[1] RYOJI T, SHIRO I, ZENYA I, et al. Complications and outcomes of posterior fusion in children with atlantoaxial instability. Eur Spine J. 2012;21:1346-1352.
[2] OMAR A, EMELINE B, DIDIER L, et al. Pediatric cervical spine in emergency: radiographic features of normal anatomy,variants and pitfalls. Skeletal Radiol. 2016;45:1607-1617.
[3] GARRIDO BJ, SASSO RC. Occipitocervical fusion. Orthop Clin North Am. 2012;43:(1):1-9.
[4] BAILEY CS, FISHER CG, BOYD MC, et al. En bloc marginal excision of a multilevel cervical chordoma: case report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006; 4(5):409-414.
[5] RHINES LD, FOURNEY DR, SIADATI A, et al. En bloc resection of multilevel cervical chordoma with C -2 involvement: case report and description of operative technique. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2(2):199-205.
[6] SAR C, ERALP L. Transoral resection and reconstruction for primary osteogenic sarcoma of the second cervical vertebra. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(17):1936-1941.
[7] JI W, TONG J, HUANG ZP, et al. A clivus plate fifixation for reconstruction of ventral defect of the craniovertebral junction: a novel fifixation device for craniovertebral instability. Eur Spine J. 2015;24:1658-1665.
[8] JI W, WANG XY, XU HZ, et al. The anatomic study of clival screw fixation for the craniovertebral region. Eur Spine J. 2012;21:1483-1491.
[9] DHALIWAL PP, HURLBERT RJ, SUTHERLAND GS. Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging and neuronavigation for transoral approaches to upper cervical pathology. Neurosurg. 2012;78:164-169.
[10] LAINE T, LUND T, YLIKOSKI M, et al. Accuracy of pedicle screw insertion with and without computer assistance: a randomised controlled clinical study in 100 consecutive patients. Eur Spine J. 2000;9(3):235-240.
[11] 陈前芬,肖增明,张忠民,等.寰椎椎弓根螺钉技术的剖面解剖和三维CT应用研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2009,27(2):166-169.
[12] TAUCHI R, IMAGAMA S, ITO Z, et al. Complications and outcomes of posterior fusion in children with atlantoaxial instability. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(7):1346-1352.
[13] YIN QS, AI FZ, ZHANG K, et al. Transoral atlantoaxial reduction plate internal fifi xation for the treatment of irreducible atlantoaxial dislocation: a 2- to 4-year follow-up. Orthop Surg. 2010;2:149-155.
[14] KANDZIORA F, PFLFL UGMACHER R, LUDWIG K, et al. Biomechanical comparison of four anterior atlantoaxial plate systems. J Neurosurg. 2002;96:313-320.
[15] GUPPY KH, CHAKRABARTI I, ISAACS RS, et al. En bloc resection of a multilevel high-cervical chordoma involving C-2: new operative modalities: technical note. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;1:232-242.
[16] DEANDRADE J, MACNAB I. Anterior occipitocervical fusion in rheumatoid arthritis:report of a case. Arthritis Rheum. 1969;12:423-426.
[17] SUCHOMEL P, BUCHVALD P, BARSA P, el al. Single-stage total C-2 intralesional spondylectomy for chordoma with three-chlumn reconstruction.Technical note. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6(6):611-618.
[18] 鲍剑峰,米明珊,梁小弟,等.前后联合入路治疗儿童颈椎重度骨折脱位[J].中国现代医学杂志,2014,24(35):84-87.
[19] MENEZES AH. Craniocervical fusions in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2012;7(9):573-585.
[20] 王建华,张东升,郑勇强,等.蝶形枕颈内固定系统在低龄儿童上颈椎手术的初步应用[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2016,8(3): 141-145.
[21] 张少杰,王星,李志军.应用数字化技术对儿童寰枢椎椎弓根形态及其置钉方式的初步探讨[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2015,3(5):373-377.
[22] 薛文,刘林,钱耀文.CT 测量儿童枢椎椎弓根和椎板数据及其螺钉 固定的可行性研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(1):13-15.
[23] 王建华,夏虹,尹庆水,等.儿童枢椎椎弓根及椎板螺钉内固定的解剖学研究[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2013,5(6):331-334.
[24] 孙月荣,王天瑞,潘荣芳,等.枢椎交叉椎板螺钉轨道的模拟设计[J].中国组织工程杂志,2018,22(27):4332-4336.
[25] KRMPOTIC-NEMANIC J, VINTER I, KELOVIZC Z, et al. Postnatal changes of the clivus. Ann Anat. 2005;187:277-280.
[26] JI W, KONG GG, ZHENG MH, et al. Computed Tomographic Morphometric Analysis of Pediatric Clival Screw Placement at the Craniovertebral Junction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(5):E259-E265.
[27] RODGERS WB, CORAN DL, KHARRAZI FD, et al. Increasing lordosis of the occipitocervical junction after arthrodesis in young children: the occipitocervical crankshaft phenomenon. J Pediatr Orthop. 1997;17: 762-765.
[28] HOFMANN H, PRESCHER A. The Clivus Anatomy, Normal Variants and Imaging Patholog. Clin Neuroradiol. 2012;22(3):123-139.
[29] COBEN SE. The spheno-occipital synchondrosis: the missing link between the profession’s concept of craniofacial growth and orthodontic. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1998;114(6):709-714.
[30] ROSENBERG P, ARLIS HR, HAWORTH RD, et al. The role of the cranial base in facial growth: experimental craniofacial synostosis in the rabbit. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;99(5):1396-1407.
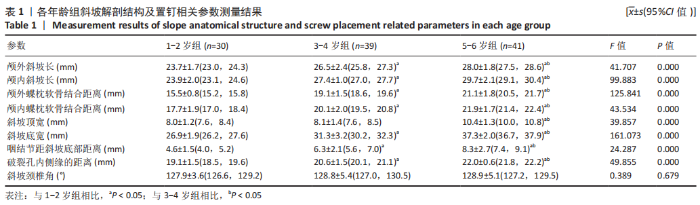
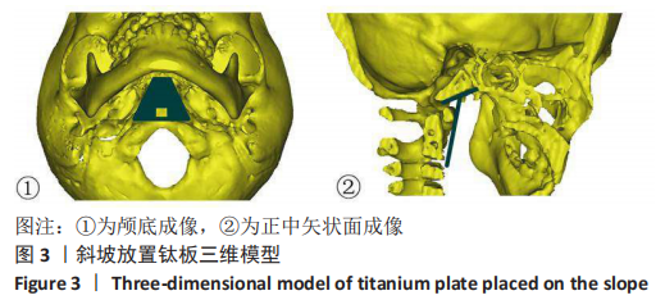
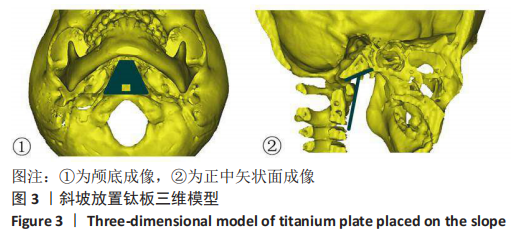
|