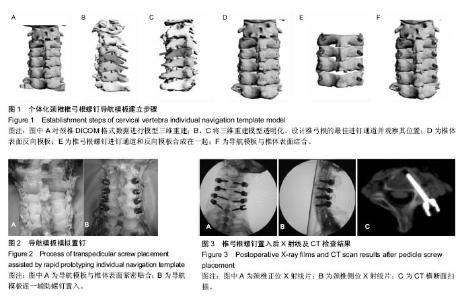
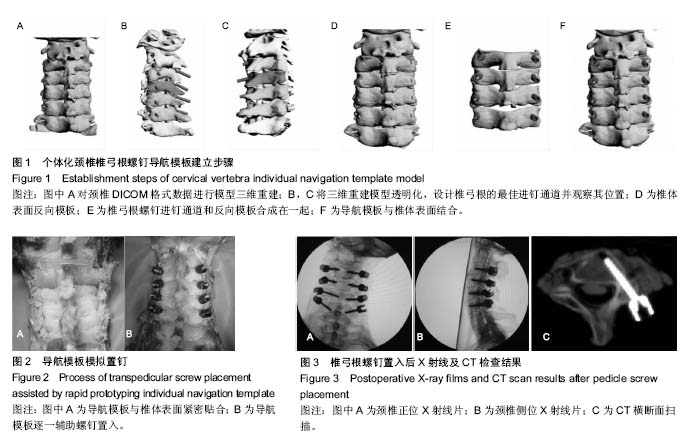
| [1] 刘景堂,唐天驷,王东来,等.颈椎椎弓根螺钉内固定系统的临床应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(10):590-594.[2] 田纪伟,袁文,张清港.颈椎椎弓根钉内固定系统研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2006,14(4):308-310.[3] 陆声,徐永清,李严兵,等.脊柱椎弓根定位数字化导航模板的设计[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2008,10(2):128-131.[4] 张漾杰.下颈椎椎弓根螺钉内固定的临床应用研究[D].昆明:昆明医学院, 2007.[5] 陆声,徐永清,李严兵,等.脊柱椎弓根定位数字化导航模板的设计[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2008,10(2):128-131.[6] 毛克政,王庆德,梅伟,等. 3D打印个体化导板辅助颈椎椎弓根螺钉置钉的可行性研究[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2016,32(1):47-50.[7] 王远政,田晓滨,刘洋,等. Mimics及颈椎模型用于下颈椎椎弓根个体化置钉的应用研究[J].第三军医大学学报, 2012,34(15): 1543-1547.[8] Abumi K, Itoh H, Taneichi H, et al. Transpedicular screw fixation for traumatic lesions of the middle and lower cervical spine: description of the techniques and preliminary report. J Spinal Disord. 1994;7(1):19-28.[9] Abumi K, Kaneda K. Pedicle screw fixation for nontraumatic lesions of the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22(16):1853-1863.[10] 刘景堂,唐天驷,刘兴炎,等.两种长度的颈椎椎弓根螺钉与侧块螺钉拔出试验比较[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2005,15(3):177-179.[11] 胡巍,陈水连,柯宝毅,等.后路钉棒系统在经寰枢椎椎弓根治疗可复性寰枢椎不稳定中的应用[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2014, 24(31): 103-106.[12] 金宇恒,杨光,郝玉刚,等.颈椎椎弓根钉棒系统内固定在下颈椎骨折脱位治疗中的临床应用[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志:电子版, 2015, 7(11):69-73.[13] 邱贵兴.计算机辅助导航技术在骨科手术中的应用[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2006,26(10):651-652.[14] 熊健,佘远举,许永涛,等.颈椎椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗无骨折脱位型颈脊髓损伤[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2014,13(11):909-911.[15] 张立, 陈安富, 王勇, 等. 下颈椎椎弓根钉徒手置钉准确性的Ct扫描评价及置钉技术要领[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2012,28(19): 3253-3257.[16] Esses SI, Sachs BL, Dreyzin V. Complications associated with the technique of pedicle screw fixation. A selected survey of ABS members. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(15): 2231-2238.[17] Rosen CD. Complications of pedicle screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991;16(5):599.[18] Hicks JM, Singla A, Shen FH, et al. Complications of pedicle screw fixation in scoliosis surgery: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(11):E465-470.[19] West JL 3rd, Ogilvie JW, Bradford DS. Complications of the variable screw plate pedicle screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991;16(5):576-579.[20] Blumenthal S, Gill K. Complications of the Wiltse Pedicle Screw Fixation System. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(13): 1867-1871.[21] Faraj AA, Webb JK. Early complications of spinal pedicle screw. Eur Spine J. 1997;6(5):324-326.[22] 毛广平,赵建宁,王与荣,等.三维定位器置钉方法的研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2005,13(18):1404-1407.[23] Ogihara N, Takahashi J, Hirabayashi H, et al. Long-term results of computer-assisted posterior occipitocervical reconstruction. World Neurosurg. 2010;73(6):722-728.[24] Seichi A, Takeshita K, Nakajima S, et al. Revision cervical spine surgery using transarticular or pedicle screws under a computer-assisted image-guidance system. J Orthop Sci. 2005;10(4):385-390.[25] Zheng G, Nolte LP. Computer-Assisted Orthopedic Surgery: Current State and Future Perspective. Front Surg. 2015;2:66.[26] 宁金沛,吴卫东,覃求,等. 3D 打印个体化导航模板在胸椎和颈椎椎弓根螺钉植入的临床应用[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2015,11(5): 385-389.[27] Mavrogenis AF, Savvidou OD, Mimidis G, et al. Computer-assisted navigation in orthopedic surgery. Orthopedics. 2013;36(8):631-642.[28] 中华医学会骨科学分会. 计算机导航辅助脊柱外科手术指南[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2016,36(13):817-825.[29] 霍莉峰,倪衡建.数字骨科应用与展望:更精确、个性、直观的未来前景[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(9):1457-1462.[30] 陈雁西,邵志民.数字化骨科临床研究平台的构建及应用[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2009,29(11):993-999.[31] 霍莉峰,倪衡建.数字骨科应用与展望:更精确、个性、直观的未来前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(9):1457-1462.[32] 段彦静, 孙文磊. 逆向工程和快速成型技术及医学应用[J]. 医疗卫生装备, 2006,27(10):31-32.[33] 李久权,王平,王永强,等.逆向工程及其在Cad软件中的实现[J]. 微计算机信息, 2006,22:141-143.[34] 林山,尹庆水,夏虹,等.数字化重建与快速成型技术在复杂上颈椎疾患诊治中的应用[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011,21(1):16-20.[35] 江静,祁文军,阿地力,等.快速成型技术在医学上的应用[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2011,5:254-256.[36] 陆声,徐永清,李严兵,等.脊柱椎弓根定位数字化导航模板的设计[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2008,10(2):128-131.[37] 谭海涛,谢兆林,江建中,等. 数字化导航模板在颈椎椎弓根螺钉置入中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2015,25(6):497-502.[38] 黄轩,李凤宁,张帆,等.三维打印成型导航模板辅助枢椎椎板螺钉置入的实验研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014,24(4):366-371.[39] 陆声,徐永清,张元智,等. 快速成形个体化导航模板辅助枢椎椎板螺钉的植入[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2009,29(8):739-743.[40] 陆声,徐永清,张元智,等.数字化导航模板在上颈椎椎弓根定位中的初步临床应用[J].中华外科杂志, 2009,47(5):359-362.[41] van Dijk M, Smit TH, Jiya TU, et al. Polyurethane real-size models used in planning complex spinal surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(17):1920-1926.[42] 卢腾,李浩鹏,臧全金,等.椎弓根螺钉导航模板在上颈椎手术中的应用[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2015,12(6):29-32, 36,插4.[43] 陈宣煌,许卫红,黄文华,等.基于3D打印的腰椎椎弓根螺钉数字化置入及临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(17): 2752-2757.[44] 张宇鹏,史亚民,王华东,等.个体化数字导航模板在脊柱侧凸手术中的应用研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2015,14(3):219-223.[45] 黄轩,李凤宁,张帆,等.个体化三维打印导航模板辅助下颈椎椎弓根置钉的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(20):1880- 1884.[46] 师继红,陆声,张元智,等.数字化脊柱椎弓根导航模板在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2008,10(2):138-141.[47] 陈雁西,邵志民.数字化骨科临床研究平台的构建及应用[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2009,29(11):993-999. |