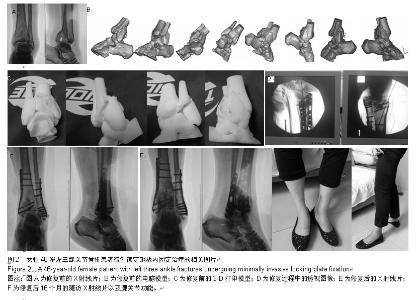
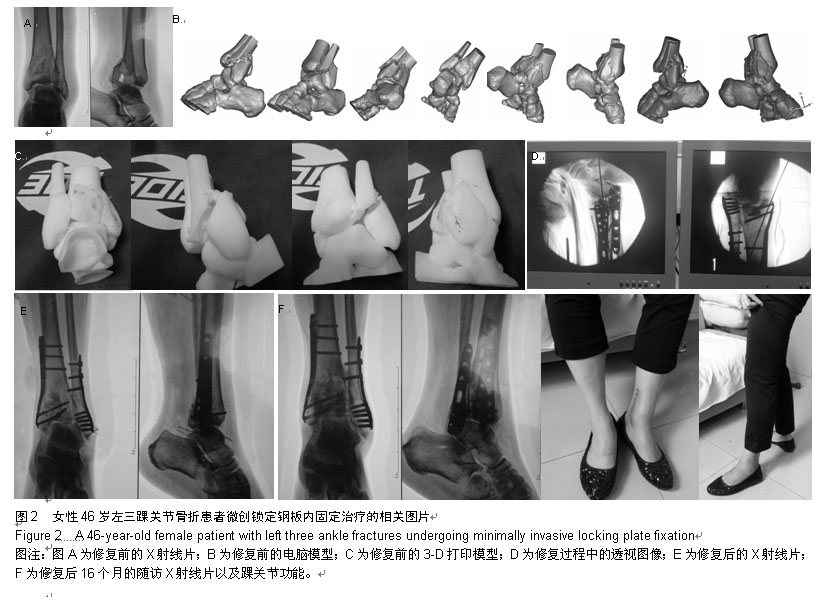
| [1] Giovinco NA, Dunn SP, Dowling L, et al. A novel combination of printed 3-dimensional anatomic templates and computer-assisted surgical simulation for virtual preoperative planning in Charcot foot reconstruction. Foot Ankle Surg. 2012;5-6(3):387-393.
[2] 冯万文,蒋纯志,徐毓林,等. 应用数字化技术设计胫骨远端后侧解剖钢板的研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(10):889-892.
[3] 章莹,万磊,尹庆水,等.计算机快速成型辅助个体化三踝骨折的手术治疗[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2009,11(6):509-511.
[4] 张伟,张铁良.三维重建及快速成型在骨科临床的应用研究[D]. 天津医科大学,2010.
[5] 黄若昆,谢鸣,余嘉,等.应用数字化技术设计胫骨远端后侧解剖钢板的研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,10(15):889-892.
[6] 陈孝平,石应康,邱贵兴.外科学(供8年制及7年制临床医学等专业用)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:138.
[7] Mazur JM, Schwartz E, Sheldon RS.Ankle arthrodesis: Long-term follow-up with gait analysis.J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1979;61:964-968.
[8] 黄若昆,谢鸣,余嘉,等.应用数字化技术设计胫骨远端后侧解剖钢板的研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(10):889-892.
[9] 王德顺,朱云森,王永青,等.多排螺旋CT及二维、三维重建技术在踝部骨折中的应用[J].浙江创伤外科杂志,2011,16(1):116-118.
[10] 裴国献,刘永刚.三维数字化骨折分型及其临床应用价值[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(12):1111-1115.
[11] 章莹,夏远军,万磊,等. 计算机三维仿真技术在复杂足踝部骨折手术中的应用[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2010,2(2): 98-101.
[12] 朱培杨,周玮,李建有,等.多层螺旋CT三维重建技术在踝关节骨折诊断和术后评估中的应用价值[J].中国现代医生,2014, 52(30):34-36.
[13] 黄宏宇,刘国平,尤微,等. 数字化技术辅助手术治疗Pilon骨折疗效分析[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2014,35(5):341-344.
[14] 王丹,裴国献,刘永刚,等.三维数字化骨折分型及其临床应用价值[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(12):1111-1115.
[15] 张元智,陆声,赵建民,等.数字化技术在骨科的临床应用[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(12):1161-1165.
[16] 张元智,陆声,赵建民,等. 3D打印技术:骨科最新冲击波[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(1):8-9.
[17] 王丹,裴国献,刘宏建,等.股骨远端骨折的可视化仿真手术研究[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(5):1144-1146.
[18] 王丹,金丹,裴国献,等. 股骨转子间骨折与股骨远端骨折的可视化仿真手术研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(5):410-414.
[19] 裴国献.创建我国数字骨科促进骨科技术发展[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(1):5-6.
[20] 孟国林,刘建,胡蕴玉,等. 快速成型模型在制定胫骨平台复杂骨折手术方案中的指导作用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(12): 1135-1138.
[21] 孟国林,刘建,裴国献,等. 快速成型模型在跟骨骨折诊断分型中的辅助指导作用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(1):59-62.
[22] 程建岗,刘建,孟国林,等.快速成型技术在肱骨近端骨折诊断与治疗中的辅助作用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(1):55-58.
[23] 章莹,李宝丰,王新宇,等. 术前3D打印技术模拟复杂骨盆骨折手术提高疗效的可行性研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(1): 29-33.
[24] 徐润冰,丁亮华,何双华,等. 计算机辅助设计数字化钢板置入修复髋臼后壁骨折伴髋脱位[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(44): 7172-7177.
[25] 孟波,孙海钰,李明,等.计算机辅助在骨盆骨折诊断与治疗方面的临床价值[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(17):2673-2678.
[26] 刘百伟,李云峰,陆坚,等. 快速成型髋臼后缘锁定钢板治疗髋臼后缘骨折的初步应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,17(2):155-157.
[27] 韦葛堇,林舟丹,吴家昌,等.计算机三维仿真技术在复杂骨盆骨折手术中的应用[J]. 广西医科大学学报,2014,31(1):78-80.
[28] Chung KJ, Hong do Y, Kim YT, et al. Preshaping plates for minimally invasive fixation of calcaneal fractures using a real-size 3D-printed model as a preoperative and intraoperative tool. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;35(11):1231-1236.
[29] Bartoní?ek J, Rammelt S, Kostlivý K, et al.Anatomy and classification of the posterior tibial fragment in ankle fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(4):505-516.
[30] Dubois-Ferrière V, Assal M. Benefit of computer assisted surgery in foot and ankle surgery. Rev Med Suisse. 2014; 10(420): 562-564.
[31] Davidovitch RI, Weil Y, Karia R, et al. Intraoperative syndesmotic reduction: three-dimensional versus standard fluoroscopic imaging. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(20) : 1838-1843.
[32] Dresing K. Minimally invasive osteosynthesis of pilon fractures. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2012;24(4-5): 368-382.
[33] Brunner A, Heeren N, Albrecht F, et al.Effect of three-dimensional computed tomography reconstructions on reliability. Foot Ankle Int. 2012;33(9):727-733.
[34] von Recum J, Wendl K, Vock B, et al. Intraoperative 3D C-arm imaging. State of the art. Unfallchirurg. 2012;115(9): 196- 201.
[35] Beerekamp MS, Sulkers GS, Ubbink DT, et al. Accuracy and consequences of 3D-fluoroscopy in upper and lower extremity fracture treatment: a systematic review. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81(420):4019-4028.
[36] Beerekamp MS, Ubbink DT, Maas M, et al. Fracture surgery of the extremities with the intra-operative use of 3D-RX: a randomized multicenter trial (EF3X-trial). BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;7(6):151.
[37] Ruan Z, Luo C, Shi Z, et al. Intraoperative reduction of distal tibiofibular joint aided by three-dimensional fluoroscopy. Technol Health Care. 2011;19(3):161-166.
[38] Richter M, Zech S. Intraoperative 3-dimensional imaging in foot and ankle trauma-experience with a second-generation device (ARCADIS-3D). J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(3):213- 220.
[39] Ruan Z, Luo C, Shi Z, et al. Intraoperative reduction of distal tibiofibular joint aided by three-dimensional fluoroscopy. Technol Health Care. 2011;19(3):161-166.
[40] Qiang M, Chen Y, Zhang K, et al. Measurement of three-dimensional morphological characteristics of the calcaneus using CT image post-processing. J Foot Ankle Res. 2014;7(1):19. |