AKBAR N, YAROSSI M, MARTINEZ-GOST M, et al. Mapping Motor Cortex Stimulation to Muscle Responses: A Deep Neural Network Modeling Approach. Int Conf Pervasive Technol Relat Assist Environ. 2020;9(15):3156-3159.
[33] 沈建成,王元利.腰背肌锻炼联合腹部收缩及仰卧卷腹锻炼治疗慢性非特异性下腰痛[J].颈腰痛杂志,2019,40(1):2.
[34] 伍磊鑫,李巍.腰伸肌力量训练对持续性慢性非特异性腰痛患者功能障碍和活动能力的影响[J].颈腰痛杂志,2021,42(2):285-286.
|