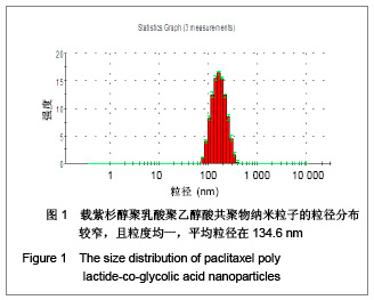
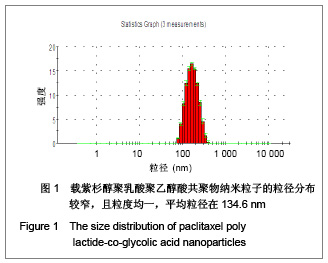
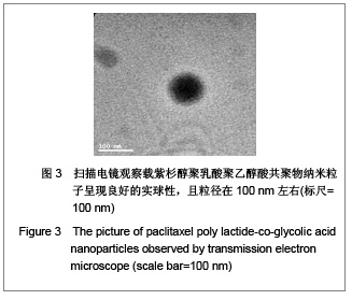
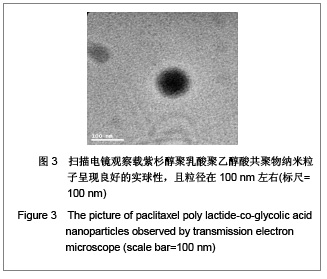
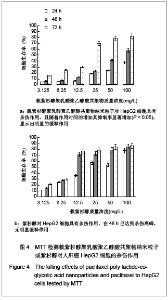
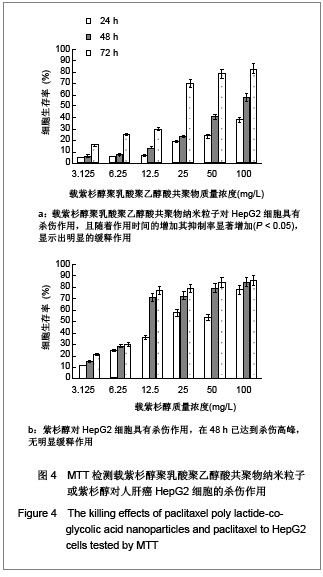
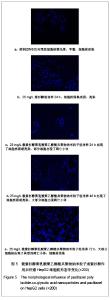
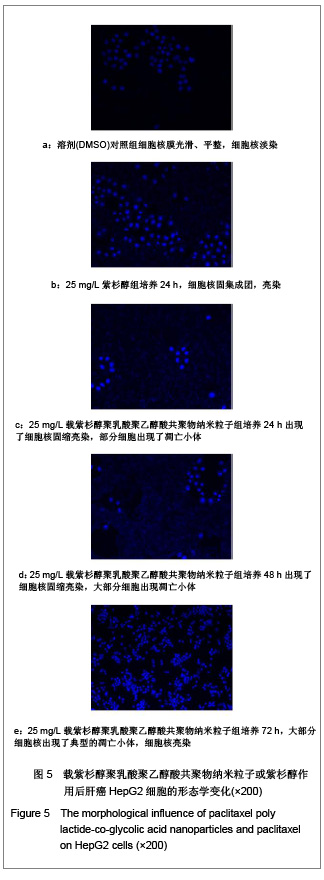
| [1] Wu B,Yang ZF.Zhongguo Yaoye.2004;13(6):77-78. 伍彬,杨宗发.紫杉类药物药理及临床研究进展[J].中国药业, 2004, 13(6):77-78.[2] Xu M,Takanashi M,Oikawa K,et al.Identification of a novel role of Septin 10 in paclitaxel-resistance in cancers through a functional genomics screen. Cancer Sci.2012; 103(4): 821-827. [3] Dong XL,Xu PF,Miao C,et al.Hypoxia decreased chemosensitivity of breast cancer cell line MCF-7 to paclitaxel through cyclin B1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2012;66(1):70-75.[4] Li S,Liao H,Zhan J,et al.Zhongguo Linchuang Yaolixue Zazhi. 2008;26(8):606-610. 李苏,廖海,詹靖,等.比较白蛋白纳米紫杉醇与含聚氧乙烯蓖麻油紫杉醇在乳腺癌患者的药代动力学[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2008,26(8):606-610.[5] Ma GL,Miao Bl,Song CX.Thermosensitive PCL-PEG-PCL hydrogels:Synthesis, characterization, and delivery of proteins. J Appl Polym Sci.2010;116(4):1985-1993.[6] Xu YJ.Suzhou Daxue.2008. 许玉杰.新型紫杉醇脂质纳米粒的临床前实验研究[D].苏州大学博士论文,2008.[7] Lee KC,Maturo C,Rodriguez R,et al. Nanomedicine-nanoemulsion. Formulation improves safety and efficacy of the anti-cancer drag paclitaxel according to preclinical assessment.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2011; 11(8): 6642-6656.[8] Yang J,Bao B,Chen YX,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(16):2869-2874. 杨菁,鲍彬,陈永霞,等. 紫杉醇纳米粒子的制备及其应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(16):2869-2874.[9] Gong C,Shi S,Wu L,et al.Biodegradable in situ gel-forming controlled drug delivery system based on thermosensitive PCL-PEG-PCL hydrogel. Part 2: sol-gel-sol transition and drug delivery behavior.Acta Biomater.2009;5(9):3358-3370.[10] Bea SJ,Suh JM,Sohn YS,et al.Thermogelling Poly(caprolactone-b-ethylene glycol-b-caprolactone)aqueous solutions. Macromolecules.2005;38(12):5260-5265.[11] Chao G,Fan L,Jia W,et al.Synthesis,characterization and hydrolytic degradation of degrable poly(butylene terephthalate)/poly(ethlene glycol)(PBT/PEG)copolymers. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2007;18(3):449-455.[12] Jeong B,Bae YH,Lee DS,et al. Biodegradable block copolymers as injectable drug- delivery system.Nature. 1997;388(6645):860-862.[13] Ron ES,Bromberg LE.Temperature-responsive gels and thermogelling polymer matrices for protein and peptide delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.1998;31(3):197-221.[14] Dong Y,Feng SS. Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactide)(MPEG-PLA)nanoparticles for controlled delivery of anticancer drugs.Biomaterials.2014; 25(14): 2843-2849.[15] Sinha VR,Bansal K,Kaushik R,et al.Poly-epsilon-caprolactone microspheres and nanospheres :an overview.Int J Pharm. 2004;278(1):1-23.[16] Espuelas MS,Legrand P,Lrache JM,et al.Puly(epsihm caprolacton) nanospheres as an alternative way to reduce amphotericin B toxicity.Int J Pharm.1997;158(1):19-27.[17] Yang J,Zeng Y,Li Y,et al.Intravascular site-specific delivery of a therapeutic antisense for the inhibition of restenosis.Eur J Pharm Sci.2008;35(5):427-434.[18] Pan QC,Xu B.Zhengzhou:Henan Yike Daxue Chubanshe. 2000:55. 潘启超,胥彬.肿瘤药理学与化学治疗学[M].郑州:河南医科大学出版社,2000:55.[19] Hickman JA.Apoptosis and chemotherspy resistance.Eur J Cancer.1996;32:921.[20] Bhalla K,Huany Y,Tang C,et al.Taxol induces intemucleosomal DNA fragmentation associated with programmed cell death in human myeloid leukemia cell. Leukemia.1993;7:563.[21] Donaldson KL,Goolsby G,Kiener PA,et al. Activation of p34cdc2 coincident with taxol-induced apoptosis.Cell Growth Differ.1994;5:1041.[22] Chen LR,Zheng S, Willingham MC,et al.Zhonghua Zhongliu Zazhi.1997;19(2):103. 陈丽荣,郑树,Willingham MC,等.紫杉醇诱发人乳癌细胞凋亡的机制研究[J].中华肿瘤杂志,1997,19(2):103. |