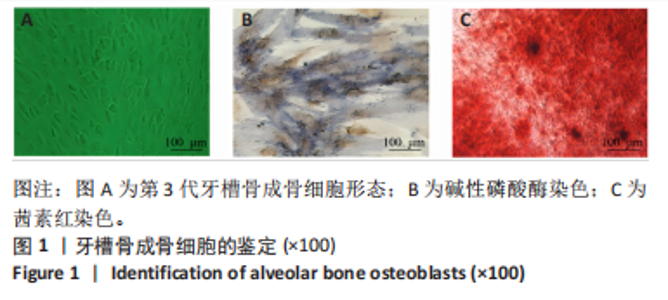
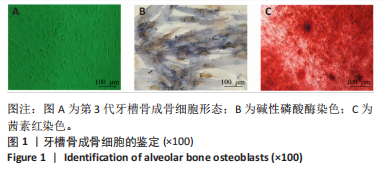
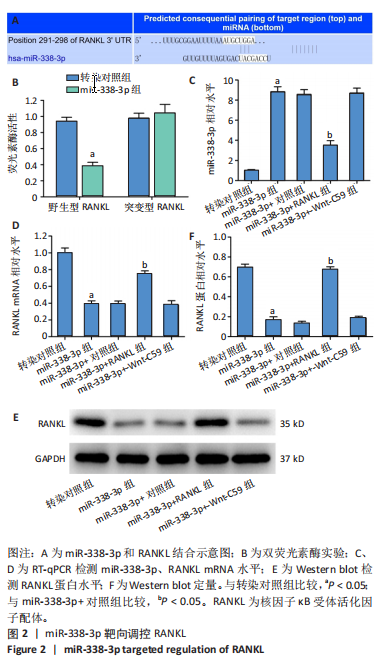
[1] NASIRI K, AMIRI MOGHADDAM M, ETAJURI EA, et al. Periodontitis and progression of gastrointestinal cancer: current knowledge and future perspective. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023;25(10):2801-2811.
[2] CHEN MH, WANG YH, SUN BJ, et al. HIF-1α activator DMOG inhibits alveolar bone resorption in murine periodontitis by regulating macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;99: 107901.
[3] JENG MD, CHIANG CP. Autogenous bone grafts and titanium mesh-guided alveolar ridge augmentation for dental implantation. J Dent Sci. 2020;15(3):243-248.
[4] ZHAO YH, PENG XL, WANG Q, et al. Crosstalk Between the Neuroendocrine System and Bone Homeostasis. Endocr Rev. 2024; 45(1):95-124.
[5] TABASSUM A. Effect of dexamethasone on the growth and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells derived from the human alveolar bone. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2022;17(4):707-714.
[6] LU XH, ZHANG YT, ZHENG Y, et al. The miRNA-15b/USP7/KDM6B axis engages in the initiation of osteoporosis by modulating osteoblast differentiation and autophagy. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(4):2069-2081.
[7] HU LC, XIE XD, XUE H, et al. MiR-1224-5p modulates osteogenesis by coordinating osteoblast/osteoclast differentiation via the Rap1 signaling target ADCY2. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(7):961-972.
[8] SUN Q, ZHANG BR, ZHU W, et al. A potential therapeutic target for regulating osteoporosis via suppression of osteoclast differentiation. J Dent. 2019;82:91-97.
[9] ZHANG XH, GENG GL, SU B, et al. MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoid-induced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(3). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15037674.
[10] NIU DQ, GONG Z, SUN XM, et al. miR-338-3p regulates osteoclastogenesis via targeting IKKβ gene. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019;55(4):243-251.
[11] 黄霞, 魏津钿, 苏琪, 等. 干细胞源性细胞外囊泡经RANKL/RANK/OPG通路促进牙槽骨成骨的研究进展[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2023,33(20):60-64.
[12] ALI R, HAMMAD A, EL-NAHRERY E, et al. Serum RANKL, osteoprotegerin (OPG) and RANKL/OPG ratio in children with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2019;28(10):1233-1242.
[13] 李家乐,罗达胜,郑刘杰,等. 人骨关节炎软骨细胞上调成骨细胞中骨保护素的作用途径[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(26): 4194-4201.
[14] ZHANG XY, LI HN, CHEN F, et al. Icariin regulates miR-23a-3p-mediated osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs via BMP-2/Smad5/Runx2 and WNT/β-catenin pathways in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Saudi Pharm J. 2021;29(12):1405-1415.
[15] 郑俊杰,陈冬冬,林佳生,等. 褪黑素对骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢及成骨细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响[J]. 福建医药杂志,2023, 45(4):111-114.
[16] 庞兰, 李佩璠, 郑蕾, 等. 利培酮通过影响Wnt/β-catenin信号通路诱导人成骨细胞系hFob1.19凋亡[J]. 基础医学与临床,2023, 43(3):374-379.
[17] WIMMERS FERREIRA MR, RODRIGO FERNANDES R, FREIRE ASSIS A. Oxidative Nanopatterning of Titanium Surface Influences mRNA and MicroRNA Expression in Human Alveolar Bone Osteoblastic Cells. Int J Biomater. 2016:9169371.
[18] 王海琴, 闫冰, 李成. 茶多酚通过miR-33a-5p/RUNX2介导人牙槽骨成骨细胞增殖和凋亡[J]. 中国药师,2021,24(6):1069-1075.
[19] LIU M, XU ZM. Berberine Promotes the Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of Alveolar Osteoblasts through Regulating the Expression of miR-214. Pharmacology. 2021;106(1-2):70-78.
[20] PAN L, ZHANG CY, ZHANG HZ, et al. Osteoclast-Derived Exosomal miR-5134-5p Interferes with Alveolar Bone Homeostasis by Targeting the JAK2/STAT3 Axis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:3727-3744.
[21] 朱丽璇, 崔玥, 罗静. 99Tc-MDP通过miR-338-3p靶向下调RANKL抑制破骨细胞活性机制研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(2):170-174+185.
[22] KURITANI M, SAKAI N, KARAKAWA A, et al. Anti-mouse RANKL Antibodies Inhibit Alveolar Bone Destruction in Periodontitis Model Mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(4):637-643.
[23] KELDER C, KLEVERLAAN CJ, GILIJAMSE M, et al. Cells Derived from Human Long Bone Appear More Differentiated and More Actively Stimulate Osteoclastogenesis Compared to Alveolar Bone-Derived Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):5072.
[24] LIU L, GUO SJ, SHI WW, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Periodontal Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(13-14):962-976.
[25] WANG CG, HU YH, SU SL, et al. LncRNA DANCR and miR-320a suppressed osteogenic differentiation in osteoporosis by directly inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp Mol Med. 2020; 52(8):1310-1325.
[26] 刘丹, 黄思柔, 刘璞, 等. 基于Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路探究金天格胶囊对肿瘤坏死因子α干预下前成骨细胞生物学功能的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2023,31(6):1-7+14.
[27] GE J, YU YJ, LI JY, et al. Activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling by autophagic degradation of APC contributes to the osteoblast differentiation effect of soy isoflavone on osteoporotic mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023;44(9):1841-1855.
[28] WEI YK, MA HL, ZHOU HQ, et al. miR-424-5p shuttled by bone marrow stem cells-derived exosomes attenuates osteogenesis via regulating WIF1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin axis. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(13):17190-17201.
[29] ZHANG TJ, JI YF, YU S, et al. Rspo1 inhibited apoptosis of glucocorticoid-induced osteoblasts via Wnt/β-catenin pathway in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2023;32(6):643-654.
[30] JANG J, SONG J, SIM I, et al. Wnt-C59 inhibits proinflammatory cytokine expression by reducing the interaction between β-catenin and NF-κB in LPS-stimulated epithelial and macrophage cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021;25(4):307-319.
[31] AYERS M, KOSAR K, XUE Y, et al. Inhibiting Wnt Signaling Reduces Cholestatic Injury by Disrupting the Inflammatory Axis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;16(6):895-921. |