Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (48): 7156-7162.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.48.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cocktail therapy reduces hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty
Shi Li-jun, Bai Yu, Gao Fu-qiang, Sun Wei, Wang Wei-guo, Cheng Li-ming, Guo Wan-shou
- Department of Orthopedics, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
-
Revised:2016-08-28Online:2016-11-25Published:2016-11-25 -
Contact:Sun Wei, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China -
About author:Shi Li-jun, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China Bai Yu, Department of Orthopedics, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81273972; the Youth Science and Technology Talent Project of China-Japan Friendship Hospital, No. 2014-QNYC-A-06
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shi Li-jun, Bai Yu, Gao Fu-qiang, Sun Wei, Wang Wei-guo, Cheng Li-ming, Guo Wan-shou . Cocktail therapy reduces hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7156-7162.
share this article
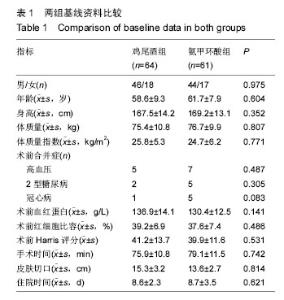
2.1 参与者数量分析 对182例将要行首次全髋关节置换的患者进行筛选和评估,31例患者由于符合排除标准不能进入研究,23例患者拒绝参加试验。因此此次试验中,共128例患者参与了试验。将这些患者进行随机化分组后,有3例患者在术前退出,最终试验中共有125例患者,其中鸡尾酒组64例、氨甲环酸组61例。 2.2 基线资料比较 两组患者的人口学基线和临床特征无显著差别(P > 0.05),见表1,观察指标主要包括患者的性别、年龄、身高、体质量、体质量指数、Harris髋关节评分、ASA评分、血红蛋白浓度、红细胞比容和术前合并症,围手术期观察指标包括手术时间、皮肤切口长度住院日,这些指标测量由2名不参与此次试验的外科医师完成。"
| [1] Magnússon B,Pétursson Þ,Edmunds K,et al.Improving Planning and Post-Operative Assessment for Total Hip Arthroplasty.Eur J Transl Myol.2015;25(2):4913.[2] Konig G,Hamlin BR,Waters JH.Topical tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rates in total hip and total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2013; 28: 1473.[3] Wei W,Wei B.Comparison of Topical and Intravenous Tranexamic Acid on Blood Loss and Transfusion Rates in Total Hip Arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2014;29:2113.[4] Alshryda S,Mason J,Sarda P,et al.Topical (Intra-Articular) Tranexamic Acid Reduces Blood Loss and Transfusion Rates Following Total Hip Replacement A Randomized Controlled Trial (TRANX-H). J Bone Joint Surg Am.2013;95:1969.[5] Lane A,Crosby E.Blood management for hip reconstruction surgery.Orthop Clin North Am.2009; 40: 417-425.[6] Stokes ME,Ye X,Shah M,et al.Impact of bleeding-related complications and/or blood product transfusions on hospital costs in inpatient surgical patients.BMC Health Serv Res.2011;11:135.[7] Murphy M,Stanworth S,Yazer M.Transfusion practice and safety: current status and possibilities for improvement. Vox Sang.2011;100:46-59. [8] Hemlata SS,Verma A.Adverse events related to blood transfusion. Indian J Anaesth.2014;58(5):543-551.[9] Lemaire R.Strategies for blood management in orthopaedic and trauma surgery.J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2008;90:1128.[10] Vaglio S,Prisco D,Biancofiore G,et al.Recommendations for the implementation of a Patient Blood Management programme. Application to elective major orthopaedic surgery in adults.Blood Transfus.2016;14(1):23-65.[11] Crescibene A,Martire F,Gigliotti P,et al.Postoperative Autologous Reinfusion in Total Knee Replacement.J Blood Transfus.2015;2015:826790.[12] Formby PM,Pickett AM,Van Blarcum GS,et al.The Use of Intravenous Tranexamic Acid in Patients Undergoing Total Hip or Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Analysis at a Single Military Institution. Mil Med.2015;180(10):1087-1090.[13] Hsu CH,Lin PC,Kuo FC,et al.A regime of two intravenous injections of tranexamic acid reduces blood loss in minimally invasive total hiparthroplasty: a prospective randomised double-blind study.Bone Joint J.2015; 97-B(7):905-910.[14] Hogan CA,Golightly LK,Phong S,et al.Perioperative blood loss in total hip and knee arthroplasty: Outcomes associated with intravenous tranexamic acid use in an academic medical center.SAGE Open Med.2016; 4: 2050312116637024.[15] Bryan AJ,Sanders TL,Trousdale RT,et al.Intravenous Tranexamic Acid Decreases Allogeneic Transfusion Requirements in Periacetabular Osteotomy. Orthopedics. 2016; 39(1):44-48.[16] Alshryda S,Mason JM,Sarda P,et al.The effect of tranexamic acid on artificial joint materials: a biomechanical study (the bioTRANX study).J Orthop Traumatol.2015; 16(1):27-34.[17] Yewlett MA,Oakley J,Mason L,et al.Does epinephrine wash reduce blood loss in primary total hip replacements? Wales Orthop J.2014;1:7. [18] Sasanuma H,Sekiya H,Takatoku K,et al.Efficient strategy for controlling postoperative hemorrhage in total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19:921.[19] Gasparini G,Papaleo P,Pola P,et al.Local infusion of norepinephrine reduces blood losses and need of transfusion in total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop.2006; 30:253.[20] Tuttle JR,Ritterman SA,Cassidy DB,et al.Cost benefit analysis of topical tranexamic acid in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2014;29(8): 1512-1515.[21] Vigna-Taglianti F,Basso L,Rolfo P,et al.Tranexamic acid for reducing blood transfusions in arthroplasty interventions: a cost-effective practice.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2014;24(4):545-551.[22] Alshryda S,Sukeik M,Sarda P,et al.A systematic review and meta-analysis of the topical administration of tranexamic acid in total hip and knee replacement.Bone Joint J.2014;96-B:1005.[23] Huang GP,Jia XF,Xiang Z,et al.Tranexamic Acid Reduces Hidden Blood Loss in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Comparative Study and Meta-Analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:797-802.[24] Chen S,Wu K,Kong G,et al.The efficacy of topical tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2016; 17(1):81.[25] Gross JB.Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution.Anesthesiology. 1983;58:277.[26] Nadler SB,Hidalgo JH,Bloch T.Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery.1962;51:224. [27] Sehat KR,Evans RL,Newman JH.Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2004;86:561. [28] Tellisi N,Kakwani R,Hulse N,et al.Autologous blood transfusion following total knee arthroplasty: is it always necessary?Int Orthop.2006;30(5):412-414.[29] Yang Y,Lv YM,Ding PJ,et al.The reduction in blood loss with intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid in unilateral total knee arthroplasty without operative drains: a randomized controlled trial.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2015;25:135.[30] Shinde A,Sobti A,Maniar S,et al.Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and need of blood transfusion in total knee arthroplasty: A prospective, randomized, double-blind study in Indian population.Asian J Transfus Sci.2015;9(2):168-172.[31] Pertlí?ek J,Stehlík J,Sadovský P,et al.The Effect of Tranexamic Acid on Blood Loss after Primary Unilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty. Prospective Single-Centre Study. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech.2015;82(6):418-423.[32] Price AJ. Hemostatic changes and postoperative deep-vein thrombosis associated with use of a pneumatic tourniquet.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1982;64:1260.[33] Hourlier H,Fennema P.Chemoprophylaxis without intra-articular wound drainage can replace autotransfusion in primary TKA.Orthopedics.2011;34:154.[34] Mannucci PM.Hemostatic drugs.N Engl J Med.1998;339: 245.[35] Burleson A,Guler N,Banos A,et al.Perioperative Factors and Their Effect on the Fibrinolytic System in Arthroplasty Patients.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost.2016; 22(3):274-279.[36] Yun-Choi HS,Park KM,Pyo MK.Epinephrine induced platelet aggregation in rat platelet-rich plasma.Thromb Res.2000;100:511.[37] Gao F,Sun W,Guo W,et al.Topical Administration of Tranexamic Acid plus diluted-epinephrine in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Double-blinded Controlled Trial.J Arthroplasty.2015.doi:10.1016/j.arth.2015.03.003. [38] Keyhani S,Esmailiejah AA,Abbasian MR,et al.Which Route of Tranexamic Acid Administration is More Effective to Reduce Blood Loss Following Total Knee Arthroplasty? Arch Bone Jt Surg.2016;4(1):65-69.[39] Özta? S,Öztürk A,Akalin Y,et al.The effect of local and systemic application of tranexamic acid on the amount of blood loss and allogeneic bloodtransfusion after total knee replacement.Acta Orthop Belg.2015;81(4):698-707.[40] Ueno M,Sonohata M,Fukumori N,et al.Comparison between topical and intravenous administration of tranexamic acid in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci.2016; 21(1):44-47. [41] Gilbody J,Dhotar HS,Perruccio AV,et al.Topical tranexamic acid reduces transfusion rates in total hip and knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2014;29:681-684.[42] Malone KJ,Matuszak S,Mayo D,et al.The effect of intra-articular epinephrine lavage on blood loss following total knee arthroplasty.Orthopedics.2009;32:100.[43] Yue C,Kang P,Yang P,et al.Topical application of tranexamic acid in primary total hip arthroplasty: a randomized double-blind controlled trial.J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(12):2452-2456.[44] Wang C,Kang P,Ma J,et al.Single-dose tranexamic acid for reducing bleeding and transfusions in total hip arthroplasty: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial of different doses.Thromb Res.2016;141:119-123.[45] Melvin JS,Stryker LS,Sierra RJ.Tranexamic Acid in Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2015; 23(12):732-740. |
| [1] | Liang Xin, Wang Heng, Li Xian-rong. Preoperative application of alprazolam for patients with anxiety and depression and pain after total knee arthroplasty: its safety and effectiveness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 985-992. |
| [2] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [3] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [4] | Lu Yao-jia, Xiong Chuan-zhi, Li Xiao-lei, Hu Han-sheng, Chen Gang, Wang Qiang, Lu Zhi-hua. Comparison of two methods for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1004-1008. |
| [5] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [6] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [7] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [8] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [9] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [10] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [11] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [12] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [13] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [14] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [15] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||