Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (19): 4011-4021.doi: 10.12307/2025.064
Previous Articles Next Articles
Panax notoginseng saponins regulate differential miRNA expression in osteoclast exosomes and inhibit ferroptosis in osteoblasts
Tao Hongcheng1, Zeng Ping2, 3, Liu Jinfu2, Tian Zhao1, Ding Qiang1, Li Chaohui1, Wei Jianjie1, Li Hao1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Guangxi Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Foundation Research, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-12-29Accepted:2024-04-18Online:2025-07-08Published:2024-09-12 -
Contact:Zeng Ping, MD, Chief physician, Professor, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Guangxi Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Foundation Research, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Co-corresponding author: Liu Jinfu, Master, Lecturer, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Tao Hongcheng, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82160913, 81960876 (to ZP); Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region PhD Innovation Project, No. YCBZ2022125 (to TZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tao Hongcheng, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Tian Zhao, Ding Qiang, Li Chaohui, Wei Jianjie, Li Hao. Panax notoginseng saponins regulate differential miRNA expression in osteoclast exosomes and inhibit ferroptosis in osteoblasts[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(19): 4011-4021.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
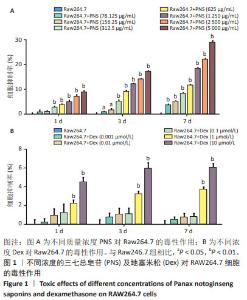
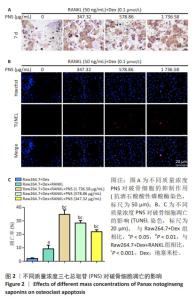
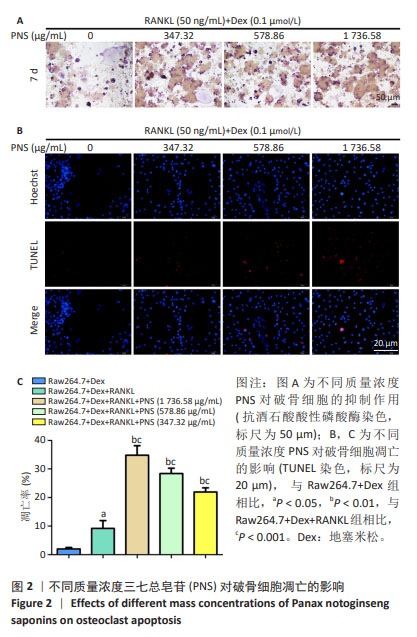
2.1 地塞米松和三七总皂苷对RAW264.7细胞系的细胞毒性 通过MTT法检测三七总皂苷和地塞米松对RAW264.7细胞的毒性。结果表明,当RAW264.7细胞孵育1 d时,0-156.25 μg/mL范围内的三七总皂苷对RAW264.7细胞增殖没有显著影响;在孵育3,7 d时,312.5-5 000 μg/mL范围内的三七总皂苷对RAW264.7细胞增殖都具有抑制作用,见图1A;在孵育7 d时,三七总皂苷的IC20值为 1 736.58 μg/mL,所以选择该质量浓度进行后续研究。1,10 μmol/L地塞米松在1,3,7 d对RAW264.7细胞增殖具有显著的抑制作用,而0.001-0.1 μmol/L范围的地塞米松对RAW264.7细胞的生长没有抑制作用,见图1B,故选择地塞米松的最大浓度为0.1 μmol/L进行后续实验。"
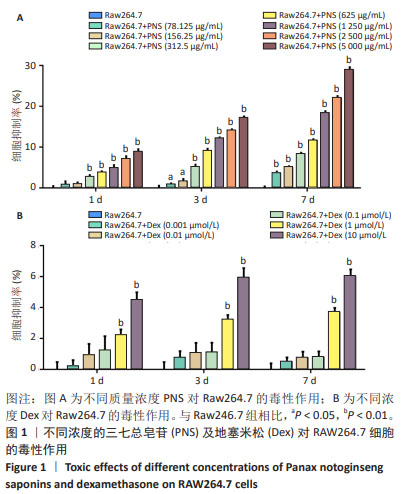

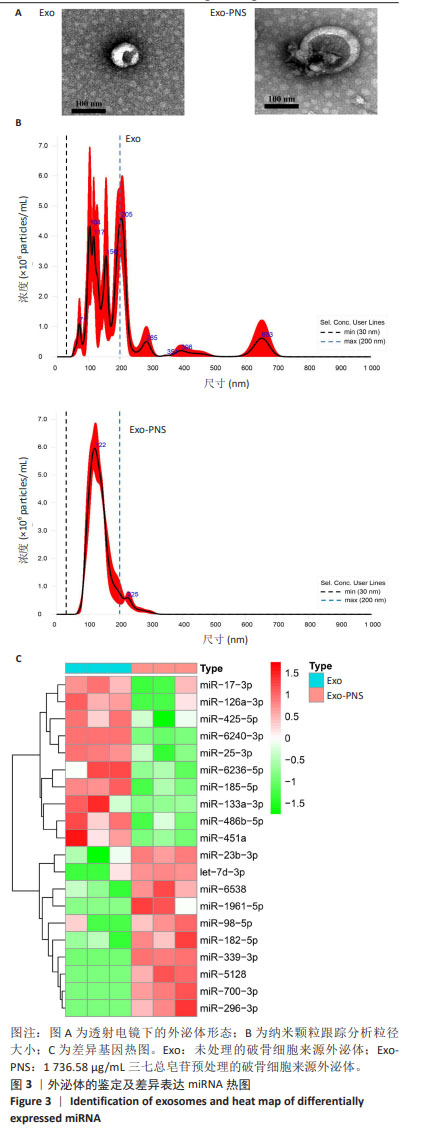
2.3 破骨细胞来源外泌体的特征和差异表达miRNA的鉴定 从1 736.58 μg/mL三七总皂苷预处理的破骨细胞和未处理的破骨细胞中提取外泌体后,在透射电镜下可以观察到典型的囊泡样外泌体,见图3A。纳米颗粒跟踪分析显示,外泌体直径在30-200 nm范围内,见图3B,与先前研究中报道的外泌体大小一致[15]。为了确定三七总皂苷对破骨细胞外泌体中miRNA表达的影响,对提取的外泌体进行miRNA测序。测序完成后,使用“limma”包最终筛选出20个差异表达miRNA[P < 0.05,|log2FC(倍数变化)|≥1]。与未处理的破骨细胞外泌体相比,三七总皂苷诱导的破骨细胞外泌体中存在10个上调的差异表达miRNA和10个下调的差异表达miRNA,见图3C。在这些差异表达miRNA中,有4个上调的差异表达miRNA(miR-23b-3p、miR-98-5p、miR-182-5p、miR-296-3p)和7个下调的差异表达miRNA(miR-17-3p、miR-25-3p、miR-126a-3p、miR-133a-3p,miR-185-5p、miR-425-5p、miR-451a)已被证明影响成骨细胞的功能。因此,三七总皂苷可能通过调节破骨细胞衍生外泌体中这些差异表达miRNA的表达来促进成骨细胞分化。 "
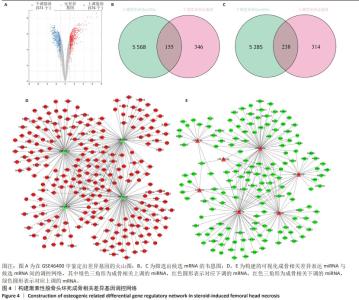
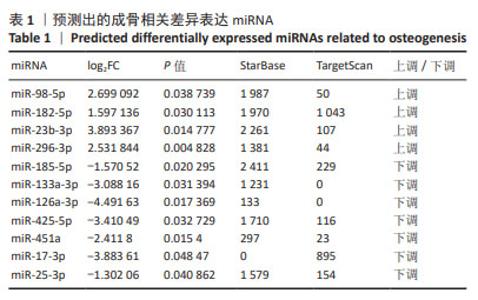
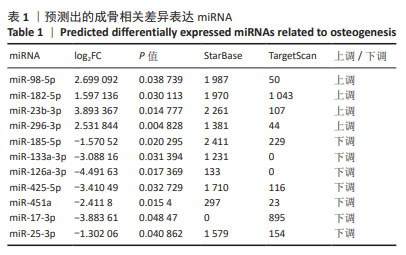
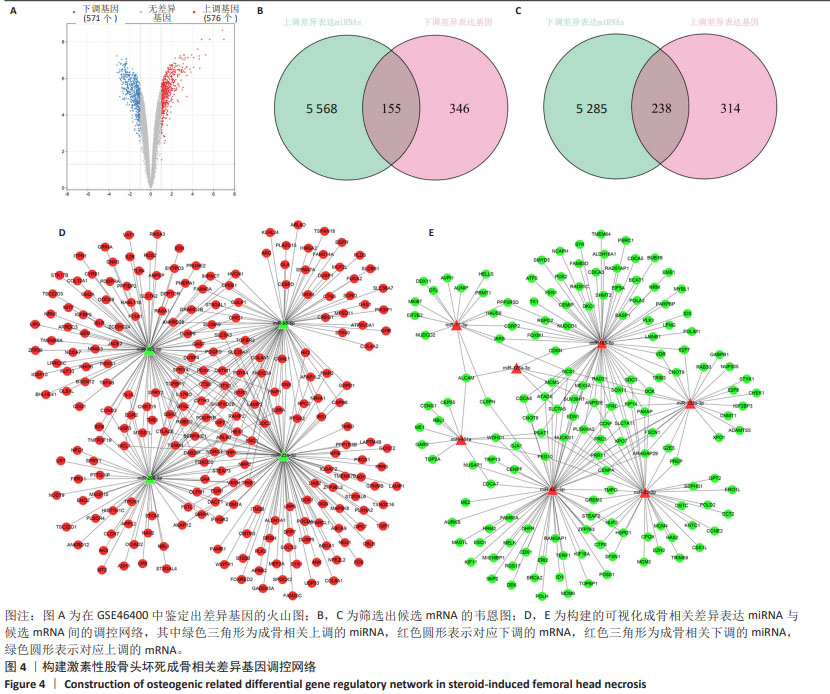
2.4 候选mRNA的鉴定 在GSE46400中,共鉴定出1 147个差异表达基因(P < 0.05和|log2FC|≥1),其中576个上调差异表达基因和571个下调相关差异表达基因,见图4A。通过StarBase和TargetScan在8 048个靶标mRNA(去除相同基因) 预测出11种成骨相关的差异表达miRNA,见表1。Venn图显示,已经鉴定了400个候选mRNA(4个上调的差异表达miRNA对应于155个下调的候选mRNA,7个下调的差异表达miRNA对应于238个上调的候选mRNA)用于进一步分析,见图4B,C。此外,通过CytoScape 3.9.1构建并可视化了“差异表达miRNA-候选mRNA网络”,见图4D,E。"
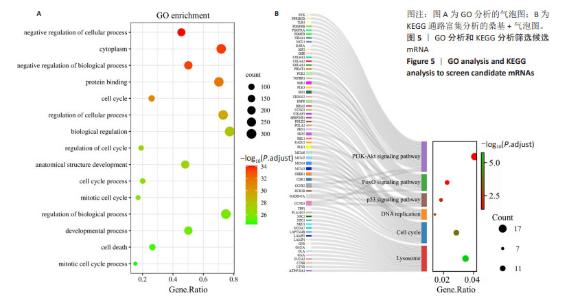
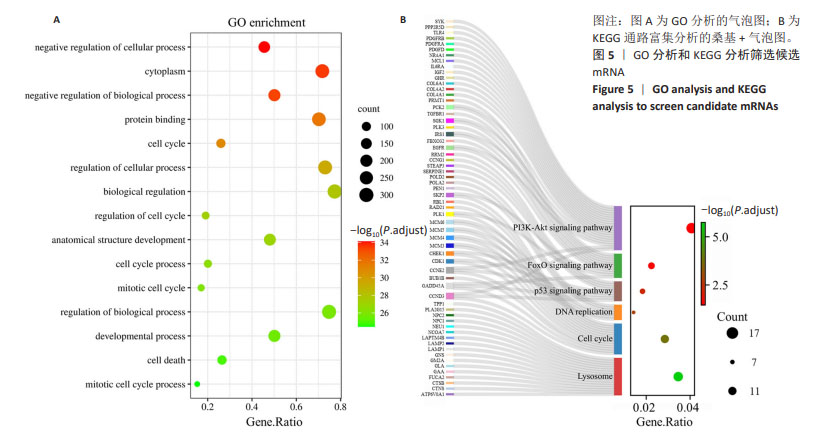
2.5 通过GO分析和KEGG分析筛选候选mRNA 对候选差异表达基因进行GO功能富集分析和KEGG通路富集分析,以进一步探索成骨相关差异表达miRNA的功能,见图5A,B。结果表明,在生物过程(biological process,BP)类别中,候选差异表达基因主要富集于细胞周期、细胞分裂、细胞增殖的正调控、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ启动子转录的负调控和有丝分裂细胞周期。细胞组分(cellular component,CC)分析表明,候选差异表达基因在细胞质、核质、细胞核、溶酶体、染色体和着丝粒区均显著富集。对于分子功能(molecular function,MF),候选差异表达基因与蛋白质结合、ATP结合、核苷酸结合、蛋白激酶结合、单链DNA依赖性ATP依赖性DNA解旋酶活性有关。KEGG通路富集分析表明,候选差异表达基因主要富集在与铁死亡相关的PI3K-Akt信号通路、p53信号通路中[16-17]。以上分析结果表明,成骨相关的差异表达miRNA可能影响成骨细胞铁死亡的过程。"
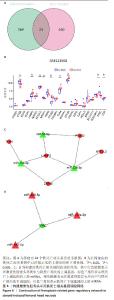
2.6 铁死亡相关基因的筛选与验证 从Ferrdb V2数据库[18]以及候选mRNA中收集了包括“铁死亡驱动因子”“铁死亡标记物”和“铁死亡抑制因子”在内的484个铁死亡相关基因,以进一步探究破骨细胞来源外泌体对成骨细胞铁死亡的影响。Venn图揭示了24个相交的铁死亡相关基因,见图6A,其中TFRC在激素性股骨头坏死中下调,PTGS2、NFE2L2、LAMP2、TLR4和ZFP36在激素性股骨头坏死中上调,与成骨细胞中各基因的表达趋势一致,见图6B。最终,构建了12个网络( miR-98-5p/PTGS2,miR-23b-3p/PTGS2,miR-425-5p/TFRC,miR-133a-3p/TFRC,miR-185-5p/TFRC,miR-23b-3p/NFE2L2,miR-23b-3p/LAMP2,miR-98-5p/LAMP2,miR-182-5p/LAMP2,miR-182-5p/TLR4,miR-23b-3p/ZFP36,miR-182-5p/ZFP36)并通过cytoscape进行可视化,见图6C,D,这些网络可能与三七总皂苷调控破骨细胞外泌体来源miRNA的表达来调节成骨细胞铁死亡有关。"

| [1] XU H, WANG C, LIU C, et al. Cotransplantation of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells for treating steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10(5): 781-796. [2] HUANG C, WEN Z, NIU J, et al. Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Novel Insight Into the Roles of Bone Endothelial Cells in Pathogenesis and Treatment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:777697. [3] CHANG C, GREENSPAN A, GERSHWIN ME. The pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical manifestations of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102460. [4] KIM HJ, ZHAO H, KITAURA H, et al. Glucocorticoids suppress bone formation via the osteoclast. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(8):2152-2160. [5] WANG F, MIN HS, SHAN H, et al. IL-34 Aggravates Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head via Promoting Osteoclast Differentiation. Immune Netw. 2022;22(3):e25. [6] YUE C, JIN H, ZHANG X, et al. Aucubin prevents steroid-induced osteoblast apoptosis by enhancing autophagy via AMPK activation. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(21):10175-10184. [7] YANG JX, XIE P, LI YS, et al. Osteoclast-derived miR-23a-5p-containing exosomes inhibit osteogenic differentiation by regulating Runx2. Cell Signal. 2020;70:109504. [8] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(4):266-282. [9] 梁学振,骆帝,李嘉程,等.激素性股骨头坏死中的PTGS2和STAT3:潜在铁死亡相关诊断生物标志物[J].中国组织工程研究, 2023,27(36):5898-5904. [10] 章家皓,刘予豪,周驰,等.氧化应激促进成骨细胞铁死亡介导激素性股骨头坏死的病理过程[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(20): 3202-3208. [11] 国家中医心血管病临床医学研究中心,中国医师协会中西医结合医师分会,中国中西医结合学会活血化瘀专业委员会,等.三七总皂苷制剂临床应用中国专家共识[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2021, 41(10):1157-1167. [12] 韩杰,陈跃平,莫坚,等.三七总皂苷干预激素性股骨头缺血坏死模型兔的超微结构评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(7): 1035-1039. [13] 方姝晨,邹季,史政康,等.三七总皂苷对股骨头坏死大鼠股骨头成骨作用影响的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(6): 6-9,15. [14] CHEN H, BOUTROS PC. VennDiagram: a package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:35. [15] PEGTEL DM, GOULD SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88: 487-514. [16] YI J, ZHU J, WU J, et al. Oncogenic activation of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling suppresses ferroptosis via SREBP-mediated lipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(49):31189-31197. [17] LI S, LEI Z, YANG X, et al. Propofol Protects Myocardium From Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Ferroptosis Through the AKT/p53 Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:841410. [18] ZHOU N, YUAN X, DU Q, et al. FerrDb V2: update of the manually curated database of ferroptosis regulators and ferroptosis-disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D571-D582. [19] NOONIN C, THONGBOONKERD V. Exosome-inflammasome crosstalk and their roles in inflammatory responses. Theranostics. 2021;11(9): 4436-4451. [20] IRIE N, TAKADA Y, WATANABE Y, et al. Bidirectional signaling through ephrinA2-EphA2 enhances osteoclastogenesis and suppresses osteoblastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(21):14637-14644. [21] SUN W, ZHAO C, LI Y, et al. Osteoclast-derived microRNA-containing exosomes selectively inhibit osteoblast activity. Cell Discov. 2016;2: 16015. [22] SUN F, ZHOU JL, LIU ZL, et al. Dexamethasone induces ferroptosis via P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;602: 149-155. [23] FANG L, ZHANG G, WU Y, et al. SIRT6 Prevents Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:6360133. [24] ZHANG J, GUO F, ZHOU R, et al. Proteomics and transcriptome reveal the key transcription factors mediating the protection of Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine. 2021;92:153613. [25] HU H, CHEN Y, ZOU Z, et al. Panax Notoginseng Saponins Prevent Bone Loss by Promoting Angiogenesis in an Osteoporotic Mouse Model. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:8412468. [26] FAN JZ, WANG Y, MENG Y, et al. Panax notoginseng saponins mitigate ovariectomy-induced bone loss and inhibit marrow adiposity in rats. Menopause. 2015;22(12):1343-1350. [27] QIANG H, LIU H, LING M, et al. Early Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of Rabbit Femoral Head and Panax notoginseng Saponins: Mechanism and Protective Effects. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015; 2015:719370. [28] LI R, RUAN Q, YIN F, et al. MiR-23b-3p promotes postmenopausal osteoporosis by targeting MRC2 and regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 2021;145(1):69-78. [29] ZHENG F, WANG F, XU Z. MicroRNA-98-5p prevents bone regeneration by targeting high mobility group AT-Hook 2. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(4): 2660-2666. [30] ZHENG F, ZHANG F, WANG F. Inhibition of miR-98-5p promotes high glucose-induced suppression of preosteoblast proliferation and differentiation via the activation of the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway by targeting BMP2. Mol Med Rep. 2022;26(3):292. [31] CHEN G, HUANG G, LIN H, et al. MicroRNA-425-5p modulates osteoporosis by targeting annexin A2. Immun Ageing. 2021;18(1):45. [32] WANG Y, MA J, QIU W, et al. Guanidinoacetic Acid Regulates Myogenic Differentiation and Muscle Growth Through miR-133a-3p and miR-1a-3p Co-mediated Akt/mTOR/S6K Signaling Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(9):2837. [33] LV H, SUN Y, ZHANG Y. MiR-133 is Involved in Estrogen Deficiency-Induced Osteoporosis through Modulating Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Med Sci Monit. 2015; 21:1527-1534. [34] WANG Q, LI Y, ZHANG Y, et al. LncRNA MEG3 inhibited osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from postmenopausal osteoporosis by targeting miR-133a-3p. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:1178-1186. [35] WU Y, JIANG Y, LIU Q, et al. lncRNA H19 promotes matrix mineralization through up-regulating IGF1 by sponging miR-185-5p in osteoblasts. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(1):48. [36] ZHANG J, XU N, YU C, et al. LncRNA PART1/miR-185-5p/RUNX3 feedback loop modulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Autoimmunity. 2021;54(7): 422-429. [37] PAN BL, TONG ZW, LI SD, et al. Decreased microRNA-182-5p helps alendronate promote osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in osteoporosis via the Rap1/MAPK pathway. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(6): BSR20180696. [38] HU Z, YIN Y, JIANG J, et al. Exosomal miR-142-3p secreted by hepatitis B virus (HBV)-hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells promotes ferroptosis of M1-type macrophages through SLC3A2 and the mechanism of HCC progression. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022;13(2):754-767. [39] YANG WS, SRIRAMARATNAM R, WELSCH ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156(1-2):317-331. [40] YI L, HU Y, WU Z, et al. TFRC upregulation promotes ferroptosis in CVB3 infection via nucleus recruitment of Sp1. Cell Death Dis. 2022; 13(7):592. [41] GAO T, LIN M, WU Y, et al. Transferrin receptor (TFRC) is essential for meiotic progression during mouse spermatogenesis. Zygote. 2021; 29(2):169-175. [42] SUN H, QIAN X, YANG W, et al. Novel prognostic signature based on HRAS, MAPK3 and TFRC identified to be associated with ferroptosis and the immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(10):6924-6940. [43] 王宁,康华丽,薛金慧,等.铁死亡相关基因TFRC在胃癌组织中的表达及其与化疗药物敏感性的关系[J].现代肿瘤医学,2023, 31(22):4183-4189. [44] CHEN X, KANG R, KROEMER G, et al. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18(5):280-296. [45] WANG K, LI Z, XUAN Y, et al. Pan-cancer analysis of NFE2L2 mutations identifies a subset of lung cancers with distinct genomic and improved immunotherapy outcomes. Cancer Cell Int. 2023;23(1):229. [46] AROLT C, DUGAN M, WILD R, et al. KEAP1/NFE2L2 Pathway Signature Outperforms KEAP1/NFE2L2 Mutation Status and Reveals Alternative Pathway-Activating Mutations in NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2023;18(11):1550-1567. [47] GÓMEZ-GARCÍA EF, CORTÉS-SANABRIA L, CUETO-MANZANO AM, et al. Association of Variants of the NFE2L2 Gene with Metabolic and Kidney Function Parameters in Patients with Diabetes and/or Hypertension. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2022;26(7-8): 382-390. [48] SUN C, ZHANG N, HU Q, et al. Ferroptosis-Related Prognostic Gene LAMP2 Is a Potential Biomarker Differential Expressed in Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Dis Markers. 2023;2023:8295113. [49] BARNDT RJ, LIU Q, TANG Y, et al. Metabolic Maturation Exaggerates Abnormal Calcium Handling in a Lamp2 Knockout Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocyte Model of Danon Disease. Biomolecules. 2022;13(1):69. [50] SHALATA A, BAR-SHAI M, HADID Y, et al. Danon Disease: Entire LAMP2 Gene Deletion with Unusual Clinical Presentation-Case Report and Review of the Literature. Genes (Basel). 2023;14(8): 1539. [51] LIU SP, LI XM, LIU DM, et al. LAMP2 as a Biomarker Related to Prognosis and Immune Infiltration in Esophageal Cancer and Other Cancers: A Comprehensive Pan-Cancer Analysis. Front Oncol. 2022; 12:884448. [52] XING R, LIU D, CHENG X, et al. MiR-207 inhibits autophagy and promotes apoptosis of cardiomyocytes by directly targeting LAMP2 in type 2 diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;520(1):27-34. [53] FU D, WANG S, LUO Y, et al. Identification of a novel splicing-altering LAMP2 variant in a Chinese family with Danon disease. ESC Heart Fail. 2023;10(4):2479-2486. [54] FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, KRYSKO DV, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis at the crossroads of cancer-acquired drug resistance and immune evasion. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019;19(7):405-414. [55] FENG R, XIONG Y, LEI Y, et al. Lysine-specific demethylase 1 aggravated oxidative stress and ferroptosis induced by renal ischemia and reperfusion injury through activation of TLR4/NOX4 pathway in mice. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(15):4254-4267. [56] ZANFI ED, FANTINI S, LOTTI R, et al. Wnt/CTNNB1 Signal Transduction Pathway Inhibits the Expression of ZFP36 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma, by Inducing Transcriptional Repressors SNAI1, SLUG and TWIST. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5692. [57] CHEN W, CHEN M, ZHAO Z, et al. ZFP36 Binds With PRC1 to Inhibit Tumor Growth and Increase 5-Fu Chemosensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7:126. [58] LYU F, LI Y, YAN Z, et al. Identification of ISG15 and ZFP36 as novel hypoxia- and immune-related gene signatures contributing to a new perspective for the treatment of prostate cancer by bioinformatics and experimental verification. J Transl Med. 2022; 20(1):202. [59] ZHANG Z, GUO M, LI Y, et al. RNA-binding protein ZFP36/TTP protects against ferroptosis by regulating autophagy signaling pathway in hepatic stellate cells. Autophagy. 2020;16(8):1482-1505. |
| [1] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [2] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [3] | Wang Wentao, Hou Zhenyang, Wang Yijun, Xu Yaozeng. Apelin-13 alleviates systemic inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [4] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [5] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [6] | Zhao Nannan, Li Yanjie, Qin Hewei, Zhu Bochao, Ding Huimin, Xu Zhenhua. Changes in ferroptosis in hippocampal neurons of vascular dementia model rats treated with Tongmai Kaiqiao Pill [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1401-1407. |
| [7] | Zhang Mingyang, Yang Xinling. Verbascoside inhibits Erastin-induced ferroptosis of dopaminergic nerve cell line MN9D cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1408-1413. |
| [8] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [9] | Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530. |
| [10] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [11] | Gao Yang, Qin Hewei, Liu Dandan. ACSL4 mediates ferroptosis and its potential role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| [12] | Xiao Fang, Huang Lei, Wang Lin. Magnetic nanomaterials and magnetic field effects accelerate bone injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 827-838. |
| [13] | Ma Weibang, Xu Zhe, Yu Qiao, Ouyang Dong, Zhang Ruguo, Luo Wei, Xie Yangjiang, Liu Chen. Screening and cytological validation of cartilage degeneration-related genes in exosomes from osteoarthritis synovial fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7783-7789. |
| [14] | Guo Jia, Ren Yafeng, Li Bing, Huang Jing, Shang Wenya, Yang Yike, Liu Huiyao. Action mechanism of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miRNAs in improving spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7827-7838. |
| [15] | Zhou Yang, Liu Kexin, Wang Deli, Sun Zhang. Regenerative effects of engineered extracellular vesicles on repairing bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7839-7847. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||