Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (36): 5832-5837.doi: 10.12307/2021.351
Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluation of natural resorption of herniated cervical intervertebral disc with different degrees of degeneration after cervical microendoscopic laminoplasty by three-dimensional volume method
Li Long, Zhang Chunlin, Shao Chenglong, Yan Xu, Wang Yongkui, Liu Xiaokang, Li Dongzhe
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2021-02-01Revised:2021-02-05Accepted:2021-03-31Online:2021-12-28Published:2021-09-18 -
Contact:Zhang Chunlin, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Li Long, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Long, Zhang Chunlin, Shao Chenglong, Yan Xu, Wang Yongkui, Liu Xiaokang, Li Dongzhe. Evaluation of natural resorption of herniated cervical intervertebral disc with different degrees of degeneration after cervical microendoscopic laminoplasty by three-dimensional volume method[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5832-5837.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
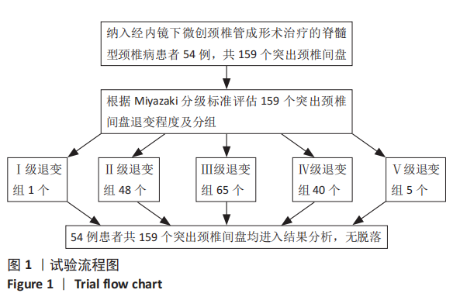
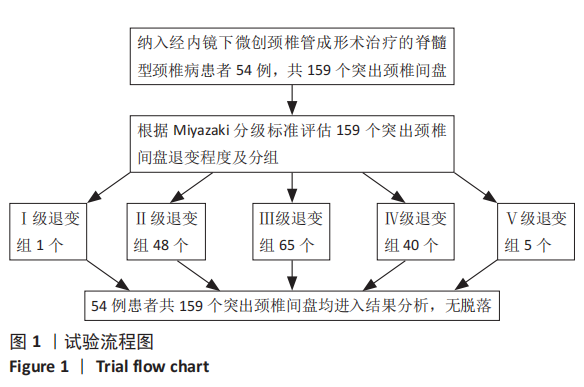
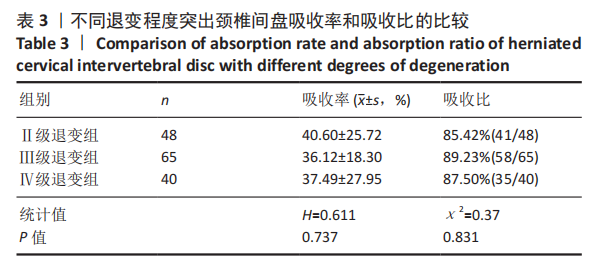
2.4 CMEL术后椎间盘退变等级的变化 139个发生RHNP的突出颈椎间盘中有77.70%(108/139)的退变等级无变化,另有22.30%(31/139)会发生退变等级增加,其中Ⅱ级变Ⅲ级22个,Ⅲ级变Ⅳ级9个。 2.5 临床疗效 54例脊髓型颈椎病患者疗效优者20例,良27例,可7例,优良率87%。 2.6 典型病例 病例1:患者女,38岁,以“颈痛伴双上肢麻木14个月,加重1个月 ”为主诉入院。MRI显示C3/4,C4/5,C5/6,C6/7盘突出(图2A),颈脊髓受压。依照Miyazaki分级,退变等级分别为Ⅱ级、Ⅱ级、Ⅲ级、Ⅲ级。C3/4,C4/5,C5/6,C6/7突出椎间盘体积分别是399.33,335.99,543.25,293.86 mm3(图2C)。行CMEL治疗后6个月随访MRI示,C3/4,C4/5,C5/6,C6/7盘退变等级未发生变化,突出椎间盘体积明显缩小(图2B),分别是189.19,133.11,233.58,23.96 mm3(图2D),吸收率分别是52.62%,60.38%,57%,90.31%。"
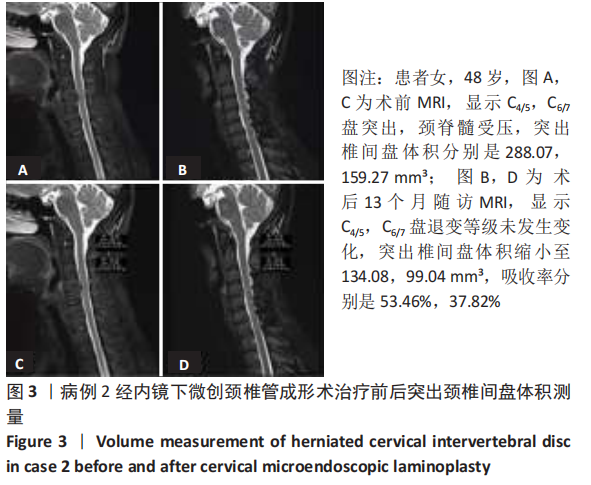
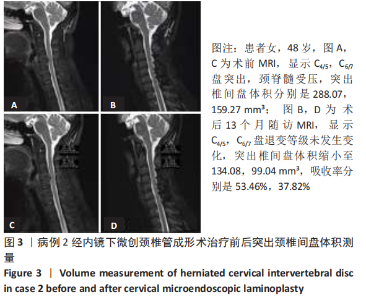
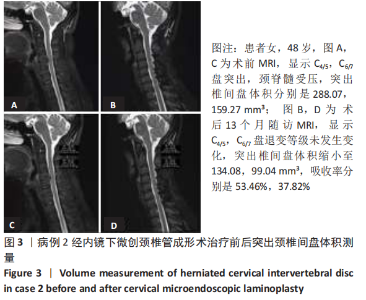
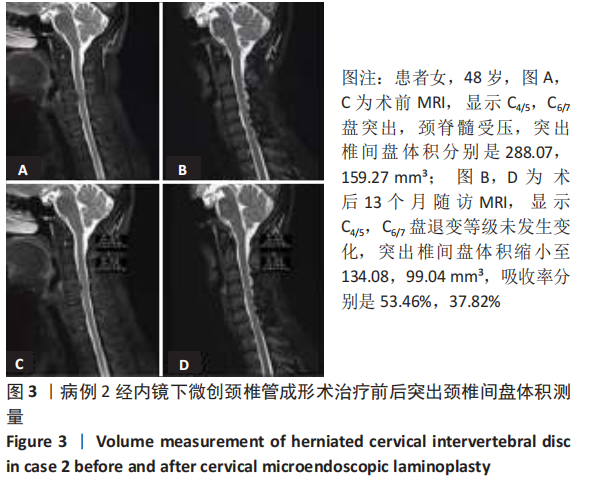
病例2:患者女,48岁,以“双下肢无力2年余,加重伴行走不稳2个月”为主诉入院,由于该患者不愿行颈前路及其他治疗方案,经知情同意并告知相关风险后要求行后路手术。MRI显示C4/5,C6/7盘突出(图3A),颈脊髓受压。依照Miyazaki分级,退变等级分别为Ⅱ级,Ⅱ级。C4/5,C6/7突出椎间盘的体积分别是288.07,159.27 mm3(图3C)。行CMEL治疗后13个月随访MRI示,C4/5,C6/7盘退变等级分别为Ⅲ级,Ⅲ级,突出椎间盘体积明显缩小(图3B),分别是134.08,99.04 mm3(图3D),吸收率分别是53.46%,37.82%。 2.7 生物相容性 颈椎后路钉板固定系统材料生物相容性良好,随访期间未发生感染、排斥等材料宿主反应。"
| [1] 潘敏,吴毅文.脊髓型颈椎病344例临床特征分析[J].中国临床康复, 2005,9(38):78-80. [2] 陈雄生,贾连顺,袁文,等.脊髓型颈椎病自然史规律研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2002,10(13):1301-1304. [3] MCCORMICK JR, SAMA AJ, SCHILLER NC, et al. Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: A Guide to Diagnosis and Management. J Am Board Fam Med. 2020;33:303-313. [4] LEBL DR, BONO CM. Update on the Diagnosis and Management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23:648-660. [5] PASSIAS PG, MARASCALCHI BJ, BONIELLO AJ. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: National trends in the treatment and peri-operative outcomes over 10years. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;42:75. [6] 贾连顺,史建刚.重视脊髓型颈椎病的诊断与严格手术指征[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(1):57-59. [7] 侯增涛,赵爱琳,郭传友,等.多节段脊髓型颈椎病治疗方式选择与疗效评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(40):6444-6450. [8] ZHANG C, LI D, WANG C, et al. Cervical Endoscopic Laminoplasty for Cervical Myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41 Suppl 19:B44-B51. [9] 张春霖,张银鹤,严旭,等.内镜下颈椎管成形术治疗脊髓型颈椎病[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(2):89-95. [10] 张春霖,刘洋,尚利杰,等.基于PACS软件定量体积测量“监控”的突出颈椎间盘体积观察[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(18): 2888-2892. [11] 吴彦禹,张春霖,邵成龙,等.二维距离法和三维体积法对内镜下微创颈椎管成形后突出椎间盘再吸收的定量测量[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(21):3390-3394. [12] 李莹,王永魁,尚利杰,等.颈后路微创椎管扩大成形术对颈椎间盘退变的影响[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2020,55(2):278-281. [13] 李莹,李龙,严旭,等.内镜下微创颈椎管成形术”诱导”突出颈椎间盘自然吸收的初步观察[J].中国实用医刊,2020,47(10):15-19. [14] MOCHIDA K, KOMORI H, OKAWA A, et al. Regression of cervical disc herniation observed on magnetic resonance images. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(9):990-995. [15] AUTIO RA, KARPPINEN J, NIINIMAKI J, et al. Determinants of spontaneous resorption of intervertebral disc herniations. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(11):1247-1252. [16] MIYAZAKI M, HONG SW, YOON SH, et al. Reliability of a magnetic resonance imaging-based grading system for cervical intervertebral disc degeneration. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008;21(4):288-292. [17] NAKASHIMA H, YUKAWA Y, SUDA K, et al. Cervical Disc Protrusion Correlates With the Severity of Cervical Disc Degeneration: A Cross-Sectional Study of 1211 Relatively Healthy Volunteers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(13):E774-779. [18] TAKASHIMA H, TAKEBAYASHI T, YOSHIMOTO M, et al. Correlation between T2 relaxation time and intervertebral disk degeneration. Skeletal Radiol. 2012;41:163-167. [19] MIYAZAKI M, HONG SW, YOON SH, et al. Kinematic analysis of the relationship between the grade of disc degeneration and motion unit of the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(2):187-193. [20] HENMI T, SAIRYO K, NAKANO S, et al. Natural history of extruded lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. J Med Invest. 2002;49(1-2):40-43. [21] HARO H, KATO T, KOMORI H, et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-induced Angiogenesis in Herniated Disc Resorption. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(3):409. [22] GEISS A, SOBOTTKE R, DELANK KS, et al.Plasmacytoid dendritic cells and memory T cells infiltrate true sequestrations stronger than subligamentous sequestrations: evidence from flow cytometric analysis of disc infiltrates. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(5):1417-1427. [23] TSURU M, NAGATA K, UENO T, et al.Electron microscopic observation of established chondrocytes derived from human intervertebral disc hernia (KTN-1) and role of macrophages in spontaneous regression of degenerated tissues. Spine J. 2001;1(6):422-431. [24] ZHU Y, LIU JT, YANG LY, et al. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibition modulates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis in spontaneous resorption of herniated intervertebral discs: An experimental study in rats. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(5):4001-4006. [25] HARO H, KOMORI H, KATO T, et al. Experimental studies on the effects of recombinant human matrix metalloproteinases on herniated disc tissues--how to facilitate the natural resorption process of herniated discs. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(2):412-419. [26] 张天宏,彭笳宸,李青,等.突出的椎间盘组织中巨噬细胞浸润及免疫复合物表达[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(Z1):87-88. [27] 宫良泰,许复郁,宋若先,等.免疫反应在实验性游离型腰椎间盘突出自然吸收中的意义[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2002,40(6): 533-534+539. [28] KATO T, HARO H, KOMORI H, et al. Sequential dynamics of inflammatory cytokine, angiogenesis inducing factor and matrix degrading enzymes during spontaneous resorption of the herniated disc. J Orthop Res. 2004; 22:895-900. [29] 钟远鸣,史明,许建文.椎间盘突出组织自然吸收的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(16):1236-1238. [30] AUTIO RA, KARPPINEN J, KURUNLAHTI M, et al. Effect of periradicular methylprednisolone on spontaneous resorption of intervertebral disc herniations. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29:1601-1607. [31] WILSON W, DONKELAAR CC, HUYGHE JM. A comparison between mechano-electrochemical and biphasic swelling theories for soft hydrated tissues. J Biomech Eng. 2005;127:158-165. [32] HUSSAIN M, NATARAJAN RN, CHAUDHARY G, et al. Relative contributions of strain-dependent permeability and fixed charged density of proteoglycans in predicting cervical disc biomechanics: a poroelastic C5-C6 finite element model study. Med Eng Phys. 2011; 33:438-445. [33] IATRIDIS JC, LAIBLE JP, KRAG MH. Influence of fixed charge density magnitude and distribution on the intervertebral disc: applications of a poroelastic and chemical electric (PEACE) model. J Biomech Eng. 2003;125:12-24. [34] GU WY, YAO H. Effects of hydration and fixed charge density on fluid transport in charged hydrated soft tissues. Ann Biomed Eng. 2003;31: 1162-1170. [35] BALDONI M, GU WY. Effect of fixed charge density on water content of IVD during bed rest: A numerical analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2019;70:72-77. [36] SOWA GA, COELHO JP, BELL KM, et al. Alterations in gene expression in response to compression of nucleus pulposus cells. Spine J. 2011; 11:36-43. [37] MACLEAN JJ, LEE CR, ALINI M, et al. The effects of short-term load duration on anabolic and catabolic gene expression in the rat tail intervertebral disc. J Orthop Res. 2005;23:1120-1127. [38] SLAVIN KV, RAJA A, THORNTON J, et al. Spontaneous regression of a large lumbar disc herniation: report of an illustrative case. Surg Neurol. 2001;56:333-336;discussion 337. [39] BOZZAO A, GALLUCCI M, MASCIOCCHI C, et al. Lumbar disk herniation: MR imaging assessment of natural history in patients treated without surgery. Radiology. 1992;185:135-141. [40] YANG B, WENDLAND MF, OCONNEL GD. Direct Quantification of Intervertebral Disc Water Content Using MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;52:1152-1162. [41] ANTONIOU J, STEFFEN T, NELSON F, et al. The human lumbar intervertebral disc: evidence for changes in the biosynthesis and denaturation of the extracellular matrix with growth, maturation, ageing, and degeneration. J Clin Invest. 1996;98:996-1003. [42] LEE TH, KIM SJ, LIM SM. Prevalence of disc degeneration in asymptomatic korean subjects. Part 2 : cervical spine. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2013;53:89-95. [43] MIKI T, NAOKI F, TAKASHIMA H, et al. Associations between Paraspinal Muscle Morphology, Disc Degeneration, and Clinical Features in Patients with Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Prog Rehabil Med. 2020;5: 20200015. [44] CORNIOLA MV, STIENEN MN, JOSWIG H, et al. Correlation of pain, functional impairment, and health-related quality of life with radiological grading scales of lumbar degenerative disc disease. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2016;158:499-505. |
| [1] | Yang Xiaoxiao, Xu Yuanjing, Li Wentao, Wang Wenhao, Ma Zhenjiang, Wang Jinwu. Experimental study on treatment of Achilles tendinitis with ultrasound-guided phacoemulsification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Yao Rubin, Wang Shiyong, Yang Kaishun. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis improves lumbar-pelvic balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1387-1392. |
| [3] | Liu Zhengpeng, Wang Yahui, Zhang Yilong, Ming Ying, Sun Zhijie, Sun He. Application of 3D printed interbody fusion cage for cervical spondylosis of spinal cord type: half-year follow-up of recovery of cervical curvature and intervertebral height [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 849-853. |
| [4] | Zhang Lei, Ma Li, Fu Shijie, Zhou Xin, Yu Lin, Guo Xiaoguang. Arthroscopic treatment of greater tuberosity avulsion fractures with anterior shoulder dislocation using the double-row suture anchor technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 895-900. |
| [5] | Luo Xuanxiang, Jing Li, Pan Bin, Feng Hu. Effect of mecobalamine combined with mouse nerve growth factor on nerve function recovery after cervical spondylotic myelopathy surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 719-722. |
| [6] | Fu Shuanhu, Qin Kai, Lu Dahan, Qin Haibiao, Gu Jin, Chen Yongxi, Qin Haoran, Wei Jiading, Wu Liang, Song Quansheng. Lumbar spinal tuberculosis implanted with artificial bone with streptomycin sulfate and percutaneous pedicle screw under transforaminal endoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 493-498. |
| [7] | Cai Xuan, Qin Jie, He Xijing, Dong Jun, Zhang Ting, Yang Wenlong, Wang Xiongxun, Wang Zili, Wang Dong, Li Haopeng, He Gaole, Lu Teng, Li Lingjiang. Three-dimensional printing motion-preserving cervical joint system implantation for treatment of cervical myelopathy: the first case report [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5810-5813. |
| [8] | Xiong Chen, He Guiping, Zhang Kun, He Xiao, Yang Jiarui, He Changjun, Wang Xiaolong, Wang Chen, Shi Zhengwei, Zhu Yangjun, Heng Lisong. Conservative treatment, open reduction, percutaneous minimally invasive plate internal fixation and intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of humeral shaft fractures: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5878-5887. |
| [9] | Yu Yang, Xie Yizhou, Shi Yin, Wu Weidong, Gu Dangwei, Fan Xiaohong. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the biomechanics of the posterior segment of lumbar facet arthroplasty with different sizes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5288-5293. |
| [10] | Zhang Weicheng, Li Rongqun, Wu Mingzhou, Zheng Kai, sun houyi, Zhang Lianfang, Zhou Jun, Xu Yaozeng. Comparison of one-stage bilateral total hip arthroplasty between SuperPATH approach and posterolateral approach based on enhanced recovery after surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5312-5317. |
| [11] | Zhao Lingtong, Hu Bing. Modified open-door laminoplasty with preserved posterior cervical musculo-ligamentous complex in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: neurological function and axial symptoms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5345-5350. |
| [12] | Zhang Chunlin, Zhao Xiao, Yan Xu, Ning Yongming, Cao Zhengming. Cervical microendoscopic laminoplasty and intervertebral disc resorption after conservative treatment assessed with three-dimensional volume method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(30): 4774-4780. |
| [13] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Zhu Zhenqi, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of sciatic scoliosis caused by lumbar disc herniation: a 2-year follow-up of coronal and sagittal balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 409-413. |
| [14] | Cui Guanyu, Shu Xiong, Liu Yajun, Sun Yuqing, He Da, Liu Bo, Tian Wei. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for the treatment of high iliac crest L5/S1 disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(27): 4333-4338. |
| [15] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||