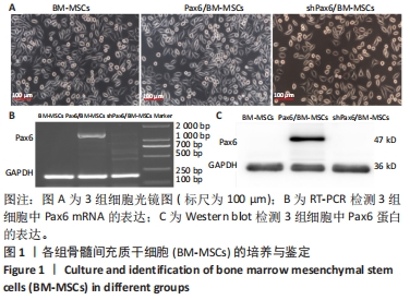
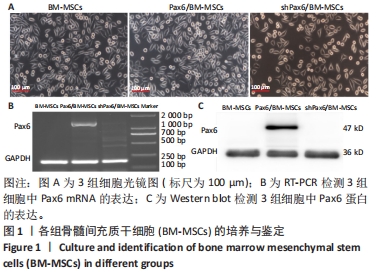
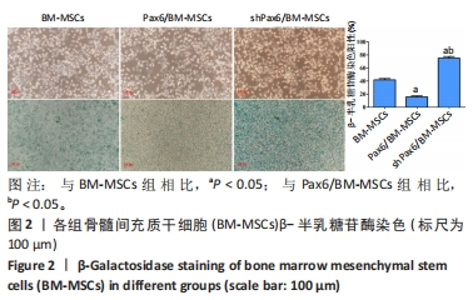
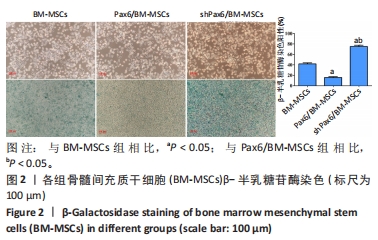
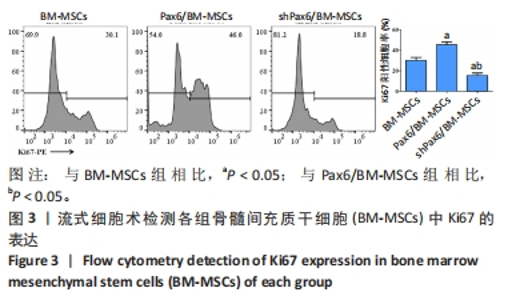
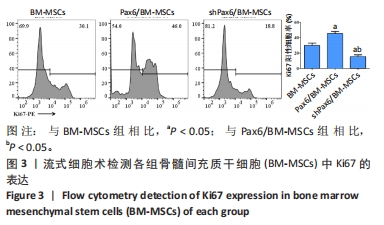
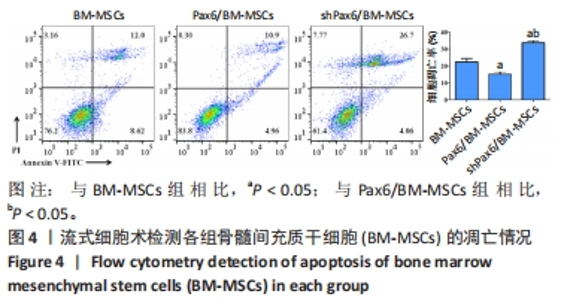
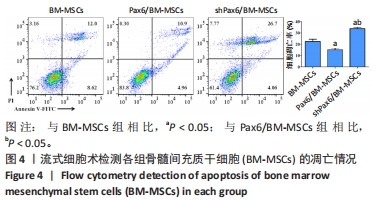
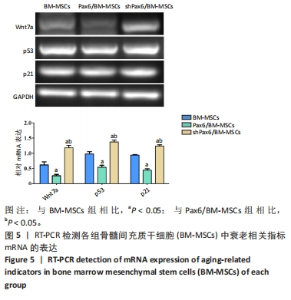
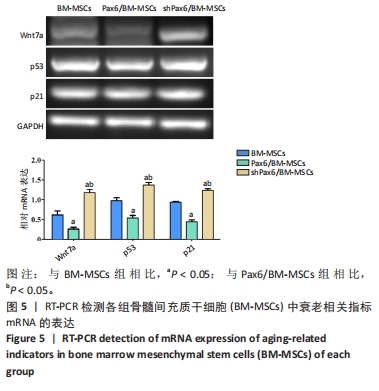
[1] WANG X, WANG S, ZHOU Y, et al. BM‑MSCs protect against liver ischemia/reperfusion injury via HO‑1 mediated autophagy. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(2):2253-2262.
[2] 李志清,黄悦,孙慧敏,等. PAX6基因在眼发育中的调控作用[J].国际眼科杂志,2013,13(4):685-687.
[3] TZAMERET A, SHER I, BELKIN M, et al. Epiretinal transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells rescues retinal and vision function in a rat model of retinal degeneration. Stem Cell Res. 2015;15(2):387-394.
[4] 周梦,余菲,邵春益,等.PAX6基因过表达促进大鼠骨髓内皮祖细胞向角膜内皮细胞分化[J].组织工程与重建外科,2021,17(1):25-29.
[5] 祁海燕,冷非,苏学刚.靶向沉默Pax6基因表达抑制视网膜母细胞瘤增殖侵袭的机制研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2017,16(16):1604-1607.
[6] GAO J, DING L, XIN Y, et al. Pax6-Induced Proliferation and Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Into Limbal Epithelial Stem Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2023;32(13-14):410-421.
[7] BABIZHAYEV MA, YEGOROV YE. Reactive Oxygen Species and the Aging Eye: Specific Role of Metabolically Active Mitochondria in Maintaining Lens Function and in the Initiation of the Oxidation-Induced Maturity Onset Cataract--A Novel Platform of Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants With Broad Therapeutic Potential for Redox Regulation and Detoxification of Oxidants in Eye Diseases. Am J Ther. 2016;23(1):e98-117.
[8] SHU DY, CHAUDHARY S, CHO KS, et al. Role of Oxidative Stress in Ocular Diseases: A Balancing Act. Metabolites. 2023;13(2):187.
[9] HSUEH YJ, CHEN YN, TSAO YT, et al. The Pathomechanism, Antioxidant Biomarkers, and Treatment of Oxidative Stress-Related Eye Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1255.
[10] DAMMAK A, PASTRANA C, MARTIN-GIL A, et al. Oxidative Stress in the Anterior Ocular Diseases: Diagnostic and Treatment. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(2):292.
[11] 孟继虹,饶青.细胞老化相关信号途径[J].医学分子生物学杂志, 2006,3(6):456-459.
[12] EBRAHIM N, EL-HALIM HEA, HELAL OK, et al. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on diabetes-induced retinal injury: Implication of Wnt/ b-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;154:113554.
[13] 袁大江,彭吾训,张飞,等.低浓度过氧化氢预处理增强骨髓间充质干细胞抗氧化应激损伤的能力[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(13): 1982-1988.
[14] 张文娟,纪卫东,杨淋清,等.人胚肺成纤维细胞复制性衰老及过氧化氢诱导的早衰研究[J].卫生研究,2009,38(2):139-143.
[15] 王惠,王飞,楚瑞雪,等.抑制Pax6基因表达对视网膜母细胞瘤增殖侵袭的影响及其作用机制[J].实用癌症杂志,2020,35(12):1961-1964.
[16] 李亮.PAX6过表达促进视网膜母细胞瘤细胞增殖机制研究[D].北京:首都医科大学,2012.
[17] 张爱平,高田,胡玉亮.银杏内酯B调控PAX6基因表达对人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和成骨分化能力的影响[J].中国药师,2021,24(9): 1612-1616.
[18] SUN J, LIU WH, DENG FM, et al. Differentiation of rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells into corneal-like epithelial cells driven by PAX6. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(2):1424-1432.
[19] SCHAALE K, NEUMANN J, SCHNEIDER D, et al. Wnt signaling in macrophages: augmenting and inhibiting mycobacteria-induced inflammatory responses. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011;90(6-7):553-559.
[20] 马蓉洁,朱良,徐俊.Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调控人神经干细胞衰老过程的研究[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2017,38(5):1-6.
[21] 周长立,任先军,蒋涛,等.Wnt7a基因对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及向神经元样细胞分化的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2013,35(8): 702-706.
[22] 谭亭. LiCl促进糖尿病角膜上皮损伤修复的机制研究[D].宜昌:三峡大学,2022.
[23] DE BOER J, WANG HJ, VAN BLITTERSWIJK C. Effects of Wnt signaling on proliferation and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(3-4):393-401.
[24] KUILMAN T, MICHALOGLOU C, VREDEVELD LC, et al. Oncogene-induced senescence relayed by an interleukin-dependent inflammatory network. Cell. 2008;133(6):1019-1031.
[25] GAMBINO V, DE MICHELE G, VENEZIA O, et al. Oxidative stress activates a specific p53 transcriptional response that regulates cellular senescence and aging. Aging Cell. 2013;12(3):435-445.
[26] MIJIT M, CARACCIOLO V, MELILLO A, et al. Role of p53 in the Regulation of Cellular Senescence. Biomolecules. 2020;10(3):420.
[27] 钟培瑞,何晓艳,廖瑛,等.P53/P21通路在电针抑制骨质疏松大鼠模型成骨细胞衰老中的机制[J].实用医学杂志,2023,39(2):192-197.
[28] ENGELAND K. Cell cycle regulation: p53-p21-RB signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(5):946-960.
[29] REGULSKI MJ. Cellular Senescence: What, Why, and How. Wounds. 2017; 29(6):168-174.
[30] BINET R, YTHIER D, ROBLES AI, et al. WNT16B is a new marker of cellular senescence that regulates p53 activity and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Cancer Res. 2009;69(24):9183-9191.
|