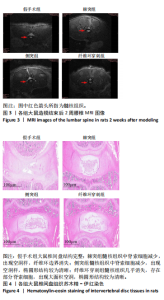
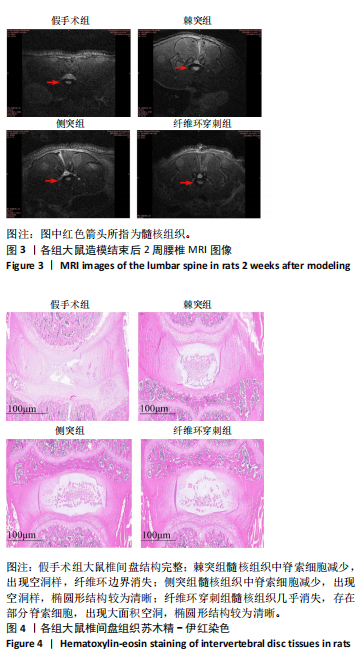
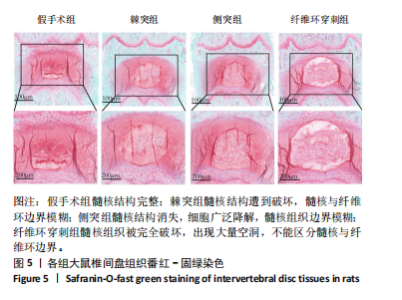
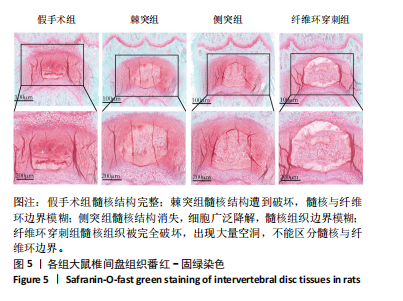
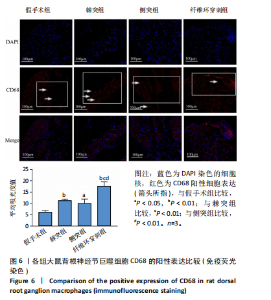
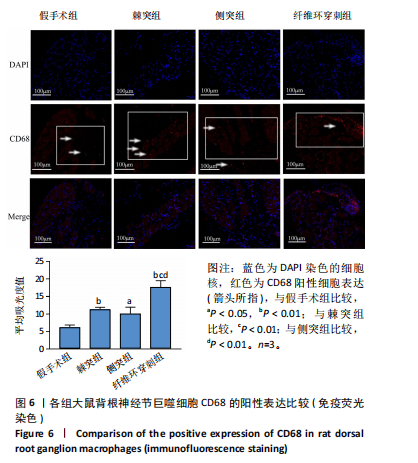
[1] ZHANG A S, XU A, ANSARI K, et al. Lumbar Disc Herniation: Diagnosis and Management. Am J Med. 2023;136(7):645-651.
[2] 中华医学会疼痛学分会脊柱源性疼痛学组. 腰椎间盘突出症诊疗中国疼痛专家共识[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2020,26(1):2-6.
[3] DELGADO-LÓPEZ PD, RODRÍGUEZ-SALAZAR A, MARTÍN-ALONSO J, et al. Hernia discal lumbar: historia natural, papel de la exploración, timing de la cirugía, opciones de tratamiento y conflicto de intereses. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2017;28(3):124-134.
[4] GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators.Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1204-1222.
[5] 杜瑞环, 张警, 李忠海. 腰椎间盘退变动物模型的研究进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(9):847-853.
[6] 张玮丽, 唐倩, 邓镇, 等. 葛根素通过抑制背根神经节Nav1.7上调治疗神经根性疼痛[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2023,29(5):332-339.
[7] 姚重界, 汤程, 黄瑞信, 等. 基于p38MAPK信号通路探讨推拿参与腰椎间盘突出症大鼠中枢镇痛的作用机制[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2023,38(7): 3348-3352.
[8] 乔松, 胡艳平, 何生华. 马钱子苷抑制CXCL12/CXCR4信号通路对腰椎间盘突出症大鼠疼痛反应的影响[J]. 天津医药,2023,51(10):1084-1089.
[9] 薛旭, 赵继荣, 陈祁青, 等. 基于VBM技术的杜仲腰痛丸干预腰椎间盘突出症慢性下肢痛模型大鼠的实验研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2020,31(12):1401-1407.
[10] 陈祁青, 马东, 赵继荣, 等. 基于网络药理学及动物实验的杜仲腰痛丸治疗腰椎间盘突出症慢性下肢痛的作用研究[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2023,25(5):1702-1713.
[11] XIE Z, CHEN J, XIAO Z, et al. TNFAIP3 alleviates pain in lumbar disc herniation rats by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(2):80.
[12] HUANG Y, ZHONG Z, YANG D, et al. Effects of swimming on pain and inflammatory factors in rats with lumbar disc herniation. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(4):2851-2858.
[13] KIM WK, SHIN J, LEE J, et al. Effects of the administration of Shinbaro 2 in a rat lumbar disk herniation model. Front Neurol. 2023;14:1044724.
[14] CAI L, HE Q, LU Y, et al.Comorbidity of Pain and Depression in a Lumbar Disc Herniation Model: Biochemical Alterations and the Effects of Fluoxetine.Front Neurol. 2019;10:1022.
[15] 吴高臣, 陈金鹏, 孟凡剑, 等. XIST对椎间盘退变大鼠髓核细胞增殖及细胞外基质合成的影响及机制[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2024,49(7):823-831.
[16] 张强, 刘萍, 秦飞, 等. 香叶木素通过抑制髓核细胞凋亡和炎症反应缓解椎间盘退变大鼠神经根性疼痛[J]. 免疫学杂志,2020,36(12):1046-1052.
[17] 刘宜军, 王静丽, 杨勇. 针灸联合柚皮素干预对腰椎间盘退变大鼠髓核NLRP3炎性小体的影响[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2023,25(3): 1061-1068.
[18] 陆志东, 金群华, 陈志荣. 大鼠非压迫性髓核突出模型的建立[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(19):1361-1363.
[19] Kim H, Hong JY, Lee J, et al. IL-1b promotes disc degeneration and inflammation through direct injection of intervertebral disc in a rat lumbar disc herniation model. Spine J. 2021;21(6):1031-1041.
[20] SHAMJI MF, ALLEN KD, RICHARDSON WJ, et al. Gait Abnormalities and Inflammatory Cytokines in an Autologous Nucleus Pulposus Model of Radiculopathy. Spine. 2009;34(7):648-654.
[21] ZHENG HD, SUN YL, KONG DW, et al. Deep learning-based high-accuracy quantitation for lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration from MRI. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):841.
[22] 张擎天,黄泽灵,陈华,等. 枳壳甘草汤调控炎性小体改善腰椎间盘突出症痛敏的实验研究 [J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2024,32(1):13-19.
[23] 王丹, 周静超, 宗景景, 等.动物试验中麻醉药物的选择应用研究进展[J].畜牧与兽医,2021,53(3):134-137.
[24] 李晓惠,李涛,黄韩榕,等. 基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路探讨按压手法延缓大鼠椎间盘软骨终板退变的机制研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2022, 40 (12):158-162+302.
[25] Djuric N, Lafeber GCM, Li W, et al.Exploring macrophage differentiation and its relation to Modic changes in human herniated disc tissue. Brain Spine. 2022;2:101698.
[26] Zhu L, Yu C, Zhang X, et al. The treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration using Traditional Chinese Medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;263:113117.
[27] 唐铭. 腰椎后方韧带复合体切除站立小鼠椎间盘退变模型的构建[D]. 衡阳:南华大学,2022.
[28] Cosamalon-Gan I, Cosamalon-Gan T, Mattos-Piaggio G, et al. Inflammation in the intervertebral disc herniation.Neurocirugia (Astur : Engl Ed). 2021;32(1):21-35.
[29] 陈祁青, 赵继荣, 蔡毅, 等. 基于静息态功能磁共振形态学腰椎间盘突出症慢性下肢痛模型大鼠的实验研究[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志,2022, 39(4):430-435.
[30] 赵继荣, 张天龙, 陈祁青, 等. 杜仲腰痛丸对腰椎间盘突出症慢性下肢痛大鼠海马BDNF-TrkB-CREB信号通路的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2022,37(10):6018-6025.
[31] Ozden M, Silav ZK. Correlations of Disc Tissue Pathological Changes With Pfirrmann Grade in Patients With Disc Herniation Treated With Microdiscectomy. Cureus. 2023;15(4):e37913.
[32] 王靖, 唐天驷, 姚啸生, 等. 纤维环穿刺诱导椎间盘退变动物模型的实验研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(4):284-287.
[33] 夏炳江, 张磊, 胡松峰, 等. 纤维环穿刺结合TNF-α注射构建大鼠尾椎间盘退变模型的实验研究[J]. 中国中医急症,2017,26(7):1167-1171.
[34] 韩忠晓, 欧雅滢, 庄薪晴, 等. 机械穿刺结合肿瘤坏死因子α及完全弗氏佐剂构建大鼠椎间盘源性腰痛模型[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(11):1672-1677. |