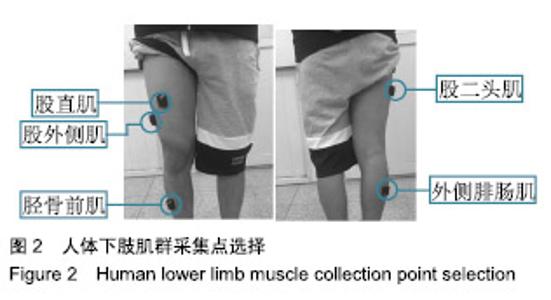
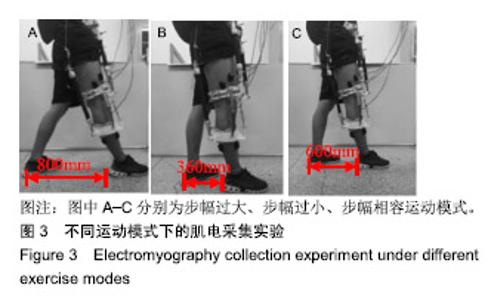
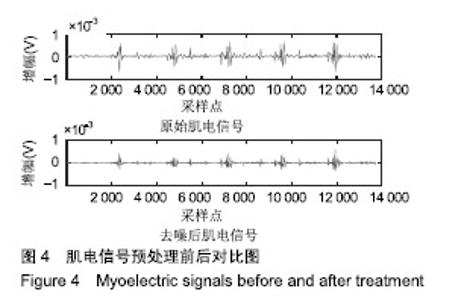
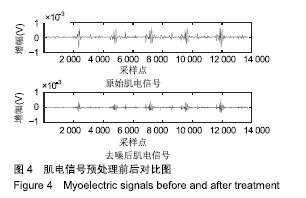
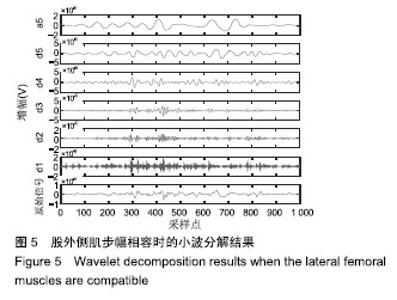
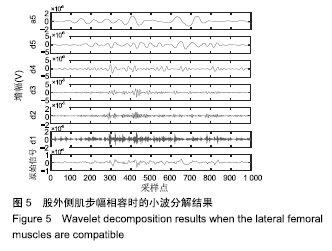
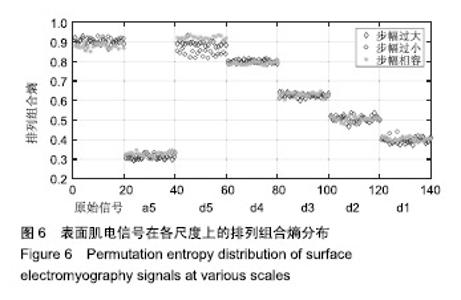
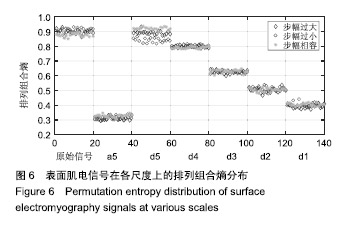
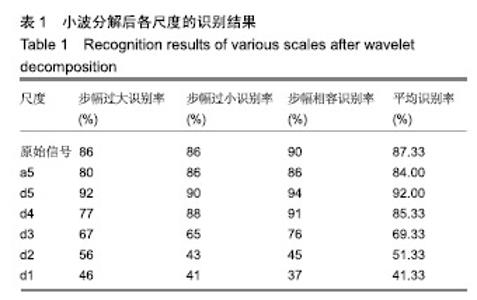
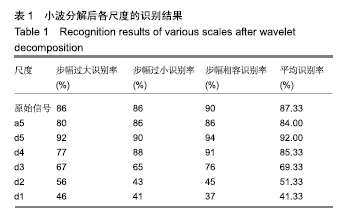
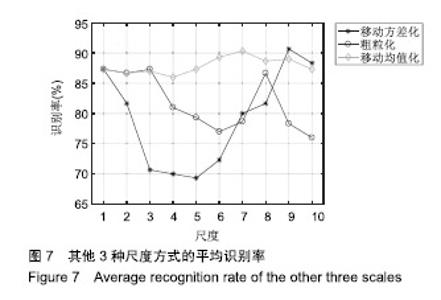
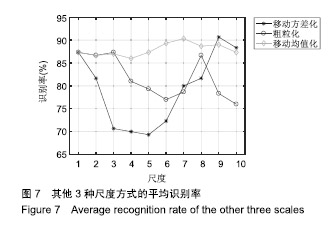
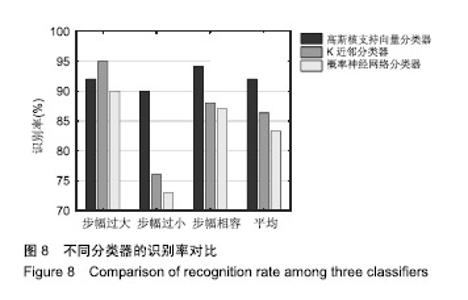
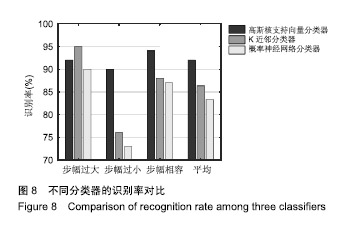
| [1]Bogue R.Robotic exoskeletons: a review of recent progress. Industrial Robot.2015;42(1):5-10.[2]Kim S,Bae J.Force-mode control of rotary series elastic actuators in a lower extremity exoskeleton using model-inverse time delay control.IEEE/ASME Trans Mech.2017;22(3):1392-1400.[3]Yepes JC, Portela MA, Álvaro J, et al. Myoelectric control algorithm for robot-assisted therapy: A hardware-in-the-loop simulation study.Biomed Eng Online.2019;18(1):3.[4]Lerner ZF,Gasparri GM,Bair MO,et al.An untethered ankle exoskeleton improves walking economy in a pilot study of individuals with cerebral palsy.IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng.2018;26(10):1985-1993.[5]Li ZJ,Kang Y,Xiao ZY,et al.Human-robot coordination control of robotic exoskeletons by skill transfers.IEEE Trans Ind Electron. 2017;64(6):5171-5181.[6]Chen ZT,Li ZJ,Chen CLP.Disturbance observer-based fuzzy control of uncertain MIMO mechanical systems with input nonlinearities and its application to robotic exoskeleton.IEEE Trans Cybern. 2017;47(4):984-994.[7]George T,George KS,Sivanandan KS.Sensing processing and application of EMG signals for HAL (Hybrid Assistive Limb) [C]. International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Intelligent Systems, 2011:749-753.[8]郭欣,王蕾,宣伯凯,等.基于有监督Kohonen神经网络的步态识别[J].自动化学报,2017,43(3):430-438.[9]陈玲玲,杨鹏,耿艳利,等.基于肌电信号的膝关节力矩识别方法[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013(s2):117-121.[10]刘磊,杨鹏,刘作军,等.采用核主成分分析和相关向量机的人体运动意图识别[J].机器人,2017,39(5): 661-669.[11]Phukpattaranont P,Thongpanja S,Anam K,et al.Evaluation of feature extraction techniques and classifiers for finger movement recognition using surface electromyography signal.Med Biol Eng Comput.2018;56(12):2259-2271.[12]Long Y,Du ZJ,Cong L,et al.Active disturbance rejection control based human gait tracking for lower extremity rehabilitation exoskeleton.ISA Trans.2017;67:389-397.[13]Yang DP,Gu YK,Liu RQ,et al.Dexterous motion recognition for myoelectric control of multifunctional transradial prostheses.Adv Robotics.2014;28(22):1533-1543.[14]Krasoulis A,Kyranou I,Erden MS,et al.Improved prosthetic hand control with concurrent use of myoelectric and inertial measurements.J Neuroeng Rehabil.2017; 14(1):71.[15]Wu Y,Jiang D,Liu X,et al.A Human–Machine interface using electrical impedance tomography for hand prosthesis control. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2018;12(6):1322-1333.[16]James EG,Karabulut M.Vascular restriction decreases EMG regularity during walking.Hum Mov Sci.2013;32(3):389-399.[17]Trybek P,Nowakowski M,Salowka J,et al.Sample entropy of sEMG signals at different stages of rectal cancer treatment. Entropy. 2018;20(11):863.[18]Dostál O,Vysata O,Pazdera L,et al.Permutation entropy and signal energy increase the accuracy of neuropathic change detection in needle EMG.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2018;2018: 5276161.[19]Wang F,Hao X,Zeng B,et al.Automated discrimination of gait patterns based on sEMG recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2013 Chinese Intelligent Automation Conference.Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2013:643-651.[20]Naik GR,Selvan SE,Arjunan SP,et al.An ICA-EBM-based sEMG classifier for recognizing lower limb movements in individuals with and without knee pathology.IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2018;26(3):675-686.[21]Xi X,Tang M,Miran SM,et al.Evaluation of feature extraction and recognition for activity monitoring and fall detection based on wearable sEMG sensors.Sensors.2017;17(6):1229.[22]Diab A,Hassan M,Marque C,et al. Performance analysis of four nonlinearity analysis methods using a model with variable complexity and application to uterine EMG signals.Med Eng Phys. 2014;36(6):761-767.[23]Guo Y,Naik GR,Huang S.Nonlinear multiscale maximal Lyapunov exponent for accurate myoelectric signal classification.Appl Soft Comput.2015;36:633-640.[24]Dmitriy M,Terry B,Edward B,et al.Quantum theory of mass potentials. PloS One.2018; 13(7):e0198929.[25]席旭刚,武昊,左静,等.基于排列组合熵和加权核Fisher的肌电跌倒检测[J].上海交通大学学报,2015, 49(11):1685-1689.[26]姚文坡,刘铁兵,戴加飞,等.脑电信号的多尺度排列熵分析[J].物理学报,2014,63(7):078704.[27]介丹,李宇驰,阴桂梅,等.基于方差的多尺度时间序列重构方法研究[J].太原理工大学学报,2017, 48(2):220-225.[28]杜艳琴,黄华.基于独立成分和小波分析的胎儿心电提取[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(13): 2394-2397.[29]张毅,冯晓林,罗元.基于改进小波包与样本熵的表面肌电信号特征提取[J].计算机应用研究,2015, 32(3):701-704.[30]Hassan VM,Ali A,Yasser B.Optimized watermarking technique using self-adaptive differential evolution based on redundant discrete wavelet transform and singular value decomposition. Expert Syst Appl.2018;114:296-312.[31]Zheng H,Zhang Y,Liu J,et al.A novel model based on wavelet LS-SVM integrated improved PSO algorithm for forecasting of dissolved gas contents in power transformers.Electr Pow Syst Res.2018;155:196-205.[32]Chen W,Pourghasemi HR, Kornejady A,et al. Landslide spatial modeling: Introducing new ensembles of ANN, MaxEnt, and SVM machine learning techniques.Geoderma.2017;305:314-327.[33]Kalantar B,Pradhan B,Naghibi SA,et al.Assessment of the effects of training data selection on the landslide susceptibility mapping: a comparison between support vector machine (SVM), logistic regression (LR) and artificial neural networks (ANN).Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk. 2018; 9(1):49-69.[34]He P,Zheng B,Zheng J.Urban PM2. 5 Diffusion Analysis Based on the Improved Gaussian Smoke Plume Model and Support Vector Machine.Aerosol Air Qual Res.2018;18:3177-3186.[35]Xue Y,Zhang L,Wang B,et al. Nonlinear feature selection using Gaussian kernel SVM-RFE for fault diagnosis.Applied Intelligence, 2018:1-26.[36]何文斌,刘群锋,熊金志.支持向量机多项式光滑函数的误差理论研究[J].计算机研究与发展,2016, 53(7):1576-1585.[37]Raghuwanshi BS,Shukla S.Class-specific kernelized extreme learning machine for binary class imbalance learning].Appl Soft Comput.2018;73:1026-1038.[38]Pimentel A, Gomes R, Olstad BH, et al. A New Tool for the Automatic Detection of Muscular Voluntary Contractions in the Analysis of Electromyographic Signals. Interact Comput.2015; 27(5):492-499.[39]张燕,郜鑫,陈玲玲,等.基于随机森林算法的地形识别系统在主动型膝上假肢控制中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(53):8609-8614.[40]王蒙,陈玲玲,耿艳利,等.基于有限状态机的智能下肢假肢控制[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(26): 4756-4759. |