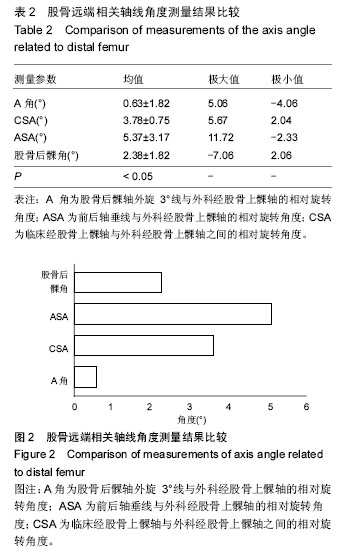
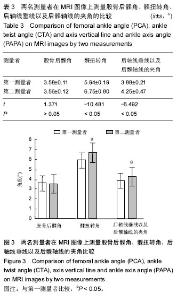
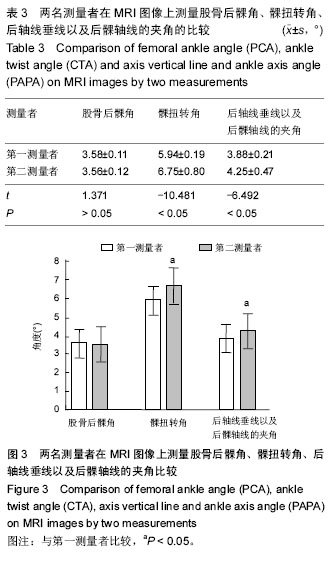
| [1] 纪小孟,刘璠,刘雅克,等.基于磁共振对股骨远端旋转参照轴线的确定及其临床意义[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2012,6(3):3938.
[2] 孙铁铮,吕厚山.晚期类风湿关节炎合并膝关节强直或僵直畸形行人工膝关节置换术[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2011,5(28):3-9.
[3] 潘江,曲铁兵,温亮,等.汉族人群正常股骨远端旋转对线的研究及其临床意义[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(4): 387-393.
[4] 李军,李阳,荆珏华,等.华南地区正常成人股骨远端髁扭转角测量及其临床意义[J].中华关节外科杂志,2013,7(3): 319-322.
[5] Gangadharan R,Deehan DJ,McCaskie AW. Distal femoral resection at knee replacement the effect of varying entry point and rotation on prosthesis position. Knee. 2010;17: 345-349.
[6] 周祺. 人工全膝关节置换术对伸膝装置影响的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(3):248-250.
[7] 周强,郑稼. 全膝关节置换术术后髌骨轨迹异常影响因素研究进展[J].中国实用医刊,2014,41(8):85-87.
[8] Yoshino N,Takai S,Ohtsuki Y,et al. Computed tomography measurement of the surgical and clinical transepicondylar axis of the distal femur in osteoarthritic knees. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16(4): 493-497.
[9] Czurda T,Fennema P,Baumgartner M,et al. The association between component malalignment and post - operative pain following navigation assisted total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;7: 863-869.
[10] Tigani D,Sabbioni G. Comparison between two computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty: gap- balancing versus measursed resection technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;10: 1304- 1310.
[11] Zwaag HM,Bos J,Heide HJ,et al. A computer tomography based study on rotational alingnment accuracy of the feoral compinent in total knee arthroplasty using computer- assisted orthopaedic surgery. Int Orthop. 2011;6: 845-850.
[12] Wang P,Zhao Z,Fu W,et al. Advancement of rotational alignment of femoral prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;25(9):1140-1144.
[13] 郑熔昭,罗张进,蒙显章,等.逆行交锁髓内钉治疗股骨远端骨折63例[J].广西医科大学学报,2010,27(4) :629-630.
[14] 徐叶清,何飞熊,徐德洪,等. AO 股骨髁支持钢板固定治疗股骨远端复杂骨折[J].实用骨科杂志, 2008,14(4): 228-229.
[15] Yoon HS, Han CD, Yang IH. Comparison of simultaneous bilateral and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty in terms of perioperative complications. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(2): 179-185.
[16] Bijlsma JW,Berenbaum F,Lafeber FP. Osteoarthritis: an update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet. 2011;377(9783):2115-2126.
[17] 周飞虎,王岩,周勇刚. 国人正常股骨远端三维模型及骨形态测量研究[J]. 中国临床康复,2005,9(6):62-63.
[18] 吴昊.全膝关节置换过程中的假体旋转对位[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(4):717-722.
[19] 王平,赵志江,付卫杰,等.人工全膝关节置换术中股骨假体旋转的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,9(10): 1140-1144.
[20] 姜侃,吴巧云,巨啸晨.新疆哈萨克族全膝关节置换术汀KA)中股骨远端旋转对线方法的研究[J].新疆医学,2013,9(8): 20-25.
[21] 窦鑫.范海建.张臻.等.多排螺旋CT对股骨标本后髁角的测量及其临床意义[J].浙江临床医学,2012,14(2): 135-137.
[22] 臧越,吴舰,孙铁铮.膝关节骨性关节炎患者下肢扭转角度CT评价的临床价值[J].影像诊断与介入放射学, 2012, 21(4):268-273.
[23] 张建雷,陆声,梁金龙,等. 基于连续断层CT扫描与三维重建技术的股骨远端旋转力线的测量[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2012,4(6):411-416.
[24] 王平,赵志江,付卫杰,等.人工全膝关节置换术中股骨假体旋转的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2011, 25(9): 1140-1144.
[25] Luyckx T,Peeters H,Vandenneucker H,et al. Is adapted measured resection superior to gap-balancing in determining femoral component rotation in total knee replacement? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94-B: 1271-1276.
[26] 戚盈杰,胡月正,吴剑彬,等.全膝关节置换术股骨及胫骨假体旋转定位研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2011, 32(4): 221-224.
[27] Kaipel M,Gergely I,Sinz K,et al. Femoral Rotation in Ligament Balanced Knee Arthroplasty A Prospective Clinical Study. J Arthroplasty. 2013;282:1103-1106.
[28] Czurda T, Fennema P, Baumgartner M, et al. The association between component malalignment and post-operative pain following navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty: results of a cohort/nested case-control study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(7): 863-869.
[29] 许鹏,李彦林,陈文栋,等. MRI影像下股骨髁间窝三维数字化解剖学数据与实体解剖测量值的差异[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(43): 8006-8009.
[30] Sun T,Lu H,Hong N,et al. Bony landmarks and rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty for Chinese osteoarthritic knees with varus or valgus deformities. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(3):427-431.
[31] 洪源,冯建民,何川,等.股骨上髁轴与股骨外旋截骨角度的相关性研究[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(14): 6329-6334.
[32] 纪小孟,刘皤,刘雅克,等.基于磁共振对股骨远端旋转参照轴线的确定及其临床意义[J]中华关节外科杂志:电子版, 2012,6(3):393-398.
[33] 姜侃,吴巧云,巨啸晨.新疆哈萨克族全膝关节置换术(TKA)中股骨远端旋转对线方法的研究[J].新疆医学, 2013, 43(9): 20-25.
[34] 龙腾河,吕国顺,崔惠勤.磁共振图像测量膝关节置换股骨假体旋转对线[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(52): 9839-9842.
[35] Thomas JH,Le RC,Jack D,et al. MRI analysis for rotation of total knee components. Knee. 2012;19(5): 571-575.
[36] 吴剑彬,余洋,王逸扬. 国人经股骨上髁轴的磁共振测量[J].解剖学报,2009,40(6): 997-1000.
[37] 岳德波,李子荣,杨连发,等. 我国北方人群股骨髁旋转角度的测量及对全膝关节置换术结果的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(7): 498-500.
[38] 纪小孟,刘璠,刘雅克,等.基于磁共振对股骨远端旋转参照轴线的确定及其临床意义[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版, 2012,6(3): 393-398.
[39] Czurda T,Fennema P,Baumgartner M,et al. The association between component malalignment and post-operative pain following navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty: results of a cohort/nested case-control study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrose. 2010;18(7):863-869.
[40] Bellemans J,Carpentier K,Vandenneucker H,et al. The John Insall Award: both morphotype and gender influence the shape of the knee in patients undergoing TKA. Clin Orthop Relar Res. 2010;468(1): 29-36.
[41] Asada S,Akagi M,Matsushita T,et al. Effects of cartilage remnants of the posterior femoral condyles on femoral component rotation in varus knee osteoarthritis. Knee. 2012;19(3): 185-189.
[42] Fujii T,Kondo M,Tomari K,et al. Posterior condylar cartilage may distort rotational alignment of the femoral component based on posterior condylar axis in total knee arthroplasty. Surg Radiol Anat. 2012;34(7): 633-638. |