Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (27): 4421-4428.doi: 10.12307/2021.207
Total hip arthroplasty versus artificial femoral head replacement for the effect of displaced femoral neck fracture: a meta-analysis of 14 randomized controlled trials
Lü Hui, Huang Denghua, Zou Longfei, Xue Hao, Xie Zonghui, Yu Peigen, Tan Meiyun
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2020-11-17Revised:2020-11-19Accepted:2020-12-25Online:2021-09-28Published:2021-04-10 -
Contact:Tan Meiyun, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Lü Hui, Master candidate, physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lü Hui, Huang Denghua, Zou Longfei, Xue Hao, Xie Zonghui, Yu Peigen, Tan Meiyun. Total hip arthroplasty versus artificial femoral head replacement for the effect of displaced femoral neck fracture: a meta-analysis of 14 randomized controlled trials[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(27): 4421-4428.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

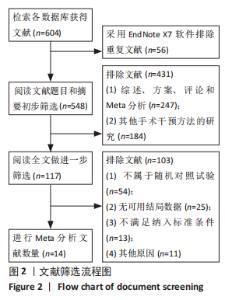
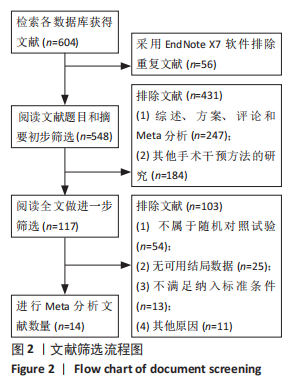
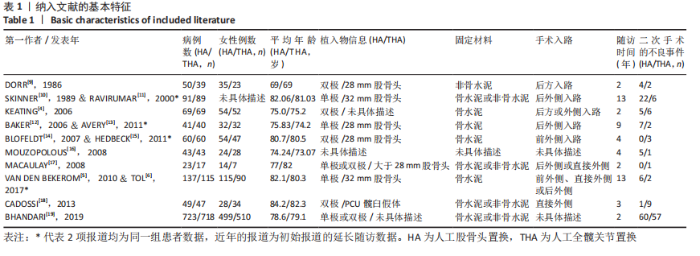
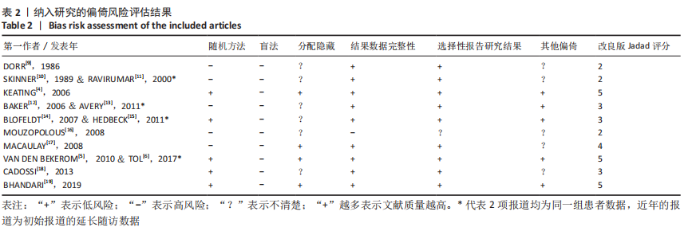
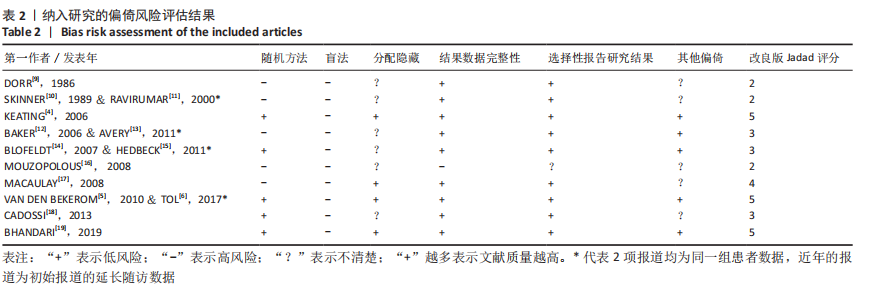
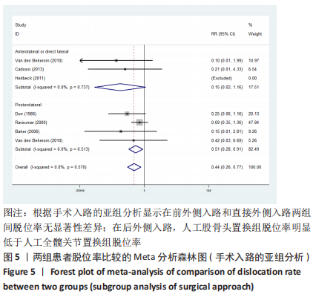
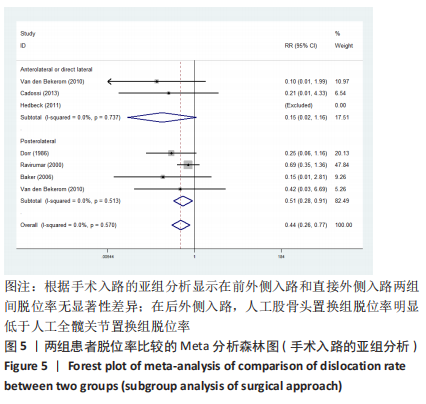
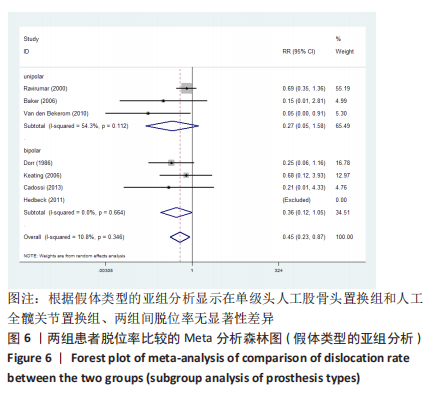
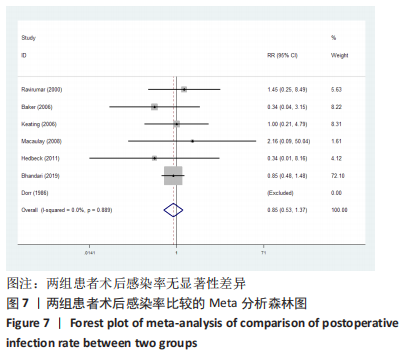
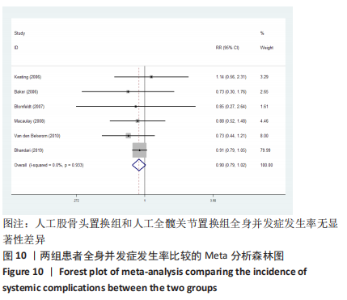
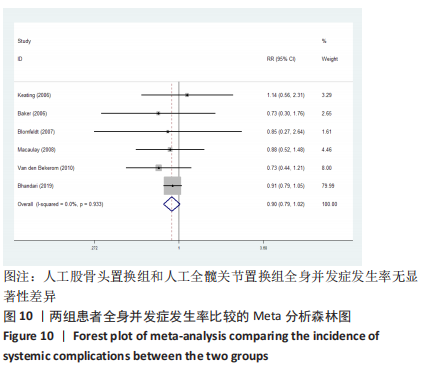
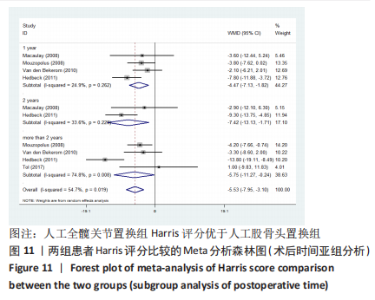
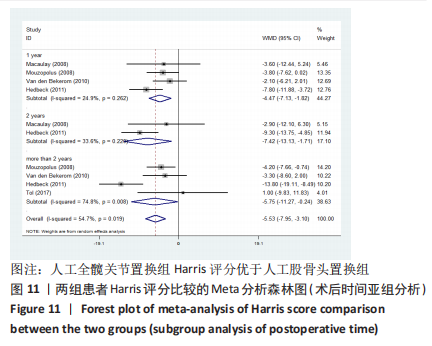
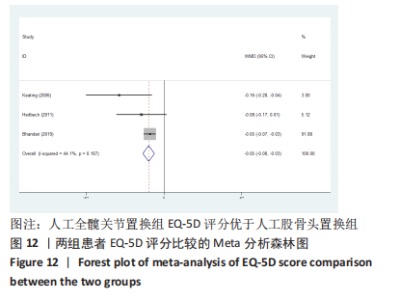
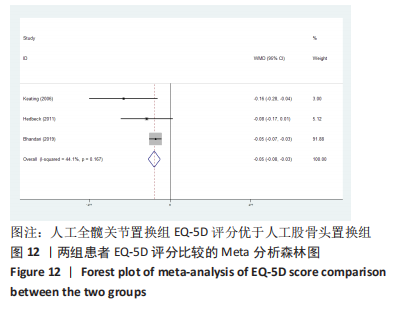
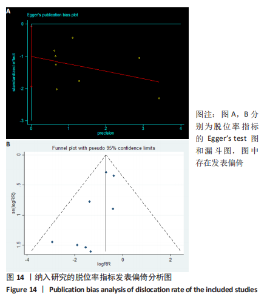
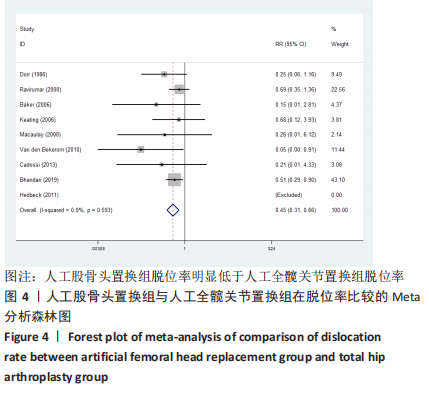
2.3.2 各组髋关节脱位率差异 共9项研究报道了脱位的数据[4-5,9,11-12,15,17-19]。研究结果未发现异质性(I2=0%,P=0.593),通过固定效应模型分析显示,人工股骨头置换组脱位率明显低于人工全髋关节置换组(RR=0.450,95%CI:0.306-0.661,P < 0.001),见图4;根据患者手术入路进行分组,并进行亚组分析。其中前外侧入路或直接前入路组,共纳入3项研究[5,15,18],人工股骨头置换组脱位率为0%(0/233),而人工全髋关节置换组脱位率为2.56%(5/195),未发现异质性(I2=0%,P=0.737),通过固定效应模型分析显示,两组间脱位率无显著性意义(RR=0.145,95%CI:0.018-1.159,P=0.069);在后外侧入路或后入路组中,共纳入4项研究[5,9,11-12],共计377例患者,人工股骨头置换组脱位率为7.49%(14/187),而人工全髋关节置换组脱位率为17.3%(33/190),未发现异质性(I2=0%,P=0.513),通过固定效应模型分析显示,人工股骨头置换组脱位率明显低于人工全髋关节置换组(RR=0.507,95%CI:0.284-0.907,P=0.022),见图5;根据患者半髋假体类型进行亚组分析,单级头人工股骨头置换组和人工全髋关节置换组 (RR=0.269,95%CI:0.046-1.580,P=0.146) [5,11,13]、双极头人工股骨头置换组和人工全髋关节置换组(RR=0.357,95%CI:0.122-1.046,P=0.060),两组间脱位率均无显著性差异[4,9,15,18],见图6。"
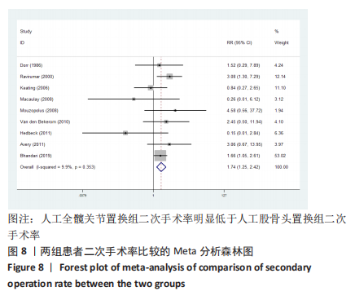
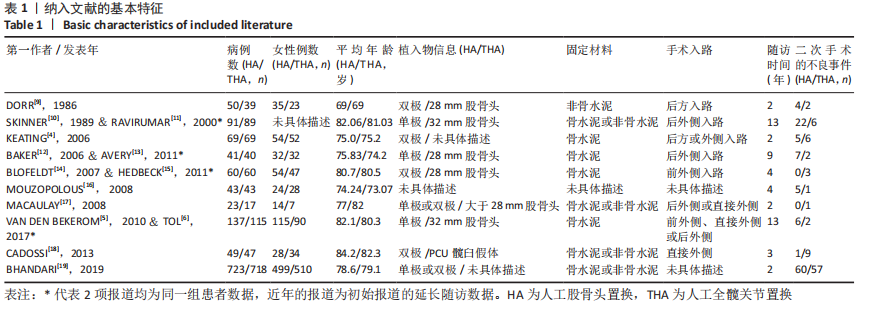
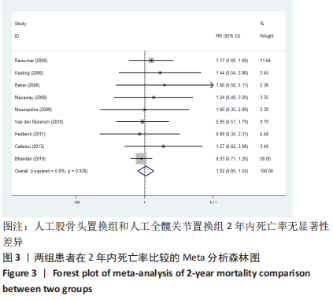
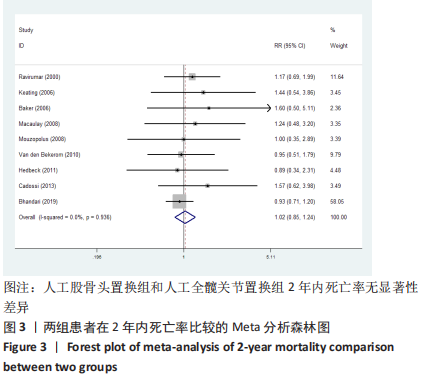
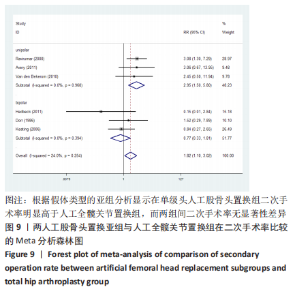
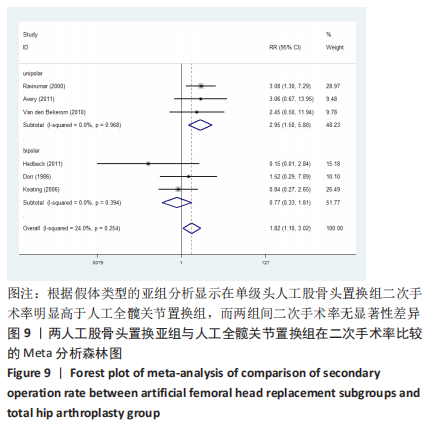
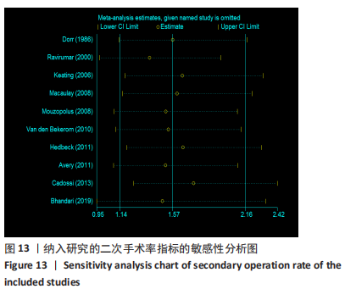
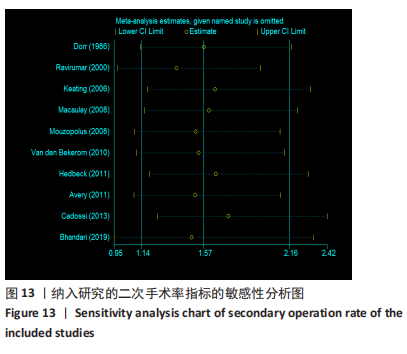
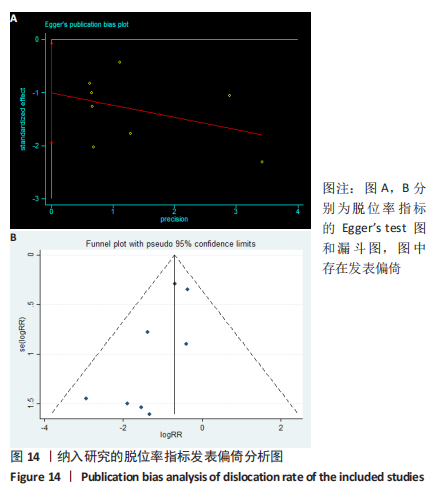
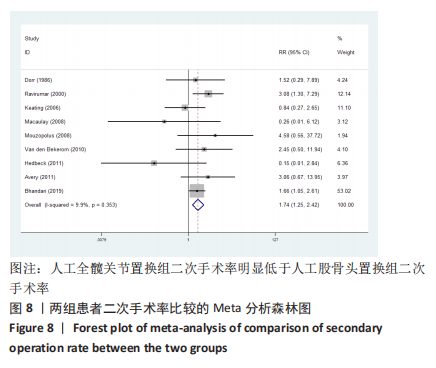
2.3.4 各组二次手术率差异 共9项研究报道了二次手术的数据[4-5,9,11,13,15-17,19]。人工股骨头置换组二次手术率为7.84%(97/1237),人工全髋关节置换组二次手术率为4.29%(51/1190)。存在异质性(I2=9.9%,P=0.353),通过固定效应模型分析显示,人工全髋关节置换组二次手术率明显低于人工股骨头置换组二次手术率(RR=1.741,95%CI:1.253-2.419,P=0.001),见图8;根据患者半髋假体类型进行亚组分析,显示在单级头人工股骨头置换组二次手术率明显高于人工全髋关节置换组(RR=2.951,95%CI:1.501-5.801,P=0.002) [5,11,13],而两组患者二次手术率无显著性差异(RR=0.797,95%CI:0.403-1.575,P=0.514) [4,9,15],见图9。"
| [1] 梁玉柱,郭洪刚.老年骨质疏松性髋部骨折:昨天、今天及未来[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(15):2438-2443. [2] BURGE R, DAWSON-HUGHES B, SOLOMON D, et al. Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005-2025. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;22(3):465-475. [3] BHANDARI M, DEVEREAUX P, TORNETTA P, et al. Operative management of displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients. An international survey. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(9):2122-2130. [4] KEATING J, GRANT A, MASSON M, et al. Randomized comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty, and total hip arthroplasty. Treatment of displaced intracapsular hip fractures in healthy older patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(2):249-260. [5] VAN DEN BEKEROM M, HILVERDINK E, SIEREVELT I, et al. A comparison of hemiarthroplasty with total hip replacement for displaced intracapsular fracture of the femoral neck: a randomised controlled multicentre trial in patients aged 70 years and over. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(10):1422-1428. [6] TOL M, VAN DEN BEKEROM M, SIEREVELT I, et al. Hemiarthroplasty or total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of a displaced intracapsular fracture in active elderly patients: 12-year follow-up of randomised trial. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B:250-254. [7] LEWIS D, Wæver D, THORNINGER R, et al. Hemiarthroplasty vs total hip arthroplasty for the management of displaced neck of femur fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(8):1837-1843.e2. [8] JADAD A, MOORE R, CARROLL D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1):1-12. [9] DORR L, GLOUSMAN R, HOY A, et al. Treatment of femoral neck fractures with total hip replacement versus cemented and noncemented hemiarthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1986;1(1):21-28. [10] SKINNER P, RILEY D, ELLERY J, et al. Displaced subcapital fractures of the femur: a prospective randomized comparison of internal fixation, hemiarthroplasty and total hip replacement. Injury. 1989;20(5):291-293. [11] RAVIKUMAR K, MARSH G. Internal fixation versus hemiarthroplasty versus total hip arthroplasty for displaced subcapital fractures of femur-13 year results of a prospective randomised study. Injury. 2000;31(10):793-797. [12] BAKER R, SQUIRES B, GARGAN M, et al. Total hip arthroplasty and hemiarthroplasty in mobile, independent patients with a displaced intracapsular fracture of the femoral neck. A randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(12):2583-2589. [13] AVERY P, BAKER R, WALTON M, et al. Total hip replacement and hemiarthroplasty in mobile, independent patients with a displaced intracapsular fracture of the femoral neck: a seven- to ten-year follow-up report of a prospective randomised controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(8):1045-1048. [14] BLOMFELDT R, T RNKVIST H, ERIKSSON K, et al. A randomised controlled trial comparing bipolar hemiarthroplasty with total hip replacement for displaced intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89(2):160-165. [15] HEDBECK C, ENOCSON A, LAPIDUS G, et al. Comparison of bipolar hemiarthroplasty with total hip arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: a concise four-year follow-up of a randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93(5):445-450. [16] MOUZOPOULOS G, STAMATAKOS M, ARABATZI H, et al. The four-year functional result after a displaced subcapital hip fracture treated with three different surgical options. Int Orthop. 2008; 32(3):367-373. [17] MACAULAY W, NELLANS K, GARVIN K, et al. Prospective randomized clinical trial comparing hemiarthroplasty to total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures: winner of the Dorr Award. J Arthroplasty. 2008; 23:2-8. [18] CADOSSI M, CHIARELLO E, SAVARINO L, et al. A comparison of hemiarthroplasty with a novel polycarbonate-urethane acetabular component for displaced intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck: a randomised controlled trial in elderly patients. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B:609-615. [19] HEALTH Investigators, Bhandari M, Einhorn TA, et al. Total hip arthroplasty or hemiarthroplasty for hip fracture. N Engl J Med, 2019;381(23):2199-208. [20] SIM F, STAUFFER R. Management of hip fractures by total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;152:191-197. [21] SAYANA M, LAKSHMANAN P, PEEHAL J, et al. Total hip replacement for acute femoral neck fracture: a survey of National Joint Registries. Acta orthop Belg. 2008;74(1):54-58. [22] HANSSON S, B LOW E, GARLAND A, et al. More hip complications after total hip arthroplasty than after hemi-arthroplasty as hip fracture treatment: analysis of 5,815 matched pairs in the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register. Acta orthop. 2020;91(2):133-138. [23] HAILER N, GARLAND A, ROGMARK C, et al. Early mortality and morbidity after total hip arthroplasty in patients with femoral neck fracture. Acta Orthop. 2016;87(6):560-566. [24] Hip fracture: the management of hip fracture in adults . NICE clinical guideline 124; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. 2011. [25] BURGERS PT, VAN GEENE AR, VAN DEN BEKEROM MP, et al. Total hip arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures in the healthy elderly: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized trials. Int Orthop. 2012;36(8):1549-1560. [26] ZI-SHENG A, YOU-SHUI G, ZHI-ZHEN J, et al. Hemiarthroplasty vs primary total hip arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the femoral neck in the elderly: a meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2012; 27(4):583-590. [27] LIAO L, ZHAO J, SU W, et al. A meta-analysis of total hip arthroplasty and hemiarthroplasty outcomes for displaced femoral neck fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(7):1021-1029. [28] SVEN YS, WESTBERG M, FIGVED W, et al. Posterior versus lateral approach for hemiarthroplasty after femoral neck fracture: early complications in a prospective cohort of 583 patients. Injury. 2017;48(7):1565-1569. [29] DIMITRIOU D, HELMY N, HASLER J, et al. The role of total hip arthroplasty through the direct anterior approach in femoral neck fracture and factors affecting the outcome. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(1):82-87. [30] ENOCSON A, HEDBECK C, TIDERMARK J, et al. Dislocation of total hip replacement in patients with fractures of the femoral neck. Acta Orthop. 2009;80(2):184-189. [31] RAVI B, PINCUS D, KHAN H, et al. Comparing complications and costs of total hip arthroplasty and hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fractures: a propensity score-matched, population-based study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(7):572-579. |
| [1] | Xu Xinzhong, Wu Zhonghan, Yu Shuisheng, Zhao Yao, Xu Chungui, Zhang Xin, Zheng Meige, Jing Juehua. Biomechanical analysis of different ways of inserting Steinmann Pins into the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Li Huo, Wang Peng, Gao Jianming, Jiang Haoran, Lu Xiaobo, Peng Jiang. Relationship between revascularization and internal microstructure changes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1323-1328. |
| [3] | Li Rui, Shi Wen, Yang Shicai, Lü Linwei, Zhang Chunqiu. Effect of splintage and Shenxiaosan cataplasm on fracture healing in rabbits with radial fracture model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1329-1333. |
| [4] | Yuan Jiabin, Zhu Zongdong, Tang Xiaoming, Wei Dan, Tan Bo, Xiao Chengwei, Zhao Ganlinwei, Liao Feng. Classification and reduction strategies for irreducible intertrochanteric femoral fracture based on anatomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1341-1345. |
| [5] | Liu Feng, Feng Yi. Finite element analysis of different Kirschner wire tension bands on transverse patella fractures during gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1367-1371. |
| [6] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [7] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [8] | Yu Chengxiang, Liu Lehong, Li Wenbo, Chen Jinshi, Ran Chunlei, Wang Zhongping. Correlation between spine-pelvic sagittal parameters and prognosis of vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1412-1417. |
| [9] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [10] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [11] | Li Canhui, Wu Zhengjie, Zeng Yanhui, He Yinghao, Situ Xiaopeng, Du Xuelian, Hong Shi, He Jiaxiong. Advantage and disadvantage of robot-assisted sacroiliac screw placement and traditional fluoroscopy in orthopedic surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1434-1438. |
| [12] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [13] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [14] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| [15] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||