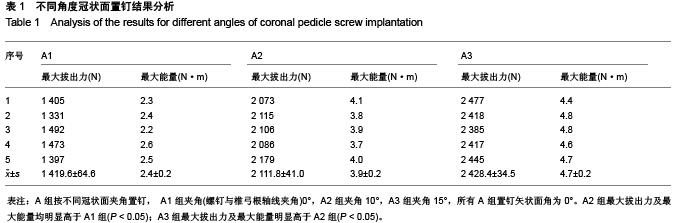
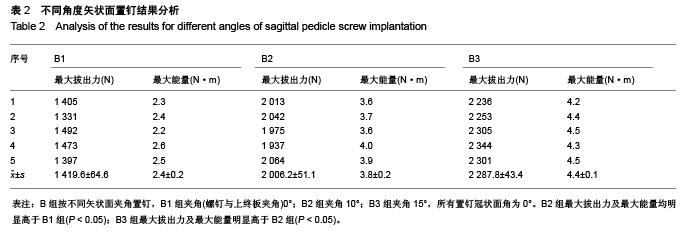
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (48): 7765-7769.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.48.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of different angles of implanted screws on the stability of pedicle screw
Pang Zhong-hui1, Liu Miao2, Zhang Ya-bin1, Yao Yong-feng1, Pei Shao-kun1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the Fourth People’s Hospital of Shaanxi, Xi’an 710043, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710056, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2015-10-28Online:2015-11-26Published:2015-11-26 -
Contact:Pang Zhong-hui, Department of Orthopedics, the Fourth People’s Hospital of Shaanxi, Xi’an 710043, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Pang Zhong-hui, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Fourth People’s Hospital of Shaanxi, Xi’an 710043, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Tissue Engineering; Spine; Pedicle; Screws
Funding: the Scientific and Technological Projects of Shaanxi Province, China, No. 2012K16-09-07
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Pang Zhong-hui, Liu Miao, Zhang Ya-bin, Yao Yong-feng, Pei Shao-kun. Effect of different angles of implanted screws on the stability of pedicle screw[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(48): 7765-7769.
share this article
| [1] 王旭,李永民,谷守山.椎弓根钉置入内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,(22): 4109-4112.[2] 胡海刚,谭伦,林旭,等.经伤椎椎弓根植骨置钉后路复位内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,(8):663-668.[3] Vu TT, Morishita Y, Yugue I, et al. Radiological Outcome of Short Segment Posterior Instrumentation and Fusion for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(3): 427-432.[4] Ökten A?, Gezercan Y, Özsoy KM, et al. Results of treatment of unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures using pedicle instrumentation with and without fracture-level screws. Acta Neurochirurgica. 2015;157(5):831-836.[5] Robinson PJ, Phelan PD. Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome in a 9 year old girl presenting with repeated haemoptysis. Aust Paediatr J. 1989;25(4):248-249. [6] Charles YP, Pelletier H, Hydier P, et al. Pullout characteristics of percutaneous pedicle screws with different cement augmentation methods in elderly spines: an in vitro biomechanical study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015; 101(3): 369-374.[7] Proietti L, Scaramuzzo L, Schirò GR, et al. Degenerative facet joint changes in lumbar percutaneous pedicle screw fixation without fusion. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(3): 375-379.[8] Reynolds GJ. Stabilization and fixation of percutaneous central venous catheters. Aust Paediatr J. 1989;25(4): 250-251.[9] 蔡斌.经皮椎弓根螺钉置入准确性的CT评价及临床疗效[D].苏州:苏州大学,2014.[10] 聂锋锋,张英华,黄寿国,等.经皮微创椎弓根螺钉内固定与开放手术治疗胸腰椎骨折:Cobb’s角与椎体前缘高度恢复的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(44):7094-7099.[11] 杨博.肾形n-HA/PA66腰椎间融合器在猪腰椎TLIF手术的体外生物力学研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2014.[12] 寿建国,应大君,曾养志.猪-人异种椎间盘移植在生化和解剖中的可行性初步研究[J].颈腰痛杂志,2004,25(3):170-173.[13] 寿建国,应大君,曾养志.猪腰椎-人颈椎异种椎间盘移植在组织结构和生物力学中的可行性初步研究[J].颈腰痛杂志,2004, 25(6):375-378.[14] 付鑫,谭杰,宋纯理,等.椎体内单次注射辛伐他汀对骨质疏松小型猪腰椎椎体骨质和椎弓根螺钉内固定稳定性的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(5):448-455.[15] 廖红荔.腰椎间关节MRI多序列成像实验性研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2009.[16] 刘珺,王维,童琼娟,等.双能X线骨密度仪(DXA)与定量CT(QCT)测量骨密度的比较研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2007,21(5): 504-507.[17] 李朦.骨质疏松相关激素与骨密度相关性研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2013.[18] 黄何平.骨密度的影响因素分析[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(40): 124-126.[19] 刘振.经皮脊柱外固定器螺钉不同角度拔出的生物力学研究[D].衡阳:南华大学,2012.[20] 段洪斌.不同水平角度置入椎弓根螺钉的拔钉生物力学研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2005.[21] 付少锋.胸椎椎弓根和椎弓根-助骨复合体的应用解剖及相关内固定技术的生物力学研究与临床评价[D].重庆:重庆医科大学, 2014.[22] 史可强,雷云霞,王海奎,等.不同矢状角度置入椎弓根螺钉的拔钉生物力学研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(4):311-313.[23] 张文志,尚希福,段丽群,等.微创经皮与传统开放椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床对比研究[J].中国骨与关节外科,2012, 5(2):109-114.[24] 段丽群,张文志,尚希福,等.微创经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床疗效分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2012,33(5):336-339.[25] 夏天,董双海,王雷,等.胸腰椎经皮椎弓根螺钉置钉的准确性分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(9):794-797.[26] 唐康,张文志,段丽群,等.微创经皮椎弓根螺钉联合伤椎置钉治疗胸腰段脊椎骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,17(3):253-257.[27] 刘达.骨质疏松条件下膨胀式椎弓根螺钉与骨水泥强化螺钉的稳定性和钉道界面的比较研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2011.[28] 史定伟,干耀恺,梁栋科,等.生物型空心松质骨螺钉的力学强度研究[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(5):574-579.[29] 田冲,张美超,欧阳钧.不同骨密度下松质骨螺钉生物力学性能的三维有限元分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30(11): 2466-2471.[30] Bianco RJ, Aubin CE, Mac-Thiong JM, et al. Pedicle Screw Fixation Under Non-Axial Loads: a Cadaveric Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015.[31] Mayer M, Stephan D, Resch H, et al. BIomechanical comparison of sacral fixation characteristics of standard s1-pedicle screw fixation vs a novel constrained s1-dual-screw anchorage in the s1-pedicle and s1-alar bone. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015.[32] Shui X, Ying X, Mao C, et al. Percutaneous Screw Fixation of Crescent Fracture-Dislocation of the Sacroiliac Joint. Orthopedics. 2015;38(11):e976-e982. [33] Hu Y, Dong WX, Kepler CK, et al. A novel anterior odontoid screw plate for c1-c3 internal fixation: an in vitro biomechanical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015.[34] Akpolat YT, ?nceo?lu S, Kinne N, et al. Fatigue performance of cortical bone trajectory screw compared to standard trajectory pedicle screw. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015.[35] Grechenig S, Gueorguiev B, Berner A, et al. A novel locking screw hip stem to achieve immediate stability in total hip arthroplasty: A biomechanical study. Injury. 2015;46 Suppl 4:S83-S87. [36] Loibl M, Korsun M, Reiss J, et al. Spinal fracture reduction with a minimal-invasive transpedicular Schanz Screw system: clinical and radiological one-year follow-up. Injury. 2015;46 Suppl 4:S75-S82. [37] Grechenig S, Gänsslen A, Gueorguiev B, et al. PMMA-augmented SI screw: a biomechanical analysis of stiffness and pull-out force in a matched paired human cadaveric model. Injury. 2015;46 Suppl 4:S125-S128. [38] Quinn JC, Patel NV, Tyagi R. Hybrid lateral mass screw sublaminar wire construct: a salvage technique for posterior cervical fixation in pediatric spine surgery. J Clin Neurosci. 2015.[39] Saleh MF, Dhenge RM, Cartwright JJ, et al.Twin screw wet granulation: Effect of process and formulation variables on powder caking during production. Int J Pharm. 2015. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||