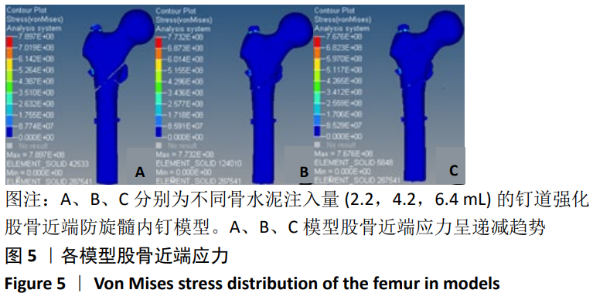
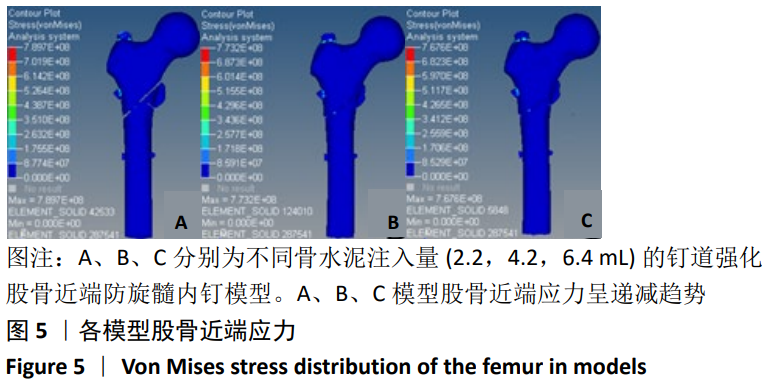
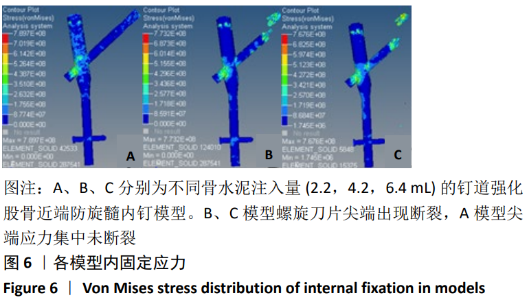
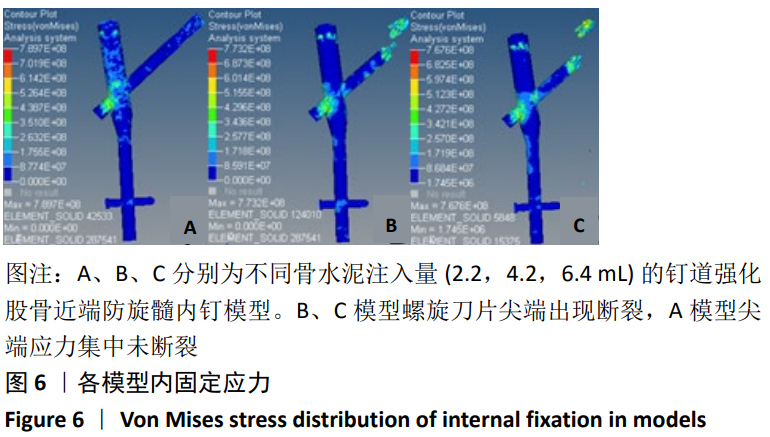
[1] XIA WB, HE SL, XU L, et al. Rapidly increasing rates of hip fracture in Beijing, China. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(1):125-129.
[2] WANG J, WANG Y, LIU WD, et al. Hip fractures in Hefei, China: the Hefei osteoporosis project. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014;32(2):206-214.
[3] ADIB HAJBAGHERY M, ABBASINIA M. Quality of life of the elderly after hip fracture surgery: a case-control study. J Caring Sci. 2013;2(1):53-59.
[4] CLOSE JD, SWARTZ K, DEU R. Hip fracture in older patients: tips and tools to speed recovery. J Fam Pract. 2013;62(9):484-492.
[5] WANG J, MA JX, LU B, et al. Comparative finite element analysis of three implants fixing stable and unstable subtrochanteric femoral fractures: Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA), Proximal Femoral Locking Plate (PFLP), and Reverse Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(1):95-101.
[6] GUO Y, YANG HP, DOU QJ, et al. Efficacy of femoral nail anti-rotation of helical blade in unstable intertrochanteric fracture. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(3 Suppl):6-11.
[7] XU R, RU J, JI F, et al. Comparison of efficacy, complications and TGF-β2 expression between DHS and PFNA in elderly patients with osteoporotic femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(1):394-399.
[8] 李尧, 胡传真, 茅凌洲, 等. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉联合小钢板重建外侧壁治疗AO/OTA 31-A3型股骨转子间骨折[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(10):1223-1227.
[9] 姜昊, 曹烈虎, 潘思华, 等. 有限切开钛缆捆扎辅助PFNA与单纯微创辅助PFNA治疗老年骨质疏松性31-A3型股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效对比[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2019,8(3):191-195.
[10] 王勇, 潘骏. 标准骨水泥强化型PFNA治疗老年股骨粗隆间不稳定骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(18):1653-1658.
[11] 陈宏峰, 杨冬松, 凌建生, 等. 骨水泥强化型股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定治疗严重骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2020,22(3):259-262.
[12] 王兆稳, 袁治国, 白登彦, 等. PFNA联合骨水泥注入治疗老年骨质疏松性股骨粗隆间骨折[J]. 甘肃医药,2017,36(12):1048-1050.
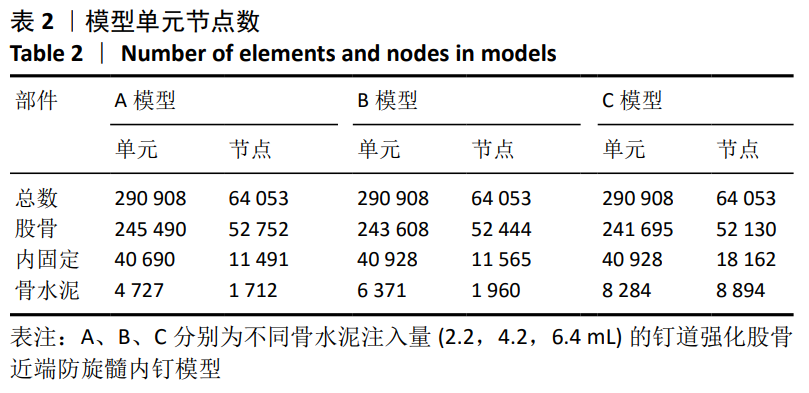
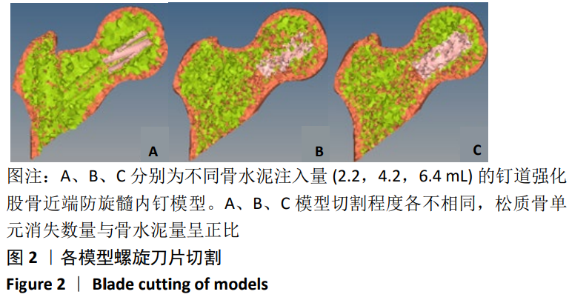
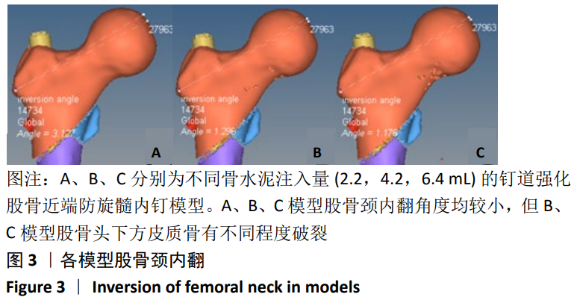
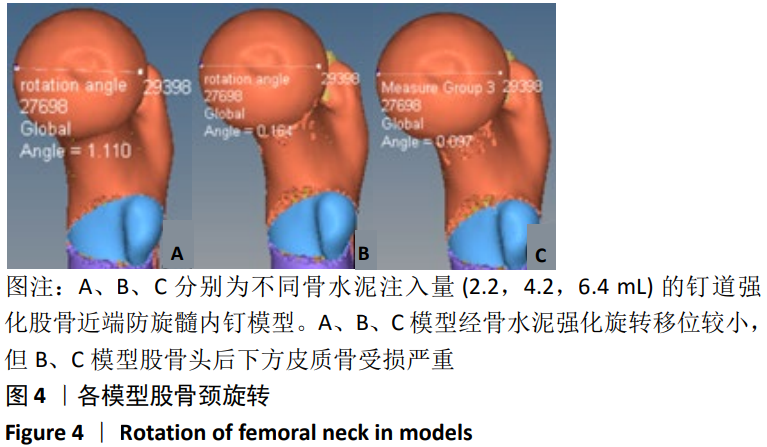
[13] 陈心敏, 罗斯嘉, 夏卓伟, 等. 钉道强化股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年A3.3型股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(27):4265-4271.
[14] 许兵, 吴银生, 王勇,等. 骨水泥强化型PFNA治疗老年性股骨粗隆间骨折的生物力学研究[G]. 第二十四届中国中西医结合骨伤科学术年会论文汇编.2017.
[15] 曾秋涛,赵洪斌,林勇,等. 带孔螺旋刀片骨水泥增强型PFNA治疗转子间骨折的疗效分析[J]. 江西医药,2017,52(12):1330-1331.
[16] 何祥鑫, 林梓凌, 李鹏飞, 等. 基于Hypermesh 14.0和LS-DYNA的老年转子间骨折有限元建模分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(11): 1725-1730.
[17] GUO S, QU X, HE X, et al. Powder injection molding of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J Mater Proc Technol. 2006;173(3):310-314.
[18] HELGASON B, VICECONTI M, RÚNARSSON TP, et al. On the mechanical stability of porous coated press fit titanium implants: a finite element study of a pushout test. J Biomech. 2008;41(8):1675-1681.
[19] CARNEY KS, PEREIRA JM, REVILOCK DM, et al. Jet engine fan blade containment using an alternate geometry. Int J Impact Eng. 2009;36(5): 720-728.
[20] HINÜBER C, KLEEMANN C, FRIEDERICHS RJ, et al. Biocompatibility and mechanical properties of diamond-like coatings on cobalt-chromium-molybdenum steel and titanium-aluminum-vanadium biomedical alloys. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;95(2):388-400.
[21] GOFFIN JM, PANKAJ P, SIMPSON AH, et al. Does bone compaction around the helical blade of a proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) decrease the risk of cut-out: A subject-specific computational study. Bone Joint Res. 2013;2(5):79-83.
[22] BOBBILI R, RAMAKRISHNA B, VEMURIMADHU V. Dynamic compressive behavior and fracture modeling of Titanium alloy IMI 834. J All Comp. 2017;714:225-231.
[23] NODA M, ADACHI K. Biomechanical study using finite element method of element ‘breakdown’ technique on cutout mechanism after gamma nailing. EC Orthop. 2018:458-466.
[24] EBERLE S, GERBER C, VON OLDENBURG G, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of orthopaedic implants for hip fractures by finite element analysis and in-vitro tests. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010;224(10): 1141-1152.
[25] DHANOPIA MB. Finite element analysis of human fractured femur bone implantation with PMMA thermoplastic prosthetic plate. Proc Eng. 2017;173:1658-1665.
[26] VAISHYA R, CHAUHAN M, VAISH A. Bone cement. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2013;4(4):157-163.
[27] Chow LC. Calcium phosphate cements. Monogr Oral Sci. 2001;18: 148-163.
[28] 张磊, 唐晓菊, 黄有荣, 等. 聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥及磷酸钙骨水泥的材料性能及改性的研究进展[J]. 广西医学,2019, 41(16): 2114-2118+2122.
[29] 伦登兴, 徐丽娜, 冯江涛, 等. 可注射性硫酸钙骨水泥的生物力学研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(10): 661-668.
[30] 郭良煜, 郭卫春. 磷酸钙骨水泥在骨修复应用研究的新进展[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(2):157-160.
[31] MONZÓN RA, COURY JG, DISSE GD, et al. Bone cement in total hip and knee arthroplasty. JBJS Rev. 2019;7(12): e6.
[32] 陈孜,赵国辉,金丹杰,等.后路短节段内固定结合伤椎强化技术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J]. 中国微创外科杂志,2019, 19(12):1088-1091.
[33] 杨红军, 苏高建, 冯智海, 等. 新型骨水泥椎弓根螺钉内固定系统治疗重度骨质疏松腰椎退变性疾病的临床研究[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2019,8(9):703-708.
[34] 陈晓峰, 李浩, 欧志聪, 等. 不同置钉和骨水泥剂量对椎弓根螺钉固定强度的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2019, 27(14): 1306-1310.
[35] 段志斌. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉术后螺旋刀片穿出股骨头的影响因素分析[D].南昌:南昌大学,2018.
[36] 武政, 刘向栋, 常宝生. PFNA治疗高龄不稳定性股骨转子间骨折内固定失败的危险因素分析[J]. 局解手术学杂志,2017,26(8):616-619.
[37] 卫禛, 张立智, 张世民. 骨水泥材料在增强股骨转子间骨折内固定中的应用进展[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2020, 22(1):84-87.
[38] THOMAS CD, MAYHEW PM, POWER J, et al. Femoral neck trabecular bone: loss with aging and role in preventing fracture. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(11):1808-1818.
[39] CHRISTOPHER JJ, RAMAKRISHNAN S. Assessment and classification of mechanical strength components of human femur trabecular bone using texture analysis and neural network. J Med Syst. 2008;32(2): 117-122.
[40] BURR DB. Bone material properties and mineral matrix contributions to fracture risk or age in women and men. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2002;2(3):201-204.
|