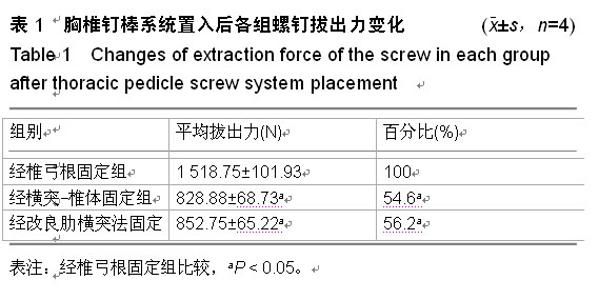
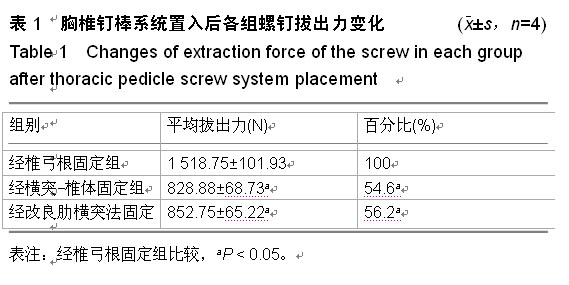
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (22): 3579-3583.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.22.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biomechanical characteristics of placement methods of the thoracic pedicle screw system
Yu De-jun1, Liu Li-jing2, Jin Song1, Tian Shao-hua1
- 1Second Department of Orthopedics, Third Hospital Affiliated to Qiqihar Medical University, Qiqihar 161042, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Third Hospital Affiliated to Qiqihar Medical University, Qiqihar 161042, Heilongjiang Province, China)
-
Received:2015-04-28Online:2015-05-28Published:2015-05-28 -
Contact:Tian Shao-hua, Chief physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, Third Hospital Affiliated to Qiqihar Medical University, Qiqihar 161042, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Yu De-jun, Master, Attending physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, Third Hospital Affiliated to Qiqihar Medical University, Qiqihar 161042, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:the Fund of Qiqihar City Project, No. SFZD-2013092
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu De-jun, Liu Li-jing, Jin Song, Tian Shao-hua. Biomechanical characteristics of placement methods of the thoracic pedicle screw system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(22): 3579-3583.
share this article
| [1] 吕豪珍,林红,张绍昆,等.经伤椎椎弓根置钉技术在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究杂志,2012,16(9):1680-1683. [2] 刘海波,朱宝华.伤椎椎弓根钉固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折疗效分析[J].现代实用医学杂志,2014,3,201. [3] Biedermann L. Biomecaianica of pedicle fixation as related to implant design presented lat the American-European Meeting on Pedicle of the Spine and Other Advanced techniques. Munich: Heidelberg: Springer Berlin, Germany. 1994. [4] Dvorak M, Macdonaid S, Gurr KR, et al. Ananatomic, radiographic,and biomechanical assessment of extrapedicaular screw fixation in the thoracic spine. Spine. 1993;18:1689-1694. [5] Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Balderston RA, et al. Placement of Pedicle Serews in the thoracic spine.Part Ⅱ: an anatomical and Radiographic assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:1200-1206. [6] Panjabi MM, O' Holleran JD, Crisco JJ, et al. Complexity of the Thoracic spine pedicle anatomy. Eur Spine J:1997;6:19. [7] George DC, Krag MH, Johnson CC, et al. Hole preparation techniques for transpedicle screws. Effeet on pull-out strength from human cadaveric vertebrae. Spine. 1991;16:181-184. [8] Willett K, Hearn TC, Cuneins AV, et al. Biomeehanical testing of a new desing for schanz pedicle serews. J Orthop Trauma. 1993;7:375. [9] Liljenqvist UR, Alkemper T, Haekenberg L, et al. Analysis of vertebral morphology in idiopathic scoliosis with use of magnetic resonance imaging and multiplanar reconstruetion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84A:359-368. [10] Dvorak M, MacDonald S, Gurr KR, et al. Ananatomic, radiographic, and biomehancial assessment of extrapedieular serew fixation in the thoracic spine. Spine. 1993;18:1698- 1694. [11] Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, et al. Segmental pedicle serew fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1995;20:1399-1405. [12] Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee SM, et al, Thoracic Pedicle serew fixation in spinal deformities: are they really safe? Spine. 2001;26:2049-2057. [13] 官众,许勇,任磊,等.经肋椎关节手术入路治疗胸椎多椎体结核的临床研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2013,11(6):337-340. [14] Morgenstern W, Merola A. Extrapedicular serew placement in the thoracic spine: a cadaverie study. Presented at: proceedings of the international meeting of advanced spine techniques. 1999. [15] WiIke HJ, Krisehak S, Claes LE. Formalin fixation strongly Influences biomeehanical propdrties of the spine. J Biomech. 1996;29:1629. [16] 王洪伟,李长青,周跃,等.用于脊柱内固定器生物力学评价的牛脊椎A型骨折模型的建立[J].第三军医大学学报,32(18):1967- 1969. [17] 王新伟,陈德玉,鲍达,等.小牛胸椎解剖、生物力学研究及其临床意义[J].脊柱外科杂志,2003,1(4):223-225. [18] 李禾,邢更彦,杨传铎,等.脊柱内固定系统生物力学研究与临床应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(8):923. [19] 丁晓琳,牟宗玲,张玲,等.利用成年猪脊柱制作胸腰段后凸畸形模型进行脊柱三围运动实验[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(5): 451-455. [20] Yu BS. Biomechical comparison of the posterolateral fusion and posterior lumber interbody fusion using pedicle screw fixationg system for anstable lumbar spine. Hoklcaido lqaka Zasshi. 2003;78(3):211-218. [21] Smit TH. The use of a quadruped as an in vivo model for the study of the spine-biomech anical considerations. Eur Spine J. 2002;1(2):137-144. [22] Wilke HJ, Krischak S, Claes L. Biomechanical comparison of calf ang human Spine. J Orthop Res. 1996;14(3):500-503. [23] Wilke HJ, Krischak ST, Wenger KH, et al. Load-displaeemental properties of the thoracolubar calf spine: experimental results and comparison to known human data. Spine. 1996;21:1957. [24] WiIke HJ, Krisehak ST, Claes L. Biomechanical comparison of calf and human spines. J Orthop Res. 1996;14:500. [25] Wang JL, Parnianpour M, Engin AE. Viscoelastic finite-element analysis of a lumbar motion segment in combined combined compression and sagittal flexion. Spine. 1999;24:2475. [26] WiIke HJ, Wenger K, Claes L. Testing criteria for spinal implants:recommendations for the standardization of invitro stability testing of spinal implants. J Eur Spine. 1998;7:148. [27] 朱青安,吕维加,王柏川,等.改进型E面ards器械固定不稳定胸腰椎骨折的生物力学评价[J].中华骨科杂志,2001,21(7):394. [28] Kettler A, Wilke HJ, Haid C, et al. Effeets of specimen length on the monsegmental motion behavior of the lumbar. Spine. 2000;25:543. [29] Wilke HJ, Jungkunz B, Wenger K, et al. Spinal segment range of motion as a function of invitro test conditions; effeets of exposure Period, accumulated cycles, angular-deformationrate, and moisture condition. Anat Rec. 1998;251:15. 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
|
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||