Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 456-462.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2946
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
Zhong Yuanming1, Wan Tong2, Zhong Xifeng2, Wu Zhuotan2, He Bingkun2, Wu Sixian2
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2020-03-03Revised:2020-03-10Accepted:2020-04-11Online:2021-01-28Published:2020-11-19 -
Contact:Zhong Yuanming, Doctoral supervisor, Professor, Chief physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhong Yuanming, Doctoral supervisor, Professor, Chief physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760874; the First Class Discipline of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. GJKY(2018)12
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
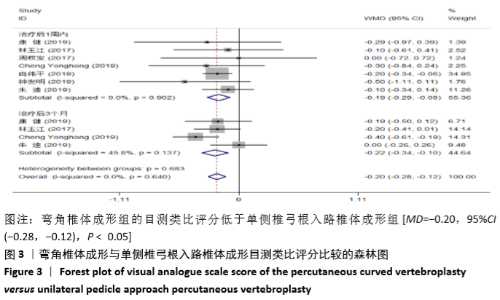
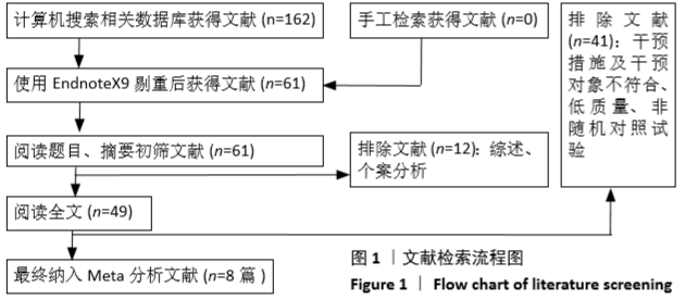
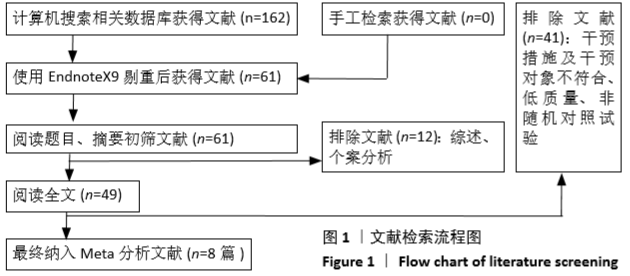
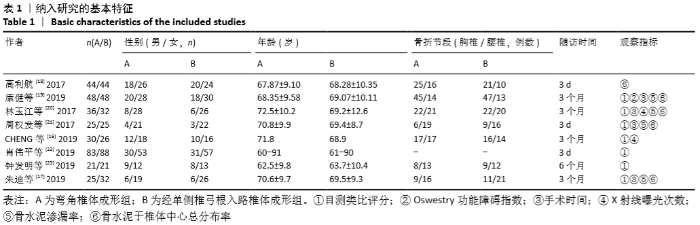
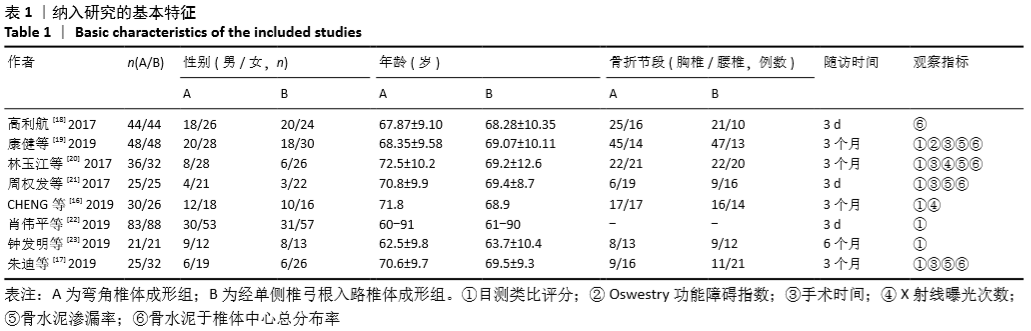
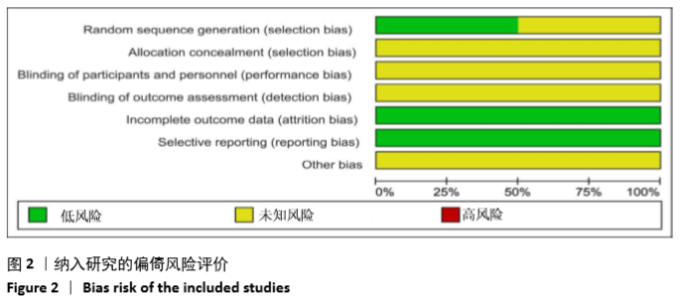
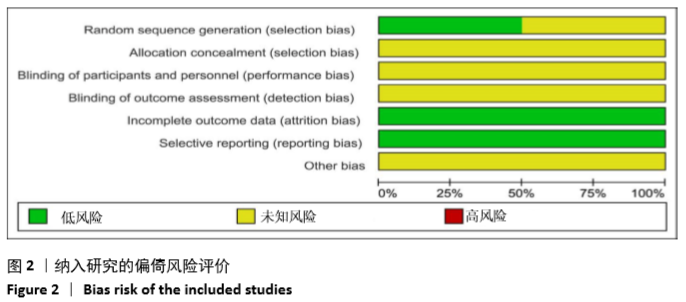
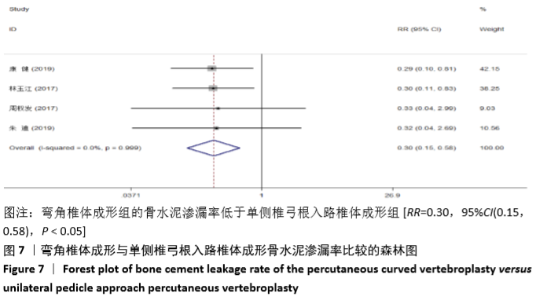
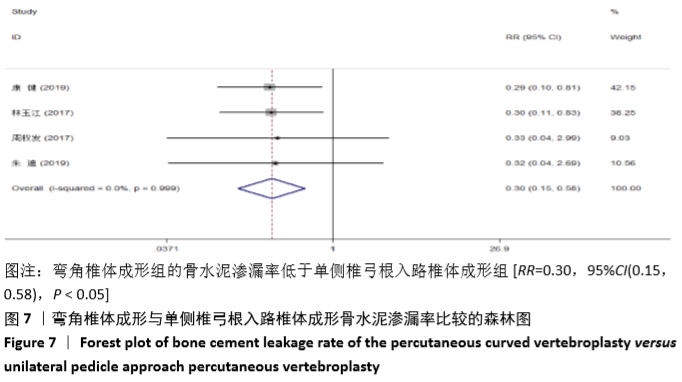
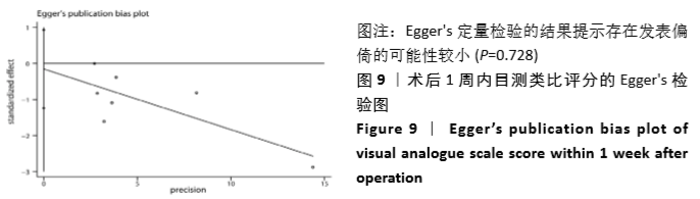
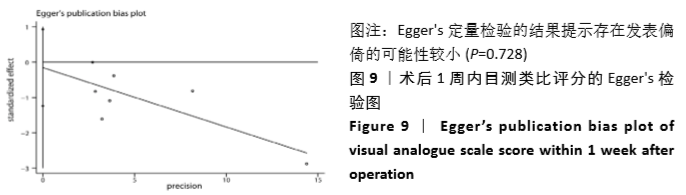
2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 术后目测类比评分 纳入的7个研究比较了2组患者经治疗后的目测类比评分[16-17,19-23]。固定效应模型Meta分析结果显示,弯角椎体成形组的目测类比评分低于单侧椎弓根入路椎体成形组,差异有显著性意义[MD=-0.20,95%CI (-0.28,-0.12),P < 0.05]。 根据治疗后时间点的不同进行亚组分析,固定效应模型Meta分析结果显示:①治疗后1周内弯角椎体成形组的目测类比评分低于单侧椎弓根入路椎体成形组,差异有显著性意义[MD=-0.19,95%CI(-0.29,-0.08),P=0.001];②治疗后3个月弯角椎体成形组的目测类比评分低于单侧椎弓根入路椎体成形组,差异有显著性意义[MD=-0.22,95%CI (-0.34,-0.10),P < 0.05],见图3。"

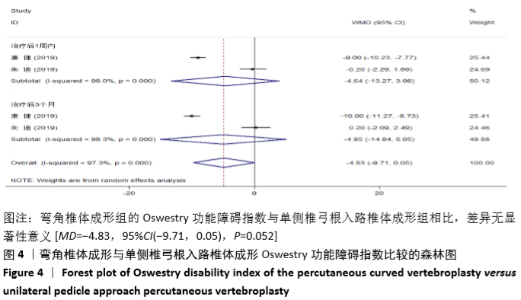
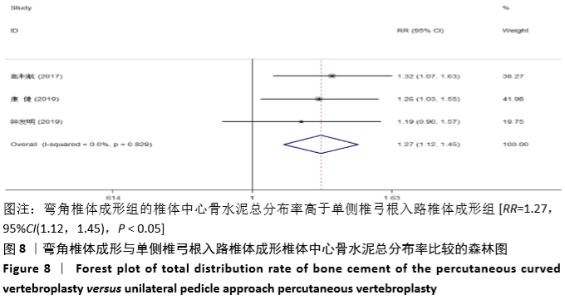
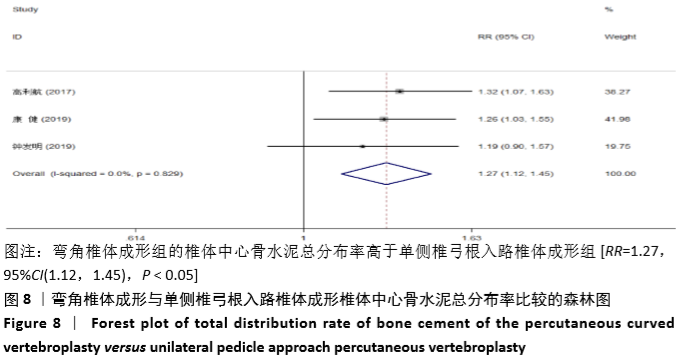
2.3.2 术后ODI 纳入的2个研究比较了2组患者经治疗后的ODI[17,19]。随机效应模型Meta分析结果显示,弯角椎体成形组的ODI与单侧椎弓根入路椎体成形组相比,差异无显著性意义[MD= -4.83,95%CI(-9.71,0.05),P=0.052]。 根据治疗后时间点的不同进行亚组分析,随机效应Meta分析结果显示:①治疗后1周内弯角椎体成形组的ODI与单侧椎弓根入路椎体成形组相比,差异无显著性意义[MD=-4.64,95%CI (-13.27,3.98),P=0.291];②治疗后3个月弯角椎体成形组的ODI与单侧椎弓根入路椎体成形组相比,差异无显著性意义[MD=-4.95,95%CI(-14.94,5.05),P=0.332],见图4。"

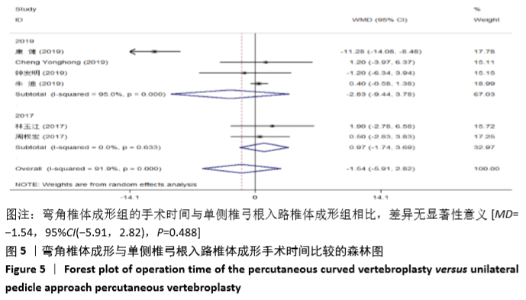
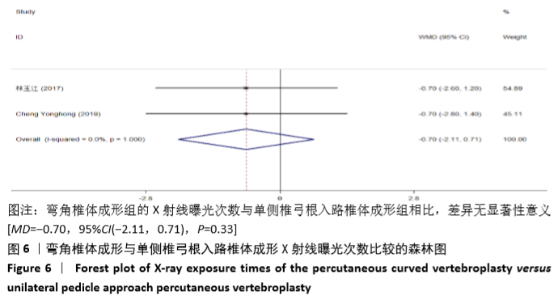
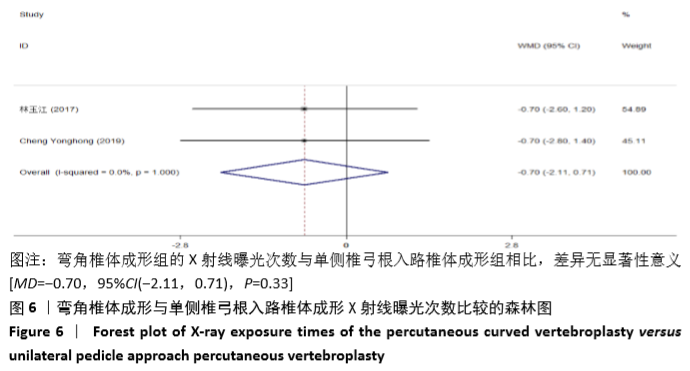
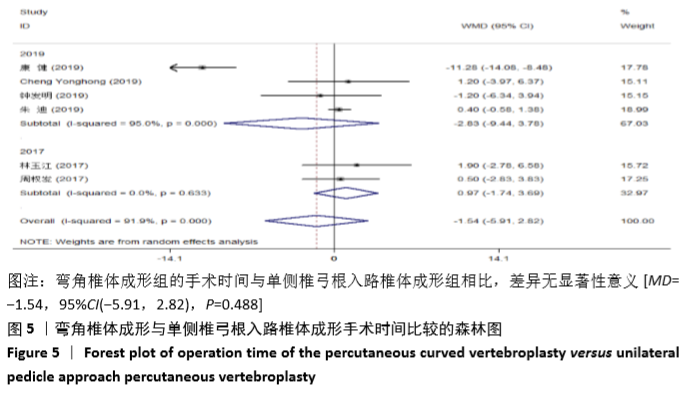
2.3.3 手术时间 纳入的6个研究比较了2组患者手术所需手术时间[16-17,19-21,23]。随机效应模型Meta分析结果显示,弯角椎体成形组的手术时间与单侧椎弓根入路椎体成形组相比,差异无显著性意义[MD= -1.54,95%CI(-5.91,2.82),P=0.488]。 根据文献发表时间进行亚组分析,随机效应Meta分析结果显示:①2019年发表的研究亚组分析结果表明:弯角椎体成形组的手术时间与单侧椎弓根入路椎体成形组相比,差异无显著性意义[MD=-2.83,95%CI(-9.44,3.78),P=0.402];②2017年发表的研究亚组分析结果表明:弯角椎体成形组的手术时间与单侧椎弓根入路椎体成形组相比,差异无显著性意义[MD=0.97,95%CI (-1.74,3.69),P=0.488],见图5。"
| [1] WU Q, XIAO X, XU Y. Evaluating the Performance of the WHO International Reference Standard for Osteoporosis Diagnosis in Postmenopausal Women of Varied Polygenic Score and Race. J Clin Med. 2020;9(2):499. [2] LA BARBERA L, CIANFONI A, FERRARI A, et al. Stent-Screw Assisted Internal Fixation of Osteoporotic Vertebrae: A Comparative Finite Element Analysis on SAIF Technique. Front Bioeng Biotechnol . 2019;7: 291. [3] ZHONG R, LIU J, WANG R, et al. Unilateral curved versus bipedicular vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. BMC Surg. 2019;19(1): 193. [4] HOSOGANE N, NOJIRI K, SUZUKI S, et al. Surgical Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture with Neurological Deficit-A Nationwide Multicenter Study in Japan. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2019;3(4): 361-367. [5] ZHU Y, CHENG J, YIN J, et al. Therapeutic effect of kyphoplasty and balloon vertebroplasty on osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine. 2019; 98(45): e17810. [6] FUSCO A. Benefits and harms of percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a cochrane review summary with commentary. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2019;98(12): 1151-1152. [7] ORHURHU V, AGUDILE E, CHU R, et al. Socioeconomic disparities in the utilization of spine augmentation for patients with osteoporotic fractures: an analysis of National Inpatient Sample from 2011 to 2015. Spine J. 2020;20(4):547-555. [8] ZHANG Y, LIU H, HE F, et al. Safety and efficacy of percutaneous kyphoplasty assisted with O-arm navigation for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures at T6 to T9 vertebrae. Int Orthop. 2020;44(2): 349-355. [9] BALAZSFI M, KIS D, TOTH T, et al. Radiofrequency facet joint denervation efficiency based on the severity of spondylarthrosis and in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. A retrospective study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019;186:105497. [10] ZUO XH, ZHU XP, BAO HG, et al. Network meta-analysis of percutaneous vertebroplasty, percutaneous kyphoplasty, nerve block, and conservative treatment for nonsurgery options of acute/subacute and chronic osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) in short-term and long-term effects. Medicine. 2018;97(29): e11544. [11] WANG B, ZHAO CP, SONG LX, et al. Balloon kyphoplasty versus percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):264. [12] TSOUMAKIDOU G, TOO C W, KOCH G, et al. CIRSE guidelines on percutaneous vertebral augmentation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017;40(3):331-42. [13] ZHAO S, XU C Y, ZHU A R, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of 3 treatments for patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A network meta-analysis. Medicine. 2017;96(26):e7328. [14] ZHANG Z, JIAO F, HUANG H, et al. A second puncture and injection technique for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):413. [15] 印平,马远征,马迅,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的治疗指南[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):643-648. [16] CHENG Y, LIU Y. Percutaneous curved vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Int Med Res. 2019;47(6):2424-2433. [17] 朱迪,尚春风,刘宏建,等.弯角穿刺针椎体成形技术治疗胸、腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(12):737-746. [18] 高利航.弯角穿刺经皮椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的效果分析[J].河南医学研究,2017,26(22):4159-4160. [19] 康健,陈文明,黄华伟.弯角椎体成形术在骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的临床应用[J].临床医药实践,2019,28(6):426-428. [20] 林玉江,林茜,杨利民,等.弯角椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017, 27(5):423-428. [21] 周权发,刘宏建,寇红伟,等.弯角椎体成形装置的早期疗效评估及对骨水泥分布的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(10):892-897. [22] 肖伟平,邱全河,余艺萍,等.单侧弯角椎体成形术与传统椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体骨折的疗效比较[J].江西中医药大学学报,2019,31(6):45-49. [23] 钟发明,肖伟平,邱全河,等.弯角经皮椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折临床疗效研究[J].重庆医学,2019,48(A01):213-215. [24] SARACEN A, KOTWICA Z. Vertebroplasty (PVP) is effective in the treatment of painful vertebral hemangiomas . Acta orthopaedica Belgica. 2018; 84(1):105-107. [25] RAHIMIZADEH A. Kyphosis and canal compromise due to refracturing of an L1 cemented vertebra managed with posterior surgery alone. Surg Neurol Int. 2019;10:212. [26] ALHASHASH M, SHOUSHA M, BARAKAT A S, et al. Effects of polymethylmethacrylate cement viscosity and bone porosity on cement leakage and new vertebral fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a prospective study. Global Spine J. 2019; 9(7): 754-760. [27] ZHANG Y, SHI L, TANG P, et al. Comparison of the efficacy between two micro-operative therapies of old patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a network meta-analysis. J Cell Biochem. 2017; 118(10): 3205-3212. [28] MA Y, WU X, XIAO X, et al. Effects of teriparatide versus percutaneous vertebroplasty on pain relief, quality of life and cost-effectiveness in postmenopausal females with acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: A prospective cohort study. Bone. 2020;131:115154. [29] TANG J, GUO WC, HU JF, et al. Unilateral and bilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty for thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fractures. J Coll Phys Surg Pak. 2019;29(10): 946-950. [30] KHAN M, KUSHCHAYEV SV. Percutaneous vertebral body augmentations: the state of art. Neuroimaging Clin North Am. 2019;29(4): 495-513. [31] SUN X, LIU X, WANG J, et al. The effect of early limited activity after bipedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty to treat acute painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Pain Physician. 2020; 23(1):E31-e40. [32] LI J, LIN J, XU J, et al. A Novel Approach for Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Based on Preoperative Computed Tomography-Based Three-Dimensional Model Design. World Neurosurg. 2017;105:20-26. [33] 寇红伟,周权发,刘宏建, 等.弯角椎体成形装置对单侧椎弓根穿刺角度及骨水泥分布的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2017,34(2): 338-341. [34] HUNT CH, KALLMES DF, THIELEN KR. A unilateral vertebroplasty approach using a curved injection cannula for directed, site-specific vertebral body filling. J Vasc Int Radiol.2009; 20(4): 553-555. [35] 周晓,陈宝,戴加平,等.单侧弯角椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性压缩性骨折的疗效[J].临床骨科杂志,2018,21(3):287-290. [36] 邓书洲.弯角穿刺经皮椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的临床研究[J].颈腰痛杂志,2019,40(5):645-647. [37] 钟睿,姜威,熊森, 等.单侧弯角与直行入路椎体成形治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折疗效的对照研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2018, 34(2): 102-108. [38] OH Y, LEE B, LEE S, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment using a transdermal fentanyl patch for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2019;62(5): 594-602. [39] HU W, KAN SL, XU HB, et al. Thoracic aggressive vertebral hemangioma with neurologic deficit: A retrospective cohort study. Medicine. 2018; 97(41): e12775. [40] 郑昊,杜伟,吕游,等.弯角式椎体成形套管在老年骨质疏松椎骨压缩性骨折中的应用价值分析[J].心理月刊,2018,13(10):174+173. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||