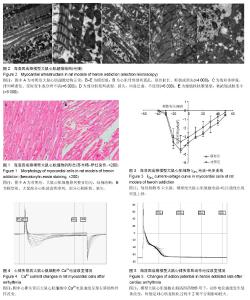
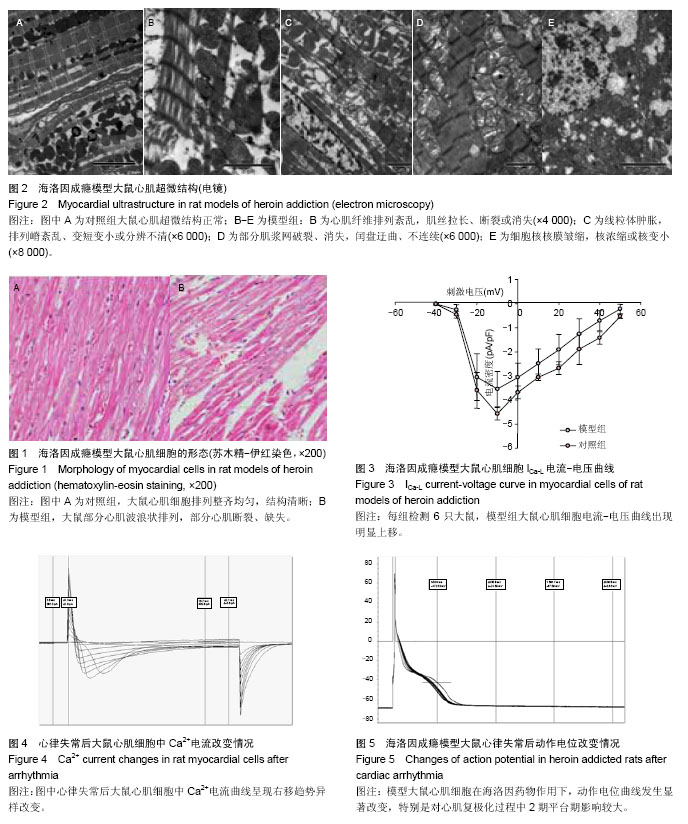
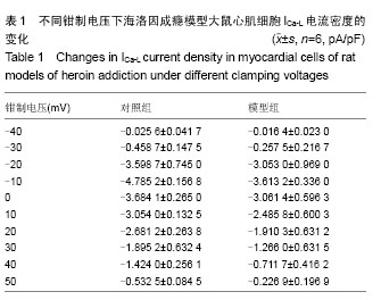
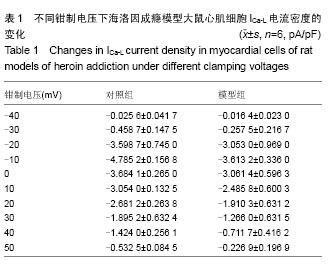
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (18): 2843-2848.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.18.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Action potential and L-type calcium channel currents in myocardial cells of rat models of heroin addiction
Pu Hong-wei1, Su Li-ping2, Wang Xue-mei3, Chen Xiao2, Zhang Li-ping2, Liu Xiao-shan4, Wang Zhi-guo5, Wang Hua2, Li Kai-chao6
- 1Science and Education Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Basic Medical School, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Clinical Research Institute, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 4Department of Forensic Medicine, Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; 5Forensic Science and Technology Institute of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 6Public Security Bureau of Habahe County of Aletai area, Habahe 836700, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2015-02-12Online:2015-04-30Published:2015-04-30 -
Contact:Liu Xiao-shan, M.D., Legal physician in chief, Department of Forensic Medicine, Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Pu Hong-wei, Studying for doctorate, Associate professor, Science and Education Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China Su Li-ping, Studying for master’s degree, Basic Medical School, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China Pu Hong-wei and Su Li-ping contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81260464; the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2011211B20
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Pu Hong-wei, Su Li-ping, Wang Xue-mei, Chen Xiao, Zhang Li-ping, Liu Xiao-shan, Wang Zhi-guo, Wang Hua, Li Kai-chao. Action potential and L-type calcium channel currents in myocardial cells of rat models of heroin addiction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(18): 2843-2848.
share this article
| [1] Milroy CM, Parai JL. The histopathology of drugs of abuse. Histopathology. 2011;59(4):579-593. [2] Tashkin DP. Airway effects of marijuana, cocaine, and other inhaled illicit agents. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2001;7(2):43-61. [3] Laposata EA, Mayo GL. A review of pulmonary pathology and mechanisms associated with inhalation of freebase cocaine ("crack"). Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 1993;14(1):1-9. [4] Mégarbane B, Chevillard L. The large spectrum of pulmonary complications following illicit drug use: features and mechanisms. Chem Biol Interact. 2013;206(3):444- 451. [5] Hagan IG, Burney K. Radiology of recreational drug abuse. Radiographics. 2007;27(4):919-940. [6] Rojas R, Riascos R, Vargas D, et al. Neuroimaging in drug and substance abuse part I: cocaine, cannabis, and ecstasy. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;16(3):231-238. [7] Frishman WH, Del Vecchio A, Sanal S, et al. Cardiovascular manifestations of substance abuse: part 2: alcohol, amphetamines, heroin, cannabis, and caffeine. Heart Dis. 2003;5(4):253-271. [8] Sarnyai Z, Kovács GL. Role of oxytocin in the neuroadaptation to drugs of abuse. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1994;19(1):85-117. [9] Smith KM, Larive LL, Romanelli F. Club drugs: methylenedioxymethamphetamine, flunitrazepam, ketamine hydrochloride, and gamma-hydroxybutyrate. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2002;59(11):1067-1076. [10] 陈富华,牟霞,付青梅,等.海洛因依赖者心血管系统损害研究进展[J].中国药物滥用防治杂志,2010,16(4):222-227. [11] 石铸,肖卫民,潘速跃,等.海洛因海绵状白质脑病的病理学改变[J].临床神经病学杂志,2010,23(6):405-407. [12] 周亮,林敏仕,尹恝.线粒体呼吸链复合物Ⅰ缺陷与海洛因海绵状白质脑病的关系[J].南方医科大学学报,2013(9):1357-1361. [13] Darke S, Duflou J, Torok M. The comparative toxicology and major organ pathology of fatal methadone and heroin toxicity cases. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010;106(1):1-6. [14] 刘小山,陈玉川,李朝晖,等.海洛因成瘾大鼠心电图及心肌超微结构改变的研究[J].法医学杂志,2004,20(3):129-132,135. [15] 武俊华.海洛因依赖者心电图异常变化分析[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2009,7(7):850-851. [16] 刘牧.重症海洛因中毒的误诊分析[J].临床合理用药杂志,2011, 4(19):158. [17] 梁纲,黄绍标,李飞,等.海洛因依赖者中抗-HIV抗体阳性人群的心电图分析[J].广西医科大学学报,2012,29(5):702-704. [18] Yin R, Lu C, Chen Q, et al. Microvascular damage is involved in the pathogenesis of heroin induced spongiform leukoencephalopathy. Int J Med Sci. 2013;10(3):299-306. [19] 刘小山,刘水平,李朝晖,等.海洛因成瘾大鼠心肌超微结构改变及凋亡检测[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2005,26(1):61-64,83. [20] Zhou Y, Leri F, Ho A, et al. Suppression of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis by acute heroin challenge in rats during acute and chronic withdrawal from chronic heroin administration. Neurochem Res. 2013;38(9): 1850-1860. [21] 宋建国,侯月梅.豚鼠心肌细胞分离方法及电生理特性的观察[J].新疆医科大学学报,2007,30(5):490-493,497. [22] Koch A, Reiter A, Meissner C, et al. Cause of death in heroin users with low blood morphine concentration. Arch Kriminol. 2002;209(3-4):76-87. [23] Thandroyen FT, Morris AC, Hagler HK, et al. Intracellular calcium transients and arrhythmia in isolated heart cells. Circ Res. 1991;69(3):810-819. [24] 胡丽叶,何振山,崔俊玉,等.模拟缺血对三层心室肌细胞快钠通道I-V曲线的影响及临床意义[J].河北医科大学学报,2004,25(1): 11-14. [25] 于婵娟,刘亚华,田亮,等.依托咪酯对大鼠海马CA1区神经元突触结构电流-电压曲线的离子通道机制研究[J].新疆医科大学学报, 2014(8):985-988. [26] 李喆.缺血再灌注致心律失常大鼠模型钙调蛋白介导的L型离子通道电流的变化[J].海南医学院学报,2013,19(12):1627-1630. [27] Tamargo J, Caballero R, Gómez R, et al. Pharmacology of cardiac potassium channels. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;62(1): 9-33. [28] 柯琴梅,杜以梅,唐明,等.血小板活化因子对豚鼠心室肌细胞钾电流及动作电位的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2007,23(1): 58-62. [29] 郑明奇,刘刚,田立.溶血磷脂酰胆碱对T型钙离子通道的心肌细胞内信号调控机制[J].中华心脏与心律电子杂志,2013, 1(1): 24-26. [30] Dai DZ. CPU86017: a novel Class III antiarrhythmic agent with multiple actions at ion channels. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2006;24(2):101-115. [31] Xiao B, Zhong G, Obayashi M, et al. Ser-2030, but not Ser-2808, is the major phosphorylation site in cardiac ryanodine receptors responding to protein kinase A activation upon beta-adrenergic stimulation in normal and failing hearts. Biochem J. 2006;396(1):7-16. [32] Bodi I, Mikala G, Koch SE, et al. The L-type calcium channel in the heart: the beat goes on. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(12): 3306-3317. [33] Christ T, Boknik P, Wöhrl S, et al. L-type Ca2+ current downregulation in chronic human atrial fibrillation is associated with increased activity of protein phosphatases. Circulation. 2004;110(17):2651-2657. [34] 刘刚,郑明奇,王玮,等.溶血磷脂酰胆碱对心肌细胞T型钙离子通道的调控[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2011,43(6):804-808. [35] 洪葵,刘欣.心脏钙离子通道疾病[J].中国心脏起搏与心电生理杂志,2011,25(3):189-191. [36] 陈金玉,刘杰.钙漏流与心律失常[J].岭南心血管病杂,2011,17(6): 515-517. [37] Chen Y, Escoubet B, Prunier F, et al. Constitutive cardiac overexpression of sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase delays myocardial failure after myocardial infarction in rats at a cost of increased acute arrhythmias. Circulation. 2004;109(15):1898-1903. [38] Arai M. Function and regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase: advances during the past decade and prospects for the coming decade. Jpn Heart J. 2000;41(1): 1-13. [39] Saint DA. The role of the persistent Na(+) current during cardiac ischemia and hypoxi a. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006;17 Suppl 1:S96-S103. [40] Clanachan AS. Contribution of protons to post-ischemic Na(+) and Ca(2+) overload and left ventricular mechanical dysfunction. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006;17 Suppl 1: S141-S148. [41] Hilgemann DW, Yaradanakul A, Wang Y, et al. Molecular control of cardiac sodium homeostasis in health and disease. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006;17 Suppl 1:S47-S56. [42] Hiraoka M. Metabolic pathways for ion homeostasis and persistent Na(+) current. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006; 17 Suppl 1:S124-S126. [43] Allen DG, Xiao XH. Activity of the Na+/H+ exchanger contributes to cardiac damage following ischaemia and reperfusion. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2000;27(9): 727-733. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||