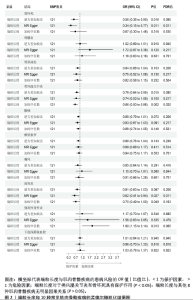
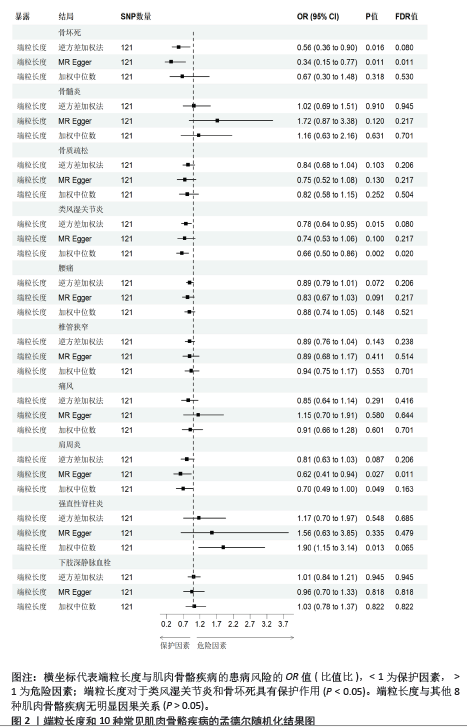
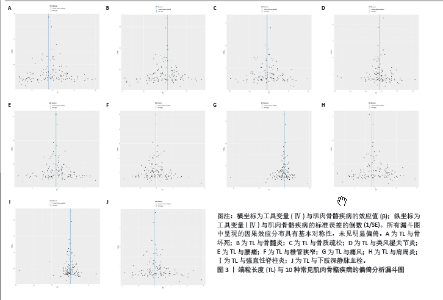
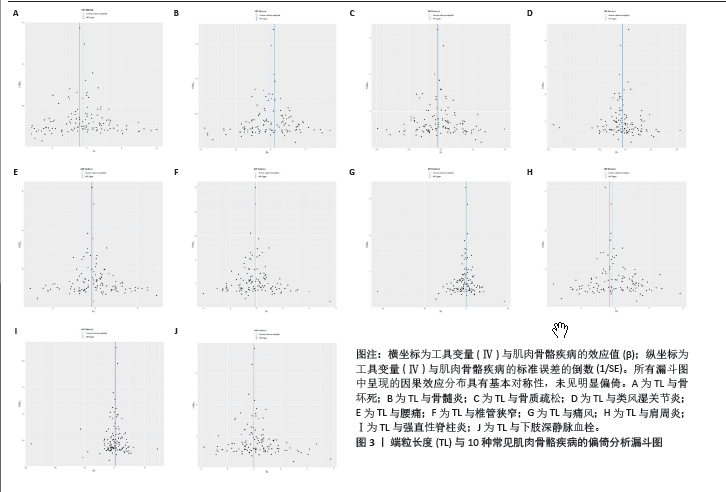
[1] MADAN I, GRIME PR. The management of musculoskeletal disorders in the workplace. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2015;29(3):345-355.
[2] SAFIRI S, KOLAHI AA, CROSS M, et al. Prevalence, deaths, and disability-adjusted life years due to musculoskeletal disorders for 195 countries and territories 1990-2017. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73(4):702-714.
[3] LOPEZ-OTIN C, BLASCO MA, PARTRIDGE L, et al. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013; 153(6):1194-1217.
[4] HAYCOCK PC, HEYDON EE, KAPTOGE S, et al. Leucocyte telomere length and risk of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2014;349:g4227.
[5] ZHAO J, MIAO K, WANG H, et al. Association between telomere length and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013; 8(11):e79993.
[6] RODE L, NORDESTGAARD BG, BOJESEN SE. Peripheral blood leukocyte telomere length and mortality among 64, 637 individuals from the general population. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107(6):djv074.
[7] NIELSEN BR, LINNEBERG A, BENDIX L, et al. Association between leukocyte telomere length and bone mineral density in women 25-93 years of age. Exp Gerontol. 2015;66: 25-31.
[8] TAO L, HUANG Q, YANG R, et al. The age modification to leukocyte telomere length effect on bone mineral density and osteoporosis among Chinese elderly women. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(6): 1004-1012.
[9] HARBO M, DELAISSE JM, KJAERSGAARD-ANDERSEN P, et al. The relationship between ultra-short telomeres, aging of articular cartilage and the development of human hip osteoarthritis. Mech Ageing Dev. 2013;134(9):367-372.
[10] BAYLIS D, NTANI G, EDWARDS MH, et al. Inflammation, telomere length, and grip strength: a 10-year longitudinal study. Calcif Tissue Int. 2014;95(1):54-63.
[11] SEKULA P, DEL GRECO MF, PATTARO C, et al. Mendelian randomization as an approach to assess causality using observational data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(11):3253-3265.
[12] GREEN HD, JONES A, EVANS JP, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies 5 loci associated with frozen shoulder and implicates diabetes as a causal risk factor. PLoS Genet. 2021;17(6):e1009577.
[13] LOH PR, KICHAEV G, GAZAL S, et al. Mixed-model association for biobank-scale datasets. Nat Genet. 2018;50(7):906-908.
[14] GIBSON MJ, SPIGA F, CAMPBELL A, et al. Reporting and methodological quality of studies that use Mendelian randomisation in UK Biobank: a meta-epidemiological study. BMJ Evid Based Med. 2023;28(2):103-110.
[15] CODD V, DENNIFF M, SWINFIELD C, et al. Measurement and initial characterization of leukocyte telomere length in 474, 074 participants in UK Biobank. Nat Aging. 2022;2(2):170-179.
[16] SHIM H, CHASMAN DI, SMITH JD, et al. A multivariate genome-wide association analysis of 10 LDL subfractions, and their response to statin treatment, in 1868 Caucasians. PLoS One. 2015;10(4): e0120758.
[17] BORENSTEIN M, HEDGES LV, HIGGINS JP, et al. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. 2010;1(2):97-111.
[18] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C, et al. Improving the accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: moving beyond the NOME assumption. Int J Epidemiol. 2019;48(3):728-742.
[19] HARTWIG FP, DAVEY SMITH G, BOWDEN J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46(6):1985-1998.
[20] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525.
[21] HEMANI G, ZHENG J, ELSWORTH B, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife. 2018;7:e34408.
[22] COLMEGNA I, DIAZ-BORJON A, FUJII H, et al. Defective proliferative capacity and accelerated telomeric loss of hematopoietic progenitor cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(4):990-1000.
[23] TAMAYO M, MOSQUERA A, REGO JI, et al. Differing patterns of peripheral blood leukocyte telomere length in rheumatologic diseases. Mutat Res. 2010;683(1-2):68-73.
[24] GAMAL RM, HAMMAM N, ZAKARY MM, et al. Telomere dysfunction-related serological markers and oxidative stress markers in rheumatoid arthritis patients: correlation with diseases activity. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(12):3239-3246.
[25] LEE YH, BAE SC. Association between shortened telomere length and rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Z Rheumatol. 2018;77(2):160-167.
[26] ZENG Z, ZHANG W, QIAN Y, et al. Association of telomere length with risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(5):940-947.
[27] WAGNER CL, HANUMANTHU VS, TALBOT CC JR., et al. Short telomere syndromes cause a primary T cell immunodeficiency. J Clin Invest. 2018;128(12):5222-5234.
[28] RODIER F, COPPE JP, PATIL CK, et al. Persistent DNA damage signalling triggers senescence-associated inflammatory cytokine secretion. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(8): 973-979.
[29] YADAV S, MAURYA PK. Correlation between telomere length and biomarkers of oxidative stress in human aging. Rejuvenation Res. 2022;25(1):25-29.
[30] LEE SW, LIM KH, LEE KJ, et al. No association between telomere length and osteonecrosis of the femoral head. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):176.
[31] DJORDJEVIC K, MILOJEVIC SAMANOVIC A, VESELINOVIC M, et al. Oxidative stress mediated therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(11):1938.
[32] POONPET T, SAETAN N, TANAVALEE A, et al. Association between leukocyte telomere length and angiogenic cytokines in knee osteoarthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21(1):118-125.
[33] WANG H, CHEN Q, LEE SH, et al. Impairment of osteoblast differentiation due to proliferation-independent telomere dysfunction in mouse models of accelerated aging. Aging Cell. 2012;11(4):704-713.
[34] WILLEIT P, WILLEIT J, BRANDSTATTER A, et al. Cellular aging reflected by leukocyte telomere length predicts advanced atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease risk. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010; 30(8):1649-1656.
[35] SANDERS JL, CAULEY JA, BOUDREAU RM, et al. Leukocyte telomere length is not associated with BMD, osteoporosis, or fracture in older adults: results from the health, aging and body composition study. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(9):1531-1536.
[36] DENG S, LIU S, XU S, et al. Shorter telomere length in peripheral blood leukocytes is associated with post-traumatic chronic osteomyelitis. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2020;21(9):773-777.
[37] LE MAITRE CL, FREEMONT AJ, HOYLAND JA. Accelerated cellular senescence in degenerate intervertebral discs: a possible role in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(3):R45.
[38] DECHSUPA S, YINGSAKMONGKOL W, LIMTHONGKUL W, et al. Relative telomere length and oxidative DNA damage in hypertrophic ligamentum flavum of lumbar spinal stenosis. PeerJ. 2018;6:e5381.
[39] KALSON NS, BROCK TM, MANGINO M, et al. Reduced telomere length is associated with fibrotic joint disease suggesting that impaired telomere repair contributes to joint fibrosis. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0190120.
[40] VAZIRPANAH N, KIENHORST LBE, VAN LOCHEM E, et al. Patients with gout have short telomeres compared with healthy participants: association of telomere length with flare frequency and cardiovascular disease in gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76(7):1313-1319.
[41] QI M, YU J, PING F, et al. Leukocyte telomere length independently predicts hyperuricemia risk in a longitudinal study of the Chinese population. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2024;34(1):230-234.
[42] TAMAYO M, PERTEGA S, MOSQUERA A, et al. Individual telomere length decay in patients with spondyloarthritis. Mutat Res. 2014;765:1-5. |