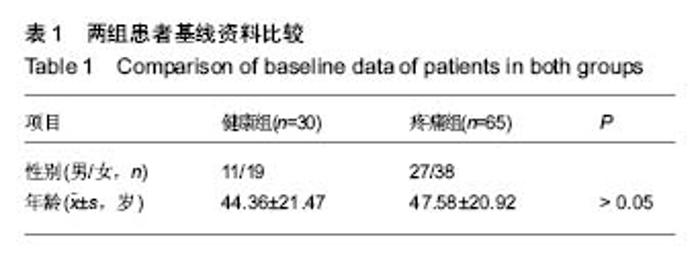
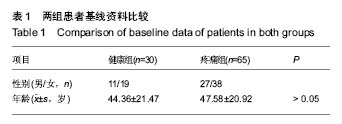
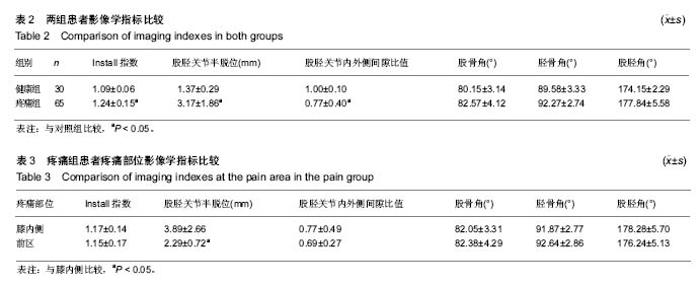
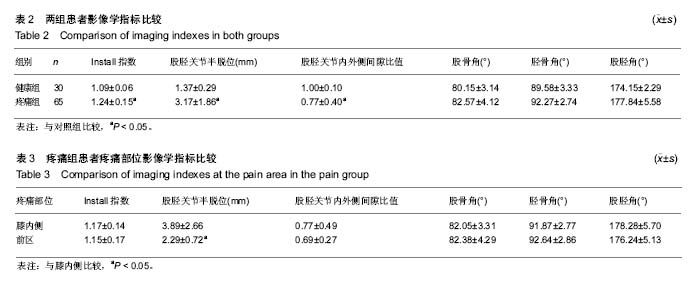
| [1] 陆川,刘海霞,张国秋,等. 膝骨性关节炎疼痛与骨髓水肿MRI 影像学改变的相关性[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2015,21(3): 242-245.[2] 王佳佳.膝关节骨关节炎与膝关节轴线角的相关性研究[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2015.[3] Sharma L,Song J, Felson D T, et al. The role of knee alignment in discase progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis.JAMA.2001;286(2) : 188-195.[4] Cahue S,Dunlop D,Hayes K,et al.Varus-valgus alignment in the progression of patellofemoral osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum.2004;50(7) : 2184-2190.[5] 郭新全, 王亦进, 宋作才, 等. 原发膝关节骨关节炎病人全下肢立位力线测量研究[J].中国临床医学影像杂志, 2001, 12(2) : 126.[6] Block JA,Shakoor N.Lower limb osteoarthritis: biomechanical alterations and implications for therapy.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010,22(5):544-550.[7] 国家中医药管理局医政司.22个专业95个病种中医临床路径(合订本)[M].北京:中国中医药出版社.2010:127-131.[8] 张爽,杨卓. 膝关节骨性关节炎影像学特征与膝部疼痛的相关性研究[J].天津医药,2010,3(1):19.[9] 金立昆,谢利民.膝骨性关节炎 X 线诊断评价进展[J].中医正骨, 2008,20(12) : 61-63.[10] 夏亚一,孙正义,黑坂昌弘,等.下肢力学轴线与膝关节骨关节炎的关系[J].中国药物与临床,2002,2(1) : 30-32.[11] 高兴华,刘永轶,王敏聪,等.膝关节置换术后皮肤麻痹的解剖基础及相关临床研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2016,34(2):121-125.[12] 罗志鸿,余存泰,谢琦,等.膝关节骨性关节炎摄影体位的探讨及临床应用价值[J].医学研究杂志,2009,38(2).63-65.[13] 王庆甫, 黄沪.膝关节骨性关节之的 X 线影像学分析[J].中国骨伤, 2000,13(6) : 348.[14] 陈宇,杨林,吴煊.足阳明经筋型膝骨关节炎临床影像学研究[J].广州中医药大学学报,2016,33(5):658-661.[15] 罗滨,徐能全,吴东保,等.髌骨测量参数分析及其在髌骨假体设计中的意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2004,22:608-610.[16] 蔡余力, 王少山.膝关节骨性关节炎的X线测量与分析[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2006,4(5):358-360.[17] 褚立希,王锋. 膝骨关节炎X片生物力学及形态学测量分析[J].中西医结合学报,2004, 2(6):432.[18] Verstraete KL,Almqvist F,Verdonk P,et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of cartilage and cartilage repair.Clin Radiol.2004;59(8):674-689.[19] Lachance L,Sowers M,Jamadar D,et al.The experience of painand emergent osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthr Cartilage.2001;9(6):527-532. |