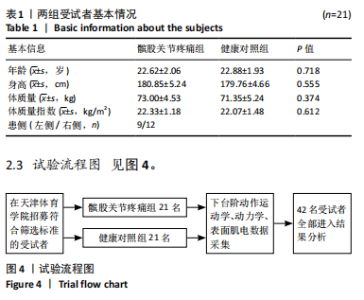
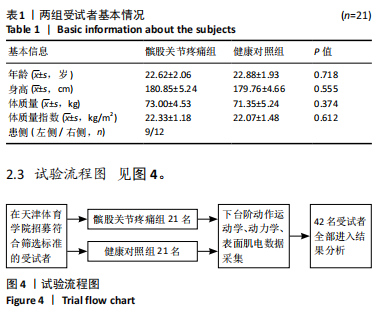
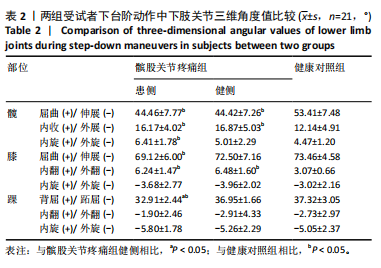
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (32): 6913-6919.doi: 10.12307/2025.925
Previous Articles Next Articles
Lower extremity biomechanical characterization during step-down test in patients with patellofemoral pain
Gao Yuan, Xiong Zheyu, Zheng Wei, Chen Haonan, Chen Fangyuqing
- Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China
-
Received:2024-10-09Accepted:2024-11-28Online:2025-11-18Published:2025-04-26 -
Contact:Zheng Wei, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China -
About author:Gao Yuan, Master candidate, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China -
Supported by:Undergraduate Teaching Quality and Teaching Reform Research Program Project in Tianjin Higher Education Institutions, No. B231007102 (to ZW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Yuan, Xiong Zheyu, Zheng Wei, Chen Haonan, Chen Fangyuqing. Lower extremity biomechanical characterization during step-down test in patients with patellofemoral pain[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6913-6919.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] XU J, CAI Z, CHEN M, et al. Global research trends and hotspots in patellofemoral pain syndrome from 2000 to 2023: a bibliometric and visualization study. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1370258. [2] GLAVIANO NR, BAZETT-JONES DM, BOLING MC. Pain severity during functional activities in individuals with patellofemoral pain: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J Sci Med Sport. 2022;25(5):399-406. [3] HOTT A, BROX JI, PRIPP AH, et al. Predictors of pain, function, and change in patellofemoral pain. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(2):351-358. [4] THOMAS MJ, WOOD L, SELFE J, et al. Anterior knee pain in younger adults as a precursor to subsequent patellofemoral osteoarthritis: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11:201. [5] ROCHA EAB, COSTA DE ASSIS SJ, MAIA DFM, et al. Risk factors for patellofemoral pain in the military: systematic review with meta-analysis. J Athl Train. 2024. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-0526.23. [6] KAYLL SA, HINMAN RS, BRYANT AL, et al. Do biomechanical foot-based interventions reduce patellofemoral joint loads in adults with and without patellofemoral pain or osteoarthritis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2023;57(13):872-881. [7] CROSSLEY KM, VAN MIDDELKOOP M, BARTON CJ, et al. Rethinking patellofemoral pain: Prevention, management and long-term consequences. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2019;33(1):48-65. [8] CULVENOR AG, VAN MIDDELKOOP M, MACRI EM, et al. Is patellofemoral pain preventable? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Sports Med. 2021;55(7):378-384. [9] KIM S, WU Y, GLAVIANO NR, et al. Physical activity levels in persons with patellofemoral pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Health. 2024. doi: 10.1177/19417381241264494. [10] LANKHORST NE, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA SM, VAN MIDDELKOOP M. Factors associated with patellofemoral pain syndrome: a systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(4):193-206. [11] POWERS CM, WITVROUW E, DAVIS IS, et al. Evidence-based framework for a pathomechanical model of patellofemoral pain: 2017 patellofemoral pain consensus statement from the 4th International Patellofemoral Pain Research Retreat, Manchester, UK: part 3. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(24): 1713-1723. [12] CELIK D, ARGUT SK, TÜRKER N, et al. The effectiveness of superimposed neuromuscular electrical stimulation combined with strengthening exercises on patellofemoral pain: A randomized controlled pilot trial. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2020;33(4):693-699. [13] FERREIRA AS, DE OLIVEIRA SILVA D, BARTON CJ, et al. Impaired isometric, concentric, and eccentric rate of torque development at the hip and knee in patellofemoral pain. J Strength Cond Res. 2021;35(9):2492-2497. [14] FAN C, NIU Y, WANG F. Local torsion of distal femur is a risk factor for patellar dislocation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):163. [15] GLAVIANO NR, SALIBA S. Differences in gluteal and quadriceps muscle activation during weight-bearing exercises between female subjects with and without patellofemoral pain. J Strength Cond Res. 2022;36(1):55-62. [16] MIRZAIE GH, RAHIMI A, KAJBAFVALA M, et al. Electromyographic activity of the hip and knee muscles during functional tasks in males with and without patellofemoral pain. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2019;23(1):54-58. [17] FOX A, FERBER R, SAUNDERS N, et al. Gait kinematics in individuals with acute and chronic patellofemoral pain. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(3): 502-509. [18] HO KY, BARRETT T, CLARK Z, et al. Comparisons of trunk and knee mechanics during various speeds of treadmill running between runners with and without patellofemoral pain: a preliminary study. J Phys Ther Sci. 2021;33(10):737-741. [19] DE BLEECKER C, VERMEULEN S, DE BLAISER C, et al. Relationship between jump-landing kinematics and lower extremity overuse injuries in physically active populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2020;50(8):1515-1532. [20] RHODE C, LOUW QA, LEIBBRANDT DC, et al. Joint position sense in individuals with anterior knee pain. S Afr J Physiother. 2021;77(1):1497. [21] CROSSLEY KM, ZHANG WJ, SCHACHE AG, et al. Performance on the single-leg squat task indicates hip abductor muscle function. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(4):866-873. [22] ALMEIDA GP, SILVA AP, FRANÇA FJ, et al. Relationship between frontal plane projection angle of the knee and hip and trunk strength in women with and without patellofemoral pain. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2016;29(2):259-266. [23] PRIORE LB, AZEVEDO FM, PAZZINATTO MF, et al. Influence of kinesiophobia and pain catastrophism on objective function in women with patellofemoral pain. Phys Ther Sport. 2019;35:116-121. [24] HOGLUND LT, HULCHER TA, AMABILE AH. Males with patellofemoral pain have altered movements during step-down and single-leg squatting tasks compared to asymptomatic males: A cross-sectional study. Health Sci Rep. 2024;7(6):e2193. [25] MORITA ÂK, TAVELLA NAVEGA M. Women with patellofemoral pain show changes in trunk and lower limb sagittal movements during single-leg squat and step-down tasks. Physiother Theory Pract. 2024;40(9):1933-1941. [26] PIVA SR, GOODNITE EA, CHILDS JD. Strength around the hip and flexibility of soft tissues in individuals with and without patellofemoral pain syndrome. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2005;35(12):793-801. [27] KIM S, PARK J. Patients with chronic unilateral anterior knee pain experience bilateral deficits in quadriceps function and lower quarter flexibility: a cross-sectional study. Physiother Theory Pract. 2022;38(13):2531-2543. [28] 王芗斌,刘燕平,苏娟,等.《国际功能、残疾和健康分类•髌股关节疼痛》临床实践指南(二)[J].康复学报,2021;31(3):177-199. [29] SILVA DDE O, BRIANI RV, PAZZINATTO MF, et al. Q-angle static or dynamic measurements, which is the best choice for patellofemoral pain? Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2015;30(10):1083-1087. [30] IMPELLIZZERI FM, RAMPININI E, MAFFIULETTI N, et al. A vertical jump force test for assessing bilateral strength asymmetry in athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(11):2044-2050. [31] NAKAGAWA TH, MORIYA ÉT, MACIEL CD, et al. Frontal plane biomechanics in males and females with and without patellofemoral pain. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(9):1747-1755. [32] NAKAGAWA TH, MORIYA ET, MACIEL CD, et al. Trunk, pelvis, hip, and knee kinematics, hip strength, and gluteal muscle activation during a single-leg squat in males and females with and without patellofemoral pain syndrome. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012;42(6):491-501. [33] AMINAKA N, PIETROSIMONE BG, ARMSTRONG CW, et al. Patellofemoral pain syndrome alters neuromuscular control and kinetics during stair ambulation. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2011;21(4):645-651. [34] WALLIS JA, RODDY L, BOTTRELL J, et al. A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines for physical therapist management of patellofemoral pain. Phys Ther. 2021;101(3):pzab021. [35] COLLINS NJ, BARTON CJ, VAN MIDDELKOOP M, et al. 2018 Consensus statement on exercise therapy and physical interventions (orthoses, taping and manual therapy) to treat patellofemoral pain: recommendations from the 5th International Patellofemoral Pain Research Retreat, Gold Coast, Australia, 2017. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(18):1170-1178. [36] GAITONDE DY, ERICKSEN A, RObbins rc. patellofemoral pain syndrome. Am fam physician. 2019;99(2):88-94. [37] DE OLIVEIRA SILVA D, BARTON CJ, PAZZINATTO MF, et al. Proximal mechanics during stair ascent are more discriminate of females with patellofemoral pain than distal mechanics. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2016;35:56-61. [38] 杨辰,万祥林,冯茹,等.膝痛对髌股关节痛业余跑者跑步和落地起跳缓冲期膝关节生物力学特征的影响[J].中国体育科技,2022,58(2):62-68. [39] SHERMAN SL, PLACKIS AC, NUELLE CW. Patellofemoral anatomy and biomechanics. Clin Sports Med. 2014;33(3):389-401. [40] BROUWER GM, VAN TOL AW, BERGINK AP, et al. Association between valgus and varus alignment and the development and progression of radiographic osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(4):1204-1211. [41] LEE TQ, MORRIS G, CSINTALAN RP. The influence of tibial and femoral rotation on patellofemoral contact area and pressure. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2003;33(11):686-693. [42] POWERS CM. The influence of abnormal hip mechanics on knee injury: a biomechanical perspective. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2010;40(2):42-51. [43] POLLARD CD, SIGWARD SM, POWERS CM. Limited hip and knee flexion during landing is associated with increased frontal plane knee motion and moments. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2010;25(2):142-146. [44] WILLSON JD, DAVIS IS. Utility of the frontal plane projection angle in females with patellofemoral pain. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008;38(10):606-615. [45] MCKENZIE K, GALEA V, WESSEL J, et al. Lower extremity kinematics of females with patellofemoral pain syndrome while stair stepping. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2010;40(10):625-632. [46] HUBERTI HH, HAYES WC. Patellofemoral contact pressures. The influence of q-angle and tendofemoral contact. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(5):715-724. [47] 杨辰,曲峰,刘卉,等. 髌股关节痛业余跑者性别特异的下肢生物力学特征[J].医用生物力学,2020,35(6):672-678. [48] MACRUM E, BELL DR, BOLING M, et al. Effect of limiting ankle-dorsiflexion range of motion on lower extremity kinematics and muscle-activation patterns during a squat. J Sport Rehabil. 2012;21(2):144-150. [49] 董友清,魏子轩,吴海鸥,等.不同类型女性髌股关节疼痛综合征患者的下肢生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(21):4458-4468. [50] EMAMVIRDI M, HOSSEINZADEH M, LETAFATKAR A, et al. Comparing kinematic asymmetry and lateral step-down test scores in healthy, chronic ankle instability, and patellofemoral pain syndrome female basketball players: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):12412. [51] WAITEMAN MC, BRIANI RV, LOPES HS,et al. People with patellofemoral pain have bilateral deficits in physical performance regardless of pain laterality. J Athl Train. 2024;59(11):1110-1117. [52] 吕福祥,张泽根,黄雪晴,等.高水平太极拳运动员下肢功能不对称与蹬脚动作表现关联性研究[J].武汉体育学院学报,2024,58(6):89-96. [53] 杨晓巍,姚英策,吴菁,等.肌肉电刺激结合肌力训练对髌股疼痛综合征人群单腿下蹲动作生物力学特征的影响[J].体育科学,2023,43(8):52-60+66. [54] LISKA F, VON DEIMLING C, OTTO A, et al. Distal femoral torsional osteotomy increases the contact pressure of the medial patellofemoral joint in biomechanical analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(7): 2328-2333. [55] CHEN S, CHANG WD, WU JY, et al. Electromyographic analysis of hip and knee muscles during specific exercise movements in females with patellofemoral pain syndrome: An observational study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(28):e11424. [56] BRIANI RV, DE OLIVEIRA SILVA D, FLÓRIDE CS, et al. Quadriceps neuromuscular function in women with patellofemoral pain: Influences of the type of the task and the level of pain. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0207421. [57] SELKOWITZ DM, BENECK GJ, POWERS CM. Comparison of electromyographic activity of the superior and inferior portions of the gluteus maximus muscle during common therapeutic exercises. j orthop sports phys ther. 2016;46(9):794-799. [58] WILLSON JD, KERNOZEK TW, ARNDT RL, et al. Gluteal muscle activation during running in females with and without patellofemoral pain syndrome. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2011;26(7):735-740. [59] PAYNE K, PAYNE J, LARKIN TA. Patellofemoral pain syndrome and pain severity is associated with asymmetry of gluteus medius muscle activation measured via ultrasound. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;99(7):595-601. [60] DE OLIVEIRA SILVA D, MAGALHÃES FH, FARIA NC, et al. Lower amplitude of the hoffmann reflex in women with patellofemoral pain: thinking beyond proximal, local, and distal factors. arch phys med Rehabil. 2016;97(7):1115-1120. |
| [1] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [2] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [3] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [4] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [5] | Fu Enhong, Yang Hang, Liang Cheng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Yali, Jin Zhongmin. OpenSim-based prediction of lower-limb biomechanical behavior in adolescents with plantarflexor weakness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1789-1795. |
| [6] | Lu Jieming, Li Yajing, Du Peijie, Xu Dongqing. Effects of artificial turf versus natural grass on biomechanical performance of the lower limbs in young females during jump-landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1101-1107. |
| [7] | Wang Lei, Li Chengsong, Zhang Shenshen, Wang Qing. Finite element analysis of biomechanical characteristics of three internal fixation methods in treatment of inferior patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7048-7054. |
| [8] | Xu Xin, Wurikaixi·Aiyiti, Lyu Gang, Maimaiaili·Yushan, Ma Zhiqiang, Ma Chao. Finite element analysis of four different internal fixation methods for complex acetabular double-column fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7063-7071. |
| [9] | Liang Cheng, Zhuo Chuanchuan, Zhang Xiaogang, Wang Guan, Duan Ke, Li Zhong, Lu Xiaobo, Zhuo Naiqiang, Jin Zhongmin. Biomechanical characteristics of a novel sacroiliac lag screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7080-7086. |
| [10] | Ma Shuangshuang, Gao Dedong, Shan Zhongshu, Xu Wenxu, Lu Zhirui. Finite element analysis and biomechanical validation of revision pedicle screw placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7087-7095. |
| [11] | Yang Yu, Li Yinghao, Duo Zhuangzhi, Zhou Dingrong. Effect of overall functional physical exercise on lumbar biomechanics in patients with lumbar disc herniation after surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7096-7101. |
| [12] | Zhang Ziyi, Qin Qi, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Liu Yuzhe, Yusufu·Reheman, Ran Jian. Biomechanical analysis of three internal fixation schemes for Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures in young adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7102-7108. |
| [13] | Liu Mengling, Li Yongjie, Liu Hongju. Effect of increased stride length on knee kinematics and dynamics of asymmetric gait after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7109-7115. |
| [14] | Ma Tao, Li Xing, Wei Yajun, Deng Juncai. Effects of lateral screw-rod placement positions on segmental range of motion, internal fixation and cage stress during oblique lumber interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7165-7172. |
| [15] | Xu Tianyu, Chen Modi, Xie Mingru, Ye Xinghua, Pan Zhaohui. Finite element analysis of biomechanical effect of medial or lateral malleolar ligament defects on its neighboring core tendons [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7223-7230. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||