Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (30): 6426-6433.doi: 10.12307/2025.919
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation of osteoporotic femoral condylar bone defect model in rabbits and its critical value
Deng Guanghui1, Xiang Wei2, Su Qifan2, Chen Xiaoyu2, Wang Liangwei2, Wan Zhihong2, Wu Jiaqi2, Chen Xiaojun2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, The Affiliated Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, The Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-09-25Accepted:2024-11-22Online:2025-10-28Published:2025-03-27 -
Contact:Chen Xiaojun, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, The Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Deng Guanghui, MS, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, The Affiliated Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Luzhou Municipal People’s Government-Southwest Medical University of Science and Technology Strategic Cooperation Project, No. 2019LZXNYDJ37 (to CXJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Deng Guanghui, Xiang Wei, Su Qifan, Chen Xiaoyu, Wang Liangwei, Wan Zhihong, Wu Jiaqi, Chen Xiaojun. Preparation of osteoporotic femoral condylar bone defect model in rabbits and its critical value[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6426-6433.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
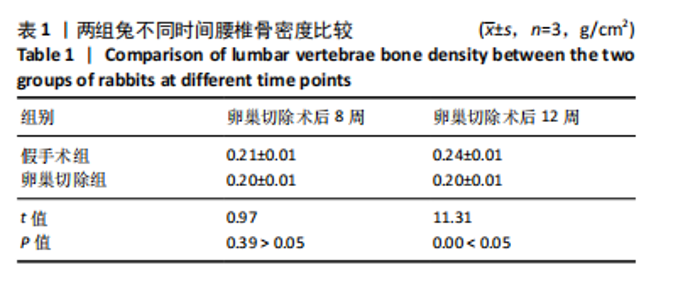
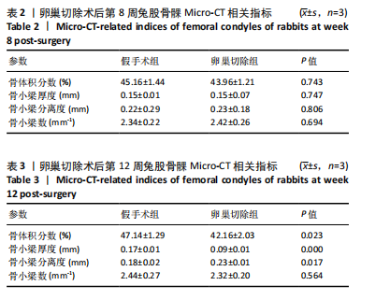
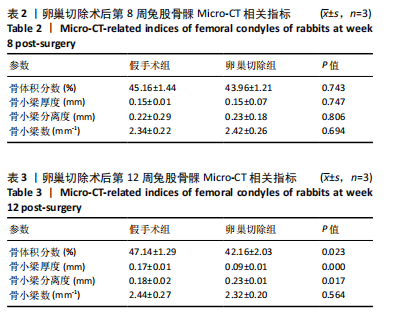
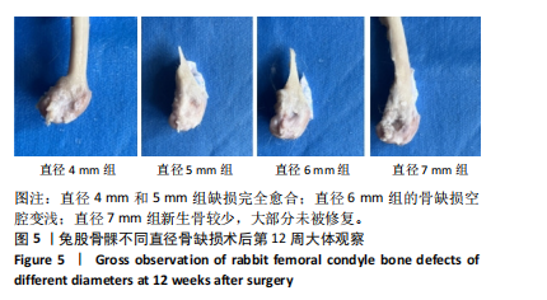
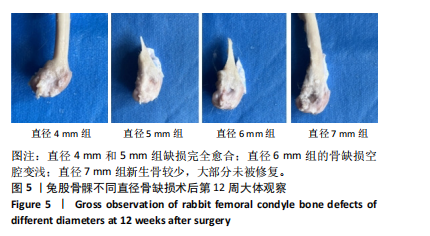
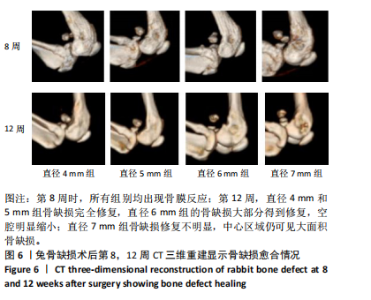
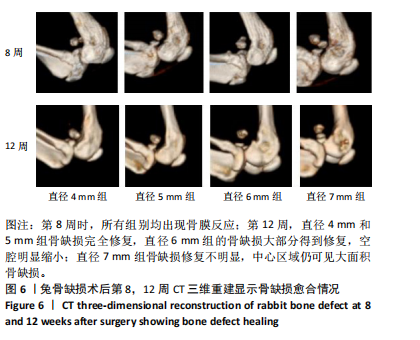
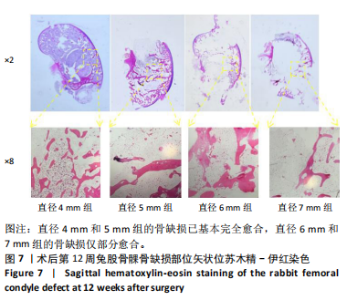
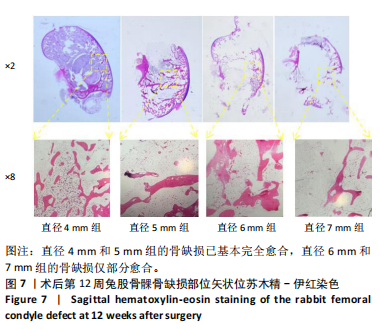
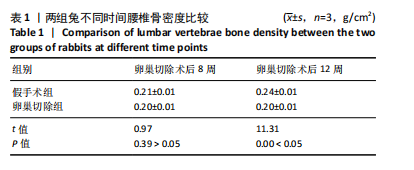
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验选用新西兰大白兔36只,随机分为卵巢切除组30只(其中6只用于骨质疏松实验,余下的24只用于骨质疏松性股骨髁骨缺损实验)和假手术组6只。在整个实验过程中无实验兔脱落,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 骨质疏松建模结果分析 2.2.1 实验动物术后一般情况 模型兔术后5-10 min麻醉苏醒,精神状态萎靡,活动减少,腹部手术切口无明显渗血,可少量觅食饮水。术后第1天,新西兰白兔精神状无明显异常,活动正常,可正常饮食,腹部手术切口未见明显渗出、红肿,缝线无脱落。术后2周腹部切口愈合良好。术后第12周,卵巢切除组较假手术组精神萎靡、体形消瘦、行动迟缓、毛色发黄失去光泽、弓背严重。 2.2.2 DXA检测结果 术后第8,12周通过DXA行兔腰椎的骨密度检测并进行统计学分析。结果显示,在术后第8周,腰椎骨密度值卵巢切除组(0.20±0.01) g/cm2与假手术组(0.21±0.01) cm2相比,差异无显著性意义(P=0.39),表明通过卵巢切除术后8周,尚未构建兔骨质疏松模型。术后第12周,腰椎骨密度值卵巢切除组(0.20±0.01) cm2较假手术组(0.24±0.01) cm2显著降低(P < 0.05),表明通过卵巢切除术后12周,可以成功构建兔骨质疏松模型,见表1。"
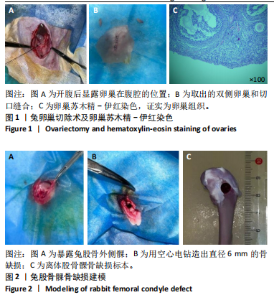
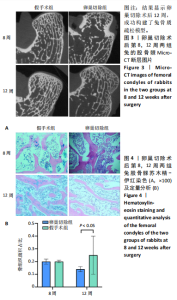
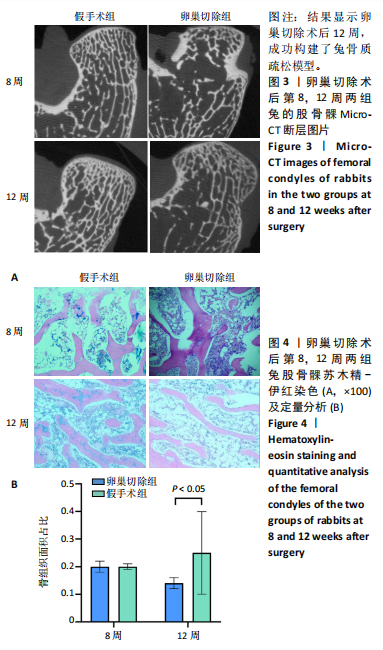
2.2.4 组织学分析 股骨髁苏木精-伊红染色显示,术后第8周卵巢切除组与假手术组镜下观察骨小梁组织形态无明显差异;术后第12周时,卵巢切除组相比于假手术组骨连通性明显丧失,骨小梁数目及直径减小(图4)。苏木精-伊红染色半定量分析,即样本在100倍显微镜视野下骨组织面积占总视野面积比定量(图4B),8周时,骨组织面积占比卵巢切除组(0.20±0.02)与假手术组(0.20±0.01)比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.14),12周时,骨组织面积占比卵巢切除组(0.14±0.02)与假手术组(0.25±0.15)比较差异有显著性意义(P=0.00),说明卵巢切除术后12周,兔骨质疏松明显,骨质疏松模型建立成功。"

| [1] BRENT MB. Pharmaceutical treatment of bone loss: From animal models and drug development to future treatment strategies. Pharmacol Ther. 2023;244:108383. [2] YANG X, WANG Q, YAN C, et al. A dual-functional strontium-decorated titanium implants that guides the immune response for osseointegration of osteoporotic rats. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024;233:113643. [3] XU J ,BAO G ,JIA B, et al. An adaptive biodegradable zinc alloy with bidirectional regulation of bone homeostasis for treating fractures and aged bone defects. Bioact Mater. 2024;38:207-224. [4] DHRUMI P, SARIKA W. Bone regeneration in osteoporosis: opportunities and challenges. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022;13(2):419-432. [5] HAO W,XINYU X,XIAOHAN M, et al. 3D-printed porous PEI/TCP composite scaffolds loaded with graphdiyne oxide on the surface for bone defect repair and near-infrared light-responsive antibacterial. Mater Design. 2024;237:112569. [6] ZHANG T, ZHOU W, YANG W, et al. Vancomycin-encapsulated hydrogel loaded microarc-oxidized 3D-printed porous Ti6Al4V implant for infected bone defects: Reconstruction, anti-infection, and osseointegration. Bioact Mater. 2024;42:18-31. [7] 李树源,杨达文,曾展鹏,等.诱导膜技术在临界尺寸骨缺损修复中的应用:优势与未来发展[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(28): 6083-6093. [8] 任纪巍.BSA改性DBM组织工程骨对大鼠颅骨缺损修复作用的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2024. [9] 郑继远,梁劭行,梁泽隆,等.膜诱导技术结合Ca(OH)2-PMMA治疗节段性骨缺损的研究进展[J].海南医学院学报,2024,30(11):868-872. [10] CUI J, YU X, YU B, et al. Coaxially Fabricated Dual-Drug Loading Electrospinning Fibrous Mat with Programmed Releasing Behavior to Boost Vascularized Bone Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022; 11(16):e2200571. [11] SADEK AA, ABD-ELKAREEM M, ABDELHAMID HN, et al. Enhancement of critical-sized bone defect regeneration using UiO-66 nanomaterial in rabbit femurs. BMC Vet Res. 2022;18(1):260. [12] CHAOXIN W, JINGE L, SHUYUAN M, et al. The effect of pore size on the mechanical properties, biodegradation and osteogenic effects of additively manufactured magnesium scaffolds after high temperature oxidation: An in vitro and in vivo study. Bioact Mater. 2023;28:537-548. [13] LAMAS GL, LOZANO D, DÍAZ JV, et al. Enriched Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Scaffolds as Bone Substitutes in Critical Diaphyseal Bone Defects in Rabbits. Acta biomater. 2024;180:104-114. [14] ELSADEK NA, ABOUKHADR MA, KAMEL FR, et al. Moringa oleifera leaf extract promotes the healing of critical sized bone defects in the mandibles of rabbits. BDJ Open. 2024;10(1):22-22. [15] NA KH, LEE HJ, LEE JE, et al. Regeneration of Rabbit Calvarial Defects with Combination of Stem Cells and Enamel Matrix Derivative: A Microcomputed Tomography and Histological Evaluation Comparing Two- and Three-Dimensional Cell Constructs. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(3):451. [16] DANESHI SS, TAYEBI L, KHOZANI TT, et al. Reconstructing Critical-Sized Mandibular Defects in a Rabbit Model: Enhancing Angiogenesis and Facilitating Bone Regeneration via a Cell-Loaded 3D-Printed Hydrogel-Ceramic Scaffold Application. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024;10(5): 3316-3330. [17] MORIMOTO A, PORFIRIO XAVIER S, RICARDO SILVA E, et al. Critical-sized marginal defects around implants in the rabbit mandible. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024;28(3):1267-1278. [18] PYO WS, PAIK W J, LEE ND, et al. Comparative Analysis of Bone Regeneration According to Particle Type and Barrier Membrane for Octacalcium Phosphate Grafted into Rabbit Calvarial Defects. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024;11(3):215. [19] 何志敏,宋天喜,胡刚,等.聚乳酸/矿化胶原复合人工骨修复材料在兔股骨髁松质骨缺损中的应用研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2022,19(3):1-6. [20] 徐石庄,王进,潘文振,等.兔股骨髁临界性骨缺损动物模型制备及临界骨缺损值[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(20):3191-3195. [21] LIAO W, LU J, WANG Q, et al. Osteogenesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles-Labeled Human Precartilaginous Stem Cells in Interpenetrating Network Printable Hydrogel. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:872149. [22] DANDAN X, YU Q, HUI G, et al. Additively manufactured pure zinc porous scaffolds for critical-sized bone defects of rabbit femur. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:12-23. [23] 周世博,关健斌,俞兴,等.股骨骨缺损动物模型制备现状及特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(4):633-638. [24] LIU JL, ZHANG YC, QIU L, et al. Assessment of alpha-calcium sulfate hemihydrate/nanocellulose composite bone graft material for bone healing in a rabbit femoral condyle model. MATERIALS EXPRESS. 2021; 11(9): 1497-1504. [25] HARRISON KD, HIEBERT BD, PANAHIFAR A, et al. Cortical Bone Porosity in Rabbit Models of Osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(11): 2211-2228. [26] 陈卫康,许玮.兔骨缺损模型构建的研究现状[J].创伤与急诊电子杂志,2023,11(4):211-215. [27] 张慧丽,李克峰,戴小丽,等.基于兔骨质疏松模型的骨质疏松症进展中骨髓代谢组学变化[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2020,40(11):1603-1611. [28] ANDRACA HARRER J, FULTON TM, SANGADALA S, et al. Local FK506 delivery induces osteogenesis in rat bone defect and rabbit spine fusion models. Bone. 2024;187:117195. [29] WEI L, YU W, XINGLAN Y, et al. Comparison of bone ingrowth between two porous titanium alloy rods with biogenic lamellar structures and diamond crystal lattice on femoral condyles in rabbits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023:641:155-161. [30] ALEYNIK YD, ZHIVTSCOV PO, YUDIN VV, et al. Specifics of Porous Polymer and Xenogeneic Matrices and of Bone Tissue Regeneration Related to Their Implantation into an Experimental Rabbit Defect. Polymers (Basel). 2024;16(8):1165. [31] ZHANG B, PEI Z, HE W, et al. 3D-printed porous zinc scaffold combined with bioactive serum exosomes promotes bone defect repair in rabbit radius. Aging (Albany NY). 2024;16(11):9625-9648. [32] SADAN M, NAEM M, TAWFEEK MH, et al. Can silver nanoparticles stabilized by Fenugreek (Trigonella foenm -graecum) improve tibial bone defects repair in rabbits? A preliminary study. Open Vet J. 2024; 14(5):1281-1293. [33] 张楠,刘娜,孙楚,等.新型微弧氧化涂层镁-锌-钙合金支架/自体颗粒骨修复兔临界性骨缺损的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(3):298-305. [34] RIVAS R, SHAPIRO F. Structural stages in the development of the long bones and epiphyses: a study in the New Zealand white rabbit. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(1):85-100. [35] LEE YM, SON SH, SUR YJ, et al. Reconstruction of large bone defect using autogenous fibular strut and iliac bone graft for revision total elbow arthroplasty. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(48):e28054. [36] PANES C, GANDUR VI, VEUTHEY C, et al. Micro-Computed Tomography Analysis of Peri-Implant Bone Defects Exposed to a Peri-Implantitis Microcosm, with and without Bone Substitute, in a Rabbit Model: A Pilot Study. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024;11(4):397. [37] 李彦冉,闫盼盼,苗艳艳,等.骨质疏松动物模型构建进展与应用特点分析[J].中国实验动物学报,2023,31(7):928-934. [38] 张春丽,李忠海,周颖,等.构建骨质疏松动物模型建模方法的改进及评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(5):754-759. [39] 扶浪,皮超,罗焘,等.骨痿愈方通过调节OPG/RANKL治疗绝经后骨质疏松的动物实验及机制研究[J].西南医科大学学报,2024, 47(5):442-446. [40] 王丹,刘一城,卢锋,等.中药治疗股骨头坏死与骨质疏松数据库的构建及“异病同治”机理[J].西南医科大学学报,2022,45(2): 139-145. [41] 田彬,刘长松,程为.骨质疏松兔颅骨骨缺损模型的建立[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2023,24(1):20-24+37. [42] 蔡立雄,霍志谦,孙丙银,等.改良兔股骨骨缺损并骨延长模型的建立[J].中医正骨,2018,30(1):25-28. [43] 陈胡贵,覃建国,李理,等.大动物节段性骨缺损模型的研究进展[J].北京生物医学工程,2021,40(2):203-208. [44] FERNÁNDEZ AI, HAUGEN JH, NOGUEIRA PL, et al. Enhanced Bone Healing in Critical-Sized Rabbit Femoral Defects: Impact of Helical and Alternate Scaffold Architectures. Polymers (Basel). 2024;16(9):1243. [45] EDWARD M, SUYONO ER, WARINDRA T. Effect of bovine hydroxyapatite composite with secretome under normoxia and hypoxia conditions on inflammatory parameters in massive bone defect of rabbit radius bone. J Biomater Appl. 2024;39(5):466-472. [46] TOSHIKI Y, KOICHIRO H, AKIRA T, et al. In vivo trial of bioresorbable mesh cages contained bone graft granules in rabbit femoral bone defects. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):12449. [47] 陈佳滨,陈志达,肖莉莉,等.慢病毒介导hBMP-2转染BMSCs复合脱钙松质骨修复兔股骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(2):212-214. [48] Shibo H, Junlei L, Kairong Q, et al. Evaluation of the performance of Ca-deficient hydroxyapatite (CDHA)/MgF2 bilayer coating on biodegradable high-purity magnesium in a femoral condyle defect model in rabbits. Regen Biomater. 2022;9:rbac066. [49] 张虎雄,李微,杨物鹏,等.3D打印淫羊藿苷/脱钙骨基质修复兔股骨髁骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(34):5461-5466. [50] RYOUNG SK, MO KL, HONG JK, et al.Biocompatibility evaluation of peo-treated magnesium alloy implants placed in rabbit femur condyle notches and paravertebral muscles. Biomater Res. 2022;26(1):29. [51] LI J, AHMED A, DEGRANDE T, et al. Histological evaluation of titanium fiber mesh-coated implants in a rabbit femoral condyle model. Dent Mater. 2022;38(4):613-621. [52] Dorlis C, Garcia-Pertierra S, Richardson J, et al. Femoral condylar fractures in four continental giant breed rabbits. J Small Anim Pract. 2022;63(4):325-330. [53] CUI X, HUANG W, ZHANG Y, et al. Evaluation of an injectable bioactive borate glass cement to heal bone defects in a rabbit femoral condyle model. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;73:585-595. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [3] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [4] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [5] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [6] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [7] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [8] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [9] | Wan Lingling, Wu Mengying, Zhang Yujiao, Luo Qingqing. Inflammatory factor interferon-gamma affects migration and apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells through pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1422-1428. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [11] | Zhang Shuai, Li Zichun, Xu Yihao, Xie Xiaofeng, Guo Zhongsheng, Zhao Qingyang. Effect of transcranial magneto-acousto-electrical stimulation on the plasticity of the prefrontal cortex network in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1108-1117. |
| [12] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [13] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [14] | Zhang Debao, Wang Peng, Li Kun, Zhang Shaojie, Li Zhijun, Li Shuwen, Wu Yimin. Epidural fibrous scar formation in rabbits following autologous ligamentum flavum intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1168-1175. |
| [15] |
Huang Xiaobin, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, He Yanyan, Xue Lipeng.
Mechanisms of different yin nourishing and kidney tonifying methods on osteoclastysis pathway in ovariectomized rats #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219.
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||