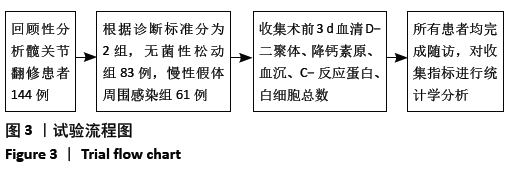
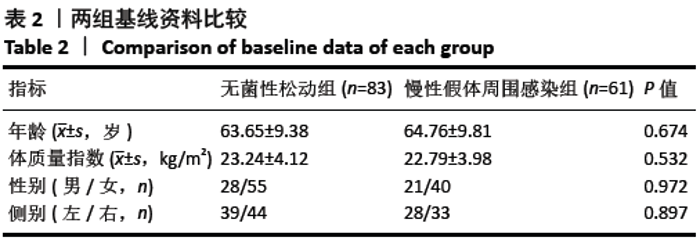
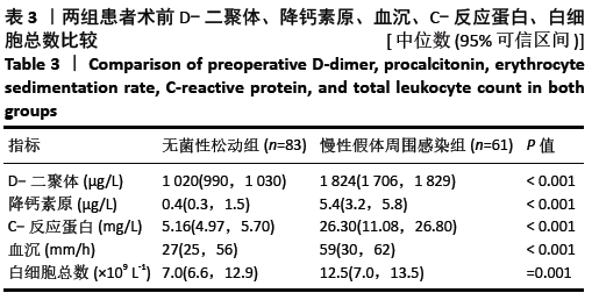
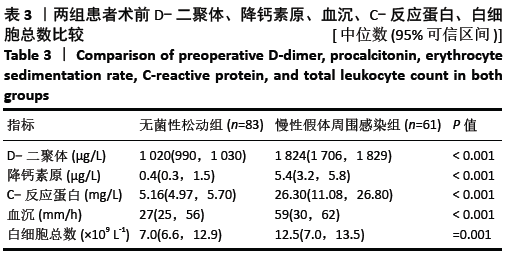
[1] 沈骏,高田田,杨杰.组配式股骨假体髋关节翻修治疗在全髋关节置换术后股骨假体周围骨折中的应用效果分析[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2020,19(8):879-882.
[2] 江劲涛,曹晓瑞,杨重飞,等.二期翻修手术在髋关节置换术后晚期慢性假体周围感染治疗中的应用[J].中华解剖与临床杂志, 2019, 24(4):396-402.
[3] PUPAIBOOL J, FULNECKY EJ, SWORDS JR RL, et al. Alphadefensin-novel synovial fluid biomarker for the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. Int Orthop. 2016;40:2447-2452.
[4] 王相选,张文明.二期翻修治疗人工髋、膝关节置换术后感染的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(12):1566-1571.
[5] 马立峰,郭艾,李强,等.二期翻修术治疗髋关节假体周围感染的中期疗效分析[J].国际外科学杂志,2019,46(7):459-464.
[6] 林志炯,高大伟,董月珍,等.骨水泥占位器在髋关节感染二期翻修术的临床疗效[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2017,11(4):338-343.
[7] FITZGERALD JR RH, NOLAN DR, ILSTRUP DM, et al. Deep wound sepsis following total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59:847-855.
[8] ISKANDER KN, OSUCHOWSKI MF, STEARNS-KUROSAWA DJ, et al. Sepsis: multiple abnormalities, heterogeneous responses,and evolving understanding. Physiol Rev. 2013;93:1247-1288.
[9] 牛辉,鲍朝辉,高乾坤,等.D-二聚体联合Wells评分在脊柱手术后深静脉血栓诊断中的应用价值[J].实验与检验医学,2020,38(2): 266-268.
[10] SHAHI A, KHEIR MM, TARABICHI M, et al. Serum Ddimer test is promising for the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection and timing of reimplantation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99:1419-1427.
[11] PARVIZI J, GEHRKE T. Definition of periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:1331.
[12] 杨明礼.人工全髋关节置换术后假体松动的诊治及预防[J].川北医学院学报,2017,32(2):239-241.
[13] Osmon DR, Berbari EF, Berendt AR, et al.Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56:1-25.
[14] Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91: 128-133.
[15] Zimmerli W. Clinical presentation and treatment of orthopaedic implantassociated infection. J Intern Med. 2014;276:111-119.
[16] 胡冰涛,李瑞延,杨帆,等.髋关节置换术后关节假体周围感染的诊断与治疗进展[J].临床误诊误治,2018,31(2):110-113.
[17] 张承清,杨晓红.D-二聚体在静脉血栓栓塞症中的诊断价值研究进展[J].新疆医学,2019,49(11):1143-1146.
[18] 刘冰,王国兴,孙雪莲.血清降钙素原和D-二聚体检测在急诊脓毒症患者病情及预后评估中的应用价值[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2020,19(3):310-313.
[19] 王永锋,王佳瑜,王立钧,等.FDP和D-二聚体联合检测在老年患者肺部感染早期诊断中的应用[J].中国实验诊断学,2019,23(6):990-992.
[20] SCHWAMEIS M, STEINER MM, SCHOERGENHOFER C, et al. D-dimer and histamine in early stage bacteremia: a prospective controlled cohort study. Eur J Intern Med. 2015;26:782-786.
[21] MELE N, TURC G. Stroke associated with recent Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: a systematic review of clinical features and presumed pathophysiological mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2018;9:1101-1109.
[22] CHEN CJ, WANG CJ, HUANG CC. The value of D-dimer in the detection of early deep-vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty in Asian patients: a cohort study. Thromb J. 2008;6:5-11.
[23] BYTNIEWSKI P, MACHALA W, ROMANOWSKI L, et al. The dynamics of D-dimer level fluctuation in patients after the cemented and cementless total hip and total knee replacement. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;9:89-96.
[24] LEE YS, LEE YK, HAN SB, et al. Natural progress of D-dimer following total joint arthroplasty: a baseline for the diagnosis of the early postoperative infection. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13:36-42.
[25] QIN L, LI F, GONG X, et al. Combined Measurement of D-Dimer and C-Reactive Protein Levels: Highly Accurate for Diagnosing Chronic Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35:229-234.
[26] TOOSSI N, ADELI B, RASOULI MR, et al. Serum white blood cell count and differential do not have a role in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(8 Suppl):51-54.
[27] MIYAMAE Y, INABA Y, KOBAYASHI N, et al. Different diagnostic properties of C-reactive protein, real-time PCR, and histopathology of frozen and permanent sections in diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. Acta Orthop. 2013;84:524-529.
[28] PEREZ-PRIETO D, PORTILLO ME, PUIG-VERDIE L, et al. Creactive protein may misdiagnose prosthetic joint infections, particularly chronic and low-grade infections. Int Orthop. 2017;41:1315-1319.
[29] CHEN A, FEI J, DEIRMEGIAN C. Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Infection:novel developments. J Knee Surg. 2014;27(4):259-265.
[30] BOUAICHA S, BLATTER S, MOOR BK, et al. Early serum procalcitonin level after primary total hip replacement. Mediators Inflamm. 2013; 2013:927636.
|