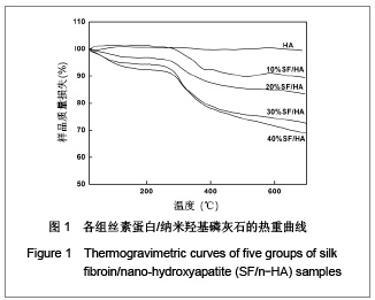
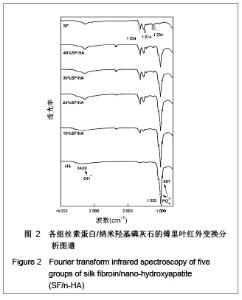
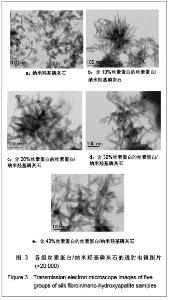
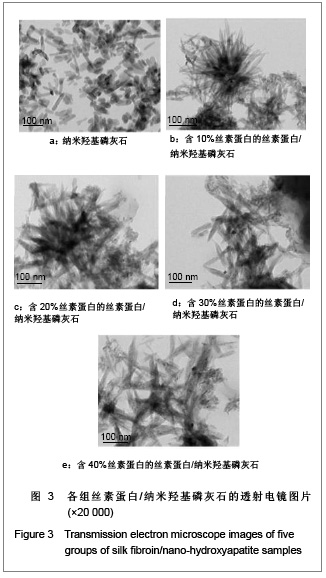
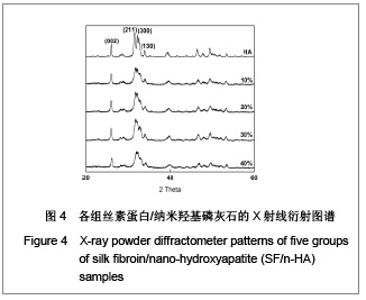
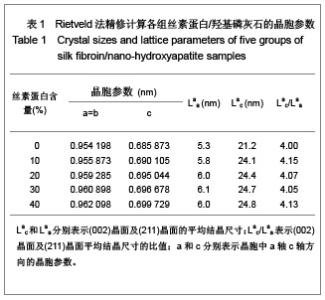
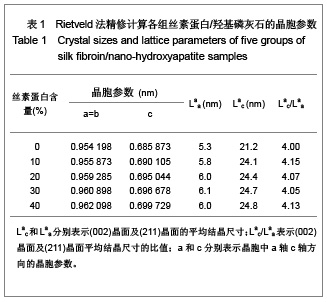
| [1] Wang Y,Kim HJ,Vunjak-Novakovic G, et al.Stem cell-based tissue engineering with silk biomaterials. Biomaterials.2006;27(36): 6064-6082.[2] Kong XD,Cui FZ,Wan XM,et al.Silk fibroin regulated mineralization of hydroxyapatite nanocrystals.J Cryst Growth. 2004;270 (1-2):197-202.[3] Wang G,Yao JB,Zhou XG,et al.Fuhe Cailiao Xuebao. 2008; 25(6): 136-139. 王刚,姚金波,周旭光,等.“一步法”制备纳米相丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石生物复合材料[J].复合材料学报,2008,25(6): 136-139.[4] Wang J ,Zuo YY,Yang WH,et al. Study on Preparation of n-HA and Silk Fibroin Bio-mineral Materia.J Inorg Mater.2009;24(2): 264-268.[5] Fan C,Li J,Xu G,et al.Facile fabrication of nano-hydroxyapatite/silk fibroin composite via a simplified coprecipitation route.J Mater Sci.2010;45(21):5814-5819.[6] Wang J, Yang WH,Shen BZ,et al.Preparation and Characterization of Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Silk Fibroin Biocomposites. Polym Mater Sci Eng .2008; 24(11):165-168.[7] Yang H,Zhang L,Zhang H,et al.Fuhe Cailiao Xuebao. 2007; 24(3):141-146. 杨辉,张林,张宏,等. 丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石复合材料的制备及性能表征[J].复合材料学报,2007,24(3):141-146.[8] Cheng X,Li YB,Lu CH,et al. Effect of Pretreatment on Fabrication of Natural Fibroin Fiber/Apatite Composites Using Alternate Soaking Method.J Inorg Mater.2011;26(1): 43-48.[9] Cao H,Chen X,Shao ZZ.Preparation of Hydroxyapatite/Silk Fibroin Electrospun Fibers and Their Application to Mineralization.Acta Chimica Sinica.2008;66(18):2059-2064.[10] Li Y,Cai Y,Kong X,et al.Anisotropic growth of hydroxyapatite on the silk fibroin films.Appl Surf Sci.2008;255 (5):1681-1685[11] Du C, Jin J, Li Y,et al. Novel silk fibroin/ hydroxyapatite composite films: Structure and properties.Mat Sci Eng C. 2009; 29(1): 62-68.[12] Liu L,Kong XD,Li YC,et al.Effect of Pretreated Silk Fibroin Films on the Regulation of Hydroxyapatite Crystal Growth. Chem J Chin Univ.2009;30(10): 1987-1991. [13] Yao JM, Wei KM, Li L, et al.E Effect of initial bombyx mori silk fibroin structure on the protein biomineralization.Acta Chim Sin.2007;65(7):635-639.[14] Kong XD, Sun XD, Cui FZ, et al. Effect of solute concentration on fibroin regulated biomineralization of calcium phosphate. Mater Sci Eng C.2006;26(4): 639-643.[15] Sun XD,Zhou YL,Ren JY,et al.Effect of pH on the fibroin regulated mineralization of calcium phosphate.Curr Appli Phy. 2007;7(S1):75-79. |