Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (31): 4630-4636.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.31.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of femoral neck fracture with different fixation ways
Xia Zhi-feng, Liang Ming, Li Ya-feng, Zeng Guan-nan
- Department of Orthopedics, Zhengzhou Central Hospital Affiliated to Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2016-04-24Online:2016-07-22Published:2016-07-22 -
About author:Xia Zhi-feng, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Zhengzhou Central Hospital Affiliated to Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xia Zhi-feng, Liang Ming, Li Ya-feng, Zeng Guan-nan. Finite element analysis of femoral neck fracture with different fixation ways[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4630-4636.
share this article
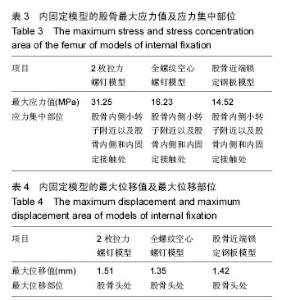
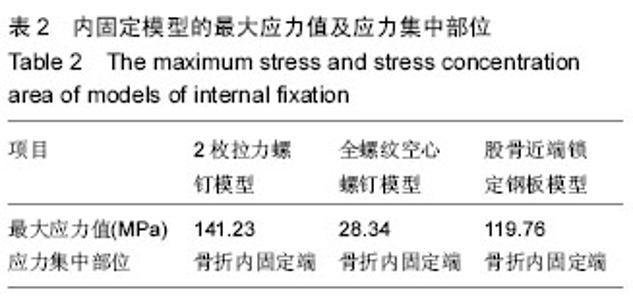
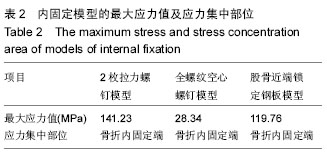
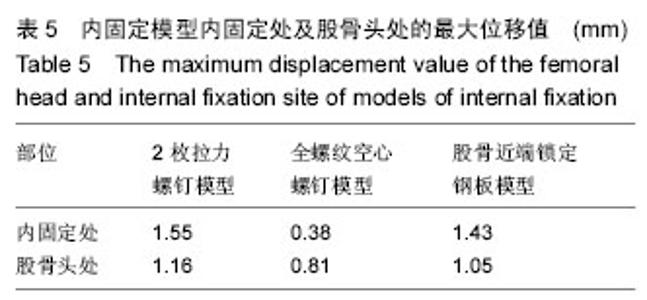
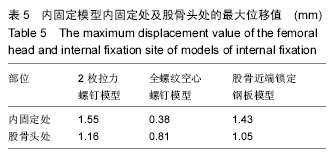
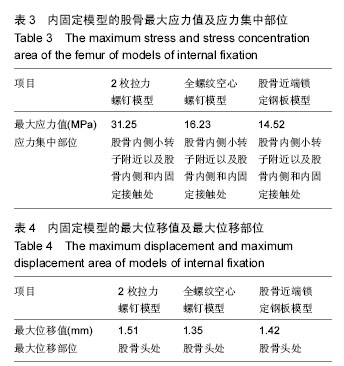
2.2 不同内固定模型股骨的应力分布情况 2枚拉力螺钉模型股骨应力分布比较集中,全螺纹空心螺钉模型和股骨近端锁定钢板模型的股骨应力分布相对比较分散。其中2枚拉力螺钉模型的股骨最大应力值最大,股骨近端锁定钢板模型的股骨最大应力值最小。2枚拉力螺钉模型、全螺纹空心螺钉模型和股骨近端锁定钢板模型的股骨最大应力均集中在股骨内侧小转子附近以及股骨内侧和内固定接触处,见表3。 2.3 不同内固定模型的最大位移分布情况 由表4可以看出,2枚拉力螺钉模型的最大位移值最大,其次为股骨近端锁定钢板模型,全螺纹空心螺钉模型的最大位移值最小。2枚拉力螺钉模型、全螺纹空心螺钉模型和股骨近端锁定钢板模型的最大位移均在股骨头处。"
| [1] 冼敬锋.全髋关节置换术与骨折内固定术治疗中老年股骨颈骨折的疗效分析[J].重庆医学,2013,42(13): 1528-1529.
[2] 陈涛,尚希福,贺瑞,等.先天性短股骨颈人工全髋关节置换时避免下肢延长的临床研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2012,26(3):289-291.
[3] 蒲晓斌,李裕标,马波,等.内固定术后股骨颈短缩的多因素分析及其对骨折的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2012, 12(17):3263-3266.
[4] 韦积华.计算机辅助骨科手术系统在股骨颈骨折经皮空心拉力螺钉技术中的实验研究[D].广西医科大学,2012.
[5] 骆东.三种内固定方式治疗股骨颈骨折的生物力学研究[D].吉林大学,2012.
[6] SooHoo NF, Farng E, Chambers L, et al.Comparison of complication rates between hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty for intracapsular hip fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(4): e384-e389.
[7] Napoli N, Schwartz AV, Palermo L, et al.Risk factors for subtrochanteric and diaphyseal fractures: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98(2): 659-667.
[8] van Embden D, Rhemrev SJ, Genelin F, et al. The reliability of a simplified Garden classification for intracapsular hip fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2012;98(4):405-408.
[9] van Embden D, Roukema GR, Rhemrev SJ, et al. The Pauwels classification for intracapsular hip fractures: is it reliable? Injury. 2011;42 (11): 1238-1240.
[10] Gaspard, Crnkovic T, Durovic D, et al. AO group, AO subgroup, Garden and Pauwels classification systems of femoral neck fractures: are they reliable and reproducible? Med Glas (Zenica). 2012;9(2): 243-247.
[11] Taha ME, Audigé L, Siegel G, et al.Factors predicting secondary displacement after non-operative treatment of undisplaced femoral neck fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(2): 243-249.
[12] Voskuijl T, Neuhaus V, Kinaci A, et al. In-hospital outcomes after hemiarthroplasty versus total hip arthroplasty for isolated femoral neck fractures. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2014;2(3): 151-156.
[13] Li SG, Sun TS, Liu Z, et al. Factors influencing postoperative mortality one year after surgery for hip fracture in Chinese elderly population. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(14): 2715-2719.
[14] Neuman MD, Donegan DJ, Mehta S. Comparative effectiveness of joint reconstruction and fixation for femoral neck fracture: inpatient and 30-day mortality. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2013;42(7): E42-E47.
[15] van den Bekerom MP, Siereveld IN, Bonke H, et al.The natural history of the hemiarthroplasty for displaced intracapsular femoral neck fractures.Acta Orthop. 2013; 84(6): 555-560.
[16] Liem IS, Kammerlander C, Raas C, et al. Is there a difference in timing and cause of death after fractures in the elderly? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(9): 2846-2851.
[17] Araujo TP, Guimaraes TM, Andrade-Silva FB, et al.Influence of time to surgery on the incidence of complications in femoral neck fracture treated with cannulated screws. Injury. 2014;45(Suppl 5): S36-S39.
[18] Papanastassiou ID, Mavrogenis AF, Kokkalis ZT, et al.Fixation of femoral neck fractures using divergent versus parallel cannulated screws. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2011;1(1): 63-69.
[19] Viberg B, Overgaard S, Lauritsen J, et al. Lower reoperation rate for cemented hemiarthroplasty than four uncemented hemiarthroplasty and internal fixation following femoral neck fracture: 12-to 19-year follow-up of patients aged 75 years or more. Acta Orthop. 2013;84(3): 254-259.
[20] Kain MS, Marcantonio AJ, Iorio R.Revision surgery occurs frequently after percutaneous fixation of stable femoral neck fractures in elderly patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(12): 4010-4014.
[21] Wang T, Sun JY, Zha GC, et al.Analysis of risk factors for femoral head necrosis after internal fixation in femoral neck fractures. Orthopedics. 2014;37(12): e1117-e1123.
[22] Tsai CH, Hsu HC, Fong YC, et al. Treatment for ipsilateral fractures of femoral neck and shaft. Injury. 2009;40 (7): 778-782.
[23] Saglam N, Kucuk Durmaz F, Kivilcim H, et al. Biomechanical comparison of anti rotator compression hip screw and cannulated screw fixations in the femoral neck fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2014;48(2): 196-201.
[24] Huang HK, Su YP, Chen CM, et al. Displaced femoral neck fractures in young adults treated with closed reduction and internal fixation. Orthopedics. 2010;33 (12): 873.
[25] Zdero R, Keast-Butler O, Schemitsch EH. A biomechanical comparison of two triple-screw methods for femoral neck fracture fixation in a synthetic bone model. J Trauma. 2010;69 (6):1537-1544.
[26] Gao H, Liu Z, Xing D, et al.Which is the best alternative for displaced femoral neck fractures in the elderly? A meta-analysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(6): 1782-1791.
[27] Hailer NP, Weiss RJ, Stark A, et al. The risk of revision due to dislocation after total hip arthroplasty depends on surgical approach, femoral head size, sex, and primary diagnosis. An analysis of 78,098 operations in the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop. 2012;83(5):442-448.
[28] Burgers PT, van Geene AR, van den Bekerom MP, et al.Total hip arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures in the healthy elderly: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized trials. Int Orthop. 2012;36(8):1549-1560.
[29] Taylor F, Wright M, Zhu M. Hemiarthroplasty of the hip with and without cement: a randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(7): 577-583.
[30] Langslet E, Frihagen F, Opland V, et al. Cemented versus uncemented hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: 5-year followup of a randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(4): 1291-1299.
[31] Middleton RG, Uzoigwe CE, Young PS, et al. Peri-operative mortality after hemiarthroplasty for fracture of the hip: does cement make a difference? Bone Joint J. 2014;96B(9): 1185-1191.
[32] Yang B, Lin X, Yin XM, et al. Bipolar versus unipolar hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures in the elder patient: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014. [Epub ahead of print].
[33] Kanto K, Sihvonen R, Eskelinen A, et al. Uni-and bipolar hemiarthroplasty with a modern cemented femoral component provides elderly patients with displaced femoral neck fractures with equal functional outcome and survivorship at medium-term Follow-up. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(9): 1251-1259.
[34] Yu L, Wang Y, Chen J. Total hip arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: meta-analysis Of randomized trials. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(8): 2235-2243.
[35] Adam P, Philippe R, Ehlinger M, et al. Dual mobility cups hip arthroplasty as a treatment for displaced fracture of the femoral neck in the elderly. A prospective, systematic,multicenter study with specific focus on postoperative dislocation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(3):296-300.
[36] Renken F, Renken SPeech A, et al.Early functional results after hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fracture: a randomized comparison between a minimal invasive and a conventional approach. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13: 141.
[37] Zi-Sheng A, You-Shui G, Zhi-Zhen J, et al. Hemiarthroplasty vs primary total hip arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the femoral neck in the elderly: a meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(4): 583-590.
[38] 黄梦全.有限元法分析后内侧骨折对近端股骨的力学影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,2(1):18-24.
[39] 钟砚琳,王海鹏.不同屈曲角度下膝关节主要韧带有限元模型的建立和验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 7(23):14-30.
[40] 袁平,王万春.膝关节三维有限元模型的建立及生物力学分析[J].中南大学学报:医学版,2010,35(1):85-89.
[41] 贾全章,张广玉,顾海栋,等. 蘑菇状股骨头表面置换体生物力学有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(6): 479-482.
[42] 马文辉,张学敏.髋臼缺损翻修中所用移植材料的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(26): 14-19.
[43] Seral B,Garcia JM,Cegonino J.Finite element study of intramedullary osteosynthesis in the treatment of trochanteric fractures of the hip,Gamma and PFN. Injury. 2010;35(2):130-135.
[44] 陈执平. 应用三维有限元分析探讨髓芯减压术后产生的空洞对股骨头应力的影响[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2009,3(5):617-623. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||