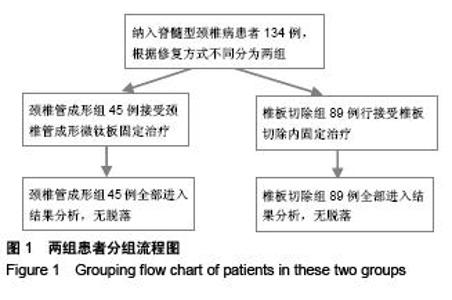
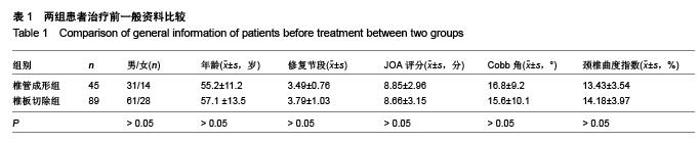
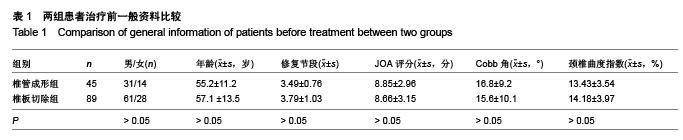
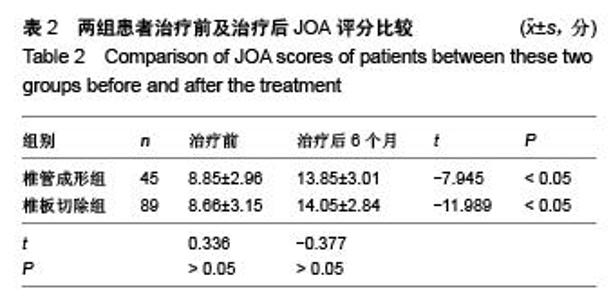
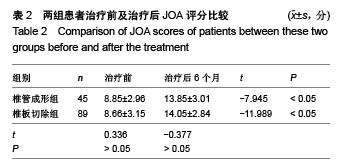
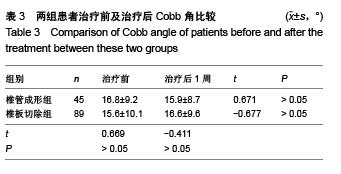
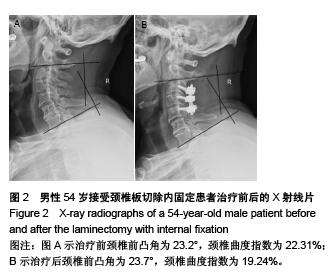
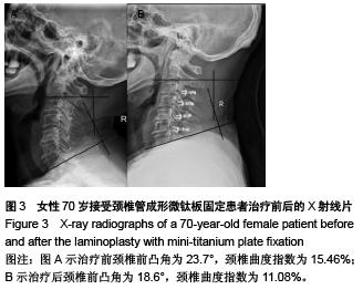
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (53): 8554-8553.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.53.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
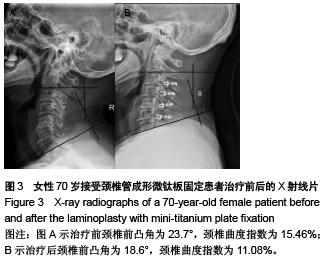
Comparison of C5 nerve root palsy after laminoplasty with mini-titanium plate fixation and laminectomy with internal fixation
Feng Da-peng1, Xu Wei-bing2, Zhao Zhi1, Yuan Liang1, Li Guang-can1, Nan Feng1, Li Zheng-wei1
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116023, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Dalian Municipal Central Hospital, Dalian 116003, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2015-10-22Online:2015-12-24Published:2015-12-24 -
Contact:Li Zheng-wei, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Spine Surgery, the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116023, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Feng Da-peng, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116023, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Feng Da-peng, Xu Wei-bing,Zhao Zhi, Yuan Liang, Li Guang-can, Nan Feng, Li Zheng-wei. Comparison of C5 nerve root palsy after laminoplasty with mini-titanium plate fixation and laminectomy with internal fixation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(53): 8554-8553.
share this article
| [1] Rhee JM, Basra S. Posterior surgery for cervical myelopathy: laminectomy, laminectomy with fusion, and laminoplasty. Asian Spine J. 2008; 2(2): 114-126.
[2] Sekhon LH. Posterior cervical decompression and fusion for circumferential spondylotic cervical stenosis: review of 50 consecutive cases. J Clin Neurosci. 2006;13(1): 23-30.
[3] Chiba K, Toyama Y, Matsumoto M, et al. Segmental motor paralysis after expansive open?door laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(19): 2108-2115.
[4] Sakanra H,Hosono N, Mukai Y, et al. C5 palsy after decompression surgery for cerviealmyelopathy. Spine. 2003; 21(1):2447-2451.
[5] Hashimoto M, Mochizuki M,Aiba A,et al. C5 palsy following anterior decompression and spinal fusion for cervical degenerative diseases.Eur Spine J. 2010;19(10):1702-1710.
[6] Cabraja M, Abbushi A, Koeppen D, et al. Comparison between anterior and posterior decompression with instrumentation for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: sagittal alignment and clinical outcome. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;28(3):E15.
[7] Kanchiku T,Imajo Y,Suzuki H,et al. Results of surgical treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy in patients aged 75 years or more: a comparative study of operative methods. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(8):1045-1050.
[8] Heller JG, Edwards CC 2nd, Murakami H, et al. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical myelopathy:an independent matched cohort analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(12):1330-1336.
[9] Uchida K, Nakajima H, Sato R, et al. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy associated with kyphosis or sagittal sigmoid alignment: outcome after anterior or posterior decompression. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11(5):521-528.
[10] Suda K, Abumi K, Ito M, et al. Local kyphosis reduces surgical outcomes of expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(12): 1258-1262.
[11] Petraglia AL, Srinivasan V, Coriddi M, et al. Cervical lamino-plasty as a management option for patients with cervical spondy-lotic myelopathy: a series of 40 patients. Neurosurgery. 2010;67(2):272-277.
[12] Dimar JR 2nd, Bratcher KR, Brock DC, et al. Instrumented open-door laminoplasty as treatment for cervical myelopathy in 104 patients. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2009;38(7): E123-128.
[13] Woods BI, Hohl J, Lee J, et al. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(3): 688-695.
[14] Kang SH, Rhim SC, Roh SW, et al. Postlaminoplasty cervical range of motion: early results. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6(5): 386-390.
[15] Yeh KT,Yu TC,Chen IH,et al. Expansive open-door laminoplasty secured with titanium miniplates is a good surgical method for multiple-level cervical stenosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;21;9:49.
[16] Miller JA,Lubelski D,Alvin MD,et al. C5 palsy after posterior cervical decompression and fusion: cost and quality-of-life implications. Spine J. 2014;14 (12):2854-2860.
[17] Epstein NE,Hollingsworth R.C5 Nerve root palsies following cervical spine surgery: A review. Surg Neurol Int. 2015; 6(Suppl 4):S154-163.
[18] Guzman JZ,Baird EO,Fields AC,et al. C5 nerve root palsy following decompression of the cervical spine: a systematic evaluation of the literature. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(7): 950-955.
[19] Satomi K, Nishu Y, Kohno T, et al. Long-term follow-up studies of open-door expansive laminoplasty for cervical stenotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(5): 507-510.
[20] Imagama S, Matsuyama Y, Yukawa Y, et al. C5 palsy after cervical laminoplasty: a multicentre study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(3):393-400.
[21] Meng H,Fang X, Hao D, et al. Incidences of C5 nerve palsy after multi-segmental cervical decompression through different approaches.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015;35(3):315-318.
[22] Gu Y, Cao P, Gao R, et al. Incidence and risk factors of C5 palsy following posterior cervical decompression: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2014;27;9(8):e101933.
[23] Sasai K, Saito T, Akagi S, et al. Preventing C5 palsy after laminoplasty. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(17):1972-1977.
[24] Hojo Y, Ito M, Abumi K, et al. A late neurological complication following posterior correction surgery of severe cervical kyphosis. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(6): 890-898.
[25] Nakashima H, Imagama S, Yukawa Y, et al. Multivariate analysis of C5 palsy incidence after cervical posterior fusion with instrumentation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;17(2): 103-110.
[26] Heller JG, Silcox DH 3rd, Sutterlin CE 3rd. Complications of posterior cervical plating. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(22): 2442-2448.
[27] Nobuyuki T, Li ZH, Ryoji A, et al. Paralysis of the arm after posterior decomp ression of the cervical sp inal cord: I. Anatomical investigation of the mechanism of paralysis. Eur Spine J. 1993;2 (4):191-196.
[28] Yamashita T, Yokogusu K, Yokozawa H,et al. C5 nerve palsyafter cervical laminoplasty: an analysis of three cases.Seikei Geka. 1996;47(3):1365-1369.
[29] Sodeyama T, Goto S, Mochizuki M,et al. Efect of deeompression enlargement laminoplasty for posterior shifting of the spinaleordSpine. 1999;24(2):1527-1531.
[30] Radcliff KE,Limthongkul W,Kepler CK,et al. Cervical laminectomy width and spinal cord drift are risk factors for postoperative C5 palsy. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(2): 86-92.
[31] Tsuzuki N, Abe R, Saiki K, et al. Extradural tethering effect as one mechanism of radiculopathy complicating posterior decompression of the cervical spinal cord. Spine. 1996;21(2): 203-211.
[32] Katsumi K,Yamazaki A,Watanabe K,et al.Analysis of C5 palsy after cervical open-door laminoplasty: relationship between C5 palsy and foraminal stenosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013; 26(4):177-182.
|
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||