Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2834-2845.doi: 10.12307/2026.083
Previous Articles Next Articles
The roles and mechanisms of axon guidance molecules in alpha-synuclein-related neurodegenerative diseases
Zhang Yingbi1, 2, Li Minghui1, 2, Zhang Xiaorui1, Yin Jihong1, 3, Wang Peng1
- 1Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Beihua University Affiliated Hospital, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China; 3Department of Critical Care II, Jilin Central General Hospital, Jilin 132013, China
-
Received:2025-05-06Accepted:2025-05-17Online:2026-04-18Published:2025-09-06 -
Contact:Wang Peng, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Zhang Yingbi, MS, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China; Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Beihua University Affiliated Hospital, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Development Program of Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. 20240402007GH (to WP); Beihua University Graduate Student Innovation Key Project, No. 2022017 (to LMH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yingbi, Li Minghui, Zhang Xiaorui, Yin Jihong, Wang Peng. The roles and mechanisms of axon guidance molecules in alpha-synuclein-related neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2834-2845.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
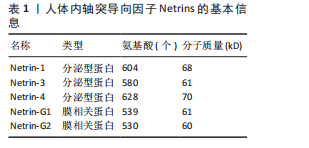
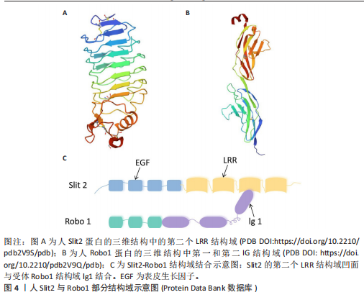
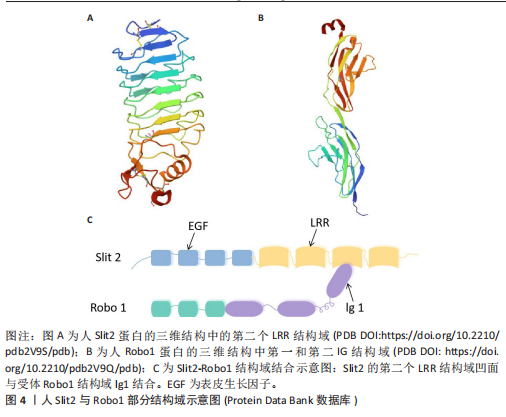
2.1 轴突导向因子的结构、受体及表达 目前科学家通过跨越物种研究,从无脊椎动物到脊椎动物,已经确定了4个轴突导向因子蛋白家族:Netrins、Ephrins、Semaphorins和Slits。 2.1.1 Netrins家族 Netrins是一个兼具分泌型和膜相关性的蛋白质家族,脊椎动物表达的分泌蛋白Netrins分为Netrins-1、Netrins-2、Netrins-3、Netrins-4和两种相关的糖基磷脂酰肌醇锚定的膜蛋白Netrin-G1和Netrin-G2。所有Netrin都由大约600个氨基酸组成,分子质量约70 kD[20]。Netrin-1、Netrin-3、Netrin-4、Netrin-G1和Netrin-G2在哺乳动物中表达,包括大鼠、小鼠和人,见表1;而Netrin-2的同源物到目前为止仅在鸡和斑马鱼中得到验证[21-22]。在"
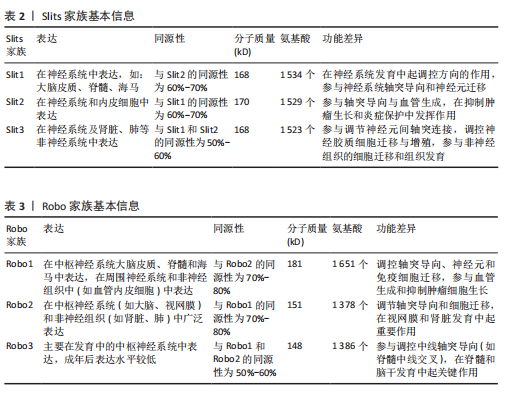
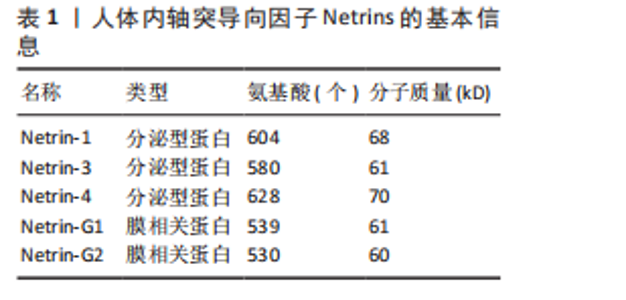
脊椎动物与部分双侧对称无脊椎动物的中枢神经系统中线发育过程中,Netrin-1发挥着高度保守的指导作用,它由脊椎动物胚胎神经管腹侧中线的底板细胞分泌,所形成的蛋白梯度具备双功能,既能吸引轴突也能排斥轴突[23]。除此之外,Netrins在血管生成中调节血管网络构建[24]、影响细胞迁移方向及速度[25]、肿瘤细胞增殖与转移过程中起着关键作用[26]。 在脊椎动物中,Netrin受体包括DCC、DCC旁腺生成素和4种UNC5蛋白(UNC5A-D),尽管DCC、生成素和UNC5蛋白都结合Netrin-1,但大多数Netrin信号传导的研究都集中在DCC上。引诱剂对Netrin-1作出反应需要DCC,相反,趋避反应需要UNC5蛋白的表达,在一些情况下需要DCC共同表达[27]。 2.1.2 Ephrins家族 Eph受体是受体酪氨酸激酶的大家族,其结合膜锚定配体后称为Ephrins,影响许多细胞功能[28]。Eph受体分别结合2个Ephrin配体亚家族:A型Eph受体(EphA1-EphA8和EphA10)结合并激活A型Ephrin(ephrinA1-ephrinA5);B型Eph受体(EphB1-EphB4和EphB6)结合并激活B型Ephrin(ephrin-B1-ephrin-B3)[29]。在结构上,EphA和EphB受体具有相似结构;在细胞外,EphA和EphB受体具有配体结合结构域和富含半胱氨酸的区域,在该结构域之后还连接着2个纤连蛋白Ⅲ型重复结构域,并且配体类别Ephrin-As和Ephrin-Bs的结构差异较大:Ephrin-Bs配体含有细胞外受体结合结构域、短跨膜结构域和短胞质尾,具有保守的酪氨酸残基和PDZ结构域结合位点。Ephrin-As较小,仅具有经由糖基磷脂酰肌醇锚栓系到膜受体结合结构域[30]。 近年来,已经发现Ephrin和Ephs在阿尔茨海默病中起关键作用。在参与记忆形成的脑区中发现了Ephrin和Ephs,如海马体、杏仁核和皮质[31]。Ephrin配体及其同源Eph受体与细胞表面相连,信号传导依赖细胞-细胞接触,使细胞能感知微环境并决定行为,如控制细胞间吸引或排斥[32]。Eph受体在胚胎中枢神经系统发育及成人维持肠细胞群中发挥重要作用[33]。 2.1.3 Semaphorins家族 Semaphorins是依据氨基序列末端、具有家族特征的结构域来识别的,这个名为“Sema”的结构域包含约500个氨基酸,其中17个氨基酸呈现出高度保守的特性。Semaphorins依据附加结构域的排列规则,被归纳为8 类[34]:1类和2类Semaphorins存在于无脊椎动物中,3至7类在脊椎动物中发现,而最后一类是发现由病毒编码的蛋白质。在脊椎动物中,4至6类中的Semaphorins是跨膜蛋白;3类与7类是分泌蛋白,通过磷脂酰肌醇键连接到细胞表面[35],其中在轴突导向方面研究最深入的是3类分泌Semaphorins (Semaphorin-3A-3G)。在脊椎动物体内,大多数Semaphorins都紧密地定位于产生它们的细胞周围,但Semaphorin-3A-3G较特殊,它们缺乏细胞表面的附着位点,其羧基末端的尾部结构可促使它们与细胞表面及细胞外基质相结合,主要参与在特定位置发生、依赖细胞间直接接触来介导的生物学过程[36]。 神经毡蛋白是细胞表面糖蛋白,充当Semaphorins和血管内皮生长因子家族成员的共同受体[37]。神经毡蛋白1同源二聚体与Semaphorin-3A存在相呼应答,神经毡蛋白2同源二聚体与Semaphorin-3F存在相呼应答,以及神经毡蛋白1和神经毡蛋白2的合作,可能通过形成异源二聚体构造与Semaphorin-3C相互响应的模型。神经毡蛋白1抗体可间接阻断Semaphorin-3A功能、部分阻断Semaphorin-3C功能,但不影响Semaphorin-3F功能[38]。敲除小鼠神经毡蛋白1后感觉神经节随即不受Semaphorin-3A影响[39]。 2.1.4 Slits家族 在不同物种间Slits展现出极为显著的高度保守性。在生物体内,Slits通常以分泌型蛋白的形式存在,在与细胞膜紧密相连的同时也能与细胞外基质发生特异性结合,进而在细胞间通讯以及细胞微环境的构建与维持等过程中发挥关键作用[40]。早期,Slit在果蝇胚胎中发现,并且被鉴定为是参与其幼虫表皮图案形成的基因。后来的研究表明,Slit在果蝇中枢神经系统中由中线胶质细胞合成[41]。Slit的同源基因在秀丽隐杆线虫和许多脊椎动物物种中被发现:从两栖动物到鱼类、鸟类,再到哺乳动物[42]。在无脊椎动物中分离出单个Slit基因,而在哺乳动物中存在3个Slit基因(Slit1、Slit2、Slit3)。多种基因共同编码一种分子质量约为200 kD的高分子量细胞外基质糖蛋白[43],从N端到C端,包含通过二硫键连接的较长富含亮氨酸重复序列、7-9个表皮生长因子样重复序列、ALPS(聚集蛋白、基底膜蛋白多糖、层粘连蛋白、Slit)结构域或层粘连蛋白G样模块结构域和半胱氨酸结[44],见图4。Slit作为结合Robo受体的分泌蛋白质,Robo受体属于细胞黏附分子免疫球蛋白超家族,存在于大多数脊椎动物中。配体Slits家族与受体Robo家族基本信息见表2,3。 2.2 轴突导向因子在α-突触核蛋白相关神经退行性疾病中的作用 轴突导向因子最初被认为是胚胎轴突的导向索,在神经纤维跨中线时起引导作用。在发育过程中,轴突导向因子通过轴突参与功能性神经回路的发育。神经元将轴突穿过中线投射到中枢神经系统的对侧,需要轴突导向因子引导连合轴突长距离到达中枢神经系统的中线[45]。最近发现轴突导向因子在发育后的神经系统也有重要作用。该文总结了4种类型轴突引导因子在α-突触核蛋白相关神经退行性疾病中的作用机制。 2.2.1 轴突导向因子在帕金森病中的作用及机制 (1) Netrins在帕金森病的作用及机制:基于胃肠道异常病理学效应的基础上,肠道中脑源性神经营养因子和Netrin-1减少可诱发帕金森病。AHN等[46]在帕金森病患者、健康对照、脑源性神经营养因子或Netrin-1肠道条件性敲除小鼠的结肠和脑样本中检测α-突触核蛋白聚集和神经炎症的路易小体,发现α-突触核蛋白聚集会导致线粒体功能障碍,进而引起慢性氧化应激,导致特定DNA序列上的C/EBP转录因子增多,增多的C/EBP促使脑源性神经营养因子和Netrin-1在帕金森病患者大脑和肠道中的表达明显减少,脑源性神经营养因子或Netrin-1肠道条件性敲除鼠表现出肠道神经系统中多巴胺能神经元损失、便秘、炎症和运动功能障碍,类似于帕金森病前驱症状。C/EBP是天冬酰胺内肽酶的转录因子,以浓度依赖的方式导致天冬酰胺内肽酶在脑中增加[47]。 抑制天冬酰胺内肽酶对Netrin1受体UNC5C的裂解作用,有助于减轻因Netrin-1缺失所引起的神经元死亡和运动障碍。天冬酰胺内肽酶裂解的UNC5C包内片段出现过表达情况,加"

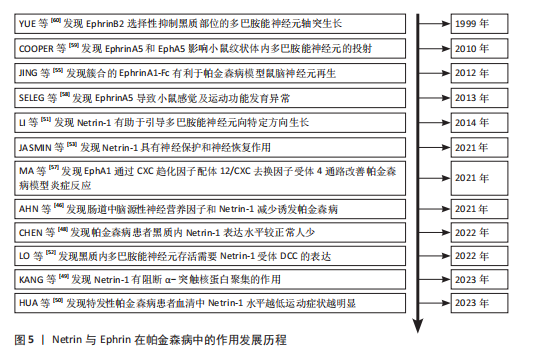
剧小鼠出现α-突触核蛋白聚集,并伴随多巴胺能神经元缺失及出现运动功能障碍等症状,表明Netrin-1水平的减少激活天冬酰胺内肽酶对UNC5C的裂解作用,裂解的UNC5C促进α-突触核蛋白聚集,加速帕金森病的病程进展[48]。 Netrin-1在健康成年人大脑的黑质中显著表达,而在帕金森病患者脑内表达较低。KANG等[49]通过基因表达综合数据库中编号GDS2821数据集分析发现,帕金森病患者黑质区域Netrin-1表达较同年龄健康对照组显著降低,Netrin-3和Netrin-4表达无差异;体外将α-突触核蛋白和Netrin-1通过1∶1比例混合,明显降低了α-突触核蛋白聚集率,证实Netrin-1有阻断α-突触核蛋白聚集的作用。 Netrin1/DCC比例失衡直接导致黑质致密部和纹状体内多巴胺能神经元减少。HUA等[50]通过注射1-甲基-4-苯基-1,2,3,6-四氢吡啶构建帕金森病小鼠模型,免疫荧光显示在多巴胺能神经元减少之前Netrin-1和DCC分布发生改变;结合对临床特发性帕金森病患者血清Netrin-1含量检测,结果表明帕金森病患者血清中Netrin-1浓度较低,与帕金森病模型小鼠实验结果不谋而合。中脑多巴胺能神经元包含2个主要亚群,其一位于腹侧被盖区,其二位于黑质致密部。LI等[51]研究发现,在Netrin-1基因敲除小鼠脑中多巴胺能神经元不能迁移到正常位置;在抗DCC存在的情况下,虽然轴突正常生长,但生长方向不指向纹状体,表明Netrin-1缺乏小鼠纹状体中的局部突触连接出现改变,腹侧被盖区和黑质多巴胺能神经元轴突生长都受到Netrin-1影响,Netrin-1缺失减少多巴胺能神经元轴突延黑质向背内侧纹状体的投射以及延腹侧被盖区向纹状体腹外侧的投射。 Netrin-1受体DCC的表达是中脑多巴胺能神经元亚群存活的必要条件,可能与帕金森病神经退行性过程相关。例如,LO等[52]借助DATcre/loxP基因靶向技术从多巴胺能神经元中选择性删除DCC,同时对成年和老年小鼠的神经元存活情况进行检测,发现DCC杂合子小鼠黑质网状部中多巴胺能神经元减少,并且在黑质中多巴胺能神经元的丢失出现不均匀分布情况,进而得出以上结论。 在黑质致密部,Netrin-1减少诱导DCC裂解,导致多巴胺能神经元显著缺失。Netrin-1在成人脑黑质中表达较强,并在黑质致密部与腹侧层多巴胺能神经元细胞体大量共定位。然而,Netrin-1缺失会导致黑质多巴胺能神经元死亡,引发运动功能障碍,同时伴随α-突触核蛋白水平升高及半胱天冬酶对受体DCC和UNC5B切割作用增强。在Netrin-1缺失的情况下,部分未结合的DCC诱导了多巴胺能神经元死亡,而敲除DCC可在一定程度上保护多巴胺能神经元、减轻运动功能障碍,并且DCC的保护作用比UNC5B更为显著。此外,Netrin-1过表达对1-甲基-4-苯基-1,2,3,6-四氢吡啶损伤的多巴胺能神经元具有神经保护和神经修复作用,同时减轻模型小鼠运动功能障碍[53]。 Netrin-1与C/EBP之间存在负反馈环路,Netrin-1水平降低加剧α-突触核蛋白聚集,而α-突触核蛋白聚集导致转录因子C/EBP增多,进一步降低Netrin-1表达,形成恶性循环;天冬酰胺内肽酶通过裂解UNC5C加剧α-突触核蛋白聚集,结合C/EBP本身对于天冬酰胺内肽酶促进作用,进一步放大病理效应,是帕金森病进展的关键调控因子;在Netrin-1缺乏的情况下,DCC受体过度表达可能通过未知信号通路诱导多巴胺能神经元死亡,并且α-突触核蛋白聚集可能直接干扰DCC功能,加剧神经元投射失败。基于这些假说,或许通过脑内注射Netrin-1可延缓因Netrin-1含量减少导致的C/EBP转录因子、天冬酰胺内肽酶和DCC受体表达水平变化,也可以开发靶向Netrin-1的基因治疗、天冬酰胺内肽酶和C/EBP的小分子抑制剂、DCC受体保护性干预药物、α-突触核蛋白聚集阻断剂以及DCC信号通路激活剂等治疗方法,通过多途径阻断帕金森病病理进程。未来需进一步研究Netrin-1与C/EBP环路、天冬酰胺内肽酶功能、DCC受体死亡机制等,并在动物模型中验证这些治疗策略的安全性和有效性,为临床转化提供依据。 (2) Ephrins在帕金森病中的作用及机制:EphrinA/EphA在帕金森病大鼠模型神经元再生中发挥作用。KIM等[54]在研究中将由抗人免疫球蛋白G Fc段抗体簇合的EphrinA1-Fc注射到由6-羟多巴诱导的单侧黑质纹状体损伤大鼠脑室中,通过免疫组织学和行为学测试发现,簇合的EphrinA1-Fc改变了脑室下小部分区域微环境,导致室管膜下区及其周围溴脱氧尿苷阳性细胞增加,提示脑室下区的细胞处于增殖状态;随后细胞迁移到纹状体分化为多巴胺能神经元和星形胶质细胞,同时促进血管新生,帕金森病模型大鼠的行为学障碍得到改善。这些结果证实,通过簇合的EphrinA1-Fc从侧脑室内激活EphrinA/EphA介导的信号转导,可能成为治疗神经退行性疾病的潜在方法[55]。 EphA1通过激活CXC趋化因子配体12/CXC趋化因子受体4信号通路来加重帕金森病小鼠模型神经病理学症状。神经炎症一直被认为是帕金森病的发生发展机制和可能的治疗靶点[56]。MA等[57]通过帕金森病患者标本、帕金森病小鼠模型和体外培养的SH-SY5Y细胞模型发现,EphA1在人帕金森病患者外周血、帕金森病小鼠和帕金森病细胞模型的黑质区高度表达,EphA1激活增加了SH-SY5Y细胞中α-突触核蛋白、炎性因子和小胶质细胞活化趋化因子的表达;免疫共沉淀实验证明,EphA1过表达导致CXC趋化因子配体12的高表达,促进CXC趋化因子配体12和CXC趋化因子受体4结合,进而加重小胶质细胞活化和炎症反应;在模型小鼠颅内注射EphA1后,炎症因子及小胶质细胞活化趋化因子表达增加,干预CXC趋化因子配体12后这种增加被抑制。由此可见,EphA1通过CXC趋化因子配体12/CXC趋化因子受体4信号通路加重帕金森病模型体内和体外的炎症反应及神经病理学症状。 EphrinA5缺乏可导致小鼠感觉、运动功能发育异常,促使鼠脑内包括多巴胺在内的单胺含量降低。SHELEG等[58]通过对EphrinA5基因敲除小鼠发育过程中睁眼、悬挂实验、空中翻正等行为学进行评估发现,EphrinA5基因敲除小鼠出现与同阶段发育小鼠相比发育延迟、移动等行为方式不成熟的现象与脑内单胺含量降低,免疫印迹分析显示EphrinA5基因敲除小鼠纹状体内多巴胺转运蛋白、酪氨酸羟化酶水平降低,表明EphrinA5在神经发育障碍疾病中发挥了重要作用。 EphrinA5配体与EphA5受体之间的相互作用,能够促进中脑内多巴胺能神经元轴突向纹状体靶向投射、生长。COOPER等[59]通过免疫组织化学法确定了EphrinA5和EphA5在发育中小鼠中脑和纹状体中多巴胺能神经元内的特异性表达,发现EphrinA5有促进多巴胺能神经元轴突生长的作用;在缺乏EphrinA5配体的情况下,表达EphA5的多巴胺能神经元无法有效识别其对应的纹状体靶标;在EphrinA5基因敲除的突变小鼠中,中脑多巴胺能神经元数量减少了14%,说明缺乏配体EphrinA5或受体EphA5均会出现中脑多巴胺能神经元向纹状体投射生长的靶向性降低,表现为投射数量减少以及效率的降低。 另外,EphrinB2和EphB1在不同多巴胺能神经元群体间以及它们所对应的目标区域中,以相互排斥的方式进行转录,进而构成不同神经通路。YUE等[60]明确了受体EphB1在中脑多巴胺能神经元中表达、配体EphrinB2在纹状体中表达,EphrinB2选择性抑制黑质部位的神经突生长,但是对于腹侧被盖区多巴胺能神经元轴突生长无抑制作用;不仅如此,存在EphrinB2时,黑质部位酪氨酸羟化酶阳性神经元数量相较于对照组减少了59%,说明EphrinB2不仅抑制黑质多巴胺能神经元突起的生长,还导致这些神经元在传导过程中丢失。 基于以上研究表明,EphrinA1在帕金森病中可能具有双重作用,既能通过增强CXC趋化因子配体12表达和炎症反应加剧α-突触核蛋白聚集,恶化疾病进程,又能通过注射簇合的EphrinA1-Fc改善运动障碍,未来需明确其促炎作用与神经保护作用的平衡点。EphrinA5在多巴胺能神经元的发育和功能维持中起关键作用,其缺乏会导致神经元数量减少、轴突生长受阻及多巴胺能神经元功能下降,因此,可通过EphrinA5替代疗法或激活EphA5受体等策略增强其信号。EphrinB2在纹状体中通过抑制多巴胺能神经突生长和诱导神经元丢失促进帕金森病病理进程,可尝试通过中小分子抑制剂阻断其毒性作用。另外,未来需深入研究Ephrin家族在不同脑区的作用差异及它与其他信号通路的交互作用,期待找到可靠靶点推动帕金森病治疗。 (3) Semaphorins在帕金森病中的作用及机制:Semaphorin对于帕金森病中多巴胺能神经元的轴突生长有引导作用。帕金森病运动症状是黑质内多巴胺能神经元变性,并伴随背侧纹状体多巴胺能神经元去神经支配后所产生。在黑质纹状体通路建立过程中,Semaphorin-3在多巴胺能神经元轴突到达纹状体途中所经过的区域表达[61]。促进多巴胺能神经元从黑质到纹状体轴突生长的一个机制是通过降解抑制性成分实现,如硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖;另一机制是通过趋化剂来引导多巴胺能神经元轴突,如 Semaphorin-3A和Semaphorin-3C促进体外胚胎干细胞衍生的多巴胺能神经元的轴突生长。TAMARIZ等[62]通过使用胚胎干细胞获得表达酪氨酸羟化酶的神经元,对应于来自腹侧中脑黑质的多巴胺能神经元进行体外培养实验,确定胚胎干细胞-酪氨酸羟化酶阳性培养物中有Semaphorin、神经毡蛋白1和神经毡蛋白2的表达,Semaphorin-3A和Semaphorin-3C均可增加轴突的长度,同时Semaphorin-3C对轴突生长方向有引导作用;通过同时加入神经毡蛋白封闭抗体降低了对轴突生长和吸引的作用,得出由神经毡蛋白介导Semaphorin-3A和Semaphorin-3C迁移这一结论。DíAZ-MARTíNEZ等[63]发现接受Semaphorin-3C处理的大鼠背侧纹状体接收到更多来自黑质的多巴胺能神经元轴突投射,产生了显著的行为能力恢复,效果类似于多巴胺能神经元向纹状体迁移;在此过程中具有抑制轴突生长作用的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖出现部分降解情况,逆行标记证明纹状体多巴胺能神经元与黑质和背侧纹状体之间建立了新的突触联系。可见Semaphorin-3C诱导多巴胺能神经元的长距离轴突生长,可以改善帕金森病样行为学障碍。 Semaphorin-3A、Semaphorin-3F均在引导多巴胺能神经元轴突到达突触靶点中起关键作用。TORRE等[64]确定了Semaphorin-3A和Semaphorin-3F及受体在中脑多巴胺能神经元表达,Semaphorin-3A和Semaphorin-3F在多巴胺能神经元轴突投射过程中起调控方向作用,Semaphorin-3F的作用更强;神经毡蛋白2基因敲除小鼠表现出中脑黑质内多巴胺能神经元投射出现轻微异常、外侧缰核到中脑的投射通路紊乱及丘脑核团中酪氨酸羟化酶阳性神经元分布异常,运动活性降低,但对可卡因的偏好与野生型小鼠无显著差异;而神经毡蛋白1基因敲除小鼠仅表现出轻微缺陷。该研究结果表明,Semaphorin-3A可能不直接参与多巴胺能神经元轴突的初始引导;Semaphorin-3F在体外对多巴胺能神经元轴突有强烈的排斥作用,但体内表型不明显,Semaphorin-3F缺失仍导致中脑-缰核通路和丘脑核团的轻微解剖学异常;Semaphorin-3A和Semaphorin-3F共同参与引导多巴胺能神经元轴突向纹状体和中脑边缘皮质前进,但由于体外反应与体内表型的差异,仍需更复杂的实验来全面解析Semaphorin-3F在中脑-端脑多巴胺通路发育中的作用。 以上研究结果表明,Semaphorin-3C通过降解硫酸软骨素聚糖促进多巴胺能神经元从黑质向纹状体的投射,并与神经毡蛋白1和神经毡蛋白2共同介导轴突生长方向,可能在轴突延伸和路径选择中起关键作用;Semaphorin-3A虽不直接参与多巴胺能神经元轴突的初始引导,但在预靶向轴突分类或新形成神经元迁移中发挥作用;Semaphorin-3F可能与受体复合物表达水平或下游信号成分有关,仍可能在微调轴突路径中发挥作用;神经毡蛋白1和神经毡蛋白2在中脑多巴胺能神经元轴突引导中具有差异性功能,神经毡蛋白2的缺失会导致更显著的轴突路径异常,表明它在多巴胺能神经元轴突发育中可能起更重要的作用。在治疗策略上,可通过增强Semaphorin-3C信号以促进其表达或调控硫酸软骨素聚糖降解、增强神经毡蛋白2功能或调控其表达比例、综合调控Semaphorin-3家族信等多种手段,改善多巴胺能神经元轴突路径异常。未来需通过体内动物模型结合研究深入探索Semaphorin-3家族信号的调控机制及治疗策略的有效性,为帕金森病的治疗提供新思路。 (4) Slits在帕金森病中的作用及机制:轴突导向因子Slit在2条多巴胺能神经元轴突投射中起调控作用,其一是中脑多巴胺能神经元经过间脑向前脑靶点上升的上行通路,另一条是自间脑A11组多巴胺能神经元向脊髓投射的下行通路[65]。DUGAN等[66]发现中脑多巴胺能神经元轴突的初始生长与Slit1、Slit2和Robo受体的表达相关,其中Slit2对中脑多巴胺能神经元轴突生长具有抑制作用,共培养实验表明,Slit2显著减少了腹内侧黑质轴突中酪氨酸羟化酶阳性神经纤维的数量和长度,并在引导中脑多巴胺能神经元轴突通过间脑中起主要作用,防止轴突进入腹侧中线或向前方视交叉投射,同时限制其进入狭窄区域,而Slit1的作用相对次要;此外,Robo受体在中脑多巴胺能神经元轴突引导中也起重要作用,Robo1具有Slit非依赖性功能,Robo2-/-胚胎的中脑多巴胺能神经元投射正常,但Robo1-/-纯合子出现中脑多巴胺能神经元投射模式错误,Robo1-/-、Robo2-/-双纯合子的表型比Robo1-/-更严重,与Slit1-/-; Slit2-/-双纯合子表型部分相似但更严重。这些发现表明,Slit和Robo信号通路在中脑多巴胺能神经元轴突的引导和限制中具有复杂的协同作用。 Slit在多巴胺能神经元延间脑脊髓束纵向延伸时起调控方向的作用。KASTENHUBER等[67]发现Robo2缺陷的多巴胺能神经元轴突逐渐向中线移动,并偶尔出现异常的中线交叉,表明Robo2介导的排斥作用对于调控多巴胺能神经元纵向轴突的侧向偏移起关键作用;此外,Slit/Robo和Netrin/DCC基因的空间表达模式与它们作为纵向多巴胺能神经元轴突引导线索的作用一致;DCC和Robo2在同一多巴胺能神经元中共同表达,而Robo1、Robo3和Robo4在多巴胺能神经元轴突早期生长阶段的间脑中未被检测到表达。通过实验分析进一步表明,纵向轴突束的侧向定位主要由Robo2的功能决定。 Slit2抑制多巴胺能神经元延伸,Netrin-1蛋白显著增强多巴胺能神经元轴突生长。LIN等[68]通过共培养实验探究了Slit2在引导多巴胺能神经元轴突生长中的作用,在腹侧中脑外植体与对照细胞聚集体的共培养中,发现神经突在胶原凝胶中生长良好;在腹侧中脑外植体与Slit2细胞聚集体的共培养中,发现大多数酪氨酸羟化酶阳性轴突和神经束位于外植体远端,近端仅有少量轴突,表明Slit2是多巴胺能神经元轴突生长的有效排斥剂,加入过量的Robo受体可消除Slit2导致的神经突延伸减少。实验探究了参与未成熟多巴胺能神经元轴突生长的轴突导向因子机制,有助于更好地理解控制多巴胺能神经元回路形成的分子机制,可能为帕金森病中轴突、突触再生和修复创造有利的条件。 胚胎干细胞源性多巴胺能神经元对轴突引导起关键作用,这有助于通过植入胚胎干细胞衍生细胞来恢复帕金森病中丢失或受损的多巴胺能神经元通路。LIN等[17]通过免疫组化法确定了胚胎干细胞分化的多巴胺能神经元可以与大脑中的同源轴突导向因子受体DCC、Robo1和Robo2相互作用,通过胚胎干细胞细胞凝胶培养体发现Slit1和Slit3可以调节胚胎干细胞源性神经元的生长,在此过程中起到抑制作用,这些抑制作用对于轴突在寻找合适的终止区的过程中发挥着至关重要的作用;与Slit1和Slit3不同,Slit2在共培养体系中因为Robo细胞外结构域的存在被测定既发挥抑制作用也发挥排斥作用。 以上研究结果表明,Slit和Robo信号通路在中脑轴突的引导和排斥中具有复杂的协同作用,其中Slit2主要通过排斥作用调控多巴胺能神经元轴突的侧向定位,防止其进入腹侧中线或异常投射,Robo2在侧向偏移中起关键作用,而Robo1具有Slit非依赖性功能,二者共同参与轴突路径的精确调控;Slit2不仅具有排斥作用,还通过与Robo受体相互作用兼具引导功能,它的双重功能对轴突的延伸和终止区域选择至关重要;此外,胚胎干细胞分化的多巴胺能神经元与同源轴突导向因子存在相互作用,Slit1和Slit3通过Robo受体抑制神经突起生长。Slit配体与Robo受体在体内起到怎样的作用、受何因素影响仍然有待研究。通过增强Slit2表达或调控Robo2功能或许可以改善多巴胺能神经元轴突路径异常,将Slit/Robo信号通路的调控与其他神经保护策略结合形成综合治疗方案,为帕金森病等神经退行性疾病的治疗提供新思路。图5。 2.2.2 轴突导向因子可能与一些自主神经功能衰竭发病均存在联系 路易体痴呆、多系统衰竭及单纯性自主神经功能衰竭均属于α-突触核蛋白相关神经退行性疾病,它们的发病机制与轴突导向因子密切相关。路易体痴呆表现出显著的神经病理学变化,这些变化包括广泛的边缘系统和皮质路易体以及由α-突触核蛋白聚集体组成的路易神经突[69],涉及脑干及边缘系统和新皮质区域(称为路易体病),中脑多巴胺能神经元细胞丢失及腹前脑核中胆碱能神经元丢失[70],这与Netrin-1和C/EBP的负反馈环路、EphrinA1的促炎作用、Semaphorin-3家族在轴突延伸和路径选择中的异常以及Slit/Robo信号通路的调控异常密切相关。 多系统衰竭是一种罕见的、快速进展的、致命的神经退行性疾病,病因尚不明确,临床特征表现为帕金森综合征、小脑损伤、自主神经和运动功能障碍[71],病理学特征为α-突触核蛋白异常聚集[72]。并且多系统衰竭与帕金森病中多巴胺能神经元耗竭程度相似[73],其发病可能与Netrin-1水平降低、EphrinA5缺乏以及Semaphorin-3家族和Slit/Robo信号通路功能异常导致的神经元存活和轴突导向受损有关。 单纯性自主神经衰竭是一种以直立性体位性低血压为特征的自主神经系统退行性疾病,通常在中年至晚年出现直立性低血压或晕厥症状[74]。在病理生理学上,单纯性自主神经衰竭是一种α-突触核蛋白病,特征在于自主神经节和神经中的α-突触核蛋白主要外周沉积。单纯性自主神经衰竭也具有多巴胺能神经元缺失,但多巴胺在中枢神经系统缺乏程度不同——在帕金森病和多系统衰竭中较为突出[75],发病可能涉及Netrin-1异常、Ephrin家族对多巴胺能神经元发育和功能的调控异常、Semaphorin-3"

家族在轴突生长和路径选择中的功能异常以及Slit/Robo信号通路对轴突导向的影响。目前,轴突导向因子与路易体痴呆、多系统衰竭及单纯性自主神经功能衰竭的关系尚不明确。轴突导向因子调控α-突触核蛋白聚集、多巴胺能神经元存活、轴突生长和路径选择,在路易体痴呆、多系统衰竭以及单纯性自主神经功能衰竭的发病机制中可能发挥重要作用,未来需进一步研究它的具体机制以开发针对性治疗策略。 2.2.3 临床转化现状 FDA药物审批:参考美国食品药品监督管理局(Food and Drug Administration,FDA)官方发布的药物审批信息,了解到目前尚无直接靶向轴突导向因子的药物获批用于治疗α-突触核蛋白疾病。 北美临床试验注册方案:根据ClinicalTrials.gov临床试验注册平台,截至2025年2月,针对帕金森病有4 049项临床试验注册方案,针对路易体痴呆有212项,多系统衰竭141项,并没有与轴突导向因子相关的注册项目。 NIH基金资助项目:美国国立卫生研究院(National Institutes of Health,NIH)通过基金项目支持了多项关于轴突导向因子在神经退行性疾病中作用的研究,这些研究旨在深入理解帕金森病和阿尔茨海默病等疾病的发病机制,并探索潜在的治疗策略。具体项目内容如下:①资助编号:1R15HD080512-01,探究Netrin-1如何调节微管动态,这种调控可能在帕金森病的发展过程中扮演关键角色;②资助编号:4R01NS054739-08,确定Slit受体Robo2和Netrin受体Frazzled如何受到转录因子(包括Hb9、Nkx6和Islet)的调节,以及这种调节如何反过来指导特定运动神经元和中间神经元群体中的通路选择;③资助号:5P01HD023315-23,Ephrin和Neurotrophin受体与下游信号蛋白之间的相互作用提供了一种机制,有助于了解它们在发育和退行性疾病(如阿尔茨海默病和帕金森病)中的作用。这些由NIH资助的研究项目,涵盖了从分子水平到整体疾病进程的不同层面,通过这些研究科学家们正在逐步揭开神经退行性疾病的复杂面纱,并为未来的诊断和治疗方法奠定基础。 临床研究成果:轴突导向因子在α-突触核蛋白相关神经退行性疾病中的临床转化尚处于起步阶段,已有动物实验表明调节轴突导向因子信号通路可改善神经退行性疾病模型症状,如减少α-突触核蛋白聚集、保护神经元、促进轴突修复再生,为临床治疗提供理论依据和潜在靶点,但需进一步临床试验验证安全性和有效性。"

| [1] SMITH G, SWEENEY ST, O’KANE CJ, et al. How neurons maintain their axons long-term: an integrated view of axon biology and pathology. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1236815. [2] KIM SW, KIM KT. Expression of Genes Involved in Axon Guidance: How Much Have We Learned? Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(10):3566. [3] YE X, QIU Y, GAO Y, et al. A Subtle Network Mediating Axon Guidance: Intrinsic Dynamic Structure of Growth Cone, Attractive and Repulsive Molecular Cues, and the Intermediate Role of Signaling Pathways. Neural Plast. 2019; 2019:1719829. [4] YUKAWA K. [Elucidating the Pathophysiology of Various Diseases by Investigating the Role of Molecules in Brain Wiring]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2025; 145(2):133-143. [5] MORELAND T, POULAIN FE. To Stick or Not to Stick: The Multiple Roles of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Neural Circuit Assembly. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:889155. [6] CORTÉS E, PAK JS, ÖZKAN E. Structure and evolution of neuronal wiring receptors and ligands. Dev Dyn. 2023;252(1):27-60. [7] CHILTON JK. Molecular mechanisms of axon guidance. Dev Biol. 2006;292(1):13-24. [8] DELPECH C, SCHAEFFER J, VILALLONGUE N, et al. Axon guidance during mouse central nervous system regeneration is required for specific brain innervation. Dev Cell. 2024;59(24):3213-3228.e8. [9] PALSAMY K, CHEN JY, SKAGGS K, et al. Microglial depletion after brain injury prolongs inflammation and impairs brain repair, adult neurogenesis and pro‐regenerative signaling. Glia. 2023; 71(11):2642-2663. [10] POLYMEROPOULOS MH, LAVEDAN C, LEROY E, et al. Mutation in the -Synuclein Gene Identified in Families with Parkinson’s Disease. Science. 1997;276(5321):2045-2047. [11] DAI L, WANG J, MENG L, et al. The cholesterol 24-hydroxylase CYP46A1 promotes α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS Biol. 2025;23(2): e3002974. [12] 王鹏,李昕,陈予东,等.α-突触核蛋白寡聚体抑制大鼠原代培养神经元突起早期生长[J].首都医科大学学报,2014, 35(5):587-591. [13] AL-AZZANI M, KNIG A, OUTEIRO T. Production of Recombinant Alpha-Synuclein: Still No Standardized Protocol in Sight. Biomolecules. 2022;12(2):324. [14] PAVY-LE TRAON A, FOUBERT-SAMIER A, FABBRI M. An overview on pure autonomic failure. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2024;180(1-2): 94-100. [15] MORRIS HR, SPILLANTINI MG, SUE CM, et al. The pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2024;403(10423):293-304. [16] DUAN Q, ZHANG Q, JIANG SL, et al. Transmission of peripheral blood α-synuclein fibrils exacerbates synucleinopathy and neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease by endothelial Lag3 endocytosis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025;328(3):C836-C855. [17] LIN L, ISACSON O. Axonal Growth Regulation of Fetal and Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Dopaminergic Neurons by Netrin-1 and Slits. Stem Cells. 2010;24(11):2504-2513. [18] GARRITSEN O, VAN BATTUM EY, GROSSOUW LM, et al. Development, wiring and function of dopamine neuron subtypes. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2023;24(3):134-152. [19] JIAO F, WANG Q, ZHANG P, et al. Expression signatures of long non-coding RNA in the substantia nigra of pre-symptomatic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2017;331:123-130. [20] GAO X, YE J, HUANG X, et al. Research progress of the netrins and their receptors in cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(8): e18241. [21] HONEYCUTT SE, N’GUETTA PY, O’BRIEN LL. Innervation in organogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2022;148:195-235. [22] PARK KW, URNESS LD, SENCHUK MM, et al. Identification of new netrin family members in zebrafish: Developmental expression of netrin2 and netrin4. Dev Dyn. 2005;234(3):726-731. [23] ZANG Y, BASHAW GJ. Systematic analysis of the Frazzled receptor interactome establishes previously unreported regulators of axon guidance. Development. 2023;150(15):dev201636. [24] HONEYCUTT SE, N’GUETTA PY, HARDESTY DM, et al. Netrin 1 directs vascular patterning and maturity in the developing kidney. Development. 2023; 150(22):dev201886. [25] RAMKHELAWON B, HENNESSY EJ, MÉNAGER M, et al. Netrin-1 promotes adipose tissue macrophage retention and insulin resistance in obesity. Nat Med. 2014;20(4):377-384. [26] DUCAROUGE B, REDAVID AR, VICTOOR C, et al. Netrin-1 blockade inhibits tumor associated Myeloid-derived suppressor cells, cancer stemness and alleviates resistance to chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitor. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30(10):2201-2212. [27] CHAUDHARI K, ZHANG K, YAM PT, et al. A human DCC variant causing mirror movement disorder reveals that the WAVE regulatory complex mediates axon guidance by netrin-1-DCC. Sci Signal. 2024; 17(856):eadk2345. [28] RASOOL D, JAHANI-ASL A. Master regulators of neurogenesis: the dynamic roles of Ephrin receptors across diverse cellular niches. Transl Psychiatry. 2024; 14(1):462. [29] ALFARO D, RODRÍGUEZ-SOSA MR, ZAPATA AG. Eph/ephrin Signaling and Biology of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells. J Clin Med. 2020;9(2):310. [30] TAYLOR H, CAMPBELL J, NOBES CD. Ephs and ephrins. Curr Biol. 2017;27(3):R90-R95. [31] AGARWAL K, FARHAT A, LAMPRECHT R. EphrinB2 in excitatory neurons and astrocytes in the basolateral amygdala controls long-term fear memory formation. Commun Biol. 2024;7(1):1165. [32] DINES M, LAMPRECHT R. The Role of Ephs and Ephrins in Memory Formation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016;19(4): pyv106. [33] GUO X, YANG Y, TANG J, et al. Ephs in cancer progression: complexity and context-dependent nature in signaling, angiogenesis and immunity. Cell Commun Signal. 2024; 22(1):299. [34] KUMANOGOH A. Semaphorins:A Diversity of Emerging Physiological and Pathological Activities. 2015.doi:10.1007/978-4-431-54385-5. [35] RAPER JA. Semaphorins and their receptors in vertebrates and invertebrates. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000;10(1):88-94. [36] CANTU-GUERRA HL, PAPAZIAN MR, GORSKY AL, et al. Cochlear hair cell innervation is dependent on a modulatory function of Semaphorin-3A. Dev Dyn. 2023;252(1):124-144. [37] QAMAR T, MISRA DP, KAR S. Semaphorins and its receptors: Emerging cellular biomarkers and therapeutic targets in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. Life Sci. 2025;361:123281. [38] HE Y, TANG J, ZHANG M, et al. Human Placenta Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplantation Reducing Cellular Apoptosis in Hypoxic-Ischemic Neonatal Rats by Down-Regulating Semaphorin 3A/Neuropilin-1. Neuroscience. 2024;536:36-46. [39] KISELEVA EP, RUTTO KV. Semaphorin 3A in the Immune System: Twenty Years of Study. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2022;87(7):640-657. [40] HE C, GU L, LI A, et al. Recombinant Slit2 attenuates tracheal fibroblast activation in benign central airway obstruction by inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway. Mol Cell Probes. 2024;73:101947. [41] GORLA M, CHAUDHARI K, HALE M, et al. A Nedd4 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Pathway Inhibits Robo1 Repulsion and Promotes Commissural Axon Guidance across the Midline. J Neurosci. 2022;42(40):7547-7561. [42] ITOH A, MIYABAYASHI T, OHNO M, et al. Cloning and expressions of three mammalian homologues of Drosophila slit suggest possible roles for Slit in the formation and maintenance of the nervous system. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998;62(2):175-186. [43] NELSON KA, LENHART F, ANLLO L, et al. The Drosophila hematopoietic niche assembles through collective cell migration controlled by neighbor tissues and Slit-Robo signaling. eLife. 2025;13:RP100455. [44] GILHAUS K, CEPOK C, KAMM D, et al. Activation of Hippo Pathway Damages Slit Diaphragm by Deprivation of Ajuba Proteins. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023;34(6): 1039-1055. [45] KAPRIELIAN Z, RUNKO E, IMONDI R. Axon guidance at the midline choice point. Dev Dyn. 2001;221(2):154-181. [46] AHN EH, KANG SS, LIU X, et al. BDNF and Netrin-1 repression by C/EBPβ in the gut triggers Parkinson’s disease pathologies, associated with constipation and motor dysfunctions. Prog Neurobiol. 2021;198:101905. [47] KULKARNI R, KUMARI S, DHAPOLA R, et al. Association Between the Gut Microbiota and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Update on Signaling Pathways and Translational Therapeutics. Mol Neurobiol. 2025;62(4):4499-4519. [48] CHEN G, AHN EH, KANG SS, et al. UNC5C Receptor Proteolytic Cleavage by Active AEP Promotes Dopaminergic Neuronal Degeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(7):e2103396. [49] KANG EJ, JANG SM, LEE YJ, et al. The couple of netrin-1/α-Synuclein regulates the survival of dopaminergic neurons via α-Synuclein disaggregation. BMB Rep. 2023;56(2):126-131. [50] HUA Y, HAN W, ZHOU L, et al. An imbalance of netrin‐1 and DCC during nigral degeneration in experimental models and patients with Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023;29(7): 1817-1829. [51] LI J, DUARTE T, KOCABAS A, et al. Evidence for topographic guidance of dopaminergic axons by differential Netrin-1 expression in the striatum. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2014; 61:85-96. [52] LO PS, RYMAR VV, KENNEDY TE, et al. The netrin-1 receptor DCC promotes the survival of a subpopulation of midbrain dopaminergic neurons: Relevance for ageing and Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 2022;161(3):254-265. [53] JASMIN M, AHN EH, VOUTILAINEN MH,et al. Netrinand its receptor DCC modulate survival and death of dopamine neurons and Parkinson’s disease features. EMBO J. 2021;40(3):e105537. [54] KIM HI, LIM J, CHOI HJ, et al. ERRγ Ligand Regulates Adult Neurogenesis and Depression-like Behavior in a LRRK2-G2019S-associated Young Female Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19(4): 1298-1312. [55] JING X, MIWA H, SAWADA T, et al. Ephrin-A1-Mediated Dopaminergic Neurogenesis and Angiogenesis in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32019. [56] AMOR S, PUENTES F, BAKER D, et al. Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology. 2010;129(2):154-169. [57] MA J, WANG Z, CHEN S, et al. EphA1 Activation Induces Neuropathological Changes in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease Through the CXCL12/CXCR4 Signaling Pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 2021; 58(3):913-925. [58] SHELEG M, YOCHUM CL, WAGNER GC, et al. Ephrin-A5 deficiency alters sensorimotor and monoaminergic development. Behav Brain Res. 2013;236(1):139-147. [59] COOPER MA, KOBAYASHI K, ZHOU R. Ephrin-A5 regulates the formation of the ascending midbrain dopaminergic pathways. Dev Neurobiol. 2010;69(1):36-46. [60] YUE Y, WIDMER DA, HALLADAY AK, et al. Specification of Distinct Dopaminergic Neural Pathways: Roles of the Eph Family Receptor EphB1 and Ligand Ephrin-B2. J Neurosci. 1999;19(6):2090-2101. [61] HERNÁNDEZ-MONTIEL HL, TAMARIZ E, SANDOVAL-MINERO MT, et al. Semaphorins 3A, 3C, and 3F in mesencephalic dopaminergic axon pathfinding. J Comp Neurol. 2008;506(3):387-397. [62] TAMARIZ E, DÍAZ-MARTÍNEZ NE, DÍAZ NF, et al. Axon responses of embryonic stem cell-derived dopaminergic neurons to semaphorins 3A and 3C. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88(5):971-980. [63] DÍAZ-MARTÍNEZ NE, TAMARIZ E, DÍAZ NF, et al. Recovery from experimental parkinsonism by semaphorin-guided axonal growth of grafted dopamine neurons. Mol Ther. 2013;21(8):1579-1591. [64] TORRE ER, GUTEKUNST CA, GROSS RE. Expression by midbrain dopamine neurons of Sema3A and 3F receptors is associated with chemorepulsion in vitro but a mild in vivo phenotype. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2010;44(2):135-153. [65] ALBANESE A, ALTAVISTA MC, ROSSI P. Organization of central nervous system dopaminergic pathways. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1986;22:3-17. [66] DUGAN JP, STRATTON A, RILEY HP, et al. Midbrain dopaminergic axons are guided longitudinally through the diencephalon by Slit/Robo signals. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011;46(1):347-356. [67] KASTENHUBER E, KERN U, BONKOWSKY JL, et al. Netrin-DCC, Robo-Slit, and Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans Coordinate Lateral Positioning of Longitudinal Dopaminergic Diencephalospinal Axons. J Neurosci. 2009; 29(28):8914-8926. [68] LIN L, RAO Y, ISACSON O. Netrin-1 and slit-2 regulate and direct neurite growth of ventral midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005;28(3):547-555. [69] FUJIWARA Y, KABUTA C, SANO T, et al. Pathology-associated change in levels and localization of SIDT2 in postmortem brains of Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies patients. Neurochem Int. 2022;152:105243. [70] SALVATORE MF. Dopamine Signaling in Substantia Nigra and Its Impact on Locomotor Function-Not a New Concept, but Neglected Reality. Int J Mol Sci. 2024; 25(2):1131. [71] NDAYISABA A, HALLIDAY GM, KHURANA V. Multiple System Atrophy: Pathology, Pathogenesis, and Path Forward. Annu Rev Pathol. 2025;20(1):245-273. [72] JELLINGER KA. The Pathobiology of Behavioral Changes in Multiple System Atrophy: An Update. Int J Mol Sci. 2024; 25(13):7464. [73] SIAN-HULSMANN J, RIEDERER P. The ‘α-synucleinopathy syndicate’: multiple system atrophy and Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2024;131(6): 585-595. [74] HOLEC SAM, KHEDMATGOZAR CR, SCHURE SJ, et al. A-synuclein prion strains differentially adapt after passage in mice. PLoS Pathog. 2024;20(12):e1012746. [75] GOLDSTEIN DS, SULLIVAN P, HOLMES C, et al. Differential abnormalities of cerebrospinal fluid dopaminergic vs. noradrenergic indices in synucleinopathies. J Neurochem. 2021;158(2):554-568. [76] GBD 2016 NEUROLOGY COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(5):459-480. [77] GEGG ME, MENOZZI E, SCHAPIRA AHV. Glucocerebrosidase-associated Parkinson disease: Pathogenic mechanisms and potential drug treatments. Neurobiol Dis. 2022;166:105663. [78] YANG Y, YANG S, SCHWIEIGHAUSER M, et al. Cryo-EM structures of α-synuclein filaments from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Biorxiv. 2022. doi:10.1101/2022.07.12.499706. [79] ELDEEB MA, THOMAS RA, RAGHEB MA,et al. Mitochondrial quality control in health and in Parkinson’s disease. Physiol Rev. 2022;102(4):1721-1755. [80] BRAAK H, DEL TREDICI K, RÜB U, et al. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24(2):197-211. [81] CONTALDI E, MAGISTRELLI L, COMI C. T Lymphocytes in Parkinson’s Disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2022;12(s1):S65-S74. [82] FLORES-PONCE X, VELASCO I. Dopaminergic neuron metabolism: relevance for understanding Parkinson’s disease. Metabolomics. 2024;20(6):116. [83] HEIDARI A, YAZDANPANAH N, REZAEI N. The role of Toll-like receptors and neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):135. [84] WU KM, XU QH, LIU YQ, et al. Neuronal FAM171A2 mediates α-synuclein fibril uptake and drives Parkinson’s disease. Science. 2025;387(6736):892-900. [85] TAPIA-ARELLANO A, CABRERA P, CORTÉS-ADASME E, et al. Tau- and α-synuclein-targeted gold nanoparticles: applications, opportunities, and future outlooks in the diagnosis and therapy of neurodegenerative diseases. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024; 22(1):248. [86] YUAN X, NIE S, YANG Y, et al. Propagation of pathologic α-synuclein from kidney to brain may contribute to Parkinson’s disease. Nat Neurosci. 2025;28(3):577-588. [87] RAY CHAUDHURI K, LETA V, BANNISTER K, et al. The noradrenergic subtype of Parkinson disease: from animal models to clinical practice. Nat Rev Neurol. 2023;19(6):333-345. [88] DUTTA AK, ARMSTRONG C, LUO D, et al. D-685 Reverses Motor Deficits and Reduces Accumulation of Human α-Synuclein Protein in Two Different Parkinson’s Disease Animal Models. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023;14(5):885-896. [89] AARSLAND D. Cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016;22 Suppl 1:S144-148. |
| [1] | Liu Huan, Zeng Shaopeng, Chen Jun, He Linqian, Yang Ying, Zhang Jing. Aging-related dysregulation of glucose metabolism: crossroads of cancer and neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1527-1538. |
| [2] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Zhao Yuxin, Liu Xihua. Effects of different neuromodulatory stimulation modalities on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [3] | Li Minghui, Zhang Yingbi, Zhang Xiaorui, Yin Jihong, Wang Peng. Glial-neuronal interactions in basal ganglia neurodegenerative diseases: regulatory mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2536-2549. |
| [4] | Li Tingwen, , Zhang Jianhua. Meta-analysis of the effects of aquatic exercise on balance function and motor ability in elderly patients with Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2560-2568. |
| [5] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [6] | Zhang Xin, Guo Baojuan, Xu Huixin, Shen Yuzhen, Yang Xiaofan, Yang Xufang, Chen Pei. Protective effects and mechanisms of 3-N-butylphthalide in Parkinson’s disease cell models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6466-6473. |
| [7] | Nan Songhua, Peng Chaojie, Cui Yinglin. Mitochondrial dysfunction and brain aging: a bibliometrics analysis based on the Web of Science Core Collection database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5642-5651. |
| [8] | Jiang Qianping, Yang Dan, , , Wan Shilei, Xu Dandan, , , , Cao Lu, , Zhou Jing, , , . Role of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine glycosylation in neurodegenerative diseases and its clinical application prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5704-5712. |
| [9] | Lei Senlin, Chen Xiaoan, Chen Ping, Wang Zhaofeng. Exercise prevention and treatment of Parkinson’ s disease mediated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor: role and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5454-5468. |
| [10] | Guan Mengya, Ren Binbin, Wang Jingying. Major histocompatibility complex regulates immune responses in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5469-5477. |
| [11] | Zhu Liuhui, Zhang Xinyue, Zhu Zhouhai, Yang Xinglong, Guan Ying, Liu Bin. Coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain-containing 2 inhibits apoptosis of Parkinson’ s disease SH-SY5Y cells by promoting mitochondrial autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5403-5413. |
| [12] | Zhao Yuxin, Zhang Deqi, Bi Hongyan. Effect of different stimulation modalities of non-invasive brain stimulation on cognitive function in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5212-5223. |
| [13] | Lin Huijie, Huang Yun, Huang Zhihua, Jiang Lixia. Hot topics on exosomes as drug delivery system in central nervous system diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5013-5021. |
| [14] | Wang Jingying, , Ren Binbin, Ma Suna, Yang Yueyue, , Wu Song, , Guan Mengya, . Mechanism of alpha-synuclein in mitochondrial damage induced by Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3668-3674. |
| [15] | Liu Ziyu, Geng Dandan, Zhang Runjiao, Liu Qing, Li Yibo, Wang Hongfang, Xie Wenmeng, Wang Wenyu, Hao Jiaxin, Wang Lei. Application of single-cell RNA sequencing technology in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 193-201. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||