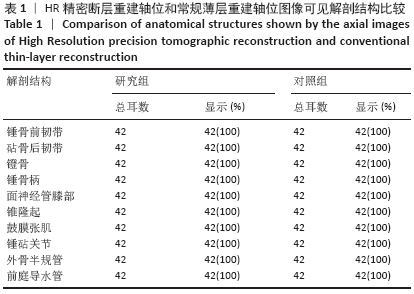
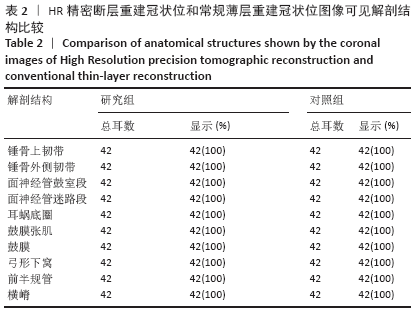
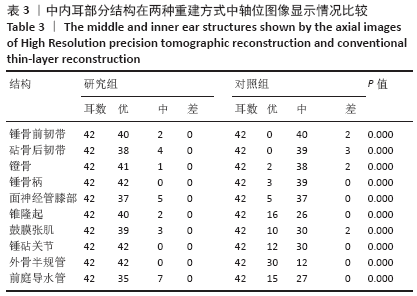
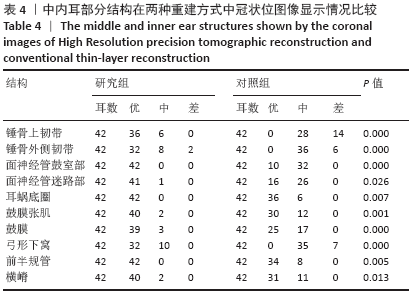
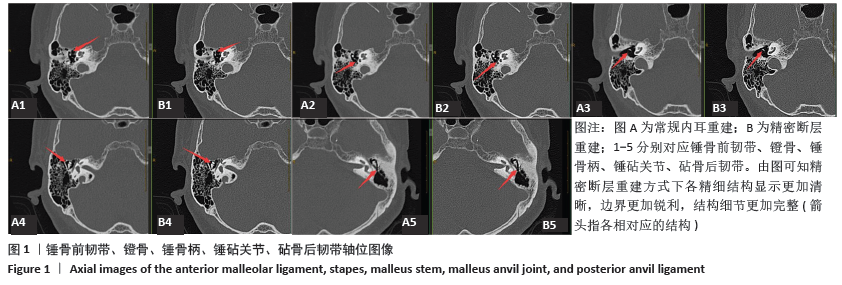
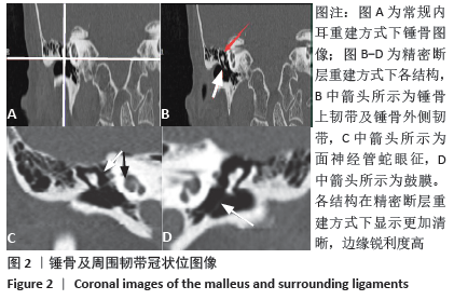
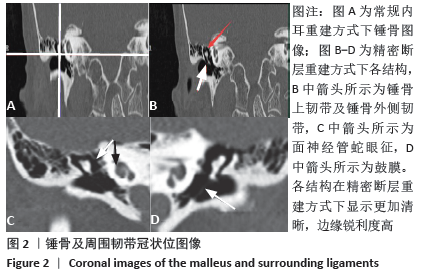
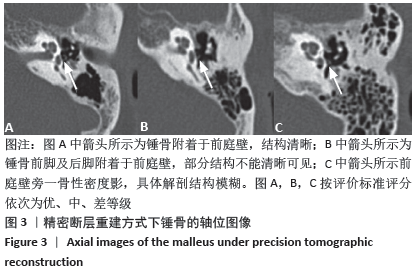
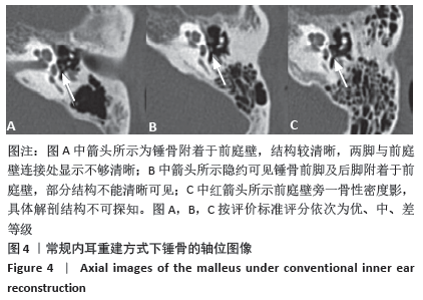
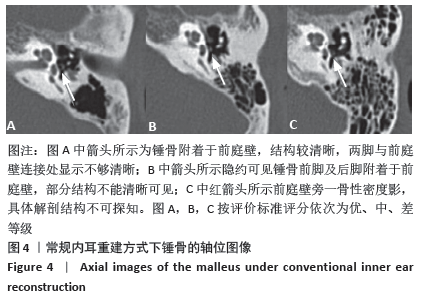
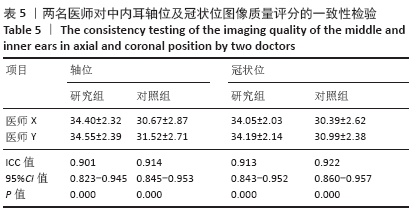
[1] 李希平, 常青林, 魏永祥. 颞骨螺旋CT三维重建及手术入路相关解剖测量[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,2013,20(5):247-249.
[2] SMET B, KOCK ID, GILLARDIN P, et al. Cone Beam CT Atlas of the Normal Suspensory Apparatus of the Middle Ear Ossicles. European Congress of Radiology. 2013;C-2036.
[3] FUJIWARA S, TOYAMA Y, MIYASHITA T, et al. Usefulness of multislice-CT using multiplanar reconstruction in the preoperative assessment of the ossicular lesions in the middle ear diseases. AurisNasus Larynx. 2016;43(3):247-253.
[4] 赵鹏飞,杨正汉,李静,等.基于高分辨率CT的成人颞骨气化评估方法学研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2017;16(9):847-851.
[5] YU ZL, WANG ZC, YANG BT, et al. The value of preoperative CT scan of tympanic facial nerve canal in tympanomastoid surgery. Acta Otolaryngol. 2011;131(7):774-778.
[6] SONGSW, JUN BC, KIM H, et al. Evaluation of temporal bone pneumatization with growth using 3D reconstructed image of computed tomography. AurisNasus Larynx. 2017;44(5):522-527.
[7] ANBARASU A, CHANDRASEKARAN K, BALAKRISHNAN S. Soft tissue attenuation in middle ear on HRCT: Pictorial review. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2012;22(4):298-304.
[8] LI XG, GONG ZP, YIN HX, et al. A 3D deep supervised densely network for small organs of human temporal bone segmentation in CT images. Neural Netw. 2020;124:75-85.
[9] MEHANNA AM, BAKI FA, EID M, et al. Comparison of different computed tomography post-processing modalities in assessment of various middle ear disorders. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;272(6):1357-1370.
[10] LANE JI, LINDELL EP, WITTE RJ, et al. Middle and inner ear: improved depiction with multiplanar reconstruction of volumetric CT data. Radiographics. 2006; 26(1):115-124.
[11] MARQUES SR, AJZEN S, D’IPPOLITO G, et al. Morphometric Analysis of the Internal Auditory Canal by Computed Tomography Imaging. Iran J Radiol. 2012;9(2):71-78.
[12] STJERNHOLM C. Aspects of temporal bone anatomy and pathology in conjunction with cochlear implant surgery. ActaRadiol Suppl. 2003;430:2-15.
[13] 张丽,于红,刘士远,等.迭代重建技术对低剂量肺部平扫CT图像质量的影响[J].中华放射学杂志,2013,47(4):316-320.
[14] 王刚. 不同剂量扫描方式对头部CT扫描患者辐射防护的影响[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志,2015,18(24):108-109.
[15] KLINGEBIEL R, BAUKNECHT HC, ROGALLA P, et al. High-resolution Petrous Bone Imaging Using Multi-slice Computerized Tomography. ActaOtolaryngol. 2001; 121(5):632-636.
[16] 胡俊岭. 低剂量个体化头颈部CT血管成像扫描方案对图像质量及辐射剂量的影响分析[J]. 科技创新导报,2015,(35):255-256.
[17] 张孔源, 王文刚, 季乐新,等. 16层螺旋CT优化扫描在婴幼儿颅脑检查中的防护价值[J]. 中国辐射卫生,2011;20(2):246-247.
[18] 阮士栋,巩武贤,樊兆民,等.慢性中耳炎患者听骨链功能状态的HRCT评价[J].医学影像学杂志,2016,26(5):791-794+803.
[19] 白玫, 刘彬, 郑钧正. 多排螺旋CT纵轴分辨力和图像噪声影响因素研究[J]. 中国医学影像技术,2008,24(7):1110-1113.
[20] CZECHOWSKI J, JANECZEK J, KELLY G, et al. Radiation dose to the lens in sequential and spiral CT of the facial bones and sinuses. EurRadiol. 2001;11(4):711-713.
[21] 梁耘.头部CT扫描受检者敏感器官体表辐射量及防护措施的初步分析[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2020, 4(3):43-44.
[22] 鲜军舫,王振常. 降低头颈部CT检查辐射剂量的策略[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2013,47(11):967-969.
[23] SEMGHOULI S, AMAOUI B, KHARRAS AE, et al. Evaluation of radiation risks during CT brain procedures for adults. Perspectives in Science. 2019.10.1016/j.pisc.2019.100407
[24] GLYBOCHKO PV, ALYAEVYG, KHOKHLACHEV SB, et al. 3D reconstruction of CT scans aid in preoperative planning for sarcomatoid renal cancer: A case report and mini-review.JXraySci Technol. 2019;27(2):389-395.
[25] 刘杰,王峰,董玉龙,等.多层螺旋CT联合三维重建技术诊断复杂性肛瘘的效果[J]. 中国医学创新,2019,16(21):110-113.
[26] DIGGE P, SOLANKI RN, SHAH DC, et al. Imaging Modality of Choice for Pre-Operative Cochlear Imaging: HRCT vs. MRI Temporal Bone. J ClinDiagn Res. 2016; 10(10):TC01-TC04.
[27] 王艳菊, 肖家和, 卓丽华, 等. 亚毫米螺旋CT 0.5mm与1.0mm层厚重建显示慢性中耳乳突炎效果的对照研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2014,13(1):51-53.
[28] ZHANG LC, TONG BS, WANG Z M, et al. A comparison of three MDCT post-processing protocols: preoperative assessment of the ossicular chain in otitis media.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;271(3):445-454.
[29] 申玲, 王知祥. CT在内耳畸形儿童术前诊治中的应用[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2018,16(6):62-64.
[30] 张英, 郭斌. 高分辨率CT对颞骨病变诊断的研究进展[J].青海医药杂志, 2016,46(2):73-76.
[31] 周琦芳, 盛茂. 多层螺旋CT三维成像对慢性中耳乳突炎的诊断价值研究[J]. 名医,2018,35(3):83.
[32] 吴雪贵, 宗炬. 探讨螺旋CT三维重建(SSD、VRT)及多平面重建(MPR)技术在骨关节骨折的临床应用[J]. 中国医疗器械信息,2018,24(24):135-136.
[33] MACK MG, SUCKFÜLLMM. Imaging of the Inner Ear Before Cochlear Implantation. Laryngorhinootologie. 2020;99(3):181-191.
[34] 金秋燕.高分辨CT对慢性中耳乳突炎诊断价值的探讨[J].影像研究与医学应用,2017,1(11):53-54.
[35] 唐永强,王栋,杨红兵,等.256层螺旋CT成像对鼓室成形术前骨质破坏评估价值[J].中国医疗设备,2019,34(6):5-8.
[36] 黄宏明,周正根,葛润梅,等.内耳畸形CT分类在人工耳蜗植入手术中的应用[J]. 中华耳科学杂志,2018,16(5):629-633.
[37] 师天祥, 陆续玲, 郝剑萍. 颞骨CT薄层扫描对感音神经性聋儿内耳畸形分型的诊断价值—基于358例感音神经性聋儿内耳畸形分型的调查[J]. 卫生职业教育,2018,36(14):154-155.
[38] 沈鹏, 郑作锋, 杨立军, 等. 迷路下入路开放内耳道手术相关解剖结构的CT测量[J].中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,2017,24(10):509-511.
[39] 卢绍辉,吴颋,刘官华,等.慢性中耳乳突炎症听骨链标准化HRCT MPR评估[J]. 赣南医学院学报,2016,36(1):42-45.
[40] 卢林民, 程广明. 颞骨高分辨CT及三维重建在先天性内耳畸形中的应用价值[J]. 影像研究与医学应用,2017,1(9):93-94.
[41] 王星, 吴文丽. 青少年感音神经性耳聋内耳畸形的高分辨CT表现[J].黑龙江医学,2019,43(2):149-151.
[42] LIU Y, YANG F, LU QH, et al. Value of section plane, MPR, and 3D-CTVR techniques in the fine differential diagnosis of ossicular chain in the case of conductive hearing loss with intact tympanic membrane. J Otol. 2017;12(2):80-85.
[43] NAGHIBI S, SEIFIRAD S, ADAMI DM, et al. Comparison of Conventional Versus Spiral Computed Tomography with Three Dimensional Reconstruction in Chronic Otitis Media with Ossicular Chain Destruction. Iran J Radiol. 2016;13(1):e9018.
[44] 李晓娜,张英华,张雪松, 等.128层螺旋CT与3.0T磁共振内耳水成像在内耳病变中的应用价值的比较[C].中国医学装备大会暨2019医学装备展览会论文汇编,2019:22-26.
[45] 魏璐璐,黄维平,尹中普,等.人工耳蜗植入术前颞骨HRCT与内耳MR的评估价值[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2018,16(12):37-40.
[46] 柯荣丹,唐安洲,唐翔龙,等.HRCT三维重建技术在外伤性听骨链中断的临床应用[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2019,33(12):1129-1133. |