Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (9): 1863-1869.doi: 10.12307/2025.124
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy
Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe
- Central Hospital Affiliated to Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110075, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2023-11-01Accepted:2024-01-12Online:2025-03-28Published:2024-10-10 -
Contact:Piao Chengzhe, Professor, Chief physician, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110075, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Ma Chi, Master candidate, Physician, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110075, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Innovation Foundation for Master's Students of Shenyang Medical College, No. Y20220526 (to MC); Science and Technology Foundation of Shenyang Medical College, No. 20191009 (to WN); Shenyang Young and Middle-aged Science and Technology Innovation Talents Support Program, No. RC220422 (to CY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
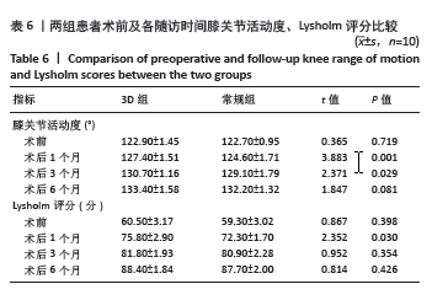
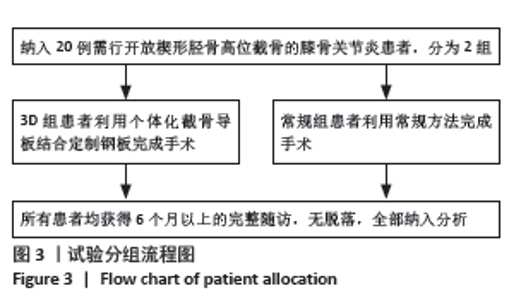
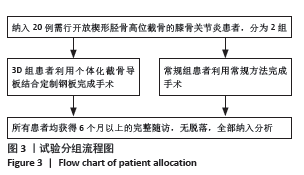
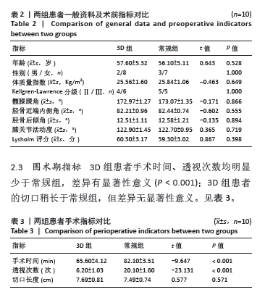
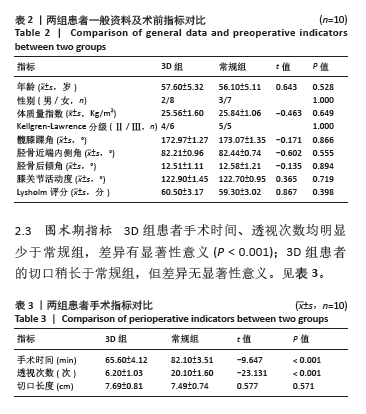
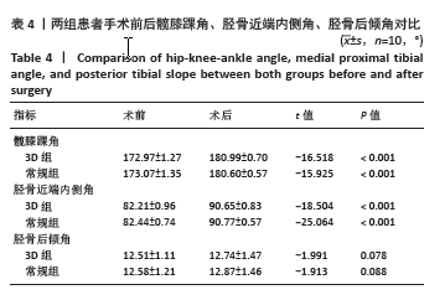
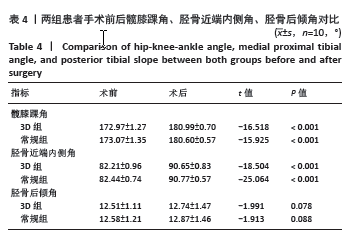
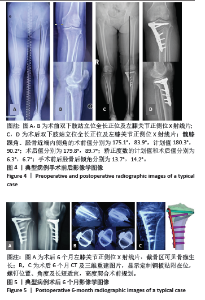
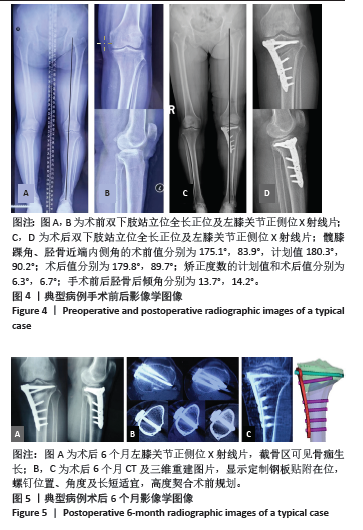
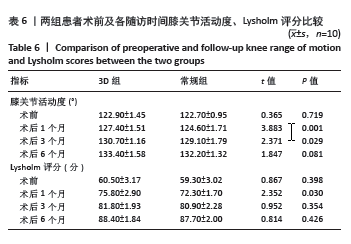
2.5 膝关节功能指标 两组患者术后膝关节活动度和Lysholm评分均逐渐增大,差异均有显著性意义(F3D组膝关节活动度=1 315.286,F3D组Lysholm评分=285.194,F常规组膝关节活动度=562.348,F常规组Lysholm评分=2 618.353,均P < 0.001)。术后1个月时,3D组的膝关节活动度和Lysholm评分较常规组高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);术后3个月时,3D组的膝关节活动度较常规组高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),而两组间Lysholm评分的差异无显著性意义;术后6个月时,两组间膝关节活动度和Lysholm评分相比差异均无显著性意义。见表6。 "
| 1] LI D, LI S, CHEN Q, et al. The Prevalence of Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis in Relation to Age, Sex, Area, Region, and Body Mass Index in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Med. 2020;7:304. [2] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组, 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨关节炎学组, 湘雅医院国家老年疾病临床医学研究中心, 等. 中国骨关节炎诊疗指南(2021年版)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2021, 41(18):1291-1314. [3] 黄野. 胫骨高位截骨术治疗膝关节骨关节炎的现状[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2016,10(5):470-473. [4] VAN DEN BEMPT M, VAN GENECHTEN W, CLAES T, et al. How accurately does high tibial osteotomy correct the mechanical axis of an arthritic varus knee? A systematic review. Knee. 2016;23(6):925-935. [5] ABDULLAH KA, REED W. 3D printing in medical imaging and healthcare services. J Med Radiat Sci. 2018;65(3):237-239. [6] MARRO A, BANDUKWALA T, MAK W. Three-Dimensional Printing and Medical Imaging: A Review of the Methods and Applications. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2016;45(1):2-9. [7] VAN GENECHTEN W, VAN TILBORG W, VAN DEN BEMPT M, et al. Feasibility and 3D Planning of a Novel Patient-Specific Instrumentation Technique in Medial Opening-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(14):1560-1569. [8] MIAO Z, LI S, LUO D, et al. The validity and accuracy of 3D-printed patient-specific instruments for high tibial osteotomy: a cadaveric study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):62. [9] 马驰, 朴成哲. 3D打印个体化截骨导板辅助开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术的应用现状[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(3):360-364. [10] 潘建科, 赵第, 金晓, 等. 内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨与植入物相关的失误和并发症分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(36): 5849-5856. [11] 侯森荣, 潘建科, 杨伟毅, 等. 胫骨高位截骨术前临床评估及适应证的选择策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(28):4576-4583. [12] KELLGREN JH, LAWRENCE JS. Radiological assessment of osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957;16(4):494-502. [13] LIU GB, LIU S, ZHU CH, et al. A novel 3D-printed patient-specific instrument based on “H-point” for medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy: a cadaver study. J Orthop Surg Res, 2022,17(1):169. [14] 钟达, 齐军. 骨关节炎阶梯化治疗,方兴未艾![J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2021,31(23):1-5. [15] CERCIELLO S, OLLIVIER M, CORONA K, et al. CAS and PSI increase coronal alignment accuracy and reduce outliers when compared to traditional technique of medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022,30(2): 555-566. [16] 仲鹤鹤, 金瑛, 刘修齐, 等. 胫骨高位截骨联合关节镜手术治疗膝内翻骨关节炎的近期疗效及二次关节镜探查结果[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(8):969-975. [17] CHERNCHUJIT B, THARAKULPHAN S, PRASETIA R, et al. Preoperative planning of medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy using 3D computer-aided design weight-bearing simulated guidance: Technique and preliminary result. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019; 27(1):615491743. [18] 李小兵, 郭新军, 冯立平, 等. 3D打印辅助高位胫骨截骨治疗内侧室膝骨关节炎[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(21):1950-1954. [19] PREDESCU V, GROSU AM, GHERMAN I, et al. Early experience using patient-specific instrumentation in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Int Orthop. 2021;45(6):1509-1515. [20] MACLEOD AR, MANDALIA VI, MATHEWS JA, et al. Personalised 3D Printed high tibial osteotomy achieves a high level of accuracy: ‘IDEAL’ preclinical stage evaluation of a novel patient specific system. Med Eng Phys. 2022;108:103875. [21] ZAFFAGNINI S, DAL FABBRO G, LUCIDI GA, et al. Personalised opening wedge high tibial osteotomy with patient-specific plates and instrumentation accurately controls coronal correction and posterior slope: Results from a prospective first case series. Knee. 2023;44:89-99. [22] YANG JC, CHEN CF, LUO CA, et al. Clinical Experience Using a 3D-Printed Patient-Specific Instrument for Medial Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:9246529. [23] VICTOR J, PREMANATHAN A. Virtual 3D planning and patient specific surgical guides for osteotomies around the knee: a feasibility and proof-of-concept study. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(11 Suppl A):153-158. [24] JONES GG, JAERE M, CLARKE S, et al. 3D printing and high tibial osteotomy. EFORT Open Reviews. 2018;3(5):254-259. [25] JÖRGENS M, KEPPLER AM, AHRENS P, et al. 3D osteotomies—improved accuracy with patient-specific instruments (PSI). Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024;50(1):3-10. [26] SAVOV P, HOLD M, PETRI M, et al. CT based PSI blocks for osteotomies around the knee provide accurate results when intraoperative imaging is used. J Exp Orthop. 2021;8(1):47. [27] GAO F, YANG X, WANG C, et al. Comparison of Clinical and Radiological Outcomes between Calibratable Patient-Specific Instrumentation and Conventional Operation for Medial Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Biomed Res Int. 2022; 2022:1378042. [28] FUCENTESE SF, MEIER P, JUD L, et al. Accuracy of 3D-planned patient specific instrumentation in high tibial open wedge valgisation osteotomy. J Exp Orthop. 2020;7(1):7. [29] 朱超华, 李佳, 刘国彬, 等. 成人胫骨平台后内侧“H”点的应用解剖学研究[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2022,28(3):220-222. [30] KIM HJ, PARK J, SHIN JY, et al. More accurate correction can be obtained using a three-dimensional printed model in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(11): 3452-3458. [31] ZHU X, QIAN Y, LIU A, et al. Comparative outcomes of patient-specific instrumentation, the conventional method and navigation assistance in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy: A prospective comparative study with a two-year follow up. Knee. 2022;39:18-28. [32] MICICOI G, CORIN B, ARGENSON JN, et al. Patient specific instrumentation allow precise derotational correction of femoral and tibial torsional deformities. Knee. 2022;38:153-163. |
| [1] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [2] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [3] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [4] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [5] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Xu Ruian, Fang Lei, Li Longfei, Liu Shuyan, Ding Lingxue, Wang Yuexi, Guo Ziyan, Tian Feng, Xue Jiajia. Gradient artificial bone repair scaffold regulates skeletal system tissue repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 846-855. |
| [7] | Fang Ying, Zhang Yanwei, Li Xi, Yan Peidong, Bi Miao. Improvements in automatic diagnosis methods for knee osteoarthritis based on deep learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7511-7518. |
| [8] | Hu Chaoran, Cen Chaode, Yang Yang, Zhou Cheng, Huang Huaxian, Yuan Honghao, Luo Qin, Cao Yongfei. 3D printing assisted minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis versus intramedullary nail for treatment of AO12-C middle-proximal humeral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7116-7122. |
| [9] | Li Guoliang, Zhao Jianyong, Lyu Deliang, Su Juyue, Liu Qilin, Wang Tieqiang, Wang Xin. Improved 3D printed splint for distal radius fracture based on clinical defects: design and rapid grid-free analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7123-7129. |
| [10] | Wei Zhiheng, Guan Tianmin, Liu Qing, Gong Jue, Xiang Xianxiang. Application of 3D printing accurate osteotomy guide combined with the revision of anterior cruciate ligament with abnormally increased posterior slope of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7130-7136. |
| [11] | Liu Ning, Sun Yingjin, Huang Long, Feng Shuo, Chen Xiangyang. Optimal rotational alignment of the tibial component during Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7158-7164. |
| [12] | Liu Xiaowu, Liu Jinping, Wu Ting, He Xian, Cai Jianxiong. Antioxidants from different sources and osteoarthritis: a genome-wide association analysis in European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 7015-7027. |
| [13] | Zhuang Yan, Wang Xinyu, Cao Yilin, Ding Yuanxin, Wang Jiaqi, Yu Miao, Luan Chunyang, Ding Yuansheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of personalized orthodontic devices for 3D printed maxillary single-rooted rotated tooth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6409-6415. |
| [14] | Zhao Xiaoxuan, Liu Shuaiyi, Xing Zheng, Li Qingwen, Chu Xiaolei, Li Qi. Research hotspots and trends in application of tissue engineering in peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6591-6600. |
| [15] | Li Jia, Liu Qianru, Xing Mengnan, Chen Bo, Jiao Wei, Meng Zhaoxiang. A network meta-analysis on therapeutic effect of different types of exercise on knee osteoarthritis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 609-616. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||