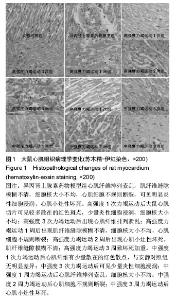
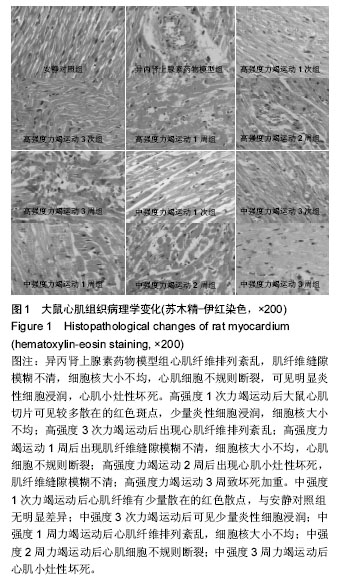
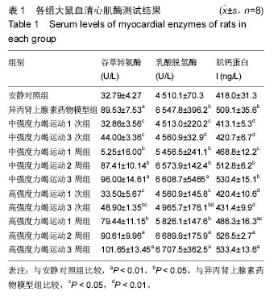
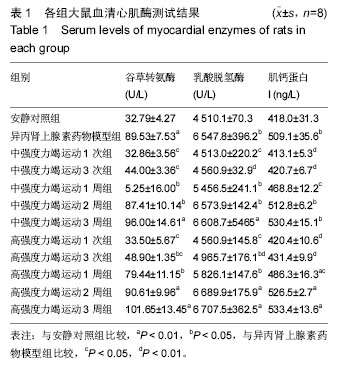
| [1] 李玉光,丁洽烽,谭学瑞,等.长时间慢性心肌缺血实验动物模型的构建技术[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(23):42-43,257
[2] 于震,刘建勋.慢性心肌缺血动物模型制备方法[J].中国药理学通报,2005,21(3):273-276.
[3] Kannan MM, Quine SD. Ellagic acid ameliorates isoproterenol induced oxidative stress: Evidence from electrocardiological, biochemical and histological study. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;659(1):45-52.
[4] 于兰.脑心康口服液对实验大鼠心肌缺血的保护作用及相关机制的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2006.
[5] Panda VS, Naik SR. Cardioprotective activity of Ginkgo biloba Phytosomes in isoproterenol-induced myocardial necrosis in rats: a biochemical and histoarchitectural evaluation. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2008; 60(4-5):397-404.
[6] 潘志,段凤力,王颖航.冠心康胶囊对大鼠急性心肌缺血保护作用的研究[J].中医药信息,2005,22(1):46-48.
[7] Zhou R, Xu Q, Zheng P, et al. Cardioprotective effect of fluvastatin on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;586(1-3):244-250.
[8] 刘瑜,林蓉.补阳还五汤对异丙肾上腺素诱导大鼠心肌缺血的保护作用[J].中药材,2009, 32(3):380-383.
[9] 高晓嶙,常芸,廉贺群.力竭运动后不同时相大鼠心肌cTnI、Mb mRNA与血清cTnI、Mb表达[J].中国运动医学杂志,2009,28(2):162-166.
[10] Wang K, Xu BC, Duan HY, et al. Late cardioprotection of exercise preconditioning against exhaustive exercise-induced myocardial injury by up-regulatation of connexin 43 expression in rat hearts. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine. 2015; 8(8):658-663.
[11] 张钧,许豪文,陈炳猛,等.力竭运动造成心肌损伤的机制探讨[J].体育科学,2001,21(5):62-64.
[12] 成玲俐,吴素华,李志梁,等.大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤动物模型的建立与评估[J].中国实验诊断学,2010,14(8): 1163-1165.
[13] 吴涛,励建安.心肌缺血动物模型制备方法[J].中国康复医学杂志,2006,21(2):180-182.
[14] Abarbanell AM, Herrmann JL, Weil BR, et al. Animal models of myocardial and vascular injury. J Surg Res. 2010;162(2):239-249.
[15] Juneau M, Roy N, Nigam A, et al. Exercise above the ischemic threshold and serum markers of myocardial injury. Can J Cardiol. 2009;25(10):e338-341.
[16] 卜于骏,丁树哲.耐力训练和一次性力竭运动对大鼠心肌和骨骼肌硫氧还蛋白还原酶的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2005,24(3):293-296.
[17] 刘子泉,陈昀赟,王天辉,等.力竭运动致大鼠心肌损伤及S100A4蛋白表达变化[J].中国公共卫生,2011,27(5): 584-586.
[18] Ascensão A, Ferreira R, Magalhães J. Exercise-induced cardioprotection--biochemical, morphological and functional evidence in whole tissue and isolated mitochondria. Int J Cardiol. 2007;117(1):16-30.
[19] Sim MK. Des-aspartate-angiotensin I, a novel angiotensin AT(1) receptor drug. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;760:36-41.
[20] Kohut ML, Arntson BA, Lee W, et al. Moderate exercise improves antibody response to influenza immunization in older adults. Vaccine. 2004;22(17-18):2298-2306.
[21] 赵敬国,王福文.大鼠力竭性游泳运动过程中心电图的动态观察[J].现代康复,2000,4(8):1194-1195.
[22] 赵敬国,王福文.力竭性运动后不同时相大鼠心肌形态结构的改变观察[J].中国运动医学杂志,2001,20(3):316-317.
[23] Mohamadin AM, Elberry AA, Mariee AD, et al. Lycopene attenuates oxidative stress and heart lysosomal damage in isoproterenol induced cardiotoxicity in rats: A biochemical study. Pathophysiology. 2012;19(2):121-130.
[24] Priscilla DH, Prince PS. Cardioprotective effect of gallic acid on cardiac troponin-T, cardiac marker enzymes, lipid peroxidation products and antioxidants in experimentally induced myocardial infarction in Wistar rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2009;179(2-3):118-124.
[25] Shiny KS, Kumar SH, Farvin KH, et al. Protective effect of taurine on myocardial antioxidant status in isoprenaline-induced myocardial infarction in rats.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005;57(10):1313-1317.
[26] Hellstrom HR. Can the premises of the spasm of resistance vessel concept permit improvement in the treatment and prevention of ischemic heart disease. Med Hypotheses. 2003;60(1):36-51.
[27] O'Brien PJ, Smith DE, Knechtel TJ, et al. Cardiac troponin I is a sensitive, specific biomarker of cardiac injury in laboratory animals. Lab Anim. 2006;40(2):153-171.
[28] 郭勇力,刘霞,张文峰,等.不同强度运动对大鼠心肌细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(9):1732-1733.
[29] Rodríguez-Calvo MS, Tourret MN, Concheiro L, et al. Detection of apoptosis in ischemic heart. Usefulness in the diagnosis of early myocardial injury. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2001;22(3):278-284.
[30] Rong F, Peng Z, Ye MX, et al. Myocardial apoptosis and infarction after ischemia/reperfusion are attenuated by kappa-opioid receptor agonist.Arch Med Res. 2009;40(4):227-234. |