Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (4): 872-880.doi: 10.12307/2025.225
Posterior cruciate ligament tibial attachment point avulsion fracture: materials, implants, and internal fixation techniques in arthroscopic treatment
Yu Ming1, Wang Wen1, 2
- 1Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital Affiliated to Jinan University, Guangzhou 510220, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-11-29Accepted:2024-01-20Online:2025-02-08Published:2024-06-04 -
Contact:Yu Ming, Master candidate, Physician, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Wang Wen, MD, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital Affiliated to Jinan University, Guangzhou 510220, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Clinical Characteristic Technology in Guangzhou (2023-2025), No. 2023C-TS11 (to WW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Ming, Wang Wen. Posterior cruciate ligament tibial attachment point avulsion fracture: materials, implants, and internal fixation techniques in arthroscopic treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 872-880.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
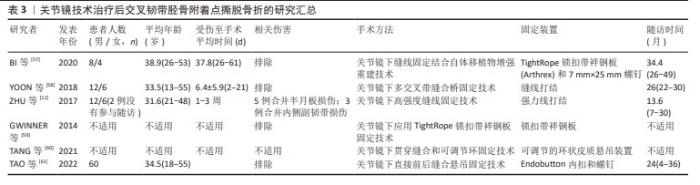
2.1 关节镜手术方法和技术 关节镜不仅仅是一种辅助检查手段,还是关节外科及运动医学领域的常用治疗手段[51]。关节镜手术已成为不可或缺的日常手术,其演变经历了漫长历史过程,经历了体腔窥镜应用阶段、膀胱镜阶段及关节镜阶段[51]。1912年,SEVERIN NORDENTOFT报道了第1篇关于用内镜观察膝关节的论文[52],至此迎来了关节镜微创手术时代。随着关节镜技术的发展,其逐渐被应用于临床。KENJI TAKAGI教授被公认为是将内窥镜用于膝关节的第一人[53],1919年,他率先使用膀胱镜探查了1例患者的膝关节。1931年,直径3.5 mm的关节镜研制成功,成为现代关节镜设备的雏形。20世纪70年代,关节镜技术在西方国家逐渐得到了进一步的发展[51]。关节镜发展历史见表1。关节镜技术提供了一种治疗后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折的可靠方法,根据MARTINEZ- MORENO等[54]在1988年对尸体膝关节进行的实验,证实这种手术是可行的。LITTLEJOHN等[55]为首次报道了这种技术在临床应用的人,他们使用关节镜技术通过3个空心螺钉将一个较大的骨折碎片固定起来。KIM等[37]于2001年描述了后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折碎片缝合固定的新关节镜技术。关节镜技术治疗后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折的发展史见表2。关节镜下缝合固定技术治疗后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折可根据入路、缝合材料的类型以及用于缝合的入路和固定胫骨隧道的数量进行分类[11,27,37,49,50,56]。目前常用于治疗后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折的关节镜术式见表3。"
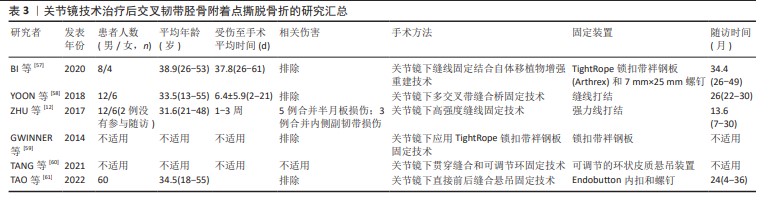
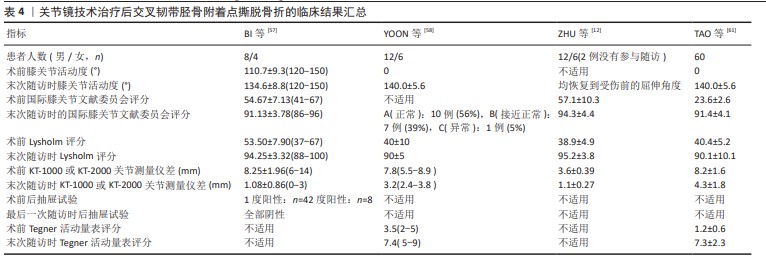
2.1.1 关节镜下缝线固定结合自体移植物增强重建技术 BI等[57]利用关节镜进行缝线固定和自体移植物增强重建治疗膝关节后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折,首先进行膝关节镜检查,在建立前内侧、前外侧入路后再建立后内侧、后外侧入路,将2号不可吸收缝线穿入膝关节,并按照相同的顺序至少包裹后交叉韧带2次,然后在骨折块下方放置定位器并建立一个7 mm的隧道,以便将缝合线的末端穿过并使用缝线进行复位。为了进一步加强重建,使用了自体半腱肌和股薄肌的肌腱折叠作为自体移植物。根据后交叉韧带的解剖走向,在股骨髁上钻取股骨隧道并在膝关节屈曲90°时穿过前外侧入路,后交叉韧带前外侧束和后内侧束交汇处是隧道的中心,在胫骨隧道中拉入移植物将缝合线绷紧并牵拉后交叉韧带,在拉紧移植物时应尽量将其置于骨折碎片的上方,以施加向下的压力。移植物被用TightRope带袢钛钢板固定在股骨侧,而用7 mm×25 mm的螺钉固定在胫骨侧。治疗15例患者(总共12例患者被纳入分析)后,使用后抽屉试验评估膝关节稳定性,并使用关节活动度、KT-1000关节测量仪、国际膝关节文献委员会评分和Lysholm评分等来评估随访时临床结果,研究显示该方法治疗迟发性后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折的效果良好。 2.1.2 关节镜下多交叉带缝合桥固定技术 YOON等[58]提出了一种新的治疗方法,首先建立前内侧和前外侧入路,随后构建后内侧和后外侧入路,用穿线器将1号聚二恶烷酮缝线(用作固定缝线)穿过后外侧入路,并从撕脱骨折碎片上方的后交叉韧带穿过,聚二恶烷酮缝线的一端通过前内侧入路回收,另一端留在后外侧入口。根据撕脱骨折碎片的大小和粉碎的程度,必要时可以进行三四次上述操作。将缝合线交叉分别从建立的2个胫骨隧道拉出并收紧实现骨折碎片复位,然后将收紧的缝线末端绑在2个胫骨隧道的开口之间的骨皮质上。该技术在20例患者(总共18例患者被纳入分析)中进行了应用,通过X射线片、Lysholm评分和Tegner评分和KT-2000关节测量仪进行随访,评估了骨折愈合、膝关节活动范围和关节的功能,结果证实该技术是一种可行的治疗方法,对于后交叉韧带胫骨止附着点撕脱骨折具有令人满意的固定稳定性及骨折部位愈合效果。 2.1.3 关节镜下高强度缝线固定技术 ZHU等[12]使用高强度缝线于关节镜下在膝关节后纵隔处固定治疗后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折,他们利用前内侧和前外侧入路进行膝关节镜检查,以确定病变,然后将关节镜和操作器械通过后内侧、后外侧入路插入。他们放置2条高强度缝合线,将其放置在撕脱骨折碎片上方的后交叉韧带上并打结,然后建立2个胫骨隧道,通过2条胫骨隧道将聚二恶烷酮缝线提至胫骨结节的前方并将强力线收紧,检查复位状态满意后打结系在胫骨结节的前部。他们对18例后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折患者均采用了这种技术,采用国际膝关节文献委员会评分和Lysholm评分来评估治疗效果,证实这项技术是一种简单、安全、可靠且微创的方法,有利于患者术后早期康复,并且可以避免进行额外的手术以移除植入物。 2.1.4 关节镜下应用TightRope锁扣带袢钢板固定技术 GWINNER等[59]提出了一种关节镜下使用TightRope锁扣带袢钢板治疗后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折的技术,该技术采用了前内侧、前外侧以及2个后内侧入路,将TightRope锁扣带袢钢板装置连接在钢丝上,经胫骨穿过骨折撕脱伤,完全复位后将钢丝绳与胫骨撕脱碎片固定在胫骨上。这项技术为患者提供了严格的解剖固定条件,有利于早期康复。 2.1.5 关节镜下贯穿缝合和可调节环固定技术 TANG等[60]介绍一种关节镜下贯穿缝合和可调节环固定技术治疗后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折,该治疗方法通过膝关节镜检查和治疗病变,利用前内侧、前外侧、低后内侧、高后内侧及后外侧入路进行手术。手术过程中使用3条超高分子聚乙烯缝线穿过后交叉韧带和外侧半月板股骨韧带之间的间隔,到达后隔室并包裹后交叉韧带,从下后内侧门穿出,在关节内交叉并打结,然后推入后交叉韧带的后方并越过骨折碎片。通过定位,建立2个胫骨隧道,将聚二恶烷酮缝线作为引导缝线植入每个隧道,借助聚二恶烷酮缝线将后交叉韧带内、外缝合线分别穿过胫骨内侧和外侧隧道,通过拉动缝合线可以观察到骨折碎片在后方及远方的移位减少。在胫骨末端建立一个横穿过胫骨脊的胫骨隧道,并将1个可调节的环状皮质悬吊装置从内向外穿过该隧道,将缝合线连接到可调节环上,最后通过可调节环拉紧骨折碎片。他们认为该技术可以作为治疗后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折的一种合理的选择。 2.1.6 关节镜下直接前后缝合悬吊固定技术 TAO等[61]提出了关节镜下直接前后缝合悬吊固定技术,用于治疗后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折。首先,通过建立前内侧及前外侧入路进行膝关节镜检查,确认是否存在孤立的后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折;然后,在关节镜引导下分别构建高后内侧入路及后内侧入路,在完成胫骨隧道准备后,将5号缝合线从前内侧门穿入,将装有不可吸收超高分子量聚乙烯缝线的钩子从撕脱骨折碎片上方的后交叉韧带的穿过,以相同的方法穿过另一条缝线。通过胫骨隧道抓住2条缝线并拉紧向胫骨隧道的方向移动,以实现骨折的复位,然后将2条缝线穿过内扣固定装置的绳索,在后内侧入口沿胫骨隧道方向拉动缝线,以复位骨折。最后,将缝合线的根部系在内扣固定装置上,放置于隧道的外口。研究人员对60例后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折患者均采用了这种技术,通过关节活动度、KT-2000关节测量仪、国际膝关节文献委员会、Tegner活动量表和Lysholm评分来评估疗效,认为这种技术具有简单可靠、能够提供良好的临床效果的优点,并且适用于任何大小的撕脱骨折碎片的固定。 2.2 关节镜技术的总体临床结果 用于记载临床结果的指标是关节活动度、Lysholm功能评分、国际膝关节文献委员会评分以及KT-2000关节测量仪差等,见表4。 2.2.1 关节活动度 4项研究采用了膝关节活动度来评估随访的临床结果[12,57-58,61],分析了术前及末次随访时的膝关节活动度。BI等[57]发现大部分患者在术后3个月出现了手术侧的膝关节纤维化,而在术后1年有7例患者恢复了正常的膝关节活动范围,其余5例患者则出现了不同程度的膝关节屈曲受限。在鼓励患者加强康复锻炼后,12例患者中的10例膝关节活动范围恢复到了正常,2例患者存在轻度的膝关节屈曲受限,但不会对日常活动产生影响。根据ZHU等[12]的研究,1例患者在术后6周进行了麻醉下的手法松解,其膝关节恢复到了受伤前的屈伸角度,另外15例患者的膝关节屈伸功能正常,并且都恢复到了受伤前状态。在剩下的2项研究中[58,61],膝关节活动范围从术前的0°改善到了140°左右。 2.2.2 Lysholm评分 Lysholm膝关节评分被应用于4项研究中的膝关节功能临床评估,并且在最末次随访时的平均评分与术前相比有显著改善[12,57-58,61]。 2.2.3 国际膝关节文献委员会评分 国际膝关节文献委员会评分用于4项研究的随访[12,57-58,61]。YOON等[58]的研究共有18例患者接受关节镜下多交叉带缝合桥固定治疗[12],其中10例患者IKDC评分为A(正常),7例患者为IKDC评分B(接近正常),1例患者为IKDC评分C(异常)。在另外的3项研究中[57-58,61], IKDC评分的末次随访结果与术前相比都有显著提高,并且这种提高具有统计学上的意义。 2.2.4 KT1000或KT2000关节测量仪差 KT1000或KT2000关节测量仪用于确定4项研究的膝关节的胫骨股骨间的移动距离差[12,57-58,61]。经过随访发现,无论采用哪种方法,膝关节的胫骨股骨间的移动距离差都有所改善,差异的范围在0-5 mm。 2.2.5 后抽屉试验 12例后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折患者接受关节镜下缝线固定结合自体移植物增强重建治疗[57],术前4例患者后抽屉试验1度阳性、8例患者为2度阳性,末次随访时所有患者的后抽屉试验检查结果都转为阴性。 2.2.6 Tegner评分 在2项研究中采用了Tegner评分对术后临床结果进行了评估[12, 61],末次随访时Tegner评分与手术前相比都有显著改善且差异均具有统计学意义。 2.3 关节镜技术影像学评估 BI等[57]的研究在术后进行X射线片随访时发现,撕脱骨折碎片通常在术后10-15周(平均3.2个月)内愈合,在随访中没有发现固定失败、再发骨折或后交叉韧带撕裂。YOON等[58]的研究对18例患者后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折在关节镜术后3,6,12和24个月拍摄了膝关节正侧位平片来随访评估,末次随访结果显示所有患者的骨折部位均牢固愈合。在ZHU等[12]的研究中,16例后交叉韧带胫骨附着点撕脱骨折患者的骨折碎片复位效果良好,通过X射线片和三维重建CT扫描可以观察到所有患者术后3个月骨折愈合。在TAO等[61]的研究中,关节镜术后立即对60例患者拍摄了膝关节的横断CT、三维CT重建和X射线片,以评估固定物位置和骨折碎片复位情况,末次影像学随访结果显示所有患者骨折部位都已牢固愈合。 2.4 关节镜技术相关并发症 在所有的研究中随访时没有患者出现严重并发症,例如创伤性关节炎、神经血管损伤、围术期伤口感染、血栓形成及骨折不愈合等。 "
| [1] ZHAO D, ZHONG J, ZHAO B, et al. Clinical outcomes of acute displaced posterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion fracture: A retrospective comparative study between the arthroscopic suture and EndoButton fixation techniques. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2021;107(2):102798. [2] 徐鸿尧,戴志宏,邹相杰,等.关节镜下缝线桥技术与切开复位内固定治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(2):186-188. [3] 史俊恒,钟的桂,范智荣,等.后交叉韧带保留型假体对比后稳定型假体用于全膝关节置换的Meta分析 [J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(8):1282-1290. [4] SABAT D, JAIN A, KUMAR V. Displaced Posterior Cruciate Ligament Avulsion Fractures: A Retrospective Comparative Study Between Open Posterior Approach and Arthroscopic Single-Tunnel Suture Fixation. Arthroscopy. 2016;32(1):44-53. [5] WIJDICKS CA, KENNEDY NI, GOLDSMITH MT, et al. Kinematic analysis of the posterior cruciate ligament, part 2: a comparison of anatomic single-versus double-bundle reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41(12):2839-2848. [6] YIN Q, RUI Y, WU Y, et al. Surgical treatment of avulsion fracture around joints of extremities using hook plate fixation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):200. [7] FANELLI GC, EDSON CJ. Posterior cruciate ligament injuries in trauma patients: Part II. Arthroscopy. 1995;11(5):526-529. [8] HOOPER PO, 3RD, SILKO C, MALCOLM TL, et al. Management of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tibial Avulsion Injuries: A Systematic Review. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(3):734-742. [9] JANOUSEK AT, JONES DG, CLATWORTHY M, et al. Posterior cruciate ligament injuries of the knee joint. Sports Med. 1999;28(6):429-441. [10] SCHULZ MS, RUSSE K, WEILER A, et al. Epidemiology of posterior cruciate ligament injuries. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2003;123(4): 186-191. [11] WIJDICKS CA, KENNEDY NI, GOLDSMITH MT, et al. Kinematic analysis of the posterior cruciate ligament, part 2: a comparison of anatomic single- versus double-bundle reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41(12):2839-2848. [12] ZHU W, LU W, CUI J, et al. Treatment of tibia avulsion fracture of posterior cruciate ligament with high-strength suture fixation under arthroscopy. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2017;43(1):137-143. [13] KATSMAN A, STRAUSS EJ, CAMPBELL KA, et al. Posterior Cruciate Ligament Avulsion Fractures. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018;11(3): 503-509. [14] HESSE E, BASTIAN L, ZEICHEN J, et al. Femoral avulsion fracture of the posterior cruciate ligament in association with a rupture of the popliteal artery in a 9-year-old boy: a case report. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14(4):335-339. [15] MISHRA AK, VIKAS R. A rare case of bony avulsion of posterior cruciate ligament from its femoral attachment. Med J Armed Forces India. 2016;72(Suppl 1):S98-s100. [16] PARK IS, KIM SJ. Arthroscopic fixation of avulsion of the posterior cruciate ligament from femoral insertion. Arthroscopy. 2005;21(11): 1397. [17] AURICH M, KOENIG V, HOFMANN G. Comminuted intraarticular fractures of the tibial plateau lead to posttraumatic osteoarthritis of the knee: Current treatment review. Asian J Surg. 2018;41(2):99-105. [18] STEVENS DG, BEHARRY R, MCKEE MD, et al. The long-term functional outcome of operatively treated tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(5):312-320. [19] 姜祖康,周红星,张保健,等.关节镜下Ethibond缝线结合可调节Endobutton固定治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折[J].中国现代手术学杂志,2021,25(3):192-195. [20] 王宁,黄建霞,高德玉,等.微创小切口下双排线桥技术治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点粉碎性骨折12例[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019, 27(2):60-63. [21] 李小建,郗海涛,李兵,等.带线锚钉结合骨桥内固定治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折的疗效分析[J].骨科,2019,10(3):184-187. [22] SCHUMAIER A, MINOUGHAN C, JIMENEZ A, et al. Treatments of Choice for Isolated, Full-Thickness Tears of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament: A Nationwide Survey of Orthopaedic Surgeons. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(8):812-819. [23] ABDALLAH AA, ARAFA MS. Treatment of posterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion by a minimally-invasive open posterior approach. Injury. 2017;48(7):1644-1649. [24] GOPINATTH V, MAMERI ES, CASANOVA FJ, et al. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Clinical Outcomes After Management of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tibial Avulsion Fractures. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023;11(9):23259671231188383. [25] BAGHERIFARD A, JABALAMELI M, KHEZRI M, et al. Conservative management of posterior cruciate ligament avulsion with a large bony fragment: a prospective cohort study. Curr Orthop Pract. 2021;32(4): 361-365. [26] GREENWALD D, SHUMWAY S, ALBEAR P, et al. Mechanical comparison of 10 suture materials before and after in vivo incubation. J Surg Res. 1994;56(4): 372-377. [27] GUI J, WANG L, JIANG Y, et al. Single-tunnel suture fixation of posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture. Arthroscopy. 2009;25(1):78-85. [28] ZHAO J, HE Y, WANG J. Arthroscopic treatment of acute tibial avulsion fracture of the posterior cruciate ligament with suture fixation technique through Y-shaped bone tunnels. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(2):172-181. [29] 杨波,吴长坤,刘建永,等.关节镜下后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折缝合固定术的中远期疗效分析[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(8): 646-651. [30] NAKAGAWA S, ARAI Y, HARA K, et al. Arthroscopic pullout fixation for a small and comminuted avulsion fracture of the posterior cruciate ligament from the tibia. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2017;29(4):316. [31] JOSHI S, BHATIA C, GONDANE A, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of isolated posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fractures: clinical and functional outcome. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2017;29(3):210. [32] HERMANOWICZ K, GÓRALCZYK A, DANOWSKA K, et al. All-Arthroscopic posterior cruciate ligament distal reattachment with extracortical fixation. Arthrosc Tech. 2019;8(11):e1425-e1430. [33] 赵智,邓煜,陈宇,等.关节镜下免打结锚钉联合Endobutton钛板治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折[J].中国骨伤,2021,34(12): 1136-1140. [34] 覃志,秦煜,黄玉文,等.关节镜下缝线“8”字捆扎固定治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折疗效探讨[J].中国临床新医学,2020,13(6): 560-564. [35] 龙治强,黄松涛,景周,等.后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折应用小切口切开复位锚钉内固定手术的分析[J].浙江创伤外科,2020, 25(6):1173-1174. [36] JOSEPH CM, GUNASEKARAN C, LIVINGSTON A, et al. Outcome of screw post fixation of neglected posterior cruciate ligament bony avulsions. Injury. 2019;50(3):784-789. [37] KIM SJ, SHIN SJ, CHO SK, et al. Arthroscopic suture fixation for bony avulsion of the posterior cruciate ligament. Arthroscopy. 2001;17(7): 776-780. [38] BALI K, PRABHAKAR S, SAINI U, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of isolated PCL fossa avulsion fractures. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(2):315-321. [39] FROSCH KH, PROKSCH N, PREISS A, et al. Treatment of bony avulsions of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) by a minimally invasive dorsal approach. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2012;24:348-353. [40] LEE KW, YANG DS, LEE GS, et al. Suture bridge fixation technique for posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture. Clin Orthop Surg. 2015;7(4):505-508. [41] WHITE EA, PATEL DB, MATCUK GR, et al. Cruciate ligament avulsion fractures: anatomy, biomechanics, injury patterns, and approach to management. Emerg Radiol. 2013;20(5):429-440. [42] YANG CK, WU CD, CHIH CJ, et al. Surgical treatment of avulsion fracture of the posterior cruciate ligament and postoperative management. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2003;54(3):516-519. [43] HUANG W, GONG X, RAHUL M, et al. Anterior arthroscopic-assisted fixation of posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fractures. Eur J Med Res. 2015;20:1-6. [44] ZHANG X, CAI G, XU J, et al. A minimally invasive postero-medial approach with suture anchors for isolated tibial avulsion fracture of the posterior cruciate ligament. Knee. 2013;20(2):96-99. [45] GWINNER C, HOBURG A, WILDE S, et al. All-arthroscopic treatment of tibial avulsion fractures of the posterior cruciate ligament. GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW. 2016;5:Doc02. [46] 袁云峰.改良Burks-Schaffer入路切开复位空心钉固定与关节镜下Endobutton带袢钢板固定治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折的疗效[J].吉林医学,2021,42(9):2141-2142. [47] CHEN CW, CHEN L, PAN ZE, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation via a posterior approach for posterior fractures of tibial plateau. Zhongguo gu Shang. 2012;25(7):561-565. [48] 王戈,高志,张威,等.关节镜下PushLock缝合锚固系统治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折40例[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020, 28(4):69-71. [49] KWON OS, PARK MJ, KELLY JD 4TH. Arthroscopic treatment of a PCL avulsion fracture in a skeletally immature patient. Orthopedics. 2011; 34(2):137. [50] CHEN LB, WANG H, TIE K, et al. Arthroscopic fixation of an avulsion fracture of the tibia involving the posterior cruciate ligament: a modified technique in a series of 22 cases. Bone Joint J. 2015;97(9): 1220-1225. [51] MAGRILL ACL, NAKANO N, KHANDUJA V. Historical review of arthroscopic surgery of the hip. Int Orthop. 2017;41(10):1983-1994. [52] KIESER CW, JACKSON RW. Severin Nordentoft: the first arthroscopist. Arthroscopy. 2001;17(5):532-535. [53] FONTES D. [Historical developments of upper limp arthroscopy]. Chir Main. 2006;25 Suppl 1:S4-7. [54] MARTINEZ-MORENO JL, BLANCO-BLANCO E. Avulsion Fractures of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament of the Knee: An Experimental Percutaneous Rigid Fixation Technique Under Arthroscopic Control. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;237:204-208. [55] LITTLEJOHN SG, GEISSLER WB. Arthroscopic repair of a posterior cruciate ligament avulsion. Arthroscopy. 1995;11(2):235-238. [56] ZHANG H, HONG L, WANG XS, et al. All-arthroscopic repair of arcuate avulsion fracture with suture anchor. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(5):728-734. [57] BI M, ZHAO C, CHEN J, et al. Arthroscopic suture fixation with autograft augmentation reconstruction for delayed tibial avulsion fractures of the posterior cruciate ligament. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020;8(8): 2325967120944047. [58] YOON JR, PARK CD, LEE DH. Arthroscopic suture bridge fixation technique with multiple crossover ties for posterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion fracture. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018; 26(3):912-918. [59] GWINNER C, KOPF S, HOBURG A, et al. Arthroscopic treatment of acute tibial avulsion fracture of the posterior cruciate ligament using the TightRope fixation device. Arthrosc Tech. 2014;3(3):e377-e382. [60] TANG J, ZHAO J. Arthroscopic suture-to-loop fixation of posterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion fracture. Arthrosc Tech. 2021;10(6): e1595-e1602.
[61] TAO T, YANG W, TAO X, et al. Arthroscopic Direct Anterior‐to‐Posterior Suture Suspension Fixation for the Treatment of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tibial Avulsion Fracture. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9):2031-2041.
[62] NICANDRI GT, KLINEBERG EO, WAHL CJ, et al. Treatment of posterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion fractures through a modified open posterior approach: operative technique and 12-to 48-month outcomes. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(5):317-324.[63] WAJSFISZ A, MAKRIDIS KG, VAN DEN STEENE JY, et al. Fixation of posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture with the use of a suspensory fixation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(5): 996-999. [64] SONG JG, NHA KW, LEE SW. Open posterior approach versus arthroscopic suture fixation for displaced posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fractures: systematic review. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2018;130(4): 275. [65] CHEN W, TANG D, KANG L, et al. Effects of microendoscopy-assisted reduction and screw fixation through a single mini-incision on posterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion fracture. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(4):429-435. [66] CHIARAPATTANAKOM P, PAKPIANPAIROJ C, LIUPOLVANISH P, et al. Isolated PCl avulsion from the tibial attachment: residual laxity and function of the knee after screw fixation. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009; 92 Suppl 6: S181-188. [67] INOUE M, YASUDA K, KONDO E, et al. Primary repair of posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture: the effect of occult injury in the midsubstance on postoperative instability. Am J Sports Med. 2004; 32(5):1230-1237. [68] WILLINGER L, IMHOFF AB, SCHMITT A, et al. Fixation of bony avulsions of the posterior cruciate ligament by a suture-bridge™ technique. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2019;31(1):3-11. [69] SHELBOURNE KD, URCH SE, FREEMAN H. Outcomes after arthroscopic excision of the bony prominence in the treatment of tibial spine avulsion fractures. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(6):784-791. [70] 刘子桃,陈善创,黄永铨,等.膝后内侧入路空心钉张力带治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点骨折13例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(8): 53-55. [71] DEHOUST J, BROJA M, MULL C, et al. Pseudarthrosis after bony avulsion fracture of the posterior cruciate ligament. Unfallchirurg. 2019;122: 784-790. [72] HOOGERVORST P, GARDENIERS JW, MORET-WEVER S, et al. Pseudo‐arthrosis repair of a posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(11):1612-1616. [73] SASAKI SU, DA MOTA E ALBUQUERQUE RF, et al. Open screw fixation versus arthroscopic suture fixation of tibial posterior cruciate ligament avulsion injuries: a mechanical comparison. Arthroscopy. 2007;23(11): 1226-1230. [74] TIFTIKÇI U, SERBEST S. Repair of isolated horizontal meniscal tears with all-inside suture materials using the overlock method: outcome study with a minimum 2-year follow-up. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):131. [75] TIFTIKÇI U, SERBEST S. Does the location of placement of meniscal sutures have a clinical effect in the all-inside repair of meniscocapsular tears? J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):87. [76] 汤睿,刘沛.关节镜下Ethibond缝线复位固定治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折的临床疗效[J].骨科,2020,11(2):125-130. [77] 孙法瑞,孙秋萍,张远金,等.关节镜下Orthocord线治疗青少年后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折[J].骨科,2022,13(4):370-372. [78] VISHWAKARMA NS, GALI JC, GALI JCF, et al. Dual postero-medial portal technique for posterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion fracture fixations. Arthrosc Tech. 2021;10(10):e2229-e2235. [79] 陈定启,潘宇朝,陈德焱,等.关节镜下Y型骨隧道缝线捆绑治疗后十字韧带胫骨附丽点撕脱骨折效果观察[J].中国临床新医学, 2017,10(7):674-676. [80] WU S, XU W, LIN W, LI H. [Comparison of early effectiveness of arthroscopic suture bridge technique and conventional double tunnel suture technique in treatment of avulsion fracture of posterior cruciate ligament insertion]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021; 35(7):829-835. [81] 熊小龙,王广积,方业汉,等.关节镜下单骨道双Endobutton固定治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折22例分析[J].临床外科杂志, 2020,28(11):1051-1054. [82] WRIGHT PB, BUDOFF JE, YEH ML, et al. Strength of damaged suture: an in vitro study. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(12):1270-1275. [83] 张中兴,许峰,金伟.带线锚钉治疗后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折 21 例报告[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016(2):120-122. [84] SUN C, DU R, LUO S, et al. A New Arthroscopic Tightrope Suture-Button Fixation Procedure for Tibial Eminence Avulsion Fracture. J Knee Surg. 2021;36(2):132-138. [85] DOMNICK C, KÖSTERS C, FRANKE F, et al. Biomechanical properties of different fixation techniques for posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fractures. Arthroscopy. 2016;32(6):1065-1071. [86] 王良勇,李建刚,张春,等.植入物固定后交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折:膝关节活动度及功能评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(24):3793-3797. [87] 姚沛全,余颖锋,张贤森.关节镜下空心钉和钢丝固定治疗胫骨髁间前棘撕脱骨折的疗效分析[J].智慧健康,2021,7(8):61-63. [88] ZHOU P, LIU J, XU Y, et al. [Early effectiveness of minimally invasive open reduction and internal fixation versus arthroscopic double-tunnel suture fixation for tibial avulsion fracture of posterior cruciate ligament]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(6): 707-712. [89] 郑杰,蒋伟亚,赵嘉懿.关节镜下TightRope治疗后交叉韧带撕脱骨折[J].中国内镜杂志,2019,25(7):22-25. [90] HAPA O, BARBER FA, SÜNER G, et al. Biomechanical comparison of tibial eminence fracture fixation with high-strength suture, EndoButton, and suture anchor. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(5):681-687. [91] 袁伶俐,徐斌,姜少伟,等.Tightrope与Endobutton应用在交叉韧带重建中的效果比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(11): 1616-1622. [92] MEYERS MH. Isolated avulsion of the tibial attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57(5):669-672. [93] SU WR, WANG PH, WANG HN, et al. A simple, modified arthroscopic suture fixation of avulsion fracture of the tibial intercondylar eminence in children. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2011;20(1):17-21. [94] EZECHIELI M, SCHÄFER M, BECHER C, et al. Biomechanical comparison of different fixation techniques for reconstruction of tibial avulsion fractures of the anterior cruciate ligament. Int Orthop. 2013;37:919-923. [95] PANDYA NK, JANIK L, CHAN G, et al. pediatric PCL insufficiency from tibial insertion osteochondral avulsions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:2878-2883. [96] XU Z, CHEN D, SHI D, et al. Case report: osteochondral avulsion fracture of the posteromedial bundle of the PCL in knee hyperflexion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470:3616-3623. [97] EGGERS AK, BECKER C, WEIMANN A, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of different fixation methods for tibial eminence fractures. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(3):404-410. |
| [1] | Chen Jing, Zhang Nan, Meng Qinghua, Bao Chunyu. Material characterization of finite element computational models of knee joints at different ages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7369-7375. |
| [2] | Chen Senlin, Zhu Zhou, Wan Qianbing. Application of Janus micro/nanoparticles in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6101-6109. |
| [3] | Lan Xiaoqian, Feng Guangli, Qin Shiyi, Zhong Lianmei, Li Qing. New ideas and opportunities for polyurethane materials in peripheral nerve repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6127-6137. |
| [4] | Zhao Yue, Xu Yan, Zhou Jianping, Zhang Xujing, Chen Yutong, Jin Zhengyang, Yin Zhitao. Differences in structural design between traditional and bionic scaffolds in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3458-3468. |
| [5] | Feng Shuqi, Zhang Shiyong, Yao Keyi, Tang Yufei, Wang Kai, Zhou Xuemei, Xiang Lin. Application of photoresponsive nanomaterials in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3469-3475. |
| [6] | He Rui, Li Chongyi, Wang Ruiyao, Zeng Dan, Fan Daidi. Application of MXene-based hydrogels in wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3486-3493. |
| [7] | Hu Zhangjie, Zhang Baoguan, Zhang Zhiwu. Application of solid collagen-based materials in medical devices [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3503-3512. |
| [8] | Ye Chao, Liu Xiaohong. Regulatory strategies for foreign body reactions in biomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3513-3520. |
| [9] | Xiao Wenqian, Han Hongjuan, Yang Haocheng, Li Bo, He Binyan. Field-driven medical micro-robots: application prospect of continuously optimizing material preparation process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2097-2104. |
| [10] | Chen Jiahan, Feng Chao, Huang Xiaoxia, Niu Minghui, Wang Xin, Teng Yong. Two-dimensional black phosphorus materials for bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2124-2131. |
| [11] | Liu Haoyang, Xie Qiang, Shen Mengran, Ren Yansong, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Wang Weiguo . Application, research hotspots, and shortcomings of degradable zinc-based alloys in bone defect repair and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 839-845. |
| [12] | Chen Yilong, Zhang Xu, Li Hong. Mechanical analysis of fiber post combined with different crown restorations for endodontically treated non-carious cervical lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 866-871. |
| [13] | Gao Xilin, Wu Si Zhang Chao Zhu Liguo, Fu Bifeng, Wang Ping. Mechanotransduction proteins in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 579-589. |
| [14] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [15] | Cheng Weilu, Wang Zehua, Zhang Yidan, Liu Yinghui. Application and regulatory challenges of organoid technology in medical field [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 202-210. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||