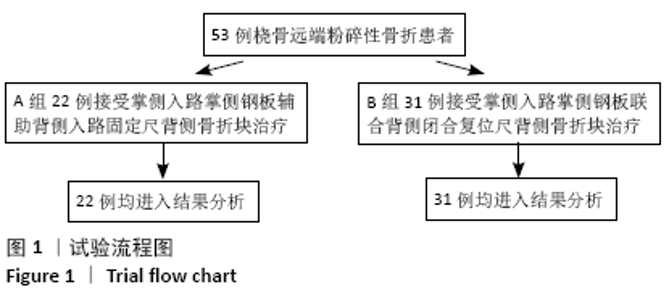
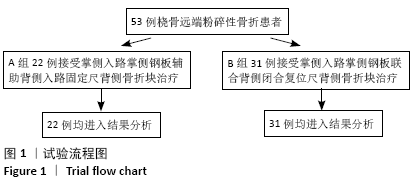
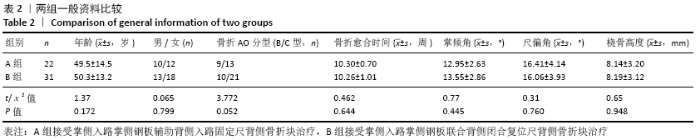
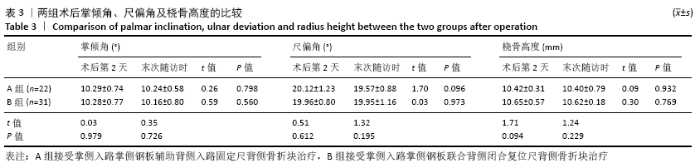
[1] DAVIS DI, BARATZ M. Soft tissue complications of distal radius fractures. Hand Clin. 2010;(2):229-235.
[2] ROSENAUER R, PEZZEI C, QUADLBAUER S, et al. Complications after operatively treated distal radius fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(5):665-673.
[3] MIYASHIMA Y, KANESHIRO Y, YANO K, et al. Size and stabilization of the dorsoulnar fragment in AO C3-type distal radius fractures. Injury. 2019;50(11):2004-2008.
[4] OBERT L, REY PB, UHRING J, et al.Fixation of distal radius fractures in adults:a review. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(2):216-234.
[5] LEIXNERING M, ROSENAUER R, PEZZEI C, et al. Indications, surgical approach, reduction, and stabilization techniques of distal radius fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(5):611-621.
[6] KASTENBERGER T, KAISER P, SCHMIDLE G, et al. Arthroscopic assisted treatment of distal radius fractures and concomitant injuries. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(5):623-638.
[7] HOVENGA EJS. Early Rehabilitation of Distal Radius Fractures Stabilized by Volar Locking Plate: A Prospective Randomized Pilot Study. J Wrist Surg. 2017;6(2):102-112.
[8] QUADLBAUER S, PEZZEI C, HINTRINGER W, et al. Clinical examination of the distal radioulnar joint. Der Orthopade. 2018,47(8):628-636.
[9] QUADLBAUER S, PEZZEI C, JURKOWITSCH J, et al. Spontaneous radioscapholunate fusion after septic arthritis of the wrist:a case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137:579-584.
[10] WALENKAMP MM, AYDIN S, MULDERS MA, et al. Predictors of unstable distal radius fractures:a sysre-matic review and meta-analysis. J HAND SURG-AM. 2015;41(5):501-515.
[11] LIDSTROM A. Fractures of the distal radius.A clinical and statis tical study of end result. Acta Orthop Scand Supply. 1959;41:1-118.
[12] DIENST M, WOZASEK GE, SELIGSON D. Dynamic external fixation for distal radiusfractums. Clin Orthop. 1997;338:160-71.
[13] 孙明宏.掌侧入路“T”型锁定钢板治疗老年桡骨远端骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2009,15(6):440-443.
[14] MIYAMURA S, OKA K, LANS J, et al. Cartilage and Subchondral Bone Distributions of the Distal Radius: A 3-Dimensional Analysis Using Cadavers. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;S1063-4584(20)31118-3.
[15] Zhou J, Tang W, Li D, et al. Morphological characteristics of different types of distal radius die-punch fractures based on three-column theory. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):390.
[16] BIONDI M, KELLER M, MERENGHI L, et al. Hook Plate for Volar Rim Fractures of the Distal Radius: Review of the First 23 Cases and Focus on Dorsal Radiocarpal Dislocation. J Wrist Surg. 2019;8(2):93-99.
[17] BUI CNH, RAFIJAH GH, LIN CC, et al. Dorsal Wrist Extrinsic Carpal Ligament Injury Exacerbates Volar Radiocarpal Instability After Intra-Articular Distal Radius Fracture. Hand (N Y). 2019. doi:10.1177/1558944719851210.
[18] HARNESS NG, JUPITER JB, ORBAY JL, Et al. Loss of fixation of the volar lunate facet fragment in fractures of the distal part of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A:1900-1908.
[19] MELONE JR CP. Articular fractures of the distal radius. Orthop Clin North Am. 1984;15:217-136.
[20] O’SHAUGHNESSY MA, SHIN AY, KAKAR S. Stabilization of volar ulnar rim fractures of the distal radius:current techniques and review of the literature. J Wrist Surg. 2016;5:113-119.
[21] DY CJ, WOLFE SW, JUPITER JB, et al. Distal radius fractures:strategic alternatives to volar plate fixation. Instr Course Lect. 2014;63:27-37.
[22] IKEDA K, OSAMURA N, TADA K. Fixation of an ulnodorsal fragment when treating an intra-articular fracture in the distal radius. Hand Surg. 2014;19:139-144.
[23] UNGLAUB F, MANZ S, BRUCKNER T, et al.Dorsal capsular imbrication for dorsal instability of the distal radioulnar joint. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2013;25:609-614.
[24] HOZACK BA, TOSTI RJ. Fragment-Specific Fixation in Distal Radius Fractures. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2019;12:190-197.
[25] SASCHA R, OLAF S, KAJETAN K, et al. Volar versus dorsal latest - genera- tion variable -angle locking plates for the fixation of AO type 23C 2. 1 distal radius fractures: a biomechanical study in cadavers.Injury. 2013;44: 523-526.
[26] FARDELLAS A, VERNET P, FACCA S, et al. Flexor tendon complications in distal radius fractures treated with volar rim locking plates. Hand Surg Rehabil. 2020;39(6):511-515.
[27] ASADOLLAHI S, KEITH PP. Flexor tendon injuries following plate fixation of distal radius fractures: a systematic review of the literature. J Orthop Traumatol. 2013;14(4):227-234.
[28] 钱军,方美园,江开明.桡骨远端尺侧块骨折的手术治疗[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(3):250-254.
|