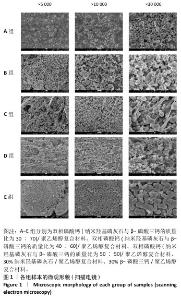
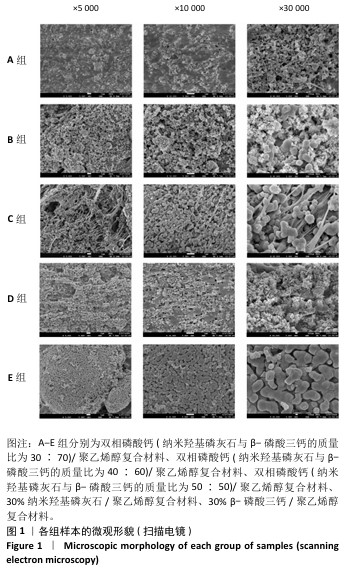
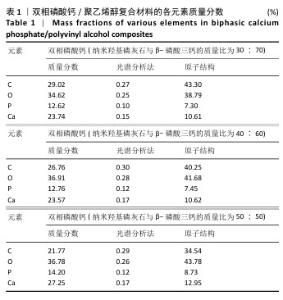
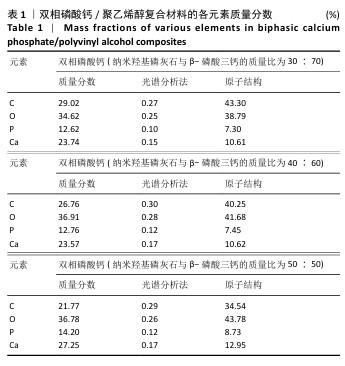
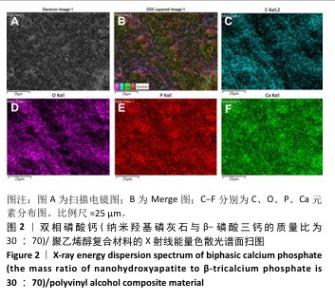
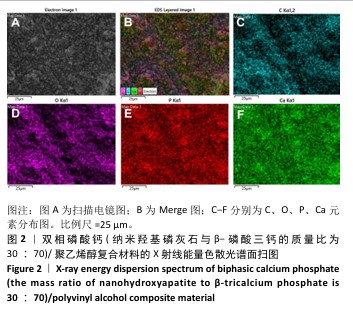
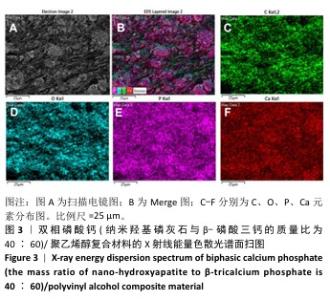
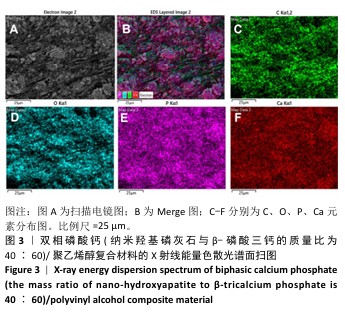
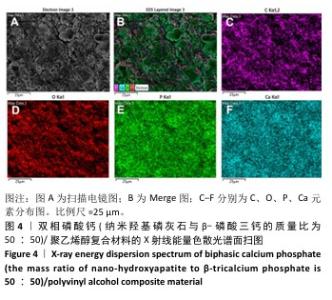
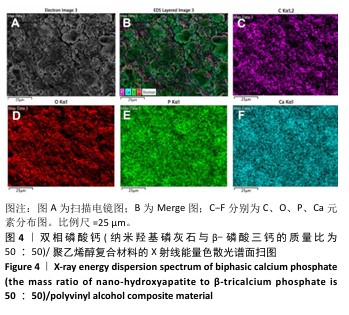
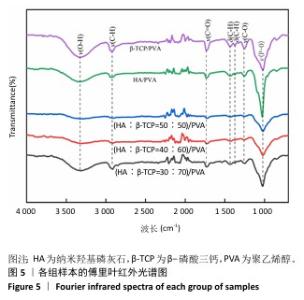
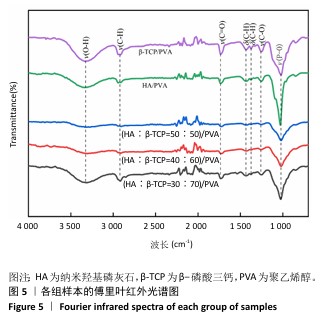
[1] DEVI MT, SAHA S, TRIPATHI AM, et al. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Herbal Extracts Added to Root Canal Sealers of Different Bases: An In Vitro Study. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2019;12(5):398-404.
[2] BUURMA HA, BUURMA BJ. The effect of smear layer on bacterial penetration through roots obturated using zinc oxide eugenol-based sealer. BMC Oral Health. 2020;20(1):88.
[3] KHANDELWAL A, JOSE J, TEJA K, et al. Comparative evaluation of postoperative pain and periapical healing after root canal treatment using three different base endodontic sealers - A randomized control clinical trial. J Clin Exp Dent. 2022;14(2):e144-e152.
[4] Alvarez-Vasquez JL, Erazo-Guijarro MJ, Dominguez-Ordonez GS, et al. Epoxy resin-based root canal sealers: An integrative literature review. Dent Med Probl. 2024;61(2):279-291.
[5] ORTEGA MA, RIOS L, FRAILE-MARTINEZ O, et al. Bioceramic versus traditional biomaterials for endodontic sealers according to the ideal properties. Histol Histopathol. 2024;39(3):279-292.
[6] SONG W, SUN W, CHEN L, et al. In vivo Biocompatibility and Bioactivity of Calcium Silicate-Based Bioceramics in Endodontics. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:580954.
[7] BAE WJ, Chang SW, Lee SI, et al. Human periodontal ligament cell response to a newly developed calcium phosphate-based root canal sealer. J Endod. 2010;36(10):1658-1663.
[8] VICTOR SP, KUMAR TS. BCP ceramic microspheres as drug delivery carriers: synthesis, characterisation and doxycycline release. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(1):283-290.
[9] DA SILVA BRUM I, FRIGO L, GONCALO PINTO DOS SANTOS P, et al. Performance of Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate and Xenogenic Hydroxyapatite on Bone Regeneration in Rat Calvarial Defects: Histomorphometric, Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural Analysis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:3473-3485.
[10] ZARKESH I, GHANIAN MH, AZAMI M, et al. Facile synthesis of biphasic calcium phosphate microspheres with engineered surface topography for controlled delivery of drugs and proteins. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;157:223-232.
[11] ZHONG Y, LIN Q, YU H, et al. Construction methods and biomedical applications of PVA-based hydrogels. Front Chem. 2024;12:1376799.
[12] SAITO H, COUSO-QUEIRUGA E, SHIAU HJ, et al. Evaluation of poly lactic‐co‐glycolic acid‐coated β‐tricalcium phosphate for alveolar ridge preservation: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. J Periodontol. 2021;92(4):524-535.
[13] HUI H, SONG Y, LIU H, et al. Integrating molecular-caged nano-hydroxyapatite into post-crosslinked PVA nanofibers for artificial periosteum. Biomater Adv. 2024;165:214001.
[14] RAY HA, TROPE M. Periapical status of endodontically treated teeth in relation to the technical quality of the root filling and the coronal restoration. Int Endod J. 1995;28(1):12-18.
[15] WANG X, XIAO Y, SONG W, et al. Clinical application of calcium silicate-based bioceramics in endodontics. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):853.
[16] AL-HADDAD A, CHE AB AZIZ ZA. Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Review. Int J Biomater. 2016;2016:9753210.
[17] ULANOWSKA M, OLAS B. Biological Properties and Prospects for the Application of Eugenol-A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(7):3671.
[18] VERTUAN GC, DUARTE MAH, MORAES IG, et al. Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of a New Root Canal Sealer. J Endod. 2018;44(3):501-505.
[19] DONNERMEYER D, BURKLEIN S, DAMMASCHKE T, et al. Endodontic sealers based on calcium silicates: a systematic review. Odontology. 2019;107(4):421-436.
[20] MCMICHEN FR, PEARSON G, RAHBARAN S, et al. A comparative study of selected physical properties of five root-canal sealers. Int Endod J. 2003;36(9):629-635.
[21] LU H, LU J, GUO J, et al. Radiographic outcomes and prognostic factors in nonvital immature permanent teeth after apexification with modified calcium hydroxide paste: a retrospective study. Clin Oral Investig. 2022;26(7):5079-5088.
[22] KANG Q, HUANG Z, QIAN W. Nicolau Syndrome with Severe Facial Ischemic Necrosis after Endodontic Treatment: A Case Report. J Endod. 2024;50(5):680-686.
[23] AL-SHEEB F, AL MANNAI G, THARUPEEDIKAYIL S. Nicolau Syndrome after Endodontic Treatment: A Case Report. J Endod. 2022;48(2): 269-272.
[24] CHEAH CW, AL-NAMNAM NM, LAU MN, et al. Synthetic Material for Bone, Periodontal, and Dental Tissue Regeneration: Where Are We Now, and Where Are We Heading Next? Materials (Basel). 2021; 14(20):6123.
[25] LEGEROS RZ, LIN S, ROHANIZADEH R, et al. Biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics: preparation, properties and applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2003;14(3):201-209.
[26] BROWN O, MCAFEE M, CLARKE S, et al. Sintering of biphasic calcium phosphates. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(8):2271-2279.
[27] EBRAHIMI M, PRIPATNANONT P, MONMATURAPOJ N, et al. Fabrication and characterization of novel nano hydroxyapatite/beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds in three different composition ratios. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(9):2260-2268.
[28] MANDATORI D, D’AMICO E, ROMASCO T, et al. A 3D in vitro model of biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) scaffold combined with human osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and endothelial cells as a platform to mimic the oral microenvironment for tissue regeneration. J Dent. 2024;151:105411.
[29] ZHANG K, LIU Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Magnesium-Doped Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Composite Hydrogel: Preparation and Characterization. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:
651-671.
[30] YANG G, LIU X, HUANG T, et al. Combined Application of Dentin Noncollagenous Proteins and Odontogenic Biphasic Calcium Phosphate in Rabbit Maxillary Sinus Lifting. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023;20(1): 93-109.
[31] RUJIRAPRASERT P, SURIYASANGPETCH S, SRIJUNBARL A, et al. Calcium phosphate ceramic as a model for enamel substitute material in dental applications. BDJ Open. 2023;9(1):25.
[32] MANSOUR AM, ABOU HAMMAD AB, EL NAHRAWY AM. Exploring nanoarchitectonics and optical properties of PAA-ZnO@BCP wide-band-gap organic semiconductors. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):3060.
[33] FRANCA R, SAMANI TD, BAYADE G, et al. Nanoscale surface characterization of biphasic calcium phosphate, with comparisons to calcium hydroxyapatite and beta-tricalcium phosphate bioceramics. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2014;420:182-188.
[34] SOARES I, SOTELO L, ERCEG I, et al. Improvement of Metal-Doped beta-TCP Scaffolds for Active Bone Substitutes via Ultra-Short Laser Structuring. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(12):1392.
[35] THUAKSUBAN N, LUNTHENG T, MONMATURAPOJ N. Physical characteristics and biocompatibility of the polycaprolactone-biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds fabricated using the modified melt stretching and multilayer deposition. J Biomater Appl. 2016; 30(10):1460-1472.
[36] GU Y, BAI Y, ZHANG D. Osteogenic stimulation of human dental pulp stem cells with a novel gelatin‐hydroxyapatite‐tricalcium phosphate scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(7):1851-1861. |