Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (6): 923-928.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2399
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion
Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong
- Second Department of Spine, Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2020-03-26Revised:2020-04-01Accepted:2020-05-09Online:2021-02-28Published:2020-12-04 -
Contact:Meng Xianzhong, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Second Department of Spine, Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Song Chengjie, Master candidate, Second Department of Spine, Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the General Project of Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, No. C2019206063
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
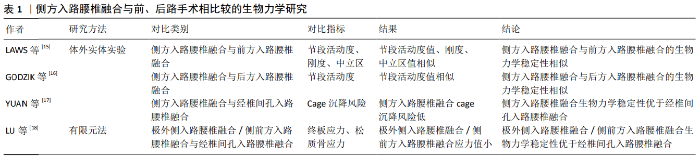
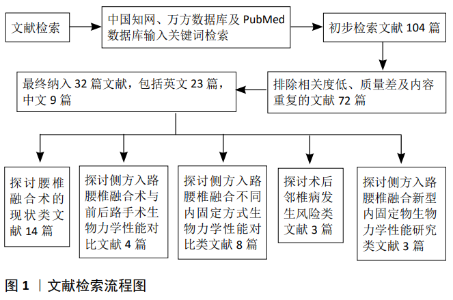
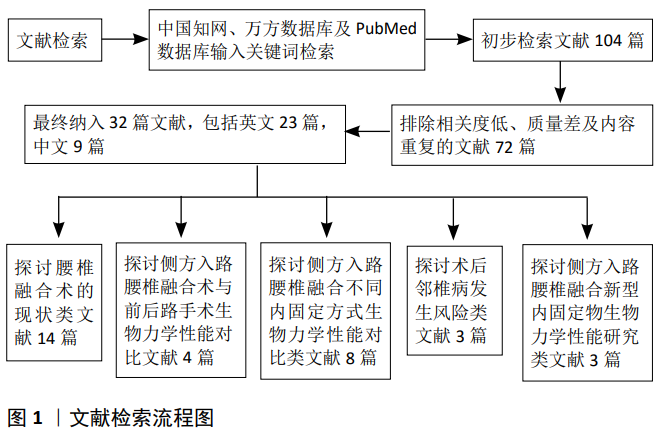
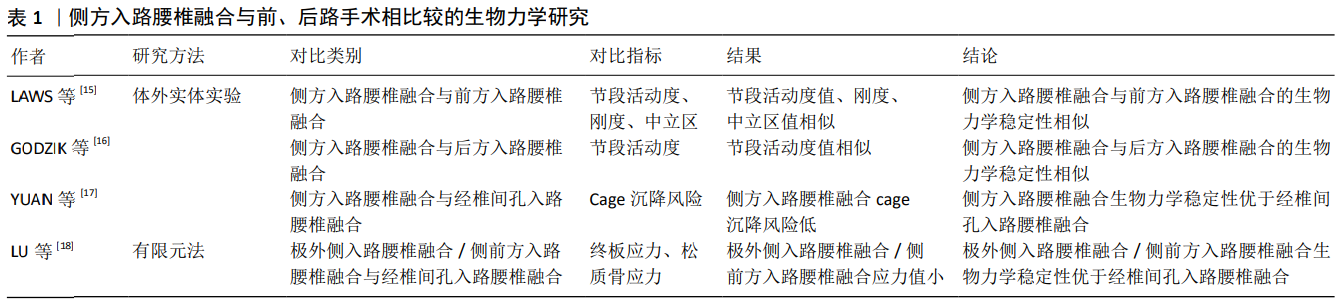
2.2 侧方入路腰椎融合与前、后路手术相比较的生物力学研究 前路腰椎融合、后路腰椎融合、经椎间孔入路腰椎融合术目前仍是治疗腰椎疾病的主要手段,侧方入路腰椎融合作为新兴微创手术,其生物力学稳定性至少与传统手术无明显差异时才能应用于临床。为此,许多学者通过体外实体实验和三维有限元法将侧方入路腰椎融合的生物力学性能与传统手术进行了对比,见表1。 2.2.1 体外实体实验生物力学研究 LAWS等[15]于2012年通过对侧方入路腰椎融合和前方入路腰椎融合术并双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的手术模型施加6 Nm扭转力矩后,发现两种手术方式合并双侧椎弓根钉棒固定目标节段的活动度和刚度无明显差异,两组中立区均接近于0°,从而得出侧方入路腰椎融合和前方入路腰椎融合并双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的生物力学稳定性相似的结论。LAWS认为单阶段侧方入路腰椎融合并双侧椎弓根钉棒固定可代替前路手术。虽然此样本量较小,但实验结果反映的趋势为临床医师选择侧方入路腰椎融合代替前路手术提供了依据。GODZIK等[16]比较了侧方入路腰椎融合和后方入路腰椎融合的生物力学稳定性,在其研究中模拟了侧方入路腰椎融合和后方入路腰椎融合伴双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的手术方式,施加7.5 Nm扭转力矩后,发现2种手术方式在屈伸、侧弯和旋转时手术节段的活动度无显著差异,得出侧方入路腰椎融合和后方入路腰椎融合的生物力学稳定性相似的结论。从生物力学理论上讲,由于侧方入路腰椎融合可放置比后方入路腰椎融合术大的椎间融合器,侧方入路腰椎融合的生物力学稳定性至少与后方入路腰椎融合相似,该实验结果可信度较高。YUAN等[17]评估了侧方入路腰椎融合cage和经椎间孔入路腰椎融合cage的沉降风险,发现高度相同的侧方入路腰椎融合cage沉降5 mm所需的压力远远大于经椎间孔入路腰椎融合cage。侧方入路腰椎融合可植入较大的cage,椎体与cage接触面积大,因而沉降风险小,此实验从侧面表明了侧方入路腰椎融合的生物力学稳定性较经椎间孔入路腰椎融合术有优势。 2.2.2 有限元法生物力学研究 LU等[18]通过施加400 N的垂直载荷和8 Nm的扭转力矩于植入香蕉型cage和直型cage的经椎间孔入路腰椎融合、极外侧入路腰椎融合、侧前方入路腰椎融合伴双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的有限元模型后,发现无论香蕉型cage还是直型cage的经椎间孔入路腰椎融合并双侧椎弓根钉棒固定,其终板应力和椎体松质骨应力均明显大于极外侧\侧前方入路腰椎融合并双侧椎弓根钉棒固定,说明无论植入香蕉型cage还是直型cage,经椎间孔入路腰椎融合的cage沉降风险均较极外侧\侧前方入路腰椎融合高,得出极外侧\侧前方入路腰椎融合并双侧椎弓根钉棒固的生物力学稳定性优于经椎间孔入路腰椎融合术并双侧椎弓根钉棒固的结论,其实验结论与YUAN等[17]相同。 通过国内外学者对侧方入路腰椎融合与前后路手术的生物力学性能研究可以得出,侧方入路腰椎融合并双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的生物力学稳定性与前方入路腰椎融合、后方入路腰椎融合相似,优于经椎间孔入路腰椎融合。综上,临床医师在选择手术方式时,在其适应证范围内,可优先考虑侧方入路腰椎融合。 "
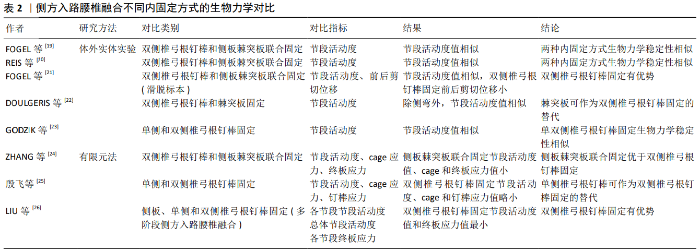
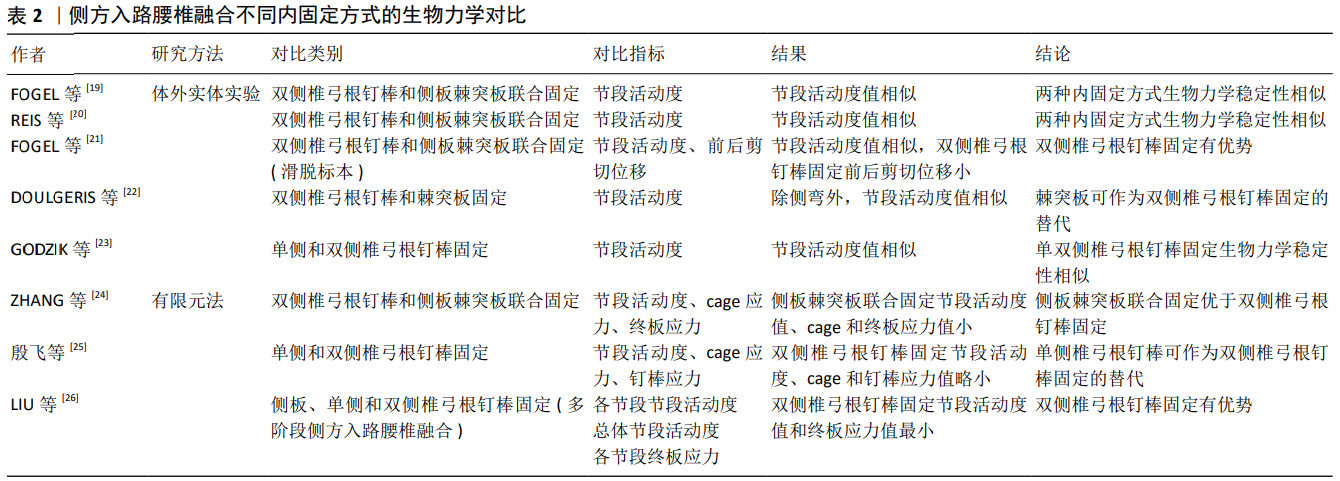
2.3 侧方入路腰椎融合不同内固定方式的生物力学研究 随着侧方入路腰椎融合应用的日益广泛,学者们发明了侧板固定、棘突板固定、侧板棘突板联合固定、单双侧椎弓根钉棒固定等不同内固定方式。而何种内固定方式能提供最强的生物力学稳定性目前并无统一定论。许多学者应用体外实体实验和有限元法对侧方入路腰椎融合不同内固定方式的生物力学性能进行了对比,见表2。 2.3.1 体外实体实验生物力学研究 FOGEL等[19]建立了双侧椎弓根钉棒固定、侧板并棘突板联合固定的极外侧入路腰椎融合的手术模型,施加7.5 Nm的纯力矩后,研究发现两种内固定方式屈伸、侧弯和旋转时目标节段的活动度无明显差别,从而得出侧板棘突板联合固定生物力学稳定性与双侧椎弓根钉棒固定相似的结论。REIS等[20]同样模拟了双侧椎弓根钉棒和侧板棘突板联合固定的侧方入路腰椎融合,施加7.5 Nm纯力矩后,得出与FOGEL等[19]相同的实验结论。从生物力学角度来说,侧板能够降低手术节段侧弯和旋转时的节段活动度,棘突板能降低屈伸时节段活动度,两者联合可提供与椎弓根螺钉相似的稳定性,且侧板棘突板联合固定不必广泛剥离后部肌肉等组织,可作为双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的一种替代方案。而应用侧方入路腰椎融合治疗腰椎滑脱时,有学者认为双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的生物力学稳定性最强,其研究表明双侧椎弓根钉棒和棘突板、侧板棘突板联合固定在屈伸时节段活动度大小相似,但双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的前后剪切位移明显小于棘突板、侧板棘突板联合固定[21]。此研究为临床医师选择侧方入路腰椎融合并双侧椎弓根钉棒固定治疗腰椎滑脱症提供了依据。 而有学者认为棘突板同样是在后方对手术节段进行固定,其生物力学稳定性与双侧椎弓根钉棒相似。DOULGERIS等[22]模拟了侧方入路腰椎融合并棘突板固定和双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的内固定方式,施加50 N载荷和5 Nm扭转力矩后,发现2种内固定方式的节段活动度在屈伸和轴向旋转时大小相似,而侧弯时椎弓根钉棒固定的节段活动度更有优势。DOULGERIS等[22]认为棘突板对人体创伤更小,可作为双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的替代。但此实验施加的载荷与人体重量差距大,且侧弯时椎弓根钉棒固定的生物力学性能较棘突板固定有优势,其结论不具说服力。 有学者认为单侧椎弓根钉棒固定的生物力学稳定性与双侧椎弓根钉棒固定相差不大,可将单侧椎弓根钉棒固定作为双侧钉棒固定的一种替代。GODZIK等[23]通过对侧方入路腰椎融合并单双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的模型施加7.5 Nm扭转力矩后,发现2种内固定方式在屈伸、侧弯、轴向旋转时目标节段的活动度无显著差异;这可能与侧方入路腰椎融合能植入较大的cage,增加了椎间融合面积有关。但该实验中并未比较单双侧椎弓根钉棒固定时cage应力和椎弓根钉棒所受应力,其结论说服力较弱。 2.3.2 有限元法生物力学研究 有学者应用三维有限元法对侧方入路腰椎融合不同内固定物所提供的生物力学稳定性进行了对比。ZHANG等[24]通过对侧板棘突板联合固定和双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的手术模型施加280 N的压缩载荷和7.5 Nm的力矩,发现侧板棘突板联合固定在屈伸、侧弯和旋转时节段活动度、cage应力和终板应力与双侧椎弓根钉棒固定相比更具优势,从而认为侧板棘突板联合固定的生物力学稳定性优于双侧椎弓根钉棒固定。此结论与以往研究有些差异,但从侧面表明了侧板棘突板联合固定可提供令人满意的的生物力学稳定性。 殷飞等[25]对侧前方入路腰椎融合术单纯cage融合,侧前方入路腰椎融合并单双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的生物力学性能进行了比较,于模型施加500 N的压缩载荷和10 Nm扭转力矩后,发现双侧椎弓根钉棒固定时手术节段的活动度、cage应力和椎弓根钉棒应力均优于单侧椎弓根钉棒固定,但单侧椎弓根钉棒固定时手术节段的活动度、cage应力均较单纯cage融合有明显改善。殷飞等[25]认为可以将单侧椎弓根钉棒固定作为双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的替代。由于此有限元结果仅体现患者术后某一瞬时的状态,且单侧椎弓根钉棒固定生物力学性能较双侧椎弓根钉棒差,因此该实验结论对临床医师指导作用有限。LIU等[26]对3节段侧方入路腰椎融合并侧板固定、单双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的模型施加400 N的垂直载荷和7.5 Nm扭转力矩后,发现在屈伸、侧弯和旋转时,各单节段的活动度、总体节段活动度及各单节段终板应力值均是双侧椎弓根钉棒固定时最小。该实验结果为临床医师选择侧方入路腰椎融合并双侧椎弓根钉棒固定治疗多节段腰椎疾病提供了依据。 通过对国内外学者对侧方入路腰椎融合不同内固定方式的生物力学研究的分析可知,双侧椎弓根钉棒固定和侧板棘突板联合固定均能为侧方入路腰椎融合提供最强的生物力学稳定性,建议临床医师将此2种内固定方式作为侧方入路腰椎融合的首选。 2.4 侧方入路腰椎融合后邻椎病发生风险的生物力学研究 有研究表明融合后有影像学表现的邻近节段退变发生率为26.6%,出现临床症状的为8.5%[27]。TANG[28]的研究表明由于经椎间孔入路腰椎融合对腰后部正常结构破坏少,其在降低邻椎病发病率方面较后方入路腰椎融合有优势。由此可知,邻椎病发生风险的大小与正常结构的破坏程度有关。WANG等[29]应用有限元法对侧前方入路腰椎融合和经椎间孔入路腰椎融合后邻椎病发生率进行了比较,在其研究中,通过对模型施加400 N轴向载荷和10 Nm扭转力矩后,发现合并双侧椎弓根钉棒固定的侧前方入路腰椎融合和经椎间孔入路腰椎融合在屈伸、侧弯、旋转时相邻节段的节段活动度和椎间盘压力大小相似,从而表明2种手术方式引起邻近节段退变的风险性相似。由于侧前方入路腰椎融合和经椎间孔入路腰椎融合均对腰后部椎板、小关节等结构破坏较小,此实验结论可信度较高。"
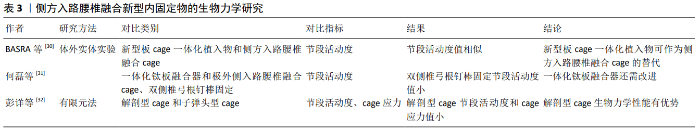
2.5 侧方入路腰椎融合新型内固定物的生物力学研究 近年来侧方入路腰椎融合内固定物不断创新发展,其生物力学性能需达到一定的标准才能应用于临床,许多学者对新型内固定物的生物力学进行了研究,见表3。 2.5.1 体外实体实验生物力学研究 Basra等[30]研究了一种侧方入路腰椎融合新型集成钛板、骨螺钉和PEEK材质cage一体化椎间植入物的生物力学性能,施加8 Nm扭转力矩后,发现新型板cage一体化植入物和侧方入路腰椎融合cage伴或不伴单双侧椎弓根钉棒固定在屈伸、侧弯和旋转时的节段活动度大小相似,得出新型板cage一体化植入物与侧方入路腰椎融合cage具有相同的生物力学稳定性,可作为侧方入路腰椎融合cage的替代的结论。但由于其实验并未对比2种内固定物的应力、终板应力和椎弓根钉棒应力,新型板cage一体化植入物的生物力学性能还有待进一步研究。何磊等[31]同样对一种极外侧入路椎间融合术一体化钛板融合器进行了生物力学稳定性测试,施加7.5 Nm纯力矩后,发现与单纯植入极外侧入路椎间融合术cage相比,新型一体化钛板融合器固定在前屈时节段活动度值较大;与双侧椎弓根螺钉相比,新型一体化钛板融合器在前屈和后伸时节段活动度值均较大,从而认为此新型内植入物还需进一步改进才能应用于临床。 2.5.2 有限元法生物力学研究 彭祥等[32]对植入解剖型cgae和子弹头型cage的侧方入路腰椎融合手术模型施加400 N压缩载荷和8 Nm扭矩后,发现植入解剖型cage时,模型在前屈、后伸、左右侧弯及左右旋转6种工况下目标节段的活动度、cage应力均明显小于植入子弹头型cage,从而认为解剖型cage具有较好的生物力学性能。由于解剖型cage已应用于临床,其实验结论可信度高。 "

| [1] PEREZ-CRUET MJ, FESSLER RG, PERIN NI. Review:complications of minimally invasive spinal surgery. Neurosurgery. 2002;51(5 suppl): S26-S36. [2] RAJARAMAN V, VINGAN R, ROTH P, et al. Visceral and vascular complications resulting from anterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg. 1999;91(1 suppl):60-64. [3] 刘金石,闫慧博,杨昌盛,等.后路腰椎内固定术后手术部位感染的危险因素分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(11):995-1000. [4] 冯治华,张建林,陈俊.腰椎后路手术后发生椎管内血肿的危险因素分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2018,39(2):143-146. [5] 李一民,邓忠良.经侧方腰椎椎间融合术的并发症及其防治策略[J].现代医药卫生,2015,31(14):2149-2151. [6] 何磊,戎利民,董健文.极外侧入路腰椎椎体间融合术入路安全性及相关并发症的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(11): 1046-1050. [7] LEE YS, PARK SW, KIM YB. Direct lateral lumbar interbody fusion:clinical and radiological outcomes. J Kor Neurosurg Soc. 2014;55(5):248-254. [8] ALIMI M, HOFSTETTER CP, TSIOURIS AJ, et al. Extreme lateral interbody fusion for unilateral symptomatic vertical foraminal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(3):346-352. [9] FRASER RD. A wide muscle-splitting approach to the lumbosacral spine. J Bone Joint surg Br. 1982;64(1):44-46. [10] OZGUR BM, ARYAN HE, PIMENTA L, et al. Extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF): a novel surgical technique for anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 2006;6(4):435-443. [11] SILVESTRE C, MAC-THIONG JM, HILMI R, et al. Complications and morbidities of mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion:oblique lumbar interbody fusion in 179 patients. Asian Spine J. 2012;6(2):89-97. [12] 唐杰,汪洋,应放,等.经侧方入路腰椎融合术(LLIF)的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(15):1399-1402. [13] KWON B, KIM DH. Lateral lumbar interbody fusion: indications, outcomes,and complications. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(2): 96-105. [14] 邓超,张宇,夏建龙.经侧方入路腰椎椎间融合术在成人退变性脊柱侧弯的应用[J].江苏医药,2019,45(11):1175-1178. [15] LAWS CJ, COUGHLIN DG, LOTZ JC, et al. Direct lateral approach to lumbar fusion is a biomechanically equivalent alternative to the anterior approach:an in vitro study. Spine. 2012;37(10):819-825. [16] GODZIK J, KALB S, REIS MT, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of interbody fixation with secondary augmentation: lateral lumbar interbody fusion versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Spine Surg. 2018;4(2): 180-186. [17] YUAN W, KALIYA-PERUMAL AK, CHOU SM, et al. Does lumbar interbody cage size influence subsidence? A Biomechanical Study. Spine. 2020; 45(2):88-95. [18] LU T, LU Y. Comparison of the biomechanical performances among PLF, TLIF, OLIF and XLIF: a finite element analysis. Spine J. 2019;9(19): 143-144. [19] FOGEL GR, PARIKH RD, RYU SI, et al. Biomechanics of lateral lumbar interbody fusion constructs with lateral and posterior plate fixation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(3):291-297. [20] REIS MT, REYES PM, ALTUN I, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of lateral lumbar interbody fusion with secondary augmentation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25(6):720-726. [21] FOGEL GR, TURNER AW, DOOLEY ZA, et al. Biomechanical stability of lateral interbody implants and supplemental fixation in a cadaveric degenerative spondylolisthesis model. Spine. 2014;39(19): E1138-E1146. [22] DOULGERIS JJ, AGHAYEV K, GONZALEZ-BLOHM SA, et al. Biomechanical comparison of an interspinous fusion device and bilateral pedicle screw system as additional fifixation for lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Clin Biomech. 2015;30(2):205-210. [23] GODZIK J, MARTINEZ-DEL-CAMPO E, Newcomb AGUS, et al. Biomechanical stability afforded by unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation with and without interbody support using lateral lumbar interbody fusion. World Neurosurg. 2018;113:e439-e445. [24] ZHANG Z, FOGEL GR, LIAO Z, et al. Biomechanical analysis of lateral lumbar interbody fusion constructs with various fixation options:Based on a validated finite element model. World Neurosurgery. 2018;114: e1120-e1129. [25] 殷飞,马荣,蔡则成,等.斜外侧椎间融合联合单侧椎弓根钉棒固定术的三维有限元分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(8):732-740. [26] LIU X, MA J, PARK P, et al. Biomechanical comparison of multilevel lateral interbody fusion with and without supplementary instrumentation:a three dimensional finite element study. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2017;18(1):63-74. [27] XIA XP, CHEN HL, CHENG HB. Prevalence of adjacent segment degeneration after spine surgery:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(7):597-608. [28] TANG SJ. Comparison of posterior versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using fifinite element analysis.Inflfluence on adjacent segmental degeneration. Saudi Med J. 2015;36(8):993-996. [29] WANG BJ, HUA WB, KE WC, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and oblique lumbar interbody fusion on the adjacent segment:a finite element analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;126:e819-e824. [30] BASRA S, BUCKLEN B, MUZUMDAR A, et al. A novel lateral lumbar integrated plate-spacer interbody implant: in vitro biomechanical analysis. Spine J. 2015;15(2):322-328. [31] 何磊,张伟,陈瑞强,等.新型腰椎侧路一体化钛板融合器的研制及生物力学测试[J].中华实验外科杂志,2017,34(2):264-266. [32] 彭祥,王文军,晏怡果,等.解剖型纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66椎间融合器在腰椎XLIF/OLIF手术中的三维有限元分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2016,34(5):557-562. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [3] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [4] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [5] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [6] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [7] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [8] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [9] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [10] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [11] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [12] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [13] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [14] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [15] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||