Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (35): 7611-7619.doi: 10.12307/2026.522
Previous Articles Next Articles
Lipophagy, exercise intervention and prevention and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Ji Long1, Chen Ziyang1, 2, Jin Pan3, Kong Xiangkui1, Pu Rui1, 2
- 1College of Education and Sports Sciences, 2Human Science Laboratory of Exercise, 3Health Science Center, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-05Accepted:2025-01-25Online:2025-12-18Published:2025-05-07 -
Contact:Kong Xiangkui, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China Co-corresponding author: Pu Rui, Lecturer, Master’s supervisor, College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China; Human Science Laboratory of Exercise, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Ji Long, College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81860386 (to JP); 2022 Jingzhou Healthcare Science and Technology Program, No. 2022HC36 (to JP); 2024 Youth Project of Social Science Foundation of Yangtze University, No. 2024csq006 (to CZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ji Long, Chen Ziyang, , Jin Pan, Kong Xiangkui, Pu Rui, . Lipophagy, exercise intervention and prevention and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7611-7619.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
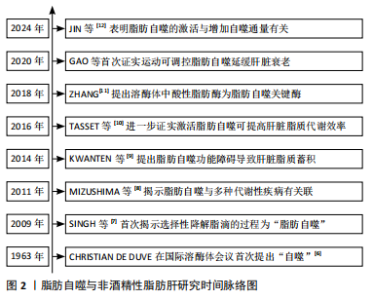
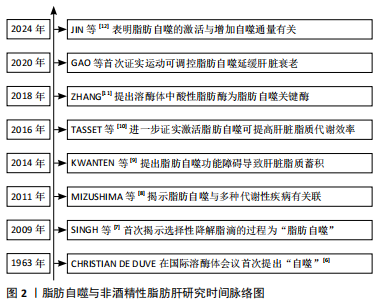
2.1 脂肪自噬概述 2.1.1 脂肪自噬的发现发展 1963年,比利时科学家Christian de Duve在溶酶体国际会议上首次提出细胞通过双层膜结构包裹细胞质和细胞器进行降解的过程为“自噬”[6]。早期关于自噬的研究主要集中在蛋白质和细胞器的降解。直到2009年,SINGH等[7]首次提出“脂肪自噬”的概念,揭示脂滴作为细胞内主要的脂质储存形式,可通过与自噬体融合并在溶酶体内降解为脂肪酸,从而维持肝脏脂质代谢稳态。2011年,MIZUSHIMa等[8]研究证实,脂肪自噬在多种代谢性疾病的防治中发挥作用,为后续研究脂肪自噬与非酒精性脂肪肝的关系提供了理论依据。KWANTEN等[9]在2014年提出脂肪自噬功能的障碍能直接导致肝脏脂质过度蓄积,从而加剧非酒精性脂肪肝的进程。2016年,TASSET等[10]的研究进一步证实激活脂肪自噬能够有效提高肝脏脂质代谢效率,从而更有力地证明了脂肪自噬在非酒精性脂肪肝防治中的作用。此外,ZHANG[11]发现溶酶体内的酸性脂肪酶作为脂肪自噬中的关键酶,对促进脂肪分解具有重要意义。最新研究表明,脂肪自噬的激活与增加自噬通量有关,进而通过降解脂滴减少肝脏脂质的病理性蓄积[12]。脂肪自噬与非酒精性脂肪肝研究时间脉络见图2。"
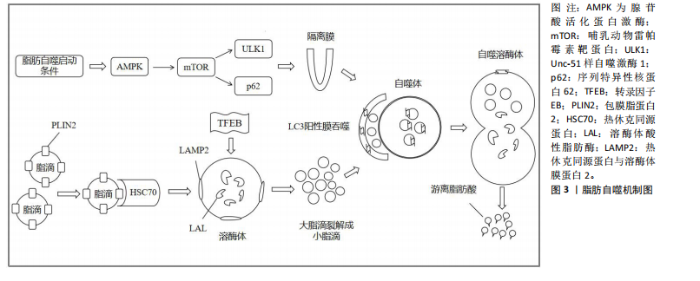
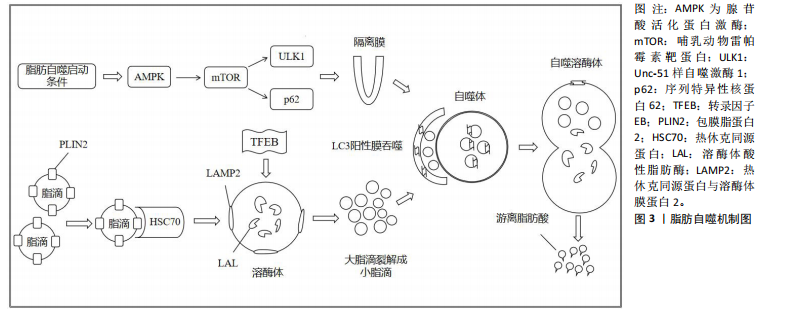
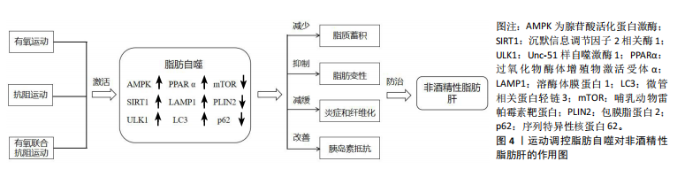
2.1.2 脂肪自噬的过程 自噬是细胞高度保守的自我降解过程,可分为巨自噬、微自噬和分子伴侣介导的自噬[13]。 脂肪自噬则是一种选择性自噬,在它启动条件下,腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)通过抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)的活性,进而上调Unc-51样自噬激酶1(Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase1,ULK1)并抑制序列特异性核蛋白62(又称p62)的表达,从而促进隔离膜逐渐闭合形成双层膜结构的自噬体[14]。此外,转录因子EB能够提高溶酶体生物合成并上调溶酶体功能,为激活脂肪自噬提供支持[15]。之后,热休克同源蛋白与溶酶体膜蛋白2协同降解包膜脂蛋白2,进而使大脂滴失去保护功能,并允许脂肪三酰甘油脂肪酶等进入启动脂肪分解过程[16-17]。经过这一过程,大脂滴被裂解成小脂滴,微管相关蛋白轻链3阳性膜吞噬小脂滴进入自噬体与溶酶体融合。最终在酸性脂肪酶的作用下,将小脂滴分解为游离脂肪酸释放到细胞质中再利用[18]。脂肪自噬机制图见图3。 2.2 脂肪自噬调控非酒精性脂肪肝的作用机制 近年来,非酒精性脂肪肝治疗领域中关于脂肪自噬调控的实证研究逐渐增多。AMPK、mTOR、转录因子EB、微管相关蛋白轻链3和p62等因子均参与脂肪自噬的调控对非酒精性脂肪肝形成与发展产生有益效应[19]。 2.2.1 AMPK与非酒精性脂肪肝 AMPK作为关键的能量感应激酶,能够调节脂肪自噬相关因子的表达提高脂质代谢效率,从而维持细胞代谢的稳态[20]。沉默信息调节因子2相关酶1(Sirtuin1,SIRT1)属于Sirtuin家族的成员,是一种烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸依赖的去乙酰化酶。新近研究表明,膳食类黄酮糖苷能够上调SIRT1表达并激活脂肪自噬,从而减缓肝脏脂质蓄积、脂肪变性及纤维化的进展[21]。CHYAU等[22]发现牛樟芝通过激活AMPK/SIRT1信号通路,可提高脂质代谢效率并降低肝脏脂肪含量。此外,LIU等[23] 研究发现,非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠在中药丹参干预后,可以激活体内AMPK/SIRT1信号通路并抑制丙氨酸氨基转移酶的表达,进而调控脂质代谢抑制脂肪蓄积和脂肪变性。另有研究表明,端粒重复结合因子2相互作用蛋白1能够通过AMPK/SIRT1信号通路激活脂肪自噬,从而减轻肝脏脂肪变性和炎症[24]。 与SIRT1同种族的沉默信息调节因子2相关酶3 (Sirtuin1,SIRT3)在脂肪自噬调控非酒精性脂肪肝中也发挥着重要作用。研究发现,SIRT3的过表达能够上调AMPK 激活脂肪自噬,从而减少肝脏的脂质蓄积[25]。ULK1是普遍存在于真核生物中的一类丝氨酸蛋白激酶,也是脂肪自噬的重要信号通路[26]。MASUDA等[27]发现萝卜硫素可通过激活AMPK并上调ULK1的表达,诱导脂肪细胞中脂肪自噬的发生,进而促进脂肪酸的释放。过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha,PPARα)能够与脂肪自噬相关因子的启动子结合调控脂肪自噬[28]。此外,对健康鸡胚以骨钙素干预可通过AMPK/PPARα途径激活脂肪自噬,从而调节脂质代谢并改善肝细胞中脂肪的堆积[29]。综上所述,AMPK介导的SIRT1、ULK1、PPARα信号通路能够调控脂肪自噬维持肝脏中脂质的代谢稳态,从而为防治非酒精性脂肪肝提供新的靶向治疗途径。 2.2.2 mTOR与非酒精性脂肪肝 mTOR是脂肪自噬重要的调控因子。DUAN等[30]研究发现,载脂蛋白J能够靶向调节mTOR酶体以恢复脂肪自噬和溶酶体活性,从而抑制肝脏脂质蓄积。黄兰蔚等[31]发现补气消脂方能够下调非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠体内酸肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路并激活自噬,进一步下调脂质代谢相关蛋白乙酰辅酶A羧化酶的表达,以抑制肝组织炎症损伤和脂质蓄积。雷帕霉素复合物1(Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1,mTORC1)是哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白的主要功能复合物。WU等[32]对非酒精性脂肪肝"
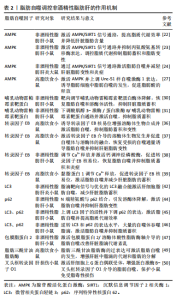
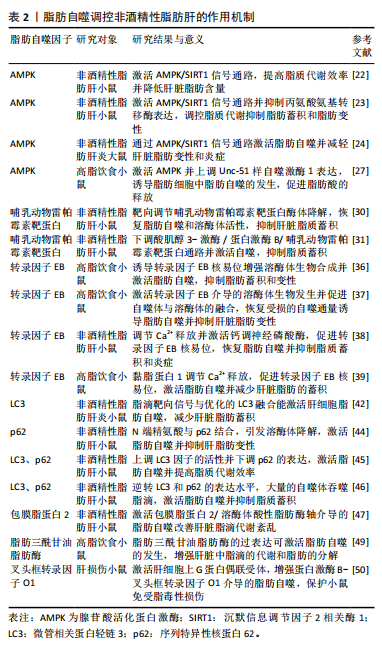
炎大鼠进行实验表明,四氢姜黄素可调节mTORC1/转录因子EB通路并恢复脂肪自噬,进而改善脂质蓄积和脂肪变性。另有研究发现,高脂饮食小鼠体内的mTORC1通过包被蛋白3磷酸化能够调节脂肪自噬,从而保护肝脏免受脂毒性损伤[33]。此外,LIU等[34]研究发现,肝脏脂毒性加重能够激活干扰素基因刺激因子1并上调mTORC1信号通路,以而抑制脂肪自噬的发生,进一步加重非酒精性脂肪肝患者的脂质蓄积。以上研究表明,mTOR表达能够调控脂肪自噬改善非酒精性脂肪肝,这可能为临床治疗非酒精性脂肪肝提供了一种候选策略。 2.2.3 转录因子EB与 非酒精性脂肪肝 转录因子EB作为自噬-溶酶体生物发生的主要调节因子,在脂肪自噬中也发挥着重要的调节作用[35]。ZHANG等[36]发现高脂饮食小鼠在筋骨草醇干预后,能诱导转录因子EB核易位增强溶酶体生物合成并激活脂肪自噬,从而抑制肝脏脂肪蓄积和变性。另有研究表明,柚皮苷可激活转录因子EB介导的溶酶体生物发生并促进自噬体与溶酶体的融合,进而恢复受损的自噬通量诱导脂肪自噬,从而抑制肝脏脂肪变性[37]。上述2项研究提示,转录因子EB核易位与介导的溶酶体生物合成在激活脂肪自噬中扮演着重要角色。ZHOU等[38]研究发现,对非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠进行连翘苷元干预能够调节内质网Ca2+释放,并激活钙调神经磷酸酶,从而促进转录因子EB核易位,进而增强自噬通量激活脂肪自噬抑制肝脏炎症。YOO等[39]也发现,非诺贝特可通过黏脂蛋白1调节溶酶体Ca2+释放,并提高钙调神经磷酸酶表达,从而促进转录因子EB核易位激活脂肪自噬减少肝脏脂肪的蓄积。以上2项研究表明,Ca2+释放和转录因子EB核易位与激活脂肪自噬紧密相关,这可能成为未来研究非酒精性脂肪肝治疗中的重要方向。此外,有研究探讨了转录因子EB与脂质代谢效率的相关性。SETTEMBRE等[40]研究发现,自噬在转录因子EB介导的脂质降解中发挥关键作用,高脂饮食小鼠转录因子EB的过表达可显著提高脂质代谢效率,而对照组小鼠则表现出脂质代谢紊乱,从而导致脂质蓄积和肥胖的发生。 2.2.4 微管相关蛋白轻链3、p62与非酒精性脂肪肝 p62是一种关键的衔接蛋白,可与自噬体中的微管相关蛋白轻链3相互作用,进而激活脂肪自噬并促进脂滴的降解[41]。 微管相关蛋白轻链3作为脂肪自噬的正向调节因子,在脂滴分解和防治非酒精性脂肪肝中发挥重要调控作用。研究表明,将脂滴靶向信号与优化的微管相关蛋白轻链3融合能够激活肝细胞脂肪自噬,从而显著减少肝脏脂肪蓄积、炎症和纤维化的进程[42]。由此提示,微管相关蛋白轻链3可靶向调控脂肪自噬对非酒精性脂肪肝产生影响。p62也是非酒精性脂肪肝等代谢疾病的关键调节因子,通过识别脂滴调节下游代谢信号通路对肝脏脂肪组织炎症起到抑制作用[43]。新进研究表明,N端精氨酸与脂滴相关蛋白p62结合可引发溶酶体降解,并将p62修饰为小分子激动剂激活脂肪自噬,以抑制肝脂肪变性[44]。由此提示,p62可能成为防治非酒精性脂肪肝等慢性代谢性疾病的有效因子。另有研究发现,非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠在利拉鲁肽干预后,肝细胞中脂滴能被自噬溶酶体吞噬和降解[45]。进一步研究表明,其机制与上调微管相关蛋白轻链3因子的活性并下调p62的表达,从而激活脂肪自噬并提高脂质代谢效率有关。相关研究结果也被ZHANG等[46]所证实,二甲双胍可逆转高脂饮食小鼠体内微管相关蛋白轻链3和p62的表达,并观察到大量的自噬体吞噬脂滴,以激活脂肪自噬抑制脂质蓄积。综上所述,肝脏脂质蓄积的减少与微管相关蛋白轻链3和p62表达水平变化所介导的脂肪自噬有关,可作为脂肪自噬的生物标记物,在非酒精性脂肪肝的预防中发挥潜在的应用价值。 2.2.5 其他因子与非酒精性脂肪肝 在脂肪自噬的激活和调控过程中,包膜脂蛋白2、脂肪三酰甘油脂肪酶和叉头框转录因子O1因子的表达也发挥着关键作用。研究表明,通过构建非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠运动模型,能够激活包膜脂蛋白2/溶酶体酸性脂肪酶轴介导的脂肪自噬改善肝脏脂滴代谢紊乱,并有效减少脂质蓄积[47]。脂肪三酰甘油脂肪酶可调控三酰甘油水解并维持肝细胞能量稳态,而激活脂肪三酰甘油脂肪酶/SIRT1信号通路能够调控脂肪自噬提高脂质代谢的效率[48]。SATHYANARAYAN等[49]发现,脂肪三酰甘油脂肪酶的过表达可激活脂肪自噬的活性,进而增强肝脏中脂滴的代谢和脂肪的分解。新进研究表明,肝细胞上G蛋白偶联受体的激活增强了蛋白激酶B-叉头框转录因子O1介导的脂肪自噬,从而保护小鼠免受脂毒性损伤[50]。上述研究提示,包膜脂蛋白2/溶酶体酸性脂肪酶、脂肪三酰甘油脂肪酶/SIRT1和蛋白激酶B-叉头框转录因子O1也是激活脂肪自噬的信号通路,这为研究脂肪自噬与非酒精性脂肪肝的防治提供了新的视角。脂肪自噬调控非酒精性脂肪肝的作用机制见表2。"
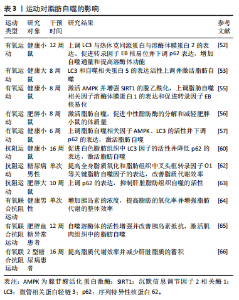
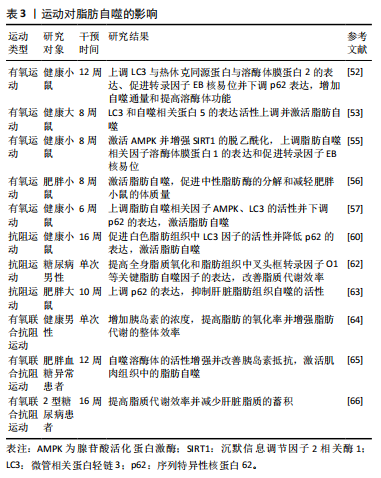
2.3 运动对脂肪自噬的影响 运动对脂肪自噬影响的研究仍处于起步阶段。研究表明,不同运动方式调控脂肪自噬的作用不同[51]。因而,此文就有氧运动、抗阻运动和有氧联合抗阻运动对调控脂肪自噬的研究进行归纳总结。 2.3.1 有氧运动对脂肪自噬的影响 有氧运动作为一种重要的运动方式,被认为可调控脂肪自噬防治慢性代谢性疾病。研究发现,为期12周的有氧运动可上调脂肪自噬相关因子微管相关蛋白轻链3与热休克同源蛋白与溶酶体膜蛋白2的表达、促进转录因子EB核易位并下调p62表达,从而增加自噬通量和提高溶酶体生物合成[52]。GUNADI等[53]研究表明,8周中等和高强度的有氧运动后,大鼠体内微管相关蛋白轻链3和自噬相关蛋白5的表达活性上调并激活脂肪自噬。溶酶体膜蛋白1是溶酶体膜的重要组成蛋白,能促进脂滴与溶酶体的融合并在脂肪自噬中发挥有益作用[54]。HUANG等[55]研究发现,有氧运动通过激活AMPK并增强SIRT1的脱乙酰化,可以上调脂肪自噬和溶酶体相关因子溶酶体膜蛋白1的表达及促进转录因子EB核易位。另有研究发现,有氧运动能够激活脂肪自噬,从而促进中性脂肪酶的分解和减轻肥胖小鼠的体质量[56]。此外,李梦影等[57]研究表明,健康小鼠在低氧环境下进行为期6周的有氧运动也能够上调脂肪自噬相关因子AMPK、微管相关蛋白轻链3的活性并下调p62的表达,进而激活脂肪自噬。 上述研究提示,有氧运动能够调节脂肪自噬相关因子的表达、增强自噬通量、提高溶酶体生物合成和促进脂肪酶的分解对调控脂肪自噬产生影响。但不同有氧运动形式对脂肪自噬的调控也存在差异,这可能与运动时间、强度及实验对象的选取有关。 2.3.2 抗阻运动对脂肪自噬的影响 抗阻运动指人体通过骨骼肌短时间内进行一次或者多次高速收缩活动来对抗自身或外部阻力的运动方式[58]。有研究表明,脂肪自噬的衍生物脂肪酸能够增强mTORC1通路的表达抑制肌肉萎缩,从而促进肌肉质量和力量的增加[59]。TAMARGO-GóMEZ等[60]通过构建动物模型发现,抗阻运动可促进白色脂肪组织中微管相关蛋白轻链3因子的活性并降低p62的表达,进而激活脂肪组织自噬。另有研究发现,为期6周的抗阻运动也能够调控脂肪组织中脂滴相关因子的表达并提高脂质代谢效率[61]。此外,BITTEL等[62]发现患有糖尿病前期肥胖男性餐后进行单次阻力运动,不仅提高全身脂质氧化水平,还上调脂肪组织中叉头框转录因子O1等关键脂肪自噬因子的表达。但有研究得出不同结果,冯燕[63]发现为期10周的抗阻运动后,高脂饮食大鼠体内p62的表达显著上调并抑制了肝脏脂肪组织自噬的活性;进一步研究发现,运动干预组相比于对照组大鼠体内炎症因子表达有显著上升趋势,提示抗阻运动后大鼠肝脏炎症增加。目前有关抗阻运动在脂肪自噬中的具体调控机制及途径尚未阐明且相关研究较少,仍需进一步深入探讨和验证。 2.3.3 有氧联合抗阻运动对脂肪自噬的影响 有氧联合抗阻运动弥补了有氧运动强度低及抗阻运动时效短的困扰。早在先前的研究中,GOTO等[64]对10名健康男性进行短时间有氧联合抗阻运动干预,发现抗阻运动能够上调健康男性体内的胰岛素浓度,进而提高有氧运动中脂肪的氧化率及增强了脂肪代谢的整体效率。这一研究提示,有氧联合抗阻运动对脂肪代谢具有调控作用,为后期研究脂肪自噬机制提供了实验依据。另有研究发现,为期12周的有氧联合抗阻运动后,肥胖血糖异常患者脂肪细胞中自噬溶酶体的活性增强并改善了胰岛素抵抗,从而激活肌肉组织中的脂肪自噬[65]。最新研究表明,有氧联合抗阻运动能够提高2型糖尿病患者的脂质代谢效率以减少肝脏脂质的蓄积[66]。但目前关于其他运动方式对脂肪自噬影响的研究尚少,未来若对其他运动方式进行深入研究可为运动干预在促进机体健康方面提供更科学的依据,并为脂肪自噬在健康促进中的潜在作用提供新的见解。运动对脂肪自噬的影响见表3。"
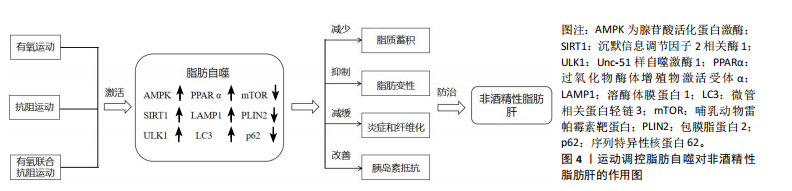
2.4 运动对非酒精性脂肪肝的影响 先前的研究证明,定期的身体锻炼能够有效控制非酒精性脂肪肝的病理进程,经常性运动被认为是目前防治非酒精性脂肪肝等相关肝脏病理学的非药物方法之一。因而,此文就不同运动方式对非酒精性脂肪肝的影响进行归纳总结。 2.4.1 有氧运动对非酒精性脂肪肝的影响 有氧运动能够通过改善肝脏炎症以及提升肝脏功能治疗非酒精性脂肪肝。研究表明,非酒精性脂肪肝患者进行有氧运动可有效改善胰岛素抵抗和提升肝脏功能[67]。BARI 等[68]发现男性运动员进行为期12周的有氧运动能够改善肝脏功能,从而有效保护肝细胞免受炎症或损伤。此外,有氧运动8周后,女大学生非酒精性脂肪肝患者脂质代谢效率提高并显著减少内脏脂肪的蓄积[69]。上述研究表明,有氧运动对防治非酒精性脂肪肝具有显著效果,可作为常规运动疗法的一种有效选择。另有研究发现,对肥胖小鼠进行有氧运动并补充维生素E干预能够激活AMPK信号通路改善乙酰辅酶A羧化酶磷酸化并减少脂肪酸合成,以减轻肝脏炎症反应和脂肪变性[70]。新进研究表明,中药活性成分姜黄素、枸杞多糖联合有氧运动也能够改善肝脏炎症和功能,从而达到治疗非酒精性脂肪肝的效果[71-72]。由此可见,有氧运动联合维生素E、姜黄素和枸杞多糖对防治非酒精性脂肪肝具有积极作用。 2.4.2 抗阻运动对非酒精性脂肪肝的影响 抗阻运动作为运动的常见形式之一,在防治非酒精性脂肪肝也发挥着有益效应。研究表明,为期8周的抗阻运动后,非酒精性脂肪肝患者肝脏脂肪变性减缓并有效提升了肝脏功能[73]。 李军汉等[74]对2型糖尿病脂肪肝大鼠进行抗阻运动,发现大鼠肝脏内质网应激水平降低,进而有效延缓脂肪肝的发生发展。此外,付洋洋等[75]发现37例非酒精性脂肪肝患者进行16周的抗阻运动能够显著减少肝脏脂肪蓄积。新近研究发现,为期12周的抗阻运动能够提高非酒精性脂肪肝患者肝脏中胆固醇和三酰甘油的转运,从而减少肝脏脂肪蓄积和改善胰岛素抵抗[76]。以上研究表明,抗阻运动也能提升肝脏功能和改善胰岛素抵抗,为不适宜进行有氧运动的人群提供了另一种运动疗法,在防治非酒精性脂肪肝展现出独特的优势。 2.4.3 有氧联合抗阻运动对非酒精性脂肪肝的影响 越来越多的研究证实,有氧联合抗阻运动对延缓非酒精性脂肪肝病理进展也具有重要意义[77]。研究表明,为期16周的有氧联合抗阻运动干预后,非酒精性脂肪肝患者肝脏中脂肪含量显著降低[78]。HUANG等[79]研究发现,为期12周的有氧联合抗阻运动干预能够显著改善非酒精性脂肪肝患者的胰岛素抵抗和提高脂质代谢效率,进而减少肝脏脂肪的蓄积。动物研究表明,有氧联合抗阻运动可上调非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠体内PPARα和SIRT1因子表达,从而改善胰岛素抵抗并降低血清谷丙转氨酶水平[80]。上述研究提示,有氧联合抗阻运动通过改善胰岛素抵抗和调节相关因子的表达参与非酒精性脂肪肝的防治。 2.5 运动调控脂肪自噬对非酒精性脂肪肝的作用 脂肪自噬与非酒精性脂肪肝密切相关,且合理的运动可作为非药物干预手段调控脂肪自噬。因此,以运动干预调控脂肪自噬减少脂质蓄积、抑制脂肪变性、减缓肝脏炎症和纤维化及改善胰岛素抵抗等途径在防治非酒精性脂肪肝中具有重要意义。 2.5.1 运动调控脂肪自噬减少脂质蓄积 脂质的过度蓄积是非酒精性脂肪肝病情进展的重要因素。Zou等[81]研究发现,高脂饲养的斑马鱼进行为期12周游泳运动可激活AMPK/SIRT1信号通路调控脂肪自噬减少肝脏脂质蓄积。GAO等[82]在一项脂细胞代谢实验中发现,饮食结合8周有氧运动能够激活AMPK/ULK1并抑制酸肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路调控脂肪自噬,从而显著降低肝脏中脂质的蓄积。同时,实验也首次证明了脂质蓄积会加剧肝脏衰老,而运动可以诱导脂肪自噬延缓肝脏衰老。上述实验研究提示,有氧运动可调控脂肪自噬减少脂质蓄积,为进一步研究运动调控脂肪自噬防治非酒精性脂肪肝提供了实验支持。赵永军等[83]发现,抗阻运动能够显著上调微管相关蛋白轻链3因子的活性并下调p62的表达,进而提高肝脏脂质代谢效率并减少脂质的蓄积。此外,在一项关于对高脂饮食小鼠限时喂养的研究中表明,为期16周的抗阻运动后,小鼠的脂质代谢紊乱得到显著改善并减少了肝脏中脂质的蓄积[84]。以上2项研究表明,抗阻运动在调控脂肪自噬减少脂质蓄积中也发挥重要作用。 2.5.2 运动调控脂肪自噬抑制脂肪变性 当肝脏内脂质过度蓄积并伴随炎症反应时,易诱发脂肪变性,抑制这一过程可有效延缓非酒精性脂肪肝的病理进程。研究发现,为期12周的游泳运动能够抑制肝脏脂肪变性[85]。此过程可能与下调脂肪酸结合蛋白1的表达并恢复溶酶体功能和自噬通量有关。此外,肝脏在脂毒性损伤下更易诱发脂肪变性。WU等[86]研究表明,高强度间歇运动可激活AMPK并促进转录因子EB核易位,进而增加自噬通量和提高自噬溶酶体活性改善脂质代谢紊乱,从而抑制肝脏脂毒性损伤引发的脂肪变性。由此可见,运动能够增强自噬通量调控脂肪自噬抑制肝脏脂肪变性。随着研究的进一步深入,中药联合运动调控脂肪自噬也取得突破性的进展。CAO等[87]研究发现,茶籽皂苷联合4周运动干预后,肥胖小鼠体内AMPK/SIRT1信号通路被激活,从而提高脂质代谢的效率并显著抑制肝脏脂肪变性。目前关于运动联合中药调控脂肪自噬的研究尚处于初步阶段,且大多集中于动物实验模型。未来若对此领域进行积极探索,或可为非酒精性脂肪肝的治疗提供新的干预措施。 2.5.3 运动调控脂肪自噬减轻肝脏炎症和纤维化 肝脏炎症和纤维化加重是非酒精性脂肪肝病情发展的重要病理特征。因此,抑制肝脏炎症和纤维化进程是改善非酒精性脂肪肝的重要方式。研究证明,肝脏炎症和纤维化的改善与脂质代谢的发生密切相关[88]。进一步发现,运动可调控脂肪自噬有效减轻肝脏炎症和纤维化,从而对非酒精性脂肪肝的病理演变产生积极作用[89]。WANG等[90]发现慢性有氧运动能够下调非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠体内p62和肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素10的表达,促进肝自噬的流入并改善脂质代谢水平,进而减轻肝脏炎症和纤维化进程。另有研究发现,有氧运动能够激活AMPK/PPARα途径抑制瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6等炎症因子的表达缓解肝脏炎症反应[91]。以上2项研究表明,运动能够调控脂肪自噬下调炎症因子的表达减轻肝脏炎症和纤维化。YANG等[92]研究发现,为期15周的跑步机运动可下调p62、包膜脂蛋白2的表达,激活脂肪自噬,减轻肝脏炎症及小叶气球样变;进一步研究发现,运动促进了非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠体内溶酶体膜蛋白1与脂滴的共定位,有效抑制了异常脂滴的蓄积。此外,肝脏是脂肪代谢的主要场所,抑制脂肪组织炎症有利于肝脏代谢稳态和脂肪自噬的激活。MARDARE等[93]发现高脂饮食小鼠进行抗阻运动能够下调脂肪组织中炎症因子的表达,进而减少脂肪组织炎症反应。上述研究表明,运动干预可靶向调控脂肪自噬减轻肝脏炎症,以延缓非酒精性脂肪肝的发生发展。 2.5.4 运动调控脂肪自噬改善胰岛素抵抗 胰岛素抵抗是非酒精性脂肪肝的重要病理特征之一,改善胰岛素抵抗是调控非酒精性脂肪肝的重要标志[94]。脂肪自噬失调会引起肝脏内质网应激并诱发机体胰岛素抵抗,而运动可调节脂肪自噬相关因子的表达改善胰岛素抵抗[95-96]。LI等[97]研究发现,游泳运动通过激活AMPK/SIRT1信号通路促进溶酶体膜蛋白1与脂滴的共定位,进而调控脂肪自噬改善肝脏脂滴代谢紊乱和胰岛素抵抗。另有研究表明,为期8周的有氧运动干预能够上调AMPK磷酸化和PPARα蛋白的表达并激活脂肪自噬,从而改善肥胖小鼠的胰岛素抵抗[91]。上述研究提示,运动干预能够激活不同信号通路调控脂肪自噬改善胰岛素抵抗,以达到防治非酒精性脂肪肝的目的。此外,最新研究探讨了胰岛素抵抗与脂质代谢效率之间的关系。SUDER等[98]发现对肥胖男性进行有氧联合抗阻运动结合饮食可显著降低脂肪因子的表达并提高脂质代谢效率,从而改善胰岛素抵抗。运动调控脂肪自噬对非酒精性脂肪肝的作用见图4。"
| [1] LUDWIG J, VIGGIANO TR, MCGILL DB, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis:Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980;55(7): 434-438. [2] POUWELS S, SAKRAN N, GRAHAM Y, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD):a review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022;14;22(1):63. [3] MASHEK DG. Hepatic lipid droplets:A balancing act between energy storage and metabolic dysfunction in NAFLD. Mol Metab. 2021;50:101-115. [4] SHIN DW. Lipophagy:Molecular Mechanisms and Implications in Metabolic Disorders. Mol Cells. 2020;43(8):686-693. [5] CHUN SK, LEE S, Yang MJ, et al. Exercise-Induced Autophagy in Fatty Liver Disease. Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews. 2017;45:181-186. [6] KLIONSKY DJ. Autophagy:From phenomenology to molecularunderstanding in less than a decade. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(11):931-937. [7] SINGH R, KAUSHIK S, WANG Y, et al. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature. 2009;458(7242):1131-5. [8] MIZUSHIMA N, KOMATSU M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 2011;147(4):728-741. [9] KWANTEN WJ, MARTINET W, MICHIELSEN PP, et al. Role of autophagy in the pathophysiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a controversial issue. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(23):7325-7338. [10] TASSET I, CUERVO AM. Role of chaperone-mediated autophagy in metabolism. FEBS J. 2016;283(13):2403-2413. [11] ZHANG H. Lysosomal acid lipase and lipid metabolism: new mechanisms, new questions, and new therapies. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2018;29(3):218-223. [12] JIN S, LI Y, XIA T, et al. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of selective autophagy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Adv Res. 2025;67:317-329. [13] GLICK D, BARTH S, MACLEOD KF. Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 2010;221(1): 3-12. [14] WIRTH M, JOACHIM J, TOOZE SA. Autophagosome formation--the role of ULK1 and Beclin1-PI3KC3 complexes in setting the stage. Semin Cancer Biol. 2013;23(5):301-309. [15] TAKLA M, KESHRI S, Rubinsztein DC. The post-translational regulation of transcription factor EB (TFEB) in health and disease. EMBO Rep. 2023;24(11): e57574. [16] KAUSHIK S, CUERVO AM. Degradation of lipid droplet-associated proteins by chaperone-mediated autophagy facilitates lipolysis. Nature Celll Biol. 2015;17(6): 759-770. [17] IKAMI Y, TERASAWA K, SAKAMOTO K, et al. The two-domain architecture of LAMP2A regulates its interaction with Hsc70. Exp Cell Res. 2022;411(1):112986. [18] ZHANG S, PENG X, YANG S, et al. The regulation, function, and role of lipophagy, a form of selective autophagy, in metabolic disorders. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(2):132. [19] FILALI-MOUNCEF Y, HUNTER C, ROCCIO F, et al. The ménage à trois of autophagy, lipid droplets and liver disease. Autophagy. 2022;18(1):50-72. [20] GE Y, ZHOU M, CHEN C, et al. Role of AMPK mediated pathways in autophagy and aging. Biochimie. 2022;195:100-113. [21] YANG JW, ZOU Y, CHEN J, et al. Didymin alleviates metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) via the stimulation of Sirt1-mediated lipophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):921. [22] CHYAU CC, WANG HF, ZHANG WJ, et al. Antrodan Alleviates High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Induced Fatty Liver Disease in C57BL/6 Mice Model via AMPK/Sirt1/SREBP-1c/PPARγ Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;6;21(1):360. [23] LIU Y, LI Y, WANG J, et al. Salvia-Nelumbinis naturalis improves lipid metabolism of NAFLD by regulating the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022;22(1): 213. [24] WANG Y, LIU S, NI M, et al. Terf2ip deficiency accelerates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis through regulating lipophagy and fatty acid oxidation via Sirt1/AMPK pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024;220:78-91. [25] ZHANG T, LIU J, SHEN S, et al. SIRT3 promotes lipophagy and chaperon-mediated autophagy to protect hepatocytes against lipotoxicity. Cell Death Differ. 2020; 27(1):329-344. [26] NGUYEN TTP, KIM DY, IM SS, et al. Impairment of ULK1 sulfhydration-mediated lipophagy by SREBF1/SREBP-1c in hepatic steatosis. Autophagy. 2021;17(12): 4489-4490. [27] MASUDA M, YOSHIDA-SHIMIZU R, MORI Y, et al. Sulforaphane induces lipophagy through the activation of AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 pathway signaling in adipocytes. J Nutr Biochem. 2022;106:109017 [28] LEE JM, WAGNER M, XIAO R, et al. Nutrient-sensing nuclear receptors coordinate autophagy. Nature. 2014;516(7529):112-115. [29] TU WJ, ZHANG YH, WANG XT, et al. Osteocalcin activates lipophagy via the ADPN-AMPK/PPARα-mTOR signaling pathway in chicken embryonic hepatocyte. Poult Sci. 2024;103(2):103293. [30] DUAN S, QIN N, PI J, et al. Antagonizing apolipoprotein J chaperone promotes proteasomaldegradation of mTOR and relieves hepatic lipid deposition. Hepatology. 2023;78(4):1182-1199. [31] 黄兰蔚,王瑞华,王宇,等. 补气消脂方调控 PI3K/AKT/mTOR 通路改善自噬减轻小鼠非酒精性脂肪肝机制研究[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2025,45(3): 241-246. [32] WU J, GUAN F, HUANG H, et al. Tetrahydrocurcumin ameliorates hepatic steatosis by restoring hepatocytes lipophagy through mTORC1-TFEB pathway in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;178:117297. [33] GARCIA-MACIA M, SANTOS-LEDO A, LESLIE J, et al. A Mammalian Target of Rapamycin-Perilipin 3 (mTORC1-Plin3) Pathway is essential to Activate Lipophagy and Protects Against Hepatosteatosis. Hepatology. 2021;74(6):3441-3459. [34] LIU K, QIU D, LIANG X, et al. Lipotoxicity-induced STING1 activation stimulates MTORC1 and restricts hepatic lipophagy. Autophagy. 2022;18(4):860-876. [35] TAN A, PRASAD R, LEE C, et al. Past, present, and future perspectives of transcription factor EB (TFEB): mechanisms of regulation and association with disease. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(8):1433-1449. [36] ZHANG H, LU J, LIU H, et al. Ajugol enhances TFEB-mediated lysosome biogenesis and lipophagy to alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Pharmacol Res. 2021; 174:105964. [37] GUAN L, GUO L, ZHANG H, et al. Naringin Protects against Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Promoting Autophagic Flux and Lipophagy. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024;68(3):e2200812. [38] ZHOU W, YAN X, ZHAI Y, et al. Phillygenin ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via TFEB-mediated lysosome biogenesis and lipophagy. Phytomedicine. 2022;103:154235. [39] YOO J, JEONG IK, AHN KJ, et al. Fenofibrate, a PPARα agonist, reduces hepatic fat accumulation through the upregulation of TFEB-mediated lipophagy. Metabolism. 2021;120:154798. [40] SETTEMBRE C, DE CEGLI R, MANSUETO G, et al. TFEB controls cellular lipid metabolism through a starvation-induced autoregulatory loop. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(6):647-658. [41] ALCOBER-BOQUET L, ZANG T, PIETSCH L, et al. The PB1 and the ZZ domain of the autophagy receptor p62/SQSTM1 regulate the interaction of p62/SQSTM1 with the autophagosome protein LC3B. Protein Sci. 2024;33(1):e4840. [42] MINAMI Y, HOSHINO A, HIGUCHI Y, et al. Liver lipophagy ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through extracellular lipid secretion. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):4084. [43] LONG M, LI X, LI L, et al. Multifunctional p62 Effects Underlie Diverse Metabolic Diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017;28(11):818-830. [44] JUNG EJ, SUNG KW, BAE TH, et al. The N-degron pathway mediates lipophagy: The chemical modulation of lipophagy in obesity and NAFLD. Metabolism. 2023;146:155644. [45] FANG Y, JI L, ZHU C, et al. Liraglutide Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis by Activating the TFEB-Regulated Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8: 602574. [46] ZHANG D, MA Y, LIU J, et al. Metformin Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance in a Mouse Model of High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Promoting Transcription Factor EB-Dependent Autophagy. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:689111. [47] FANG C, LIU S, YANG W, et al. Exercise ameliorates lipid droplet metabolism disorder by the PLIN2-LIPA axis-mediated lipophagy in mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024; 1870(3):167045. [48] ZHANG G, HAN J, WANG L, et al. The vesicular transporter TX11 governs ATGL-Smediated hepatic lipolysis and lipophagy. iScience. 2022;25(4):104085. [49] SATHYANARAYAN A, MASHEK MT, MASHEK DG. ATGL Promotes Autophagy /Lipophagy via SIRT1 to Control Hepatic Lipid Droplet Catabolism. Cell Rep. 2017; 19(1):1-9. [50] CHEN S, LU Z, JIA H, et al. Hepatocyte-specific Mas activation enhances lipophagy and fatty acid oxidation to protect against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J Hepatol. 2023;78(3):543-557. [51] SU P, CHEN JG, TANG DH. Exercise against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Possible role and mechanism of lipophagy. Life Sci. 2023;327:121837. [52] JIAN Y, YUAN S, YANG J, et al. Aerobic Exercise Alleviates Abnormal Autophagy in Brain Cells of APP/PS1 Mice by Upregulating AdipoR1 Levels. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(17):9921. [53] GUNADI JW, TARAWAN VM, DANIEL RAY HR, et al. Different training intensities induced autophagy and histopathology appearances potentially associated with lipid metabolism in wistar rat liver. Heliyon. 2020;6(5):e03874. [54] BYRNES K, BLESSINGER S, BAILEY NT, et al. Therapeutic regulation of autophagy in hepatic metabolism. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12(1):33-49. [55] HUANG J, WANG X, ZHU Y, et al. Exercise activates lysosomal function in the brain through AMPK-SIRT1-TFEB pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019;25(6):796-807. [56] LI R, LI G, HAI Y, et al. The effect of aerobic exercise on the lipophagy of adipose tissue in obese male mice. Chem Phys Lipids. 2022;247:105225. [57] 李梦影,李灵杰,马春伟,等. 不同低氧训练模式通过激活小鼠脂肪组织脂噬作用调节脂代谢[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2022,41(11):866-874. [58] 运动处方中国专家共识(2023)[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2023,42(1):3-13. [59] THERDYOTHIN A, PHIPHOPTHATSANEE N, ISANEJAD M. The Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Sarcopenia: Mechanism of Action and Potential Efficacy. Mar Drugs. 2023;13;21(7):399. [60] TAMARGO-GÓMEZ I, FERNÁNDEZ-SANJURJO M, CODINA-MARTÍNEZ H, et al. Autophagy Alterations in White and Brown Adipose Tissues of Mice Exercised under Different Training Protocols. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024;29(10):348. [61] SHAHANDEH F, FATHI R,NASIRI K. Spirulina supplement and exercise training affect lipid droplets-related genes expression in visceral adipose tissue.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2024;14(1):100-111. [62] BITTEL AJ, BITTEL DC, MITTENDORFER B, et al. A single bout of resistance exercise improves postprandial lipid metabolism in overweight/obese men with prediabetes. Diabetologia. 2020;63(3):611-623. [63] 冯燕. 抗阻运动对高脂饮食诱导的肥胖大鼠脂肪组织自噬和炎症因子的影响[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(2):867-873. [64] GOTO K, ISHII N, SUGIHARA S, et al. Effects of resistance exercise on lipolysis during subsequent submaximal exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(2):308-315. [65] LI Y, LEE S, LANGLEITE T, et al. Subsarcolemmal lipid droplet responses to a combined endurance and strength exercise intervention. Physiol Rep. 2014; 2(11):e12187. [66] DUFT RG, BONFANTE ILP, PALMA-DURAN SA, et al. Moderate-intensity Combined Training Induces Lipidomic Changes in Individuals With Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024;109(9):2182-2198. [67] MOHAMMAD RAHIMI GR, ATTARZADEH HOSSEINI SR. Effect of Aerobic Exercise Alone or in Conjunction With Diet on Liver Function, Insulin Resistance and Lipids in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biol Res Nurs. 2022;24(2):259-276. [68] BARI MA, MAHMOODALOBAIDI MA, ANSARI HA, et al. Effects of an aerobic training program on liver functions in male athletes: a randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):9427. [69] 王鹏,刘宝亮,刘岩,等. 运动结合饮食干预对肥胖非酒精性脂肪肝女大学生身体成分和脂代谢及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中国学校卫生,2023,44(8):1169-1173. [70] BAI Y, LI T, LIU J, et al. Aerobic exercise and vitamin E improve high-fat diet-induced NAFLD in rats by regulating the AMPK pathway and oxidative stress. Eur J Nutr. 2023;62(6):2621-2632. [71] 胡戈, 秦菲, 曹建民,等. 姜黄素复合有氧运动对非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠肝功能的改善作用[J/OL]. 食品科学, https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2206.ts.20240821.1403.03. [72] 马佳敏,高璐璐,张梦伟,等. 枸杞多糖联合有氧运动对非酒精性脂肪肝炎大鼠模型的改善作用及其机制研究[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2021,37(6):1348-1353. [73] JAFARIKHAH R, DAMIRCHI A, RAHMANI NIA F, et al. Effect of functional resistance training on the structure and function of the heart and liver in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):15475. [74] 李军汉,高德润,江玲玲,等. 有氧和抗阻运动对糖尿病脂肪肝大鼠肝脏内质网应激的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2021,36(1):23-31. [75] 付洋洋,孟美美,荣宁,等. 有氧运动与抗阻运动对非酒精性脂肪肝患者影响效果研究[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2018,38(4):528-531. [76] ZELBER-SAGI S, BUCH A, YESHUA H, et al. Effect of resistance training on non-alcoholic fatty-liver disease a randomized-clinical trial. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20: 4382. [77] XUE Y, PENG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Effect of different exercise modalities on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1): 6212. [78] SHOJAEE-MORADIE F, CUTHBERTSON DJ, BARRETT M, et al. Exercise Training Reduces Liver Fat and Increases Rates of VLDL Clearance But Not VLDL Production in NAFLD. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(11):4219-4228. [79] HUANG W, RUAN W, HUO C, et al. The effect of 12 weeks of combined training on hepatic fat content and metabolic flexibility of individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Protocol of an open-label, single-center randomized control trial. Front Nutr. 2023;9:1065188. [80] NIKROO H, HOSSEINI SRA, FATHI M, et al. The effect of aerobic, resistance, and combined training on PPAR-α, SIRT1 gene expression, and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced NAFLD male rats. Physiol Behav. 2020;227:113149. [81] ZOU Y, CHEN Z, SUN C, et al. Exercise Intervention Mitigates Pathological Liver Changes in NAFLD Zebrafish by Activating SIRT1/AMPK/NRF2 Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;10;22(20):10940. [82] GAO Y, ZHANG W, ZENG LQ, et al. Exercise and dietary intervention ameliorate high-fat diet-induced NAFLD and liver aging by inducing lipophagy. Redox Biol. 2020;36:101635. [83] 赵永军,胡海光,王晶,等. 抗阻、耐力运动对肥胖小鼠肝脏自噬相关蛋白表达的影响[J]. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2023,44(6):126-133. [84] DAMASCENO DE LIMA R, FUDOLI LINS VIEIRA R, ROSETTO MUÑOZ V, et al. Time-restricted feeding combined with resistance exercise prevents obesity and improves lipid metabolism in the liver of mice fed a high-fat diet. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2023;325(5):E513-E528. [85] PI H, LIU M, XI Y, et al. Long-term exercise prevents hepatic steatosis: a novel role of FABP 1 in regulation of autophagy-lysosomal machinery. FASEB J. 2019; 33(11):11870-11883. [86] WU W, JIAN Y, YUAN S, et al. Exercise-promoted adiponectin secretion activates autolysosomes to protect the liver of ApoE(-/-) mice from a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2024;15(19):9796-9812. [87] CAO W, WANG K, LIANG C, et al. Dietary tea seed saponin combined with aerobic exercise attenuated lipid metabolism and oxidative stress in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD). J Food Biochem. 2022;46(12):e14461. [88] HORN P, TACKE F. Metabolic reprogramming in liver fibrosis. Cell Metab. 2024; 36(7):1439-1455. [89] LI X, YANG Y, SUN Y, et al. Research Progress on Lipophagy-Mediated Exercise Intervention in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;9;25(6):3153. [90] WANG B, ZENG J, GU Q. Exercise restores bioavailability of hydrogen sulfide and promotes autophagy influx in livers of mice fed with high-fat diet. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017;95(6):667-674. [91] DINIZ TA, DE LIMA JUNIOR EA, TEIXEIRA AA, et al. Aerobic training improves NAFLD markers and insulin resistance through AMPK-PPAR-α signaling in obese mice. Life Sci. 2021;266:118868. [92] YANG Y, LI X, LIU Z, et al. Moderate Treadmill Exercise Alleviates NAFLD by Regulating the Biogenesis and Autophagy of Lipid Droplet. Nutrients. 2022; 14(22):4910. [93] MARDARE C, KRÜGER K, LIEBISCH G, et al. Endurance and Resistance Training Affect High Fat Diet-Induced Increase of Ceramides, Inflammasome Expression, and Systemic Inflammation in Mice. J Food Biochem. 2015;2016:4536470. [94] GRANDER C, GRABHERR F, TILG H. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: pathophysiological concepts and treatment options. Cardiovasc Res. 2023;119(9):1787-1798. [95] CANG X, WANG Y, ZENG J, et al. C9orf72 knockdown alleviates hepatic insulin resistance by promoting lipophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;588:15-22. [96] ANGULO J, EL ASSAR M, ÁLVAREZ-BUSTOS A, et al. Physical activity and exercise: Strategies to manage frailty. Redox Biol. 2020;35:101513. [97] LI H, DUN Y, ZHANG W, et al. Exercise improves lipid droplet metabolism disorder through activation of AMPK-mediated lipophagy in NAFLD. Life Sci. 2021;273: 119314. [98] SUDER A, MAKIEL K, TARGOSZ A, et al. Effects of exercise and dietary interventions on asprosin, leptin, and lipid metabolism in males with abdominal obesity, a randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):28109. |
| [1] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [4] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [5] | Zhang Zixian, Xu Youliang, Wu Shaokui, Wang Xiangying. Effects of blood flow restriction training combined with resistance training on muscle indicators in college athletes: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1705-1713. |
| [6] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [7] | Zhao Nannan, Li Yanjie, Qin Hewei, Zhu Bochao, Ding Huimin, Xu Zhenhua. Changes in ferroptosis in hippocampal neurons of vascular dementia model rats treated with Tongmai Kaiqiao Pill [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1401-1407. |
| [8] | Zhang Mingyang, Yang Xinling. Verbascoside inhibits Erastin-induced ferroptosis of dopaminergic nerve cell line MN9D cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1408-1413. |
| [9] | De Ji, Suo Langda, Wei Yuchen, Wang Bin, Awangcuoji, Renqingcuomu, Cui Jiuzeng, Zhang Lei, Ba Gui. Comprehensive analysis of genes related to endometrial receptivity and alternative splicing events in northwest Tibetan cashmere goats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1429-1436. |
| [10] | Peng Hongcheng, Peng Guoxuan, Lei Anyi, Lin Yuan, Sun Hong, Ning Xu, Shang Xianwen, Deng Jin, Huang Mingzhi . Role and mechanism of platelet-derived growth factor BB in repair of growth plate injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
| [11] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [12] | Chi Wenxin, Zhang Cunxin, Gao Kai, Lyu Chaoliang, Zhang Kefeng. Mechanism by which nobiletin inhibits inflammatory response of BV2 microglia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [13] | Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Deng Hao, Sun Tao, Cheng Qian. Icariin pretreatment enhances effect of human periodontal stem cells on M1-type macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [14] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [15] | Liu Zhezhe, Yu Meiqing, Wang Tingting, Zhang Min, Li Baiyan. Troxerutin modulates nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway to inhibit brain injury and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral infarction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1137-1143. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||